Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Alteration in Rab11-mediated endocytic trafficking of LDL receptor contributes to angiotensin II-induced cholesterol accumulation and injury in podocytes
- First Published: 14 May 2022
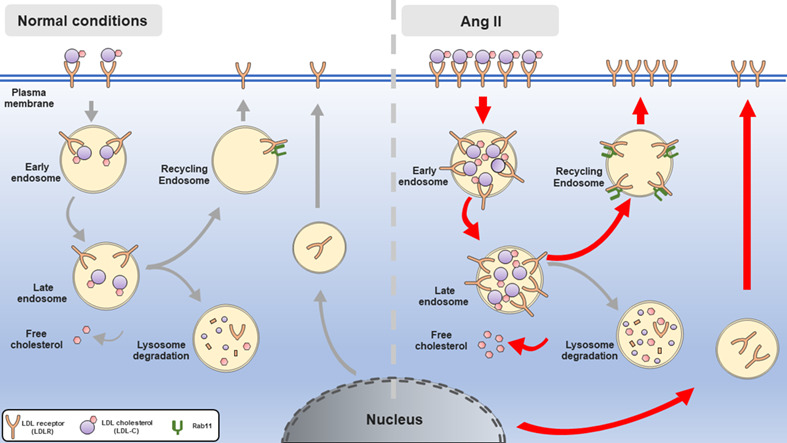
Ang II increases low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) abundance on the cell surface and causes podocyte cholesterol deposition: In addition to directly increasing LDLR expression, overactivation of Rab11-mediated recycling and reuse of LDLR contributes to Ang II-induced podocyte cholesterol accumulation and injury.
Maternal Prkce expression in mature oocytes is critical for the first cleavage facilitating maternal-to-zygotic transition in mouse early embryos
- First Published: 18 May 2022
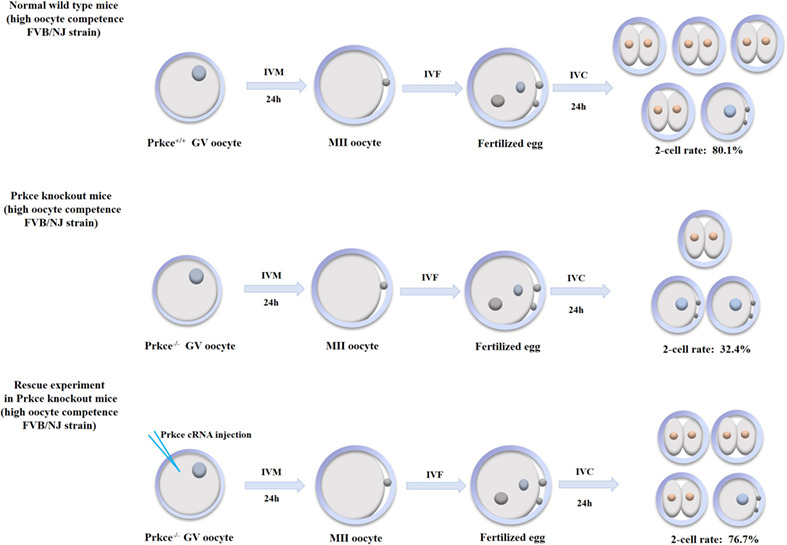
Oocyte competence is variable among different mouse strains, most likely due to the differential abundance of maternal transcripts in the oocyte during MZT. One candidate gene, Prkce, plays an essential role in facilitating MZT, especially during the first cleavage. The expression level of the Prkce transcript appears to be associated with different oocyte competence in different mice strains.
Hoxb5 reprogrammes murine multipotent blood progenitors into haematopoietic stem cell-like cells
- First Published: 17 May 2022
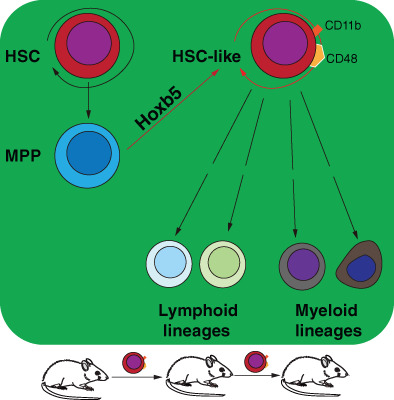
We unveiled that induced expression of Hoxb5 in mouse multipotent progenitor cells (MPP) led to the generation of a de novo Sca1+c-Kit+CD11b+CD48+ (CD11b+CD48+SK) cell type, which obtained the self-renewal ability and can repopulate long-term multilineage haematopoiesis in serial transplant recipients. RNA-seq analysis showed that CD11b+CD48+SK cells exhibited acquired features of DNA replication and cell division, which resembled natural FL HSC. In short, our current study uncovers that Hoxb5 is able to empower MPPs with self-renewal ability and indicates an alternative approach for generating HSC-like cells in vivo from blood lineage cells.
Ginsenoside Rh2 mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting apoptotic and inflammatory damage and weakening pathological remodelling in breast cancer-bearing mice
- First Published: 09 May 2022
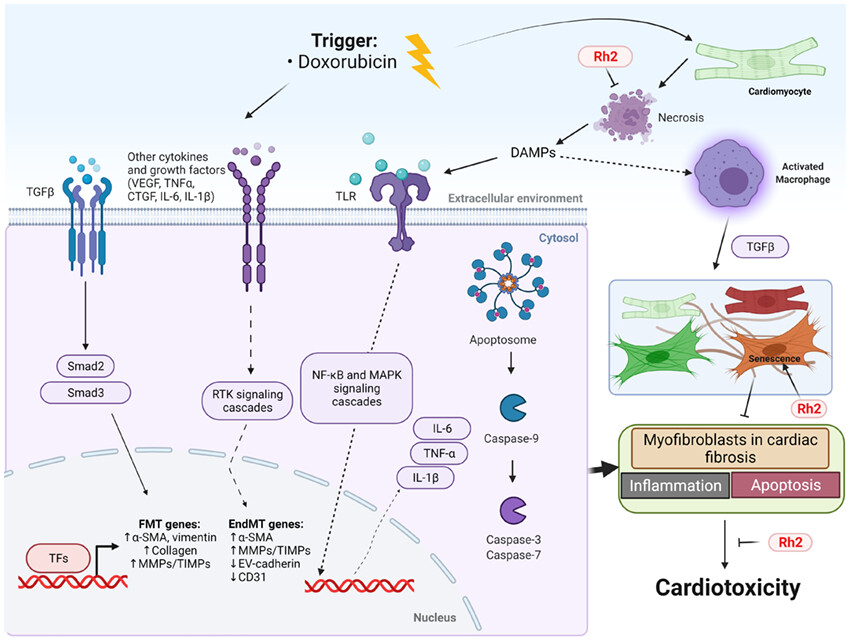
Doxorubicin is extensively reported to induce severe cardiotoxicity in clinical applications. Our work proposed a natural herbal compound, ginsenoside Rh2, as a potential candidate for attenuating this side effect. Rh2 significantly inhibited cardiac apoptosis and necrosis, inflammation, and pathological remodelling in Dox-challenged hearts.
Single-cell sequencing reveals the heterogeneity and intratumoral crosstalk in human endometrial cancer
- First Published: 13 May 2022
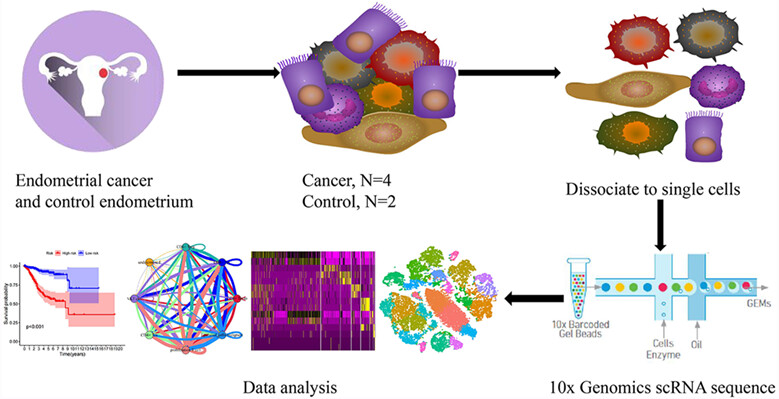
In order to comprehensively explore the heterogeneity and intra-tumoral crosstalk of human endometrial cancer, we profiled 41,358 single cells of human endometrial cancer and normal endometrial tissues. The results showed that the tumour microenvironment of human ECs remains highly heterogeneity. Malignant cells interact closely with immune cells and vCAFs which may indicate potential therapeutic targets.
Melatonin alleviates vascular endothelial cell damage by regulating an autophagy-apoptosis axis in Kawasaki disease
- First Published: 17 May 2022
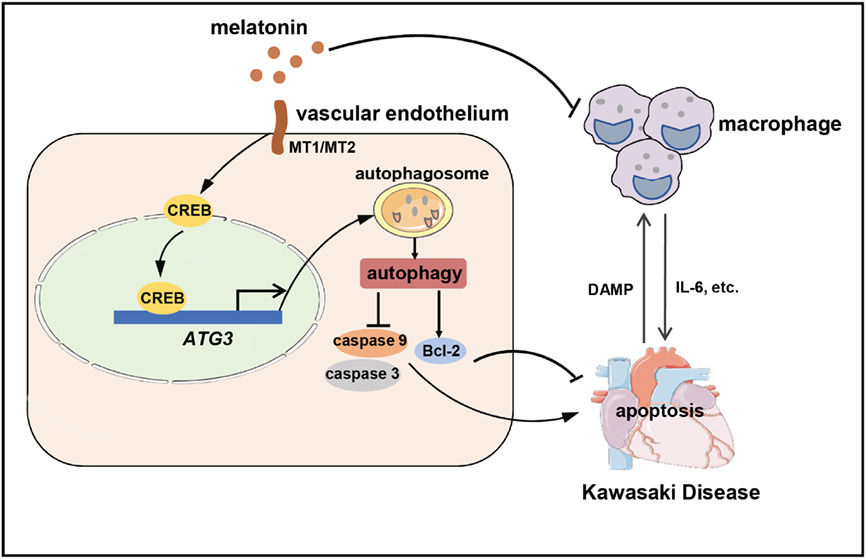
KD-related vasculitis is a crosstalk between vascular endothelial cells and immune cells, especially macrophages. Macrophages release pro-inflammatory cytokines to mediate the damage of vascular endothelial cells, when the latter is injured, it can promote the former to secrete more pro-inflammatory cytokines by releasing damage-associated molecular pattern. Melatonin alleviates vascular endothelial cells injury directly by suppressing apoptosis in an autophagy-dependent manner, it also decreases the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines released by macrophages and reduces the immunopathological damage of vascular endothelial cells in KD-related vasculitis.
Activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 protects ethanol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat model
- First Published: 14 May 2022
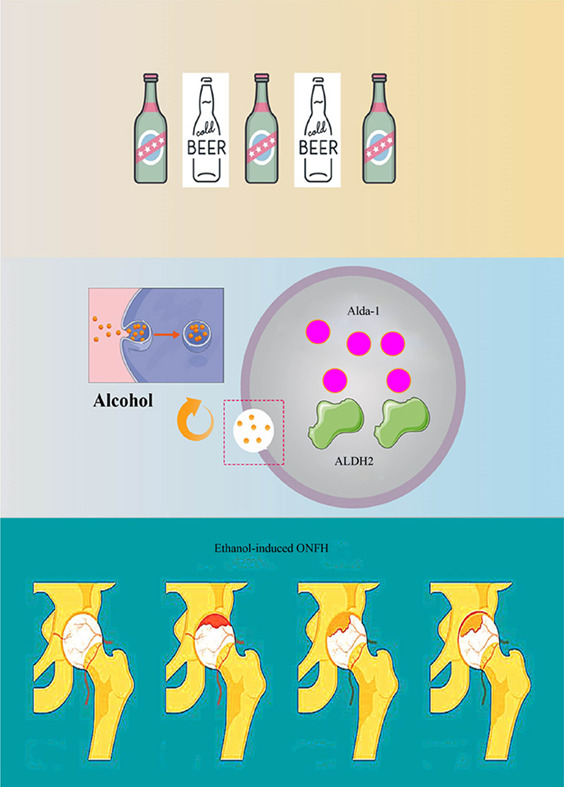
Alda-1 activation of ALDH 2 was highly demonstrated to protect ethanol-induced ONFH by triggering new bone formation, reducing adipogenesis and stimulating vascularization. Therefore, ALDH 2 may be a potential therapeutic target and small molecule Alda-1 may be promising pharmacotherapeutic for ONFH in the future.







