Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 299-301
- First Published: 06 February 2020

Cover of this issue. Distribution of cancer stem-like cells on the cell spheroid. See also Quan et al. (pp. 467–476 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this Issue: Volume 111, Issue 2, February 2020
- Pages: 302-303
- First Published: 06 February 2020
REVIEW ARTICLES
Cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype via the cGAS-STING signaling pathway in cancer
- Pages: 304-311
- First Published: 04 December 2019
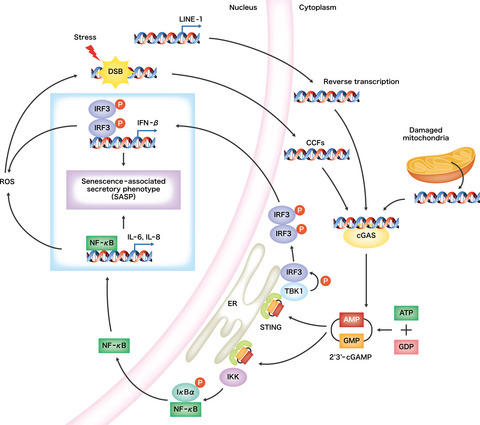
This brief review discusses the role of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) signaling pathway on cellular senescence in cancer development. We suggest that the cGAS-STING signaling pathway may be a novel target for induction of SASP.
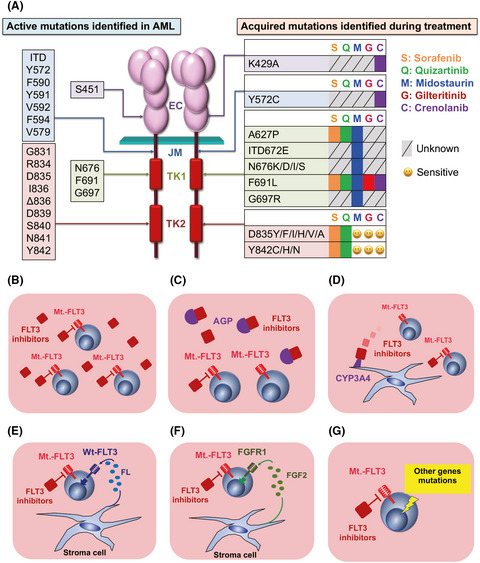
FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: Therapeutic paradigm beyond inhibitor development
- Pages: 312-322
- First Published: 10 December 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Endogenous CXCL9 affects prognosis by regulating tumor-infiltrating natural killer cells in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 323-333
- First Published: 04 December 2019
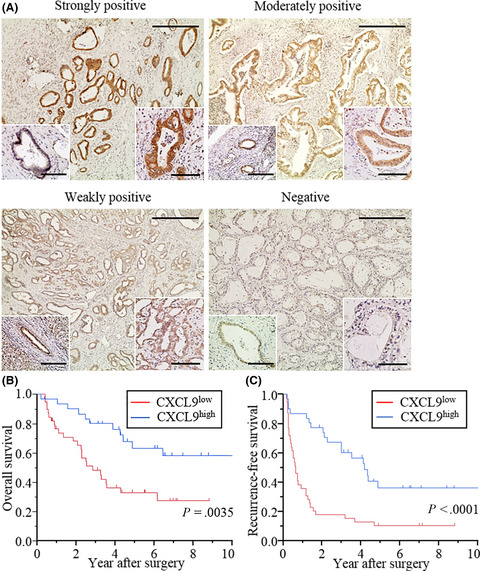
CXCL9, an IFN-γ inducible chemokine, plays versatile roles in the tumor-host interrelationship. In this study, we demonstrated that elevated intratumoral CXCL9 expression was associated with a large number of tumor-infiltrating NK cells, leading to favorable postoperative survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Upregulation of CXCL9 might be an immunotherapeutic approach for treating intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
CARCINOGENESIS
Plasma and tumoral glypican-3 levels are correlated in patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 334-342
- First Published: 27 November 2019
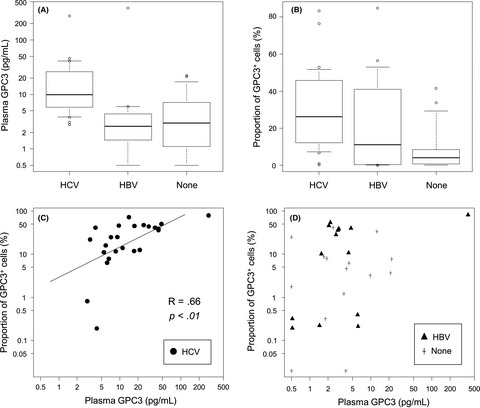
Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a cancer antigen expressed in approximately 80% of hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) and is secreted into the blood. We analyzed the relationship between GPC3 expression levels in cancer cells and in blood in 56 patients with HCC. In conclusion, plasma concentration of GPC3 could be a predictive marker of tumoral GPC3 expression in patients with HCV-related HCC, suggesting a useful biomarker for immunotherapies targeting GPC3.
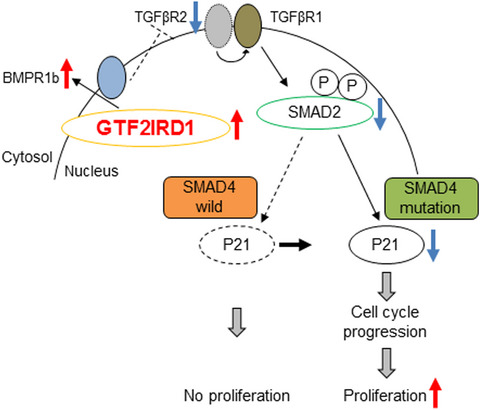
GTF2IRD1 on chromosome 7 is a novel oncogene regulating the tumor-suppressor gene TGFβR2 in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 343-355
- First Published: 23 November 2019
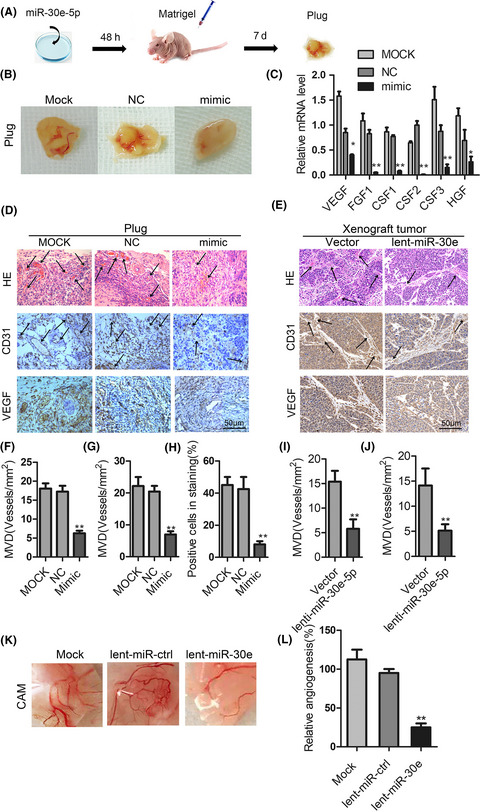
miR-30e-5p represses angiogenesis and metastasis by directly targeting AEG-1 in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- Pages: 356-368
- First Published: 28 November 2019
RNA-binding protein Musashi2 stabilizing androgen receptor drives prostate cancer progression
- Pages: 369-382
- First Published: 13 December 2019
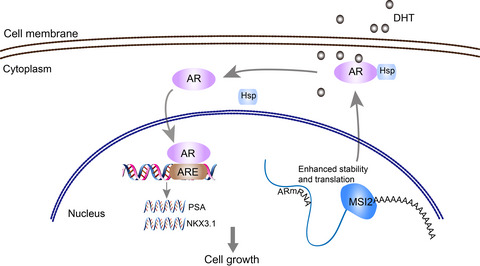
This is the first description of a role for the RNA-binding protein MSI2 in regulating AR stability in prostate cancer. MSI2 upregulates AR mRNA stability through directly binding with 3′-UTR of AR mRNA, which indicates that targeting MSI2 may be a novel and unique anti–androgen therapy for prostate cancer.
CD155 contributes to the mesenchymal phenotype of triple-negative breast cancer
- Pages: 383-394
- First Published: 12 December 2019
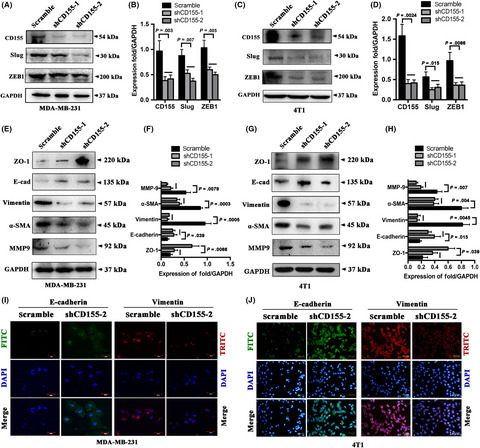
Our study identified for the first time that CD155 is overexpressed in TNBC, is associated with poor prognosis and contributes to the aggressive phenotype. Mechanistically, IL-6/Stat3 and TGF-β/Smad3 pathways may be involved in CD155-associated TNBC EMT and metastasis. CD155 knockdown suppressed TNBC cell in vitro motility and in vivo metastasis, suggesting that CD155 is a potential molecular target for TNBC.
MiR-1285-5p/TMEM194A axis affects cell proliferation in breast cancer
- Pages: 395-405
- First Published: 18 December 2019
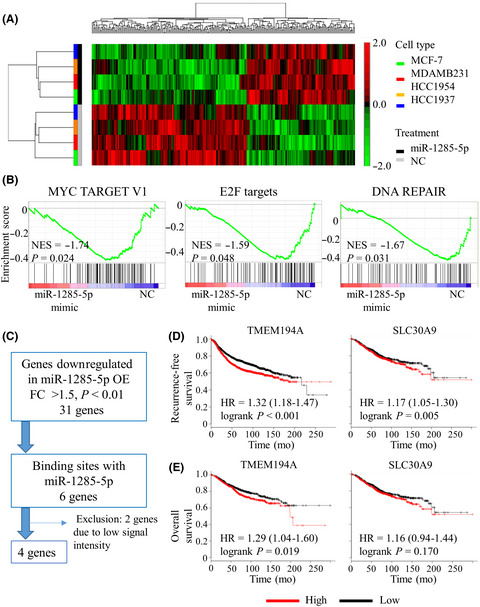
We showed the tumor-suppressive role of miR-1285-5p and detailed its mechanism of action in breast cancer. Overexpression of miR-1285-5p significantly inhibited cell proliferation in breast cancer cells regardless of the tumor subtype. We found that transmembrane protein 194A (TMEM194A) was directly regulated by miR-1285-5p. Our findings show that separation of centrosomes from the nuclear envelope was observed upon knockdown of TMEM194A or overexpression of miR-1285-5p and reveal the tumor suppressive role of miR-1285-5p via TMEM194A inhibition in breast cancer.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
STMN1 upregulation mediates hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic stellate cell crosstalk to aggravate cancer by triggering the MET pathway
- Pages: 406-417
- First Published: 29 November 2019
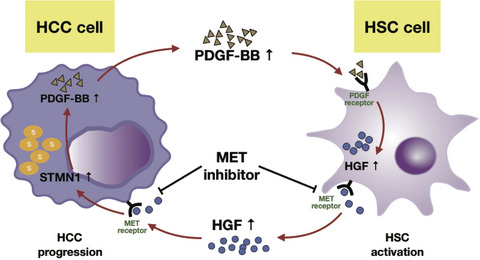
Working model of MET inhibitor inhibited the positive feedback loop between high STMN1 HCC cells and HSC cells. STMN1 mediates intricate crosstalk between HCC and hepatic stellate cells (HSC) by triggering HGF/MET signal pathway. MET inhibitor crizotinib blocked MET pathway to effectively inhibit HCC-HSC crosstalk and shrink tumor growth when both high STMN1 HCC cells and HSC were coinoculated in mice.
c-Src promotes tumor progression through downregulation of microRNA-129-1-3p
- Pages: 418-428
- First Published: 04 December 2019
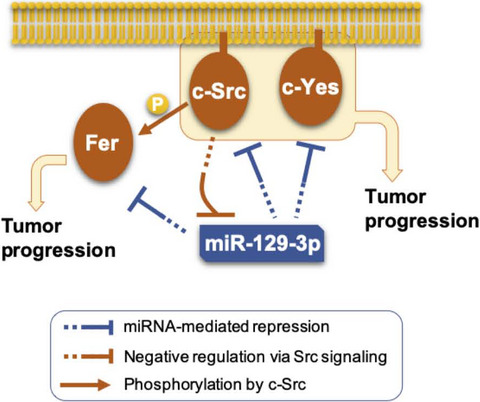
We found that microRNA (miR)-129-1-3p was repressed in the early phase of c-Src-induced cell transformation, and that reexpression of miR-129-1-3p disrupted c-Src-induced cell transformation. MicroRNA-129-1-3p was repressed in various colon cancer tissues. In addition, we showed that miR-129-1-3p directly targets c-Src, Fer, and c-Yes, which are required for cancer cell adhesion and invasion. These findings indicate that downregulation of miR-129-1-3p by early activation of c-Src synergistically promotes c-Src-related oncogenic signaling.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β as a potential therapeutic target in synovial sarcoma and fibrosarcoma
- Pages: 429-440
- First Published: 06 December 2019
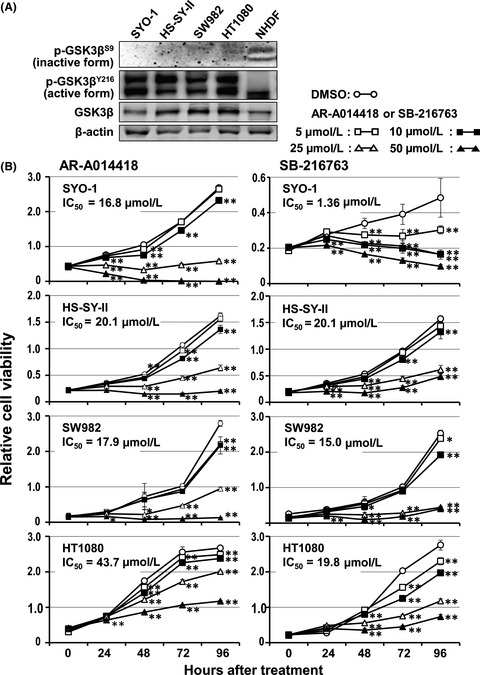
This study shows that deregulated activity of GSK3β in synovial sarcoma and fibrosarcoma is responsible for tumor cell proliferation through cyclin D1/CDK4-mediated cell cycle progression, and for tumor cell invasion via enhanced extracellular matrix degradation. The present results therefore suggest that targeting of GSK3β in tumor cells is a promising therapeutic strategy for soft tissue sarcomas.
Epidermal growth factor receptor mRNA expression: A potential molecular escape mechanism from regorafenib
- Pages: 441-450
- First Published: 10 December 2019
We identified circulating tumor cell count as a prognostic marker in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with regorafenib. Circulating tumor cell EGFR expression was significantly increased with regorafenib at the time of disease progression, suggesting this to be a mode of resistance and lending further mechanistic evidence for the synergistic effects seen with regorafenib and anti-EGFR mAbs.
Identification and characterization of the binding sequences and target genes of p53 lacking the 1st transactivation domain
- Pages: 451-466
- First Published: 13 December 2019

The tumor suppressor gene p53 encodes a transcriptional activator that has two transactivation domains (TAD) located in its amino terminus. The 1st TAD (a.a. 1-40) is essential for the induction of numerous classical p53 target genes, while the second TAD (a.a. 41-61) suffices for tumor suppression, although its precise molecular function has been unclear. In this study, we comprehensively identified the sites to which p53 lacking the 1st TAD (Δ1stTAD-p53) binds, as well as its potential target genes. We identified and analyzed the functions of three Δ1stTAD-p53 target genes, PTP4A1, PLK2 and RPS27L. These results reveal a novel Δ1stTAD-p53 downstream pathway that is dependent on the transcription activation activity of the 2nd TAD.
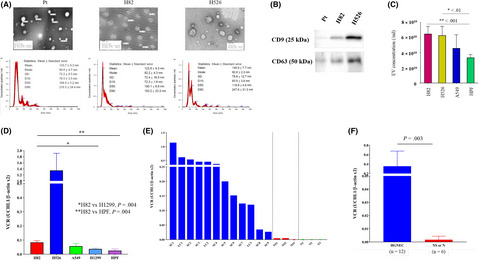
Cancer stem-like cells with hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype leading the collective invasion
- Pages: 467-476
- First Published: 17 December 2019
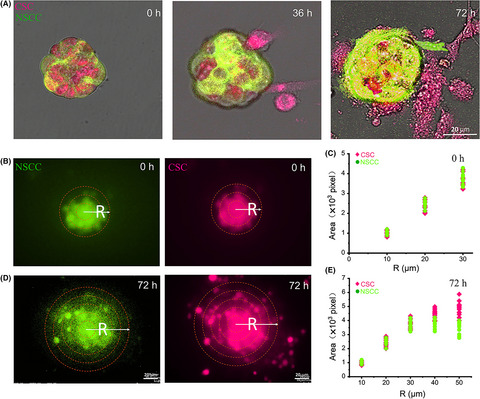
To verify the role of CSC in the collective invasion, we performed 3D assays for investigating the collective invasion from cancer cell spheroids. The results demonstrated that CSC act as leaders to promote collective invasion with hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype. Our present observations may predict a new strategy for cancer metastasis, including interventions targeting CSC.
ATP6L promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 477-488
- First Published: 15 December 2019
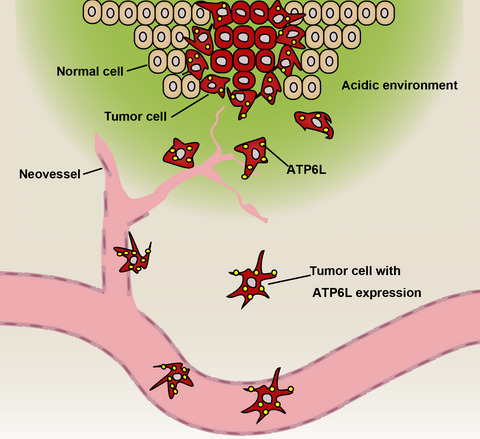
ATP6L is markedly overexpressed in the poorly differentiated colorectal cancer tissues evidently located in the invasive front and metastatic foci. More importantly, in vitro and in vivo data demonstrated that ATP6L can induce the EMT program in CRC cells. Ectopic ATP6L expression can promote microvessel density in animal xenograft tissue.
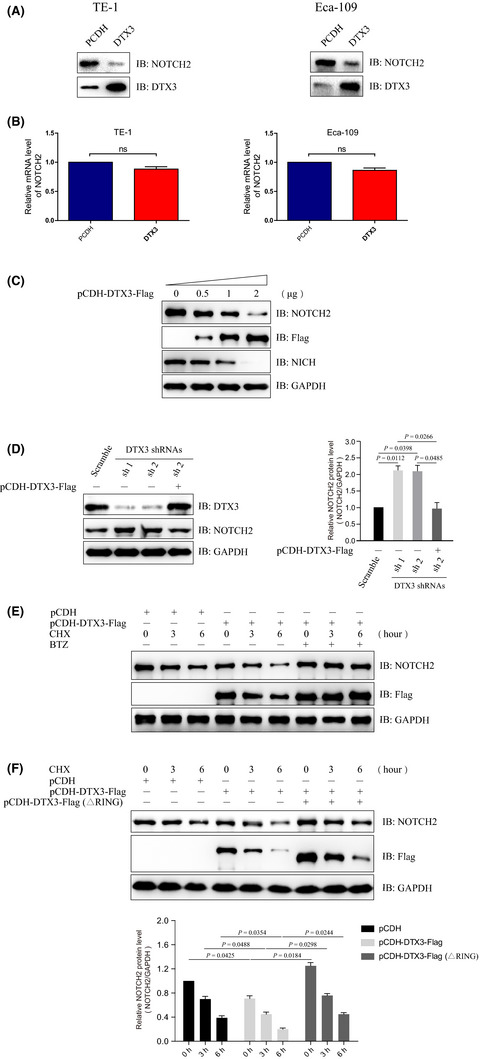
Ubiquitination of NOTCH2 by DTX3 suppresses the proliferation and migration of human esophageal carcinoma
- Pages: 489-501
- First Published: 18 December 2019
CLINICAL RESEARCH
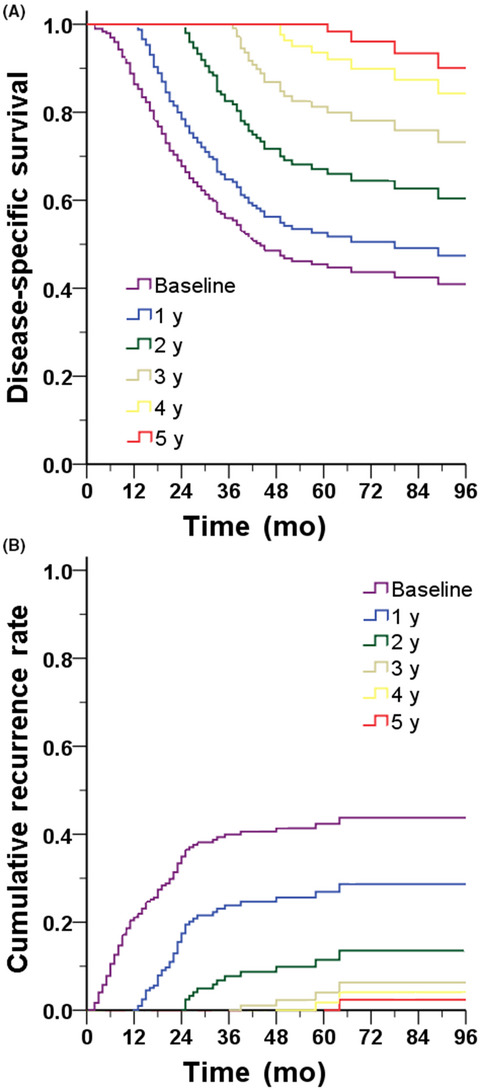
Conditional survival and recurrence of remnant gastric cancer after surgical resection: A multi-institutional study
- Pages: 502-512
- First Published: 11 November 2019
Liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma in Asian patients: Subgroup analysis of the NAPOLI-1 study
- Pages: 513-527
- First Published: 01 December 2019
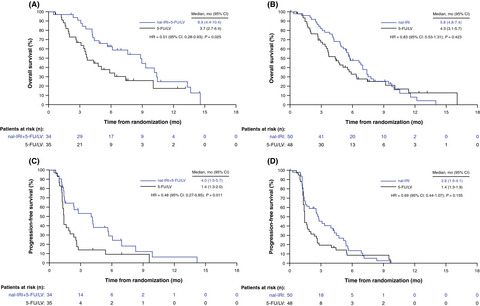
The global NAPOLI-1 phase 3 trial (NCT01494506) evaluated the safety and efficacy of liposomal irinotecan (nal-IRI) and 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin (5-FU/LV) compared with 5-FU/LV in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma that progressed following gemcitabine-based therapy. We report data from a post-hoc subgroup analysis focusing on Asian patients at centers in South Korea and Taiwan. Our findings are consistent with those from the primary analysis and show that, despite association with higher incidence of manageable grade 3-4 neutropenia, the nal-IRI+5-FU/LV regimen is an effective treatment option in Asian patients with gemcitabine-failed metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Benefit-risk assessment of nivolumab 240 mg flat dose relative to 3 mg/kg Q2W regimen in Japanese patients with advanced cancers
- Pages: 528-535
- First Published: 26 November 2019
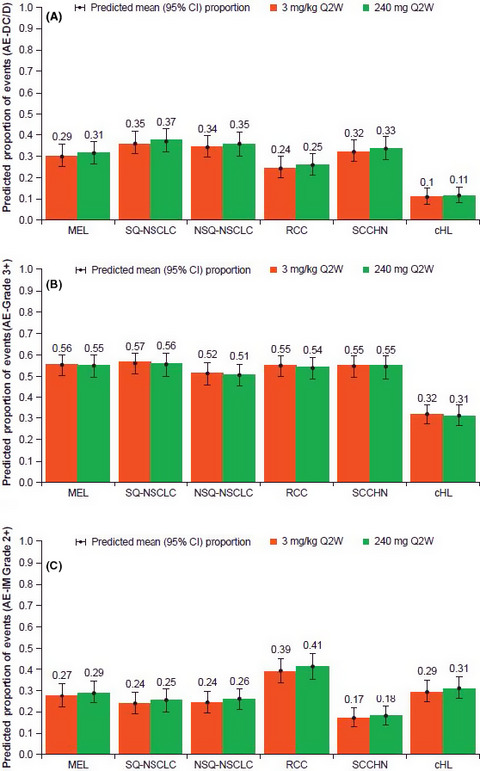
Exposure-response analyses of nivolumab in Japanese patients indicate comparable safety and efficacy outcomes for a flat dose of 240 mg every 2 weeks relative to the previously approved weight-based dose of 3 mg/kg. These data suggest that a flat dose is a safe and effective alternative to the weight-based dose in Japanese patients, across a range of tumor types.
Phase 1 study of capmatinib in MET-positive solid tumor patients: Dose escalation and expansion of selected cohorts
- Pages: 536-547
- First Published: 28 November 2019
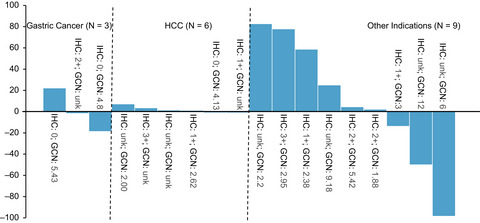
MET dysregulation is an important newly established molecular driver of tumorigenesis in various cancers and is recognized as a negative prognostic factor. The findings of this study provide the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of capmatinib and also safety and efficacy data in selected expansion cohorts treated at the RP2D.
Human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-1 expression is a predictor in patients with resected pancreatic cancer treated with adjuvant S-1 chemotherapy
- Pages: 548-560
- First Published: 28 November 2019
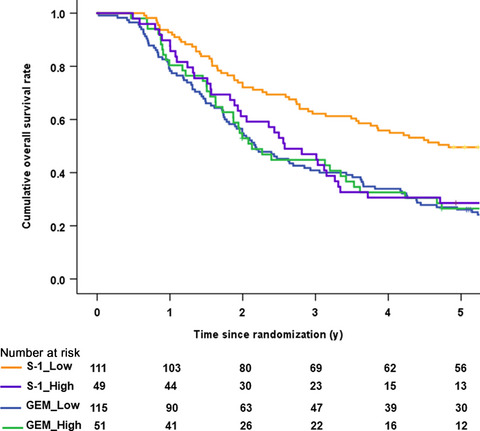
In the S-1 arm, the median overall survival (OS) with low hENT1, 58.0 months, was significantly better than that with high hENT1, 30.9 months (hazard ratio 1.75, P = .007). In contrast, there were no significant differences in OS between DPD low and high groups in the S-1 arm and neither the expression levels of hENT1 nor DPD revealed a relationship with treatment outcomes in the GEM arm.
Phase I study of vorinostat with gefitinib in BIM deletion polymorphism/epidermal growth factor receptor mutation double-positive lung cancer
- Pages: 561-570
- First Published: 29 November 2019
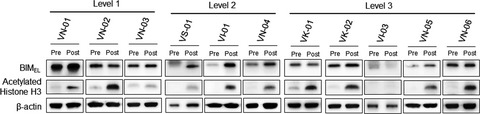
Vorinostat, in combination with gefitinib, induced acetylated histone H3 protein expression, as well as a decrease in the BIM mRNA exon 3/exon 4 ratio in PBMC from BIM deletion polymorphism/EGFR mutation double-positive NSCLC patients. These results provide proof of concept that the combined therapy can mitigate the functional effects of BIM deletion polymorphism.
First-in-human phase I study of E7090, a novel selective fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors
- Pages: 571-579
- First Published: 02 December 2019
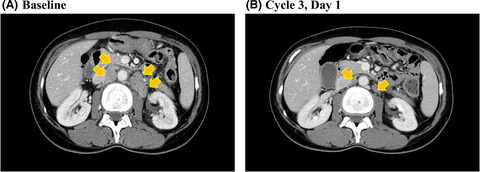
This phase I, first-in-human study in Japan evaluated the safety and tolerability of E7090, a selective fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 1-3 inhibitor, for treatment of advanced solid tumors. A total of 24 patients refractory to standard therapy or for whom no appropriate treatment was available were enrolled; no dose-limiting toxicities were observed up to 140 mg QD and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached. E7090 showed an acceptable safety profile with dose-dependent pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters; preliminary efficacy will be investigated in a follow-up expansion part restricted to gastric cancer patients with FGFR2 amplification or cholangiocarcinoma with FGFR2 fusion.
Mutation status and burden can improve prognostic prediction of patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes
- Pages: 580-591
- First Published: 05 December 2019
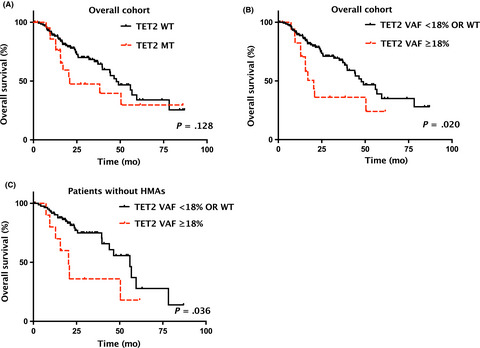
Shorter OS was associated with mutation status of ASXL1, EZH2 and JAK2, as well as TET2 VAF ≥18%. A novel prognostic scoring system based on the IPSS and the presence/absence of the four independent mutational factors further stratified LR-MDS patients into three prognostically different groups. Integration of IPSS with mutation status/burden of certain MDS-relevant genes may improve the prognostication of patients with LR-MDS and could help identify those with worse-than-expected prognosis for more aggressive treatment.
Detection of methylation status of Epstein-Barr virus DNA C promoter in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 592-600
- First Published: 13 December 2019
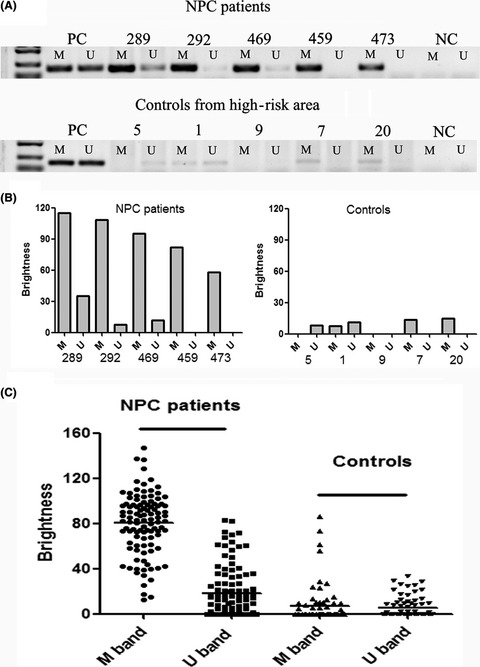
A significant difference in EBV DNA methylation was observed between NPC patients and the control group in high-risk areas. Therefore, detection of methylation status of EBV DNA C promoter in NP brushing samples shows great potential in diagnosing NPC and may provide an appealing alternative for non–invasive detection and screening of NPC without the need for clinical settings.
Spatial and temporal expansion of intrahepatic metastasis by molecularly-defined clonality in multiple liver cancers
- Pages: 601-609
- First Published: 17 December 2019
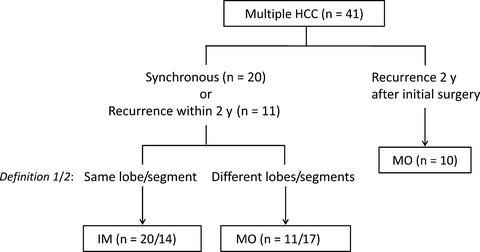
Exome sequencing was able to be used to discriminate multiple HCC as IM or MO and it became clear that liver cancer cells could spread more extensively and more slowly than previously thought. Given that the overall survival of patients with IM and MO did not differ, the accurate classification of multiple HCC is not clinically important.
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 has prognostic relevance and is a therapeutic target for high-grade neuroendocrine lung cancers
- Pages: 610-620
- First Published: 17 December 2019
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
RPV-modified epirubicin and dioscin co-delivery liposomes suppress non-small cell lung cancer growth by limiting nutrition supply
- Pages: 621-636
- First Published: 28 November 2019
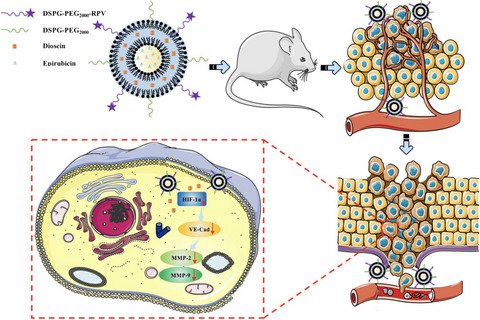
Targeted epirubicin and dioscin co-delivery liposomes modified with RPV increased cellular uptake and accumulation in the A549 cells. The RPV-modified epirubicin and dioscin co-delivery liposomes enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in vitro and in vivo. The RPV-modified epirubicin and dioscin co-delivery liposomes inhibited NSCLC migration and invasion by limiting tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry formation.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
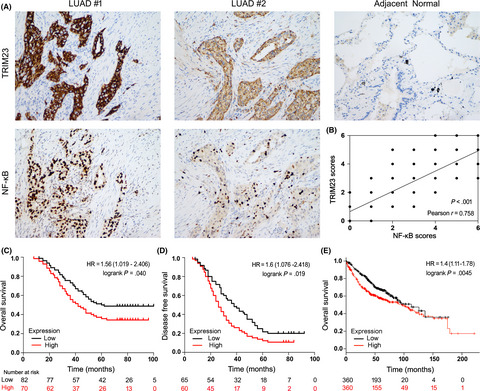
Elevated TRIM23 expression predicts cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 637-646
- First Published: 02 November 2019
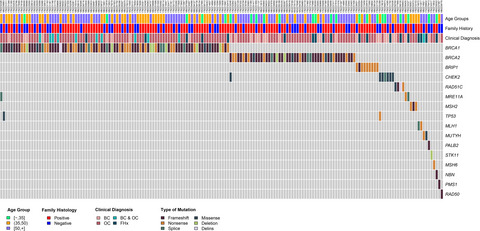
Prevalence of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) predisposition gene mutations among 882 HBOC high-risk Chinese individuals
- Pages: 647-657
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Promotion of the Warburg effect is associated with poor benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 658-666
- First Published: 11 December 2019
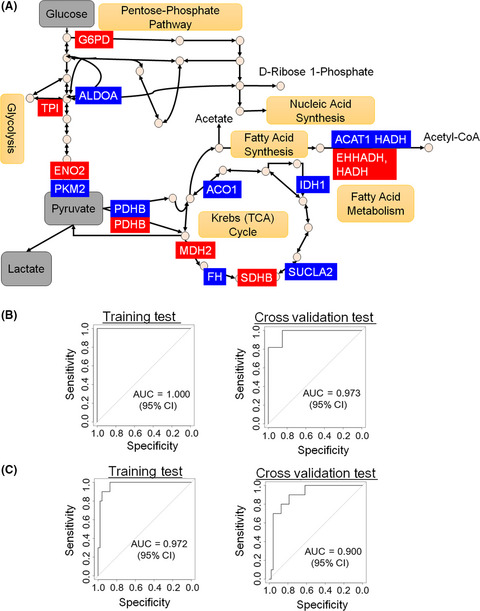
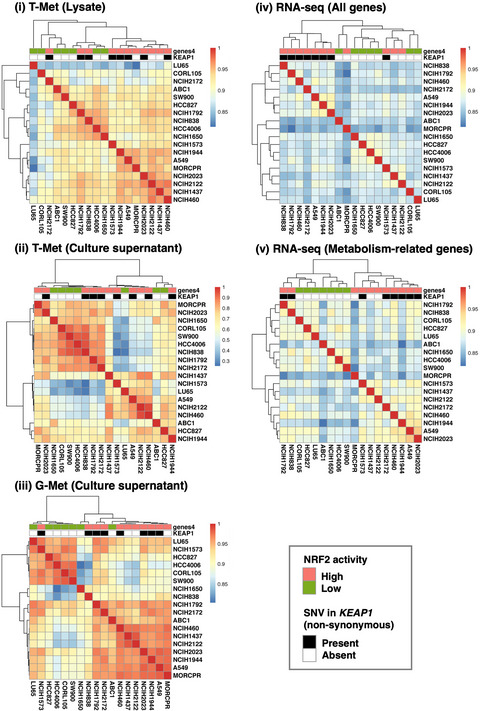
Impacts of NRF2 activation in non–small-cell lung cancer cell lines on extracellular metabolites
- Pages: 667-678
- First Published: 11 December 2019
Potential mechanism of primary resistance to icotinib in patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon mutant epidermal growth factor receptor: A multi-center study
- Pages: 679-686
- First Published: 11 December 2019
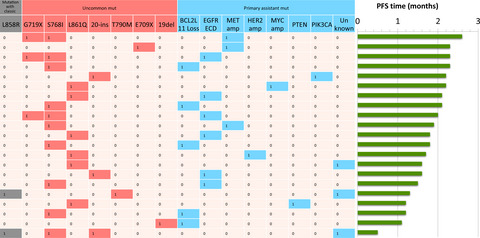
In a large-scale multi-center real-world study in China, we detected and analyzed potential primary resistance to icotinib in EGFRum patients using the next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform. EGFR extracellular domain mutation, BCL2L11 loss, PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway (PTEN, PIK3CA mutations), MET amplification, ERBB2 amplification or MYC amplification might contribute to primary resistance of icotinib in EGFRum NSCLC patients.
Japanese version of The Cancer Genome Atlas, JCGA, established using fresh frozen tumors obtained from 5143 cancer patients
- Pages: 687-699
- First Published: 21 December 2019
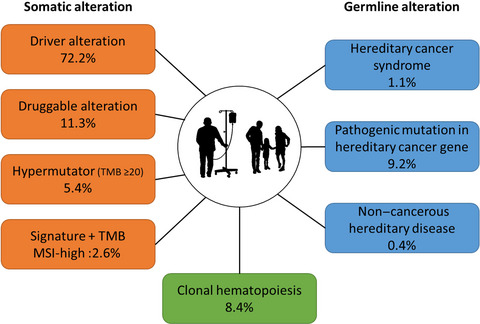
The present study aims to establish the Japanese Cancer Genome Atlas (JCGA) by analyzing fresh frozen tumor tissues obtained from 5143 Japanese cancer patients. Somatic driver and druggable alterations were detected in 72.2% and 11.3% of samples, respectively, and germline pathogenic mutations in hereditary cancer genes were identified in 9.2% of samples. The JCGA dataset and analytical procedures constitute a fundamental resource for genomic medicine for Japanese cancer patients.
PATHOLOGY
Intracellular claudin-1 at the invasive front of tongue squamous cell carcinoma is associated with lymph node metastasis
- Pages: 700-712
- First Published: 26 November 2019
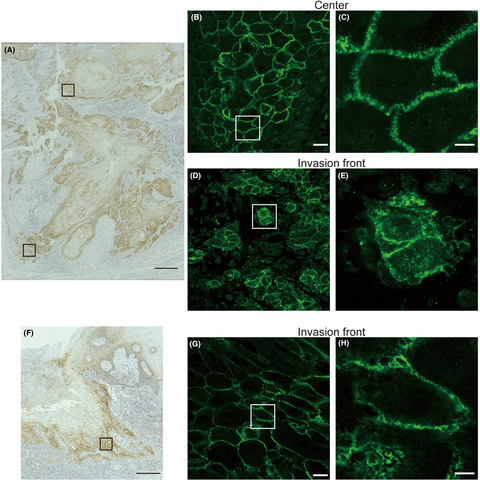
Claudin-1 was predominantly localized at the membrane in the center of the lesion, but intracellular claudin-1 localization was also observed at the invasion front in some tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) pathological specimens. Within the high claudin-1 expression group, incidence of intracellular localization of claudin-1 correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis.
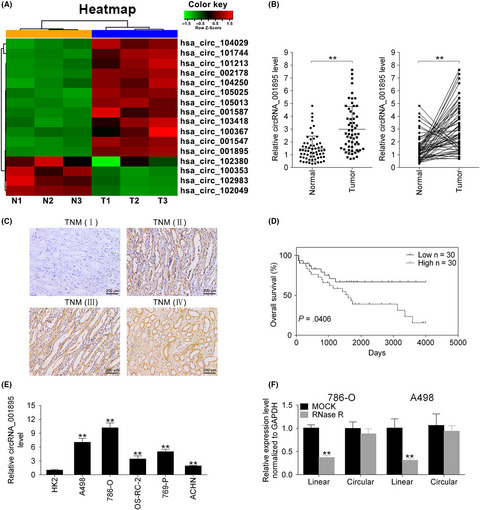
Circular RNA hsa_circ_001895 serves as a sponge of microRNA-296-5p to promote clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by regulating SOX12
- Pages: 713-726
- First Published: 29 November 2019
Infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages is involved in tumor programmed death-ligand 1 expression in early lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 727-738
- First Published: 10 December 2019
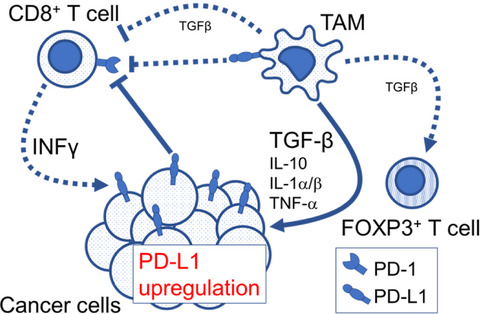
In this study, we showed that tumor-associated macrophage (TAM) infiltration was an additional factor related to tumor programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in early lung adenocarcinoma. Our in vitro experiments demonstrated that M2-differentiated macrophages facilitated tumor PD-L1 expression through transforming growth factor-β. These results suggested that TAM were extrinsic regulators of tumor PD-L1 expression and could serve as potential therapeutic targets.
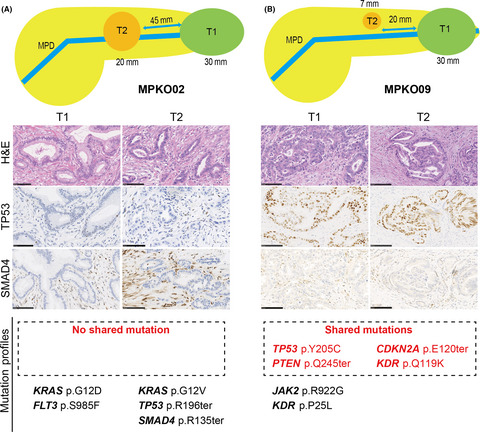
Pathogenesis of multiple pancreatic cancers involves multicentric carcinogenesis and intrapancreatic metastasis
- Pages: 739-748
- First Published: 04 December 2019
Abemaciclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, exerts preclinical activity against aggressive germinal center-derived B-cell lymphomas
- Pages: 749-759
- First Published: 17 December 2019
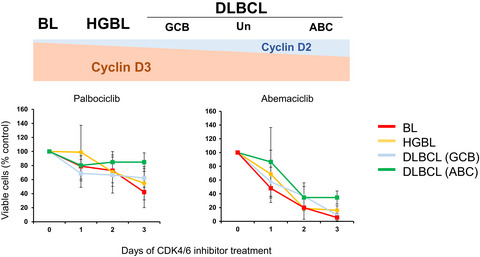
The effects of CDK4/6 inhibitors on cell proliferation in aggressive B-cell lymphoma cell lines were investigated. Abemaciclib completely suppressed cell growth irrespective of the CCND3 mutation status in GCB-like DLBCL cell lines. Abemaciclib has potential as a therapeutic agent for aggressive GC-derived B-cell lymphomas, including high-grade B-cell lymphomas.