Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 1091-1093
- First Published: 22 June 2017

Cover of this issue. Effect of Talin1 knockdown on the growth of lamellipodia. See also Chen et al. (pages 1157–1168 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLES
Integrated functions of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in regulating cancer malignancy: Beyond a proteinase
- Pages: 1095-1100
- First Published: 07 March 2017
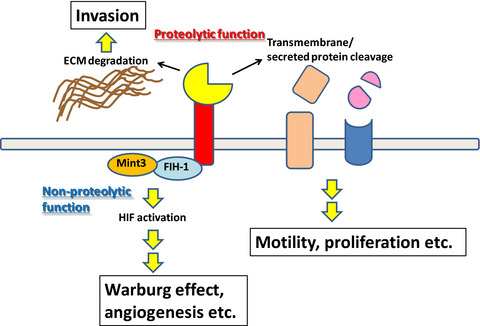
In cancer cells and activated stromal cells, MT1-MMP promotes invasion, motility, and proliferation in a proteolytic manner. MT1-MMP also activates hypoxia-inducible factor and thereby promotes the Warburg effect and angiogenesis in a non-proteolytic manner. Thus, MT1-MMP integrates malignant traits of cancer.
A vicious partnership between AKT and PHLDA3 to facilitate neuroendocrine tumors
- Pages: 1101-1108
- First Published: 12 March 2017
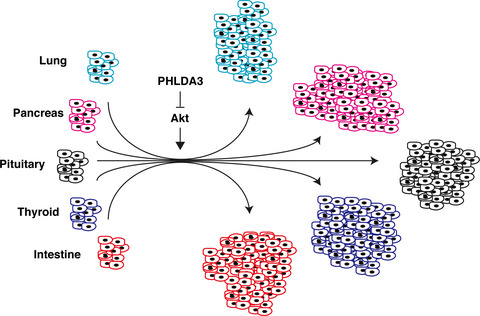
Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) are rare cancers, and a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of NET is required for accurate diagnosis and proper treatment of these tumors. It has been shown that the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway plays an important role in pancreatic NET tumorigenesis, and we previously have shown that PHLDA3, a repressor of Akt, functions as a novel tumor suppressor of pancreatic and lung NET. In this paper, we review some recent findings regarding the significance and molecular modes of action of PHLDA3 and Akt in neuroendocrine tumors.
Clinical development of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Pages: 1109-1118
- First Published: 16 March 2017
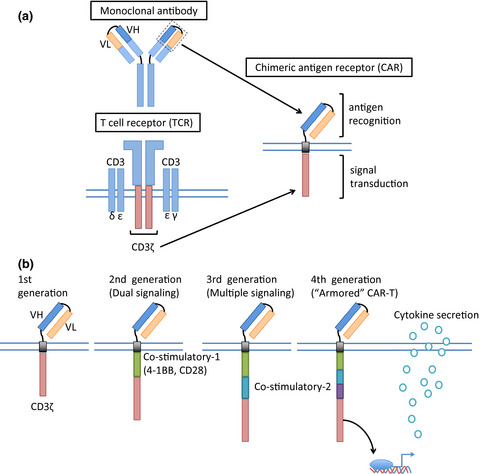
Although refined chemotherapies and several new agents have improved the prognosis of B-cell malignancies in the recent decades, we still experience a substantial number of patients with chemo-refractory disease. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is expected to be an effective adoptive cell therapy and it might have a potential to overcome the chemo-refractoriness of B-cell leukemia and lymphoma.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Programmed death-ligand 1 expression at tumor invasive front is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1119-1127
- First Published: 14 March 2017
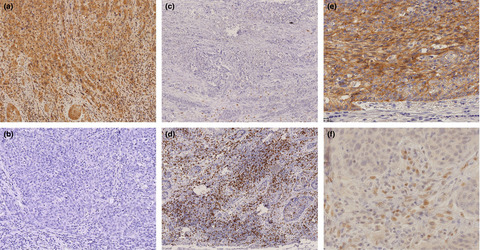
PD-L1 plays a crucial role in the host immune system in cancer progression. Its gene promoter region contains a binding site for ZEB1. Our report shows that high PD-L1 expression at the invasive front of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) was associated with greater depth of tumor invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and less CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration.
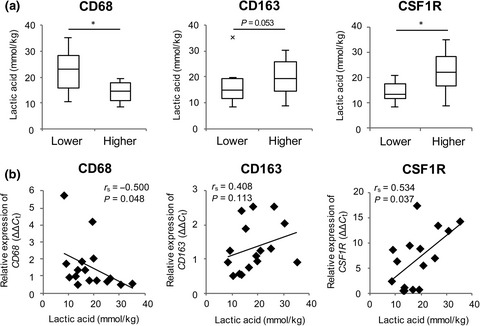
M2-like macrophage polarization in high lactic acid-producing head and neck cancer
- Pages: 1128-1134
- First Published: 01 April 2017
CARCINOGENESIS
BRAF mutations are associated with increased iron regulatory protein-2 expression in colorectal tumorigenesis
- Pages: 1135-1143
- First Published: 09 March 2017
cIAP2 promotes gallbladder cancer invasion and lymphangiogenesis by activating the NF-κB pathway
- Pages: 1144-1156
- First Published: 15 March 2017
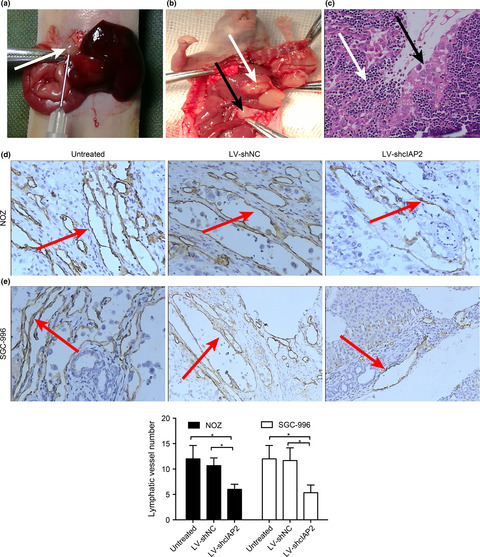
Our study suggests that cIAP2 is highly expressed in human GBC and correlates with poor prognosis; furthermore, the results showed that cIAP2 can promote gallbladder cancer invasion and lymphangiogenesis by activating the NF-κB pathway. These data indicate that cIAP2 may be a potential treatment target to prevent the invasion and lymphatic metastasis of GBC.
Downregulation of Talin1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway
- Pages: 1157-1168
- First Published: 04 April 2017
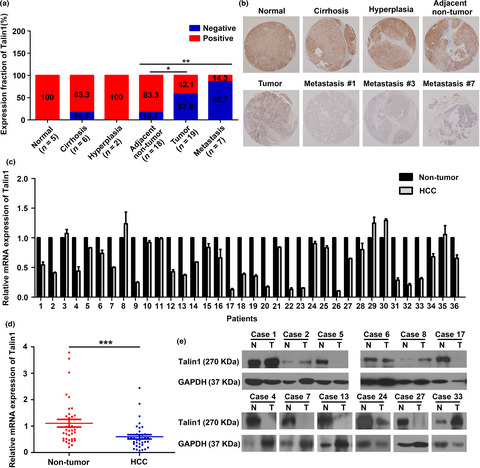
In this study, we showed a trend of gradually decreasing expression of Talin1 from normal liver tissues to hepatocirrhosis, liver hyperplasia, the corresponding adjacent non-tumor, primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and eventually metastatic foci. Furthermore, low Talin1 expression is significantly associated with tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in HCC patients. More importantly, we provided novel data to show that Talin1 inhibition can act as a positive regulator of EMT, migration and invasion in HCC cells via activation of the ERK1/2 pathway.
NUBPL, a novel metastasis-related gene, promotes colorectal carcinoma cell motility by inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 1169-1176
- First Published: 27 March 2017
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
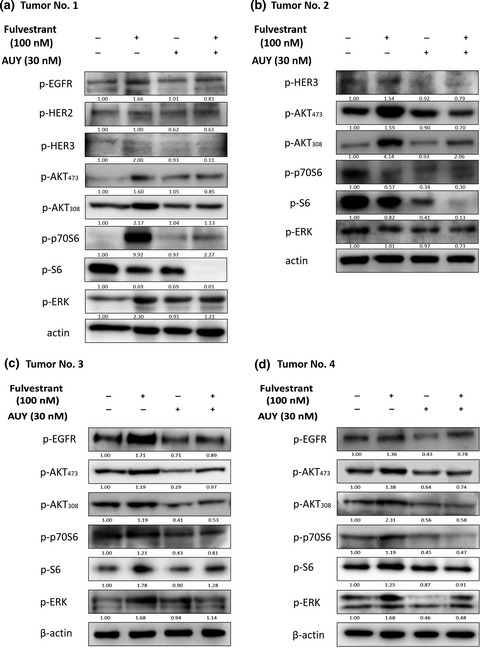
HSP90 inhibitor AUY922 can reverse Fulvestrant induced feedback reaction in human breast cancer cells
- Pages: 1177-1184
- First Published: 16 March 2017
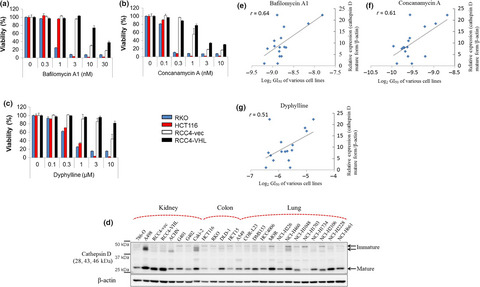
Cancer with low cathepsin D levels is susceptible to vacuolar (H+)-ATPase inhibition
- Pages: 1185-1193
- First Published: 19 March 2017
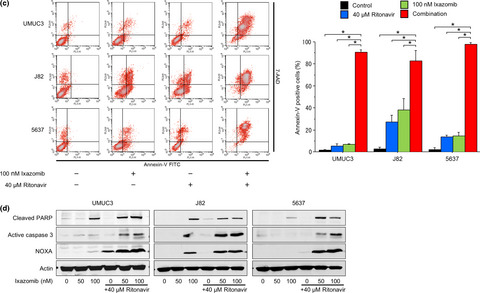
Ritonavir and ixazomib kill bladder cancer cells by causing ubiquitinated protein accumulation
- Pages: 1194-1202
- First Published: 25 March 2017
Effects of SMYD2-mediated EML4-ALK methylation on the signaling pathway and growth in non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Pages: 1203-1209
- First Published: 01 April 2017
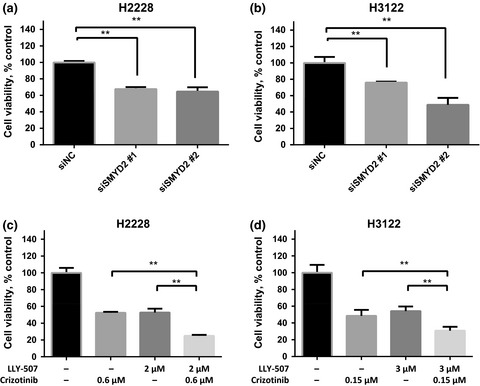
We identified that EML4-ALK as a novel substrate of the protein lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 and this methylation might play a critical role in the phosphorylation of EML4-ALK protein and its oncogenic activity. We also imply that the SMYD2 inhibitor might enhance the growth suppressive effect of ALK inhibitors.
Intratumoral bidirectional transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal cells in triple-negative breast cancer
- Pages: 1210-1222
- First Published: 01 April 2017
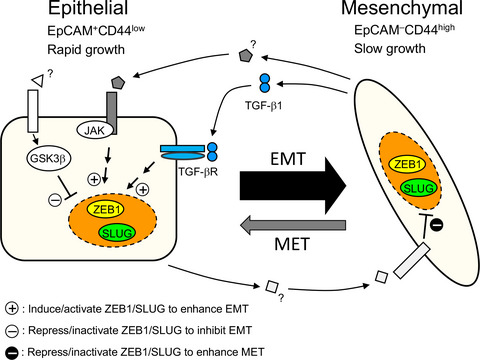
Triple negative breast cancer cell line HCC38 composed of epithelial and mesenchymal population at fixed ratio even though mesenchymal cells proliferate significantly slower than epithelial cells. Using this system, we demonstrate that the efficiency of EMT is about a magnitude higher than that of MET and that the two populations significantly enhance the transition of another population to own population. We propose that HCC38 is a suitable model to analyze the EMT-MET dynamics that could affect development of triple negative breast cancer.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Efficacy and safety of nivolumab in Japanese patients with previously untreated advanced melanoma: A phase II study
- Pages: 1223-1230
- First Published: 25 March 2017
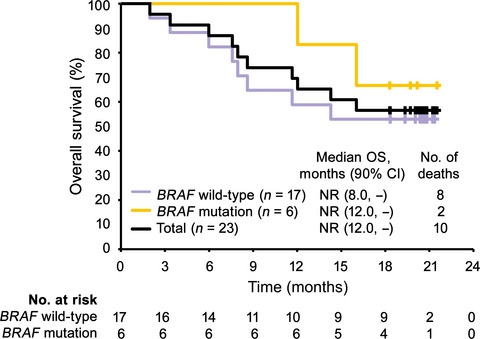
We conducted the present single-arm, open-label, multicenter, phase 2 study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nivolumab in previously untreated Japanese patients with advanced melanoma. Nivolumab administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg once every 2 weeks was tolerable and demonstrated favorable anti-cancer activity. In addition, patients with BRAF wild-type and those with BRAF mutant melanoma both experienced response.
Overall survival of first-line axitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from phase II study
- Pages: 1231-1239
- First Published: 07 March 2017
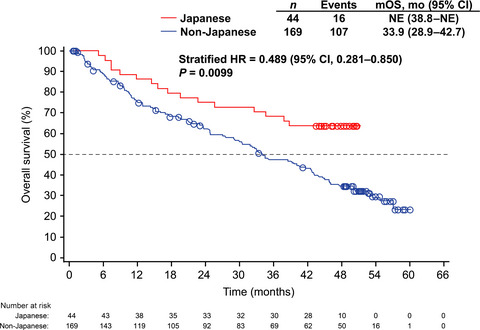
The subgroup analysis of a randomized global phase II study demonstrated the clinical activity of axitinib in treatment-naïve Japanese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma, with an acceptable toxicity profile. The estimated 3-year survival (95% confidence interval) was higher among 44 Japanese than 169 non-Japanese patients: 68.2% (54.4–81.9) versus 47.2% (39.3–55.1). The multivariate analysis identified baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status, baseline tumor burden, and time from histopathological diagnosis to treatment as potential predictors of overall survival.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
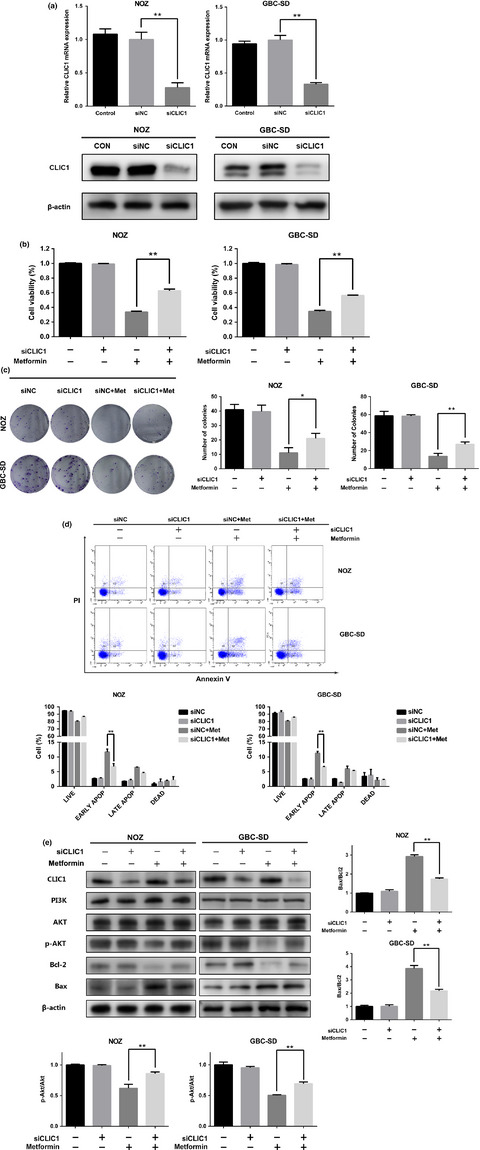
Chloride intracellular channel 1 regulates the antineoplastic effects of metformin in gallbladder cancer cells
- Pages: 1240-1252
- First Published: 05 April 2017
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
Socioeconomic factors and survival in patients with non-metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1253-1262
- First Published: 06 April 2017
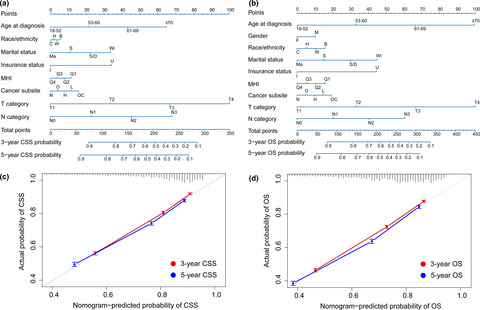
We built nomograms for CSS/OS and a prognostic score model for risk stratification based on validated socioeconomic factors, such as marital status, median household income and insurance status. Both nomograms had higher efficacies than the 6th edition TNM staging system, and the prognostic score model generated four risk subgroups with separated CSS/OS. Low-risk socioeconomic status and Chinese race/ethnicity confer protective effects on patients with non-matastatic HNSCC.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Exome sequencing deciphers a germline MET mutation in familial epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer
- Pages: 1263-1270
- First Published: 13 March 2017
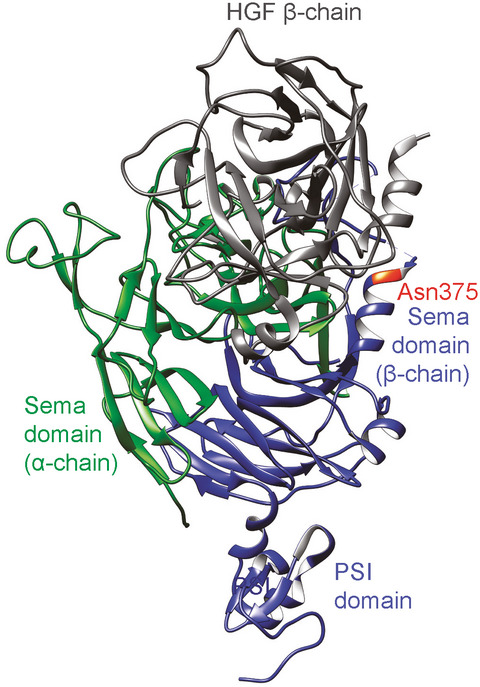
We identified a germline mutation in MET by the whole-exome sequencing analysis of familial EGFR-mutant lung cancer. The inactivating mutation in MET potentially generates oncogenic stress that induces compensatory EGFR activation for development of EGFR-mutant lung cancer. The identification of MET as the gene associated with familial EGFR-mutant lung cancer will provide valuable insights into the pathogenic mechanisms of not only familial, but also sporadic EGFR-mutant lung cancer by underscoring MET-related signaling molecules.
PATHOLOGY
Clinicopathological analysis of methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: Comparison of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma types
- Pages: 1271-1280
- First Published: 05 April 2017
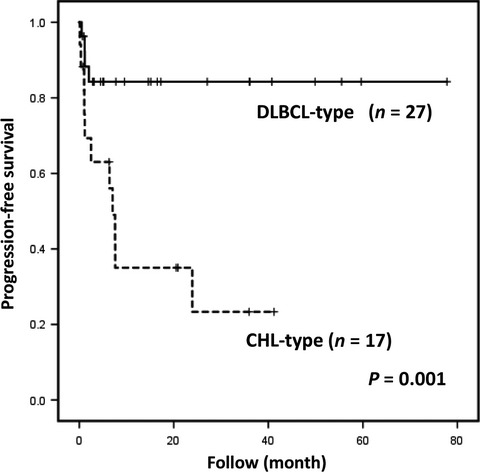
Many of the DLBCL-type MTX-LPD patients showed spontaneous remission and a better survival rate after methotrexate discontinuation. In contrast, more of the CHL-type MTX-LPD patients did not show spontaneous remission, and required additional chemotherapy. These findings are clinically relevant because the morphological differences in the pathological histology of MTX-LPD might be a prognostic factor after methotrexate discontinuation.