Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
HLA-E expression in serous ovarian cancer with HLA-E*0101*0103
- Page: May cover
- First Published: 21 May 2015
ISSUE INFORMATION
In This Issue
REVIEW ARTICLES
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition is regulated at post-transcriptional levels by transforming growth factor-β signaling during tumor progression
- Pages: 481-488
- First Published: 09 February 2015
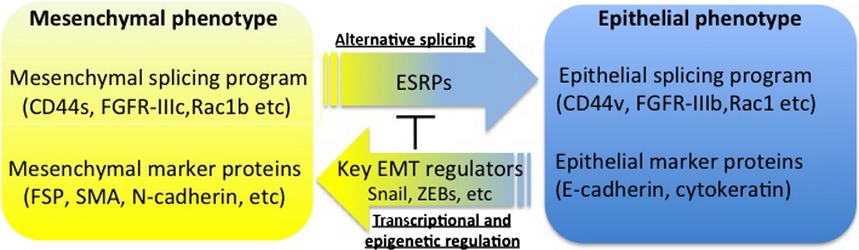
The key EMT regulators modify expressions of EMT marker proteins at the posttranscriptional, transcriptional, and epigenetic levels. TGF-β, probably secreted from cancer cells, regulates expression of the key EMT regulators and plays a role in tumor progression in cooperation with additional signals from other factors secreted from cells in the tumor microenvironment.
Intracellular signals of lung cancer cells as possible therapeutic targets
- Pages: 489-496
- First Published: 24 February 2015
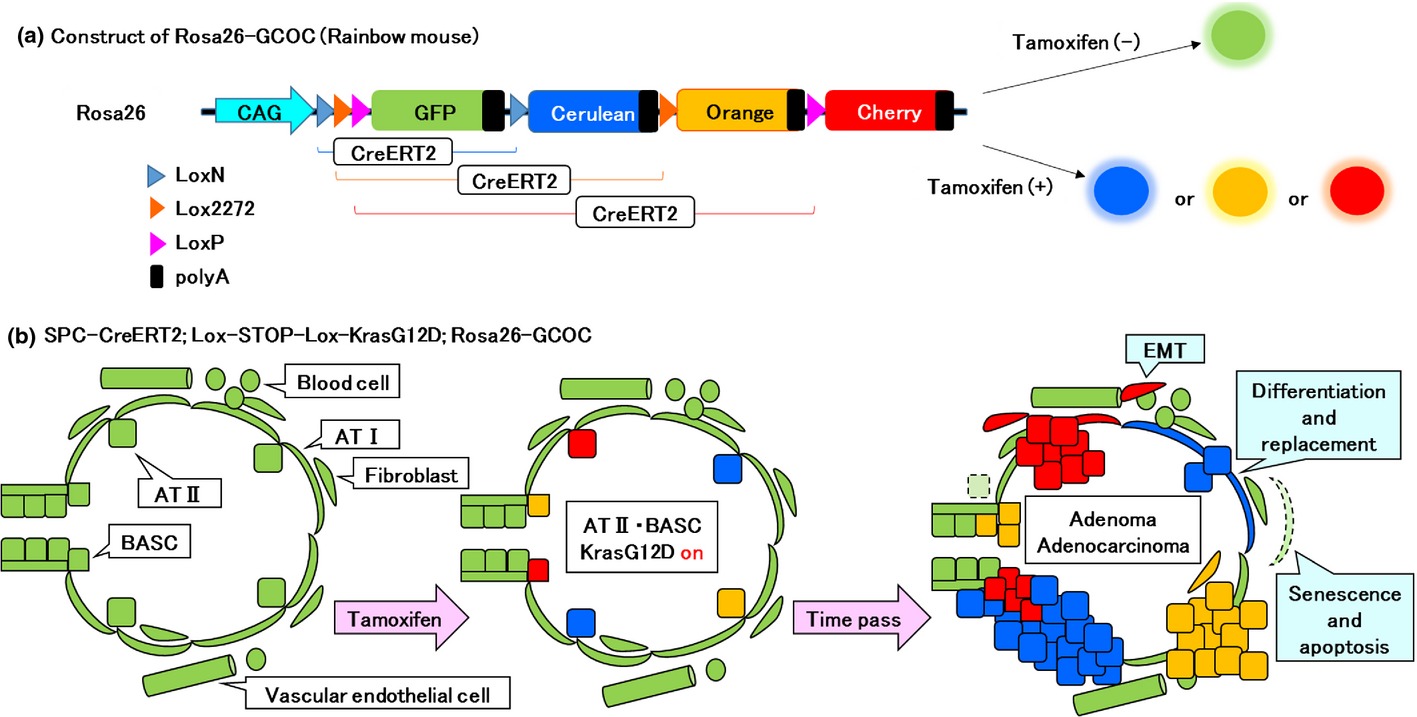
In recent years, several molecularly targeted therapies have been developed as part of lung cancer treatment and produced dramatically good results. However, among the many oncogenes that have been identified to be involved in the onset of lung cancers, a number of oncogenes are not covered by these advanced therapies. In this article, we discuss major causal genes of lung cancers and intracellular signaling pathways involving those genes, and review studies of origin cells and stem cells of lung cancers, as well as the possibility of developing molecularly targeted therapies based on these studies.
Pharmacokinetics, dynamics and toxicity of docetaxel: Why the Japanese dose differs from the Western dose
- Pages: 497-504
- First Published: 25 February 2015
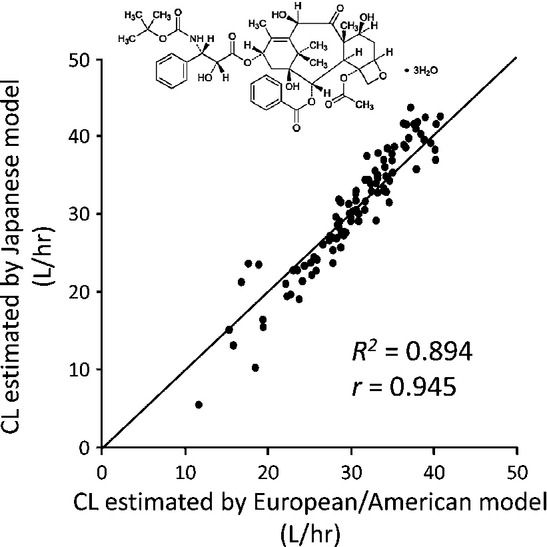
Docetaxel has been one of the most important chemotherapeutic drugs for cancer treatment, but a practical problem is discrepancy in standard dose between Japan and Western countries. This article reviews extensively the pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and toxicological profiles of docetaxel, and explains why there exists an ethnic difference in dose, and further discusses which direction we should go forward to solve this problem.
Cancer immunotherapy using novel tumor-associated antigenic peptides identified by genome-wide cDNA microarray analyses
- Pages: 505-511
- First Published: 02 March 2015
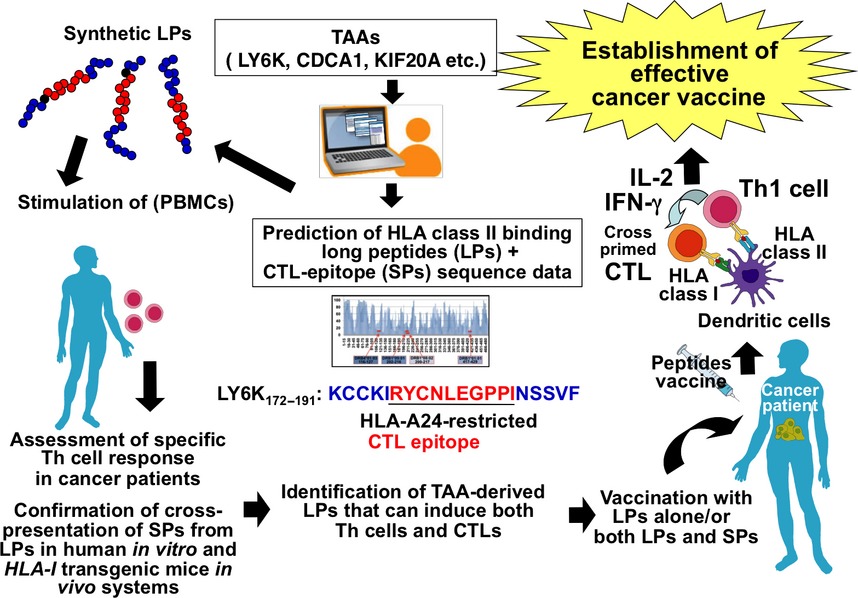
We attempted to identify TAAs-derived LPs encompassing both LPs-specific Th1 cells and CTLs epitopes in order to further improve TAAs-derived peptides-based cancer immunotherapy. We have succeeded in identification of highly immunogenic TAAs-derived LPs activating both promiscuous HLA class II-restricted Th1 cells and CTLs specific to SPs crosspresented from LPs by DCs.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
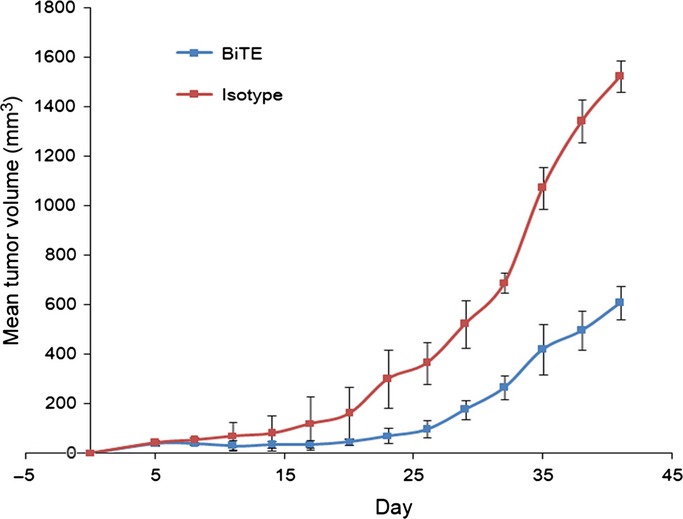
Immunotherapy based on bispecific T-cell engager with hIgG1 Fc sequence as a new therapeutic strategy in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 512-521
- First Published: 09 February 2015
Human leukocyte antigen-E alleles and expression in patients with serous ovarian cancer
- Pages: 522-528
- First Published: 24 February 2015
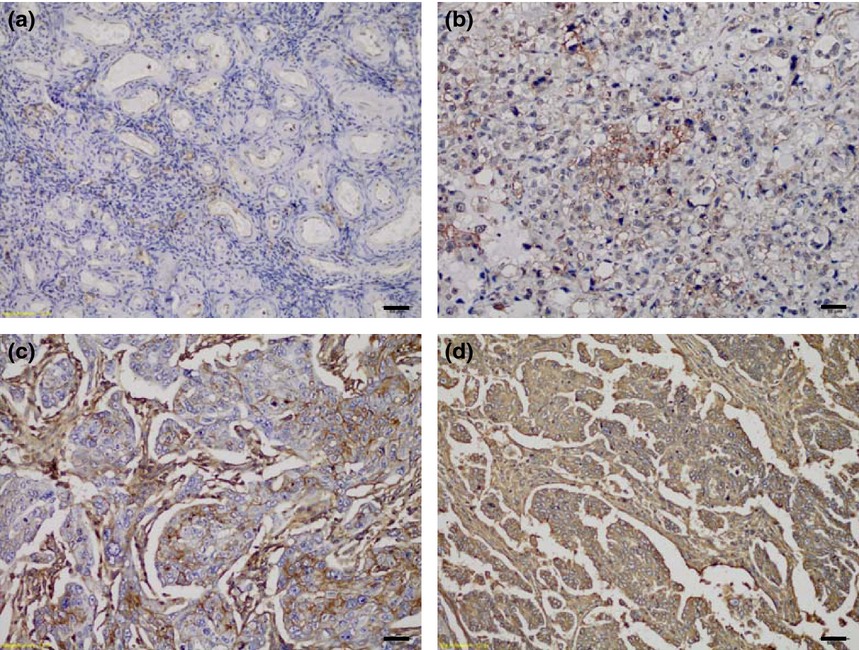
In this study, we found the frequency of HLA-E*0103 allele was increased in patients with serous ovarian cancer, and HLA-E*0103/peptides complex was stable. Thus, the elevated expression of total and cell surface HLA-E molecule with HLA-E*0103 allele increased the inhibitory effect on NK cell lysis, rendering tumor cells escape from NK immune surveillance. This study is the first one to evaluate the correlation between HLA-E alleles and serous ovarian cancer.
CARCINOGENESIS
Validation study of the combined repeated-dose toxicity and genotoxicity assay using gpt delta rats
- Pages: 529-541
- First Published: 12 February 2015
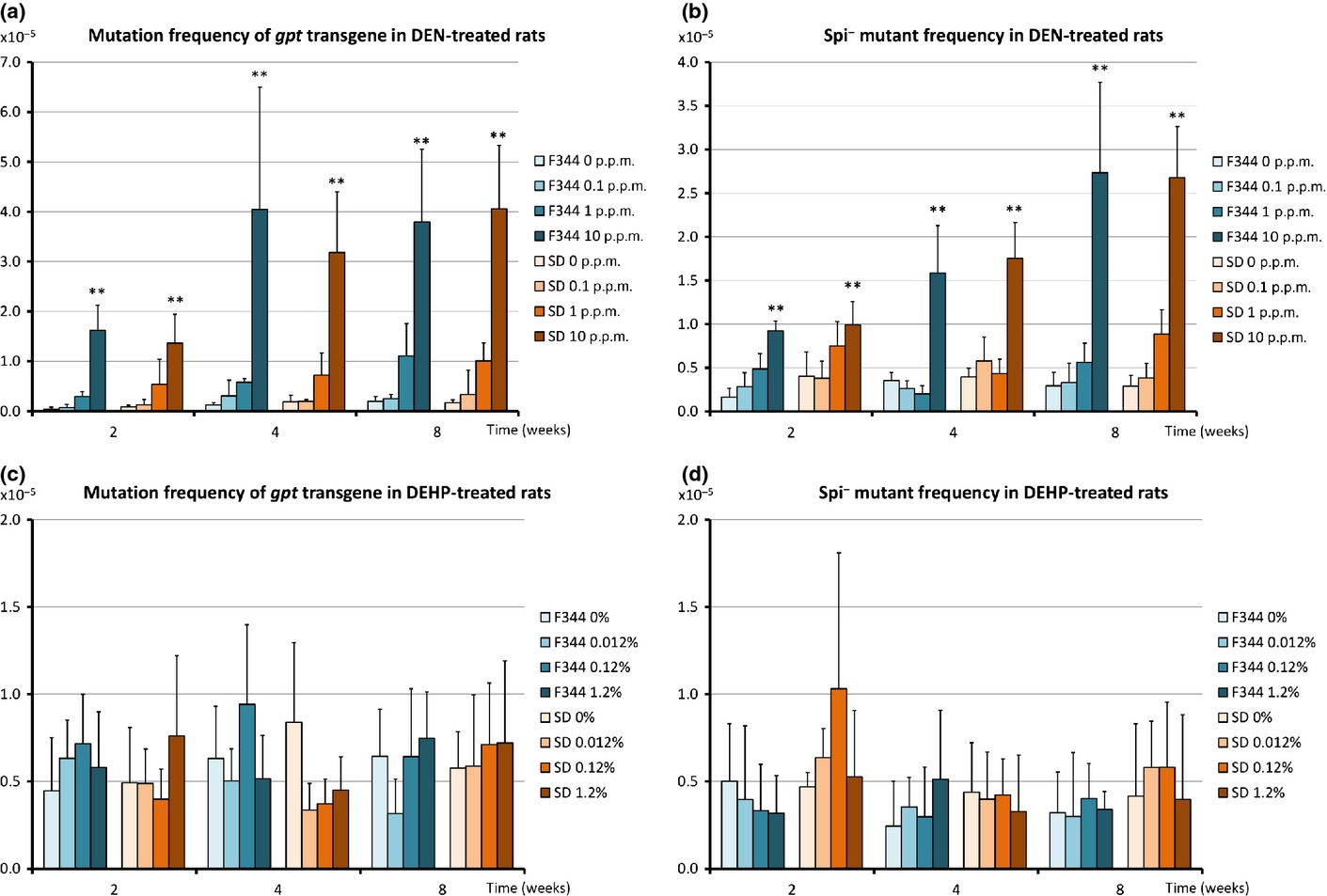
To support development of a combined assay for general toxicity and genotoxicty by using transgenic rodents, we provide evidences that indicate equivalence of gpt delta rats, which carry reporter genes to detect in vivo genotoxicity, to their parental wild type in terms of toxicological responses. DEN- or DEHP- treated F344 and SD strains of gpt delta rats display comparable general toxicity and genotoxicity to wild type. Our results indicate that the combined assay using gpt delta rats was applicable for simultaneous detection of both general toxicity and genotoxicity for short durations of administration.
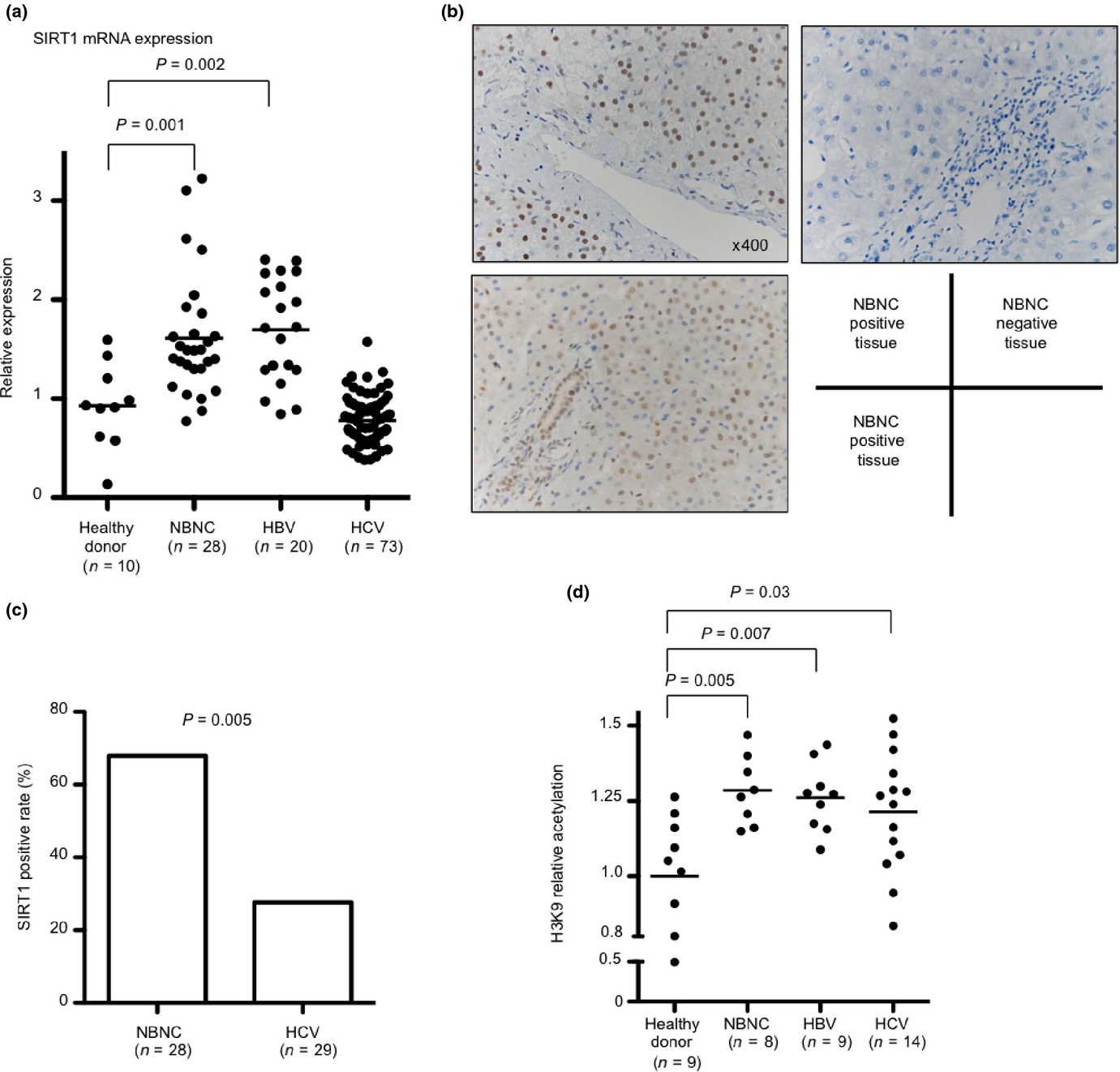
Suppression of silent information regulator 1 activity in noncancerous tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma: Possible association with non-B non-C hepatitis pathogenesis
- Pages: 542-549
- First Published: 03 March 2015
Therapeutic advances in BIG3-PHB2 inhibition targeting the crosstalk between estrogen and growth factors in breast cancer
- Pages: 550-558
- First Published: 03 March 2015
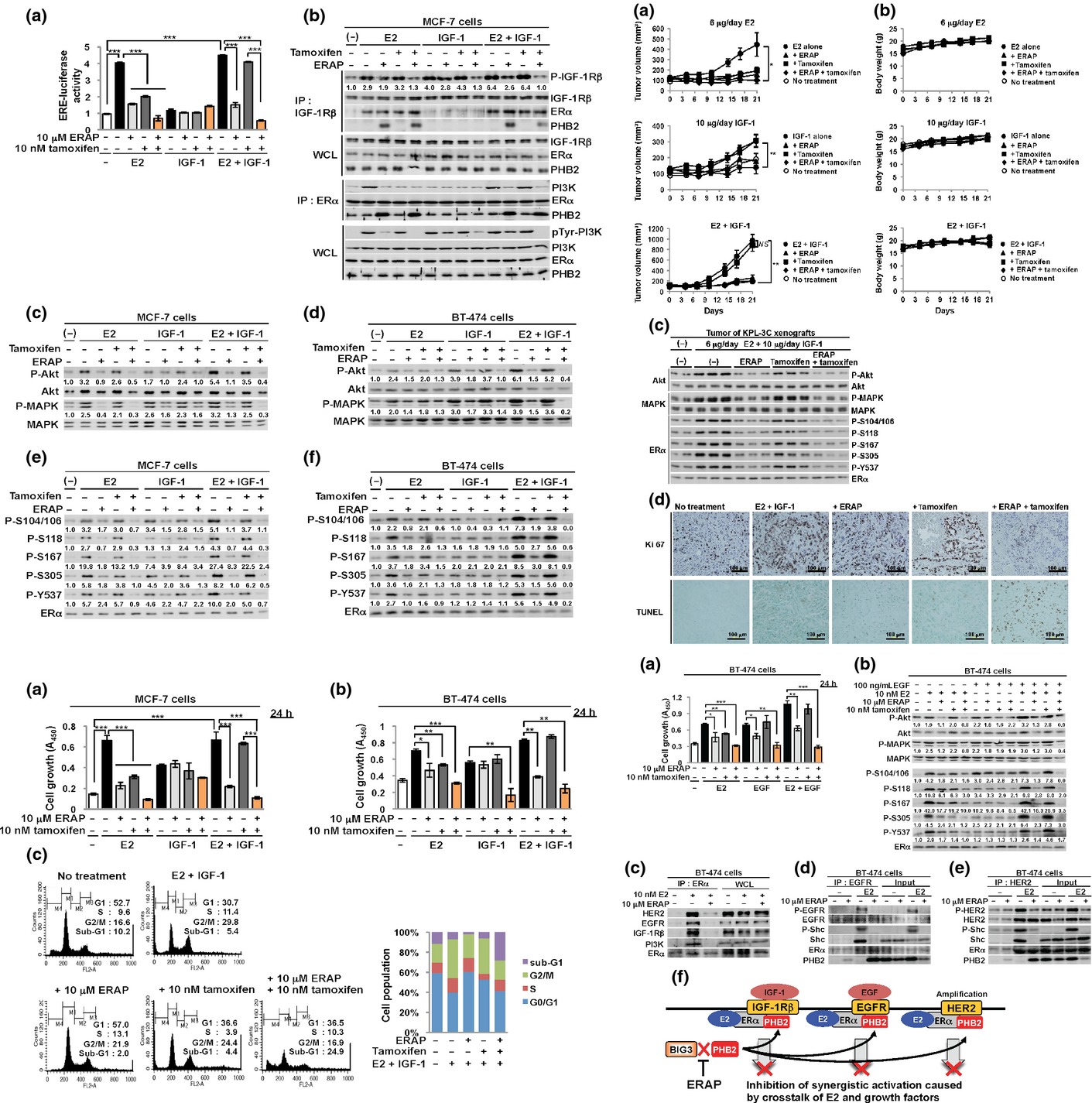
The specific disruption of BIG3-PHB2 complex, which is a critical modulator in estrogen signaling, leads to a novel therapeutic approach for endocrine-resistance in breast cancer cells activated by signaling crosstalk between estrogen and growth factors or HER2 amplification, especially in premenopausal women.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Sirtuin 6 promotes transforming growth factor-β1/H2O2/HOCl-mediated enhancement of hepatocellular carcinoma cell tumorigenicity by suppressing cellular senescence
- Pages: 559-566
- First Published: 12 February 2015
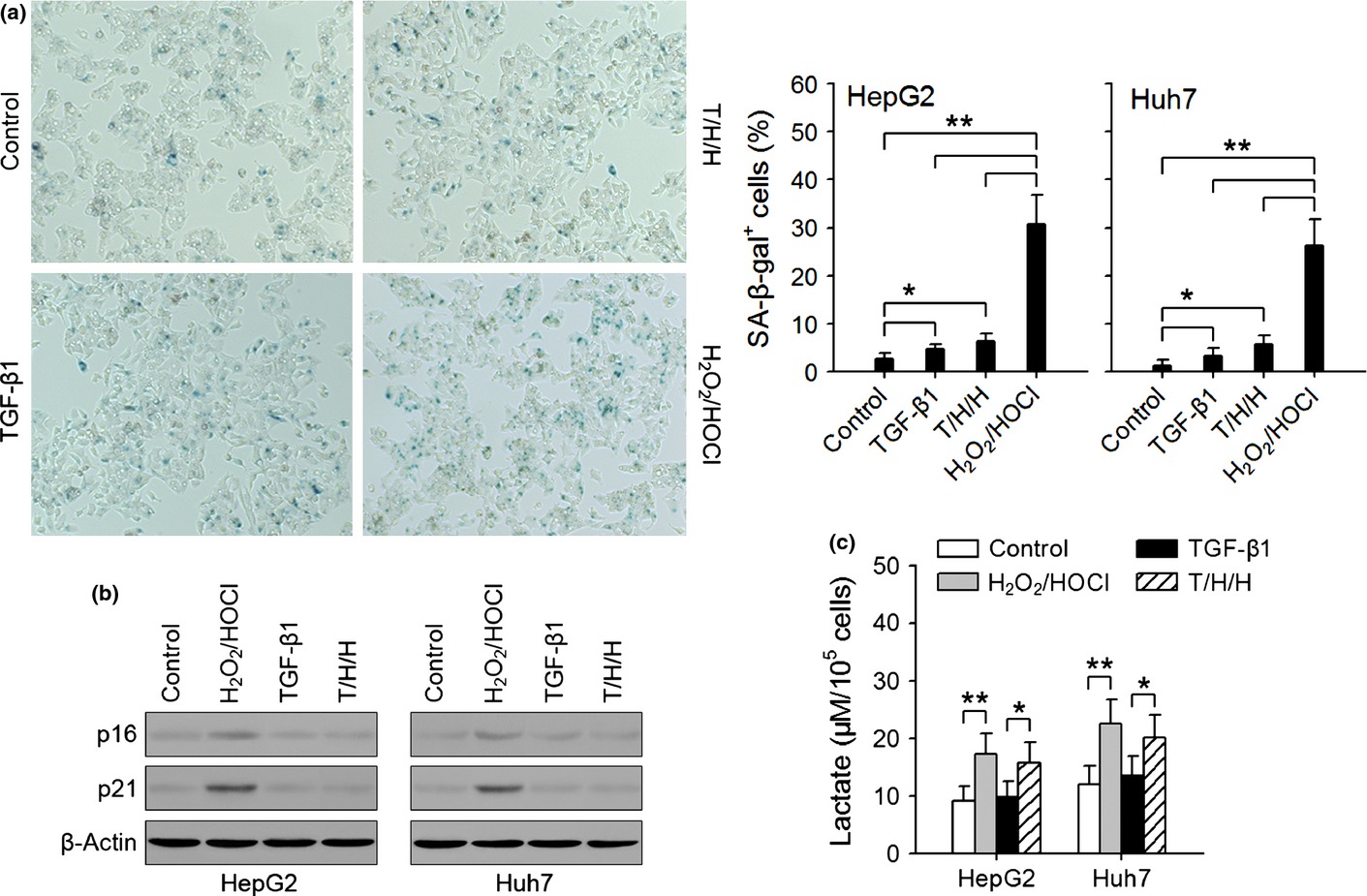
Although the function of SIRT6 could be tumor-promoting or tumor-suppressing, TGF-β1/H2O2/HOCl-mediated up-regulation of SIRT6 in HCC cells was tumor-promotional, but not tumor-suppressing. Suppressing the up-regulation of SIRT6 enabled TGF-β1/H2O2/HOCl to induce cellular senescence, thereby abrogating the enhancement of HCC cell tumorigenicity by TGF-β1/H2O2/HOCl.
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by retinoic acid sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by sorafenib
- Pages: 567-575
- First Published: 12 February 2015
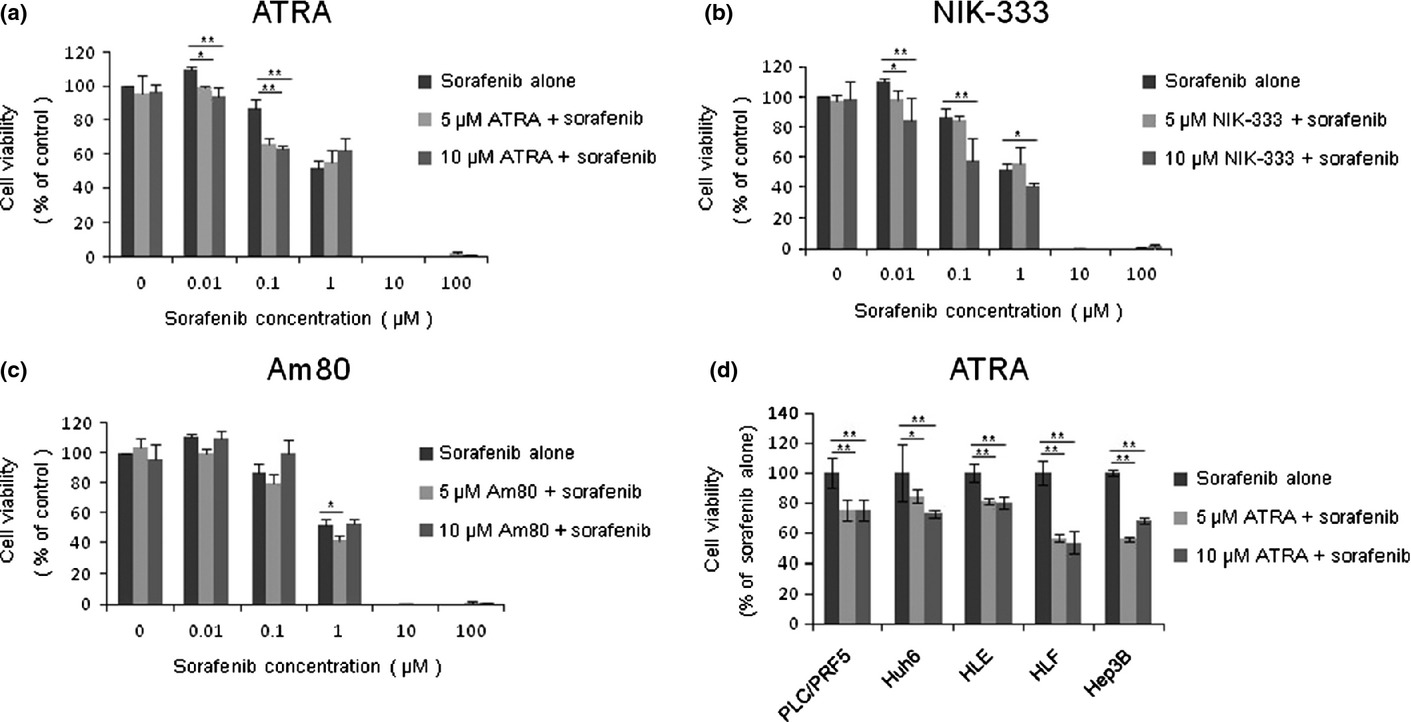
To improve the outcome of cancer chemotherapy, the strategies to enhance the efficacy of anticancer drugs are required. Suppression of glycolysis by retinoic acid sensitized hepatocellular carcinoma cells to apoptosis induced by sorafenib via AMPK activation. Our findings suggest that ATRA is useful for enhancing the cytotoxicity of sorafenib against HCC cells by regulating energy metabolism of HCC cells.
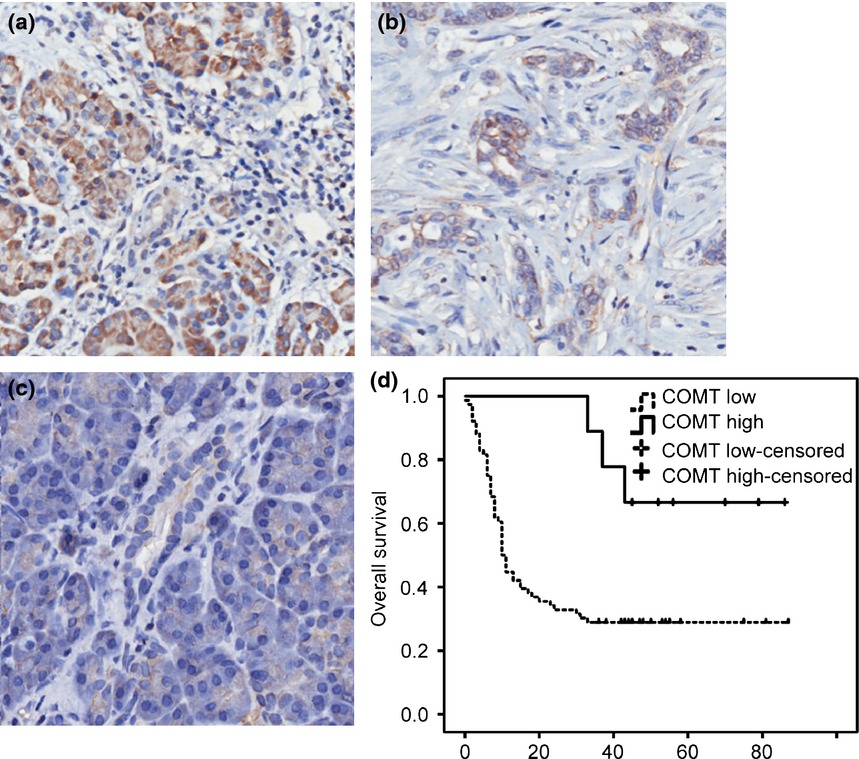
Catechol-O-methyltransferase, a new target for pancreatic cancer therapy
- Pages: 576-583
- First Published: 25 February 2015
BRCA/Fanconi anemia pathway implicates chemoresistance to gemcitabine in biliary tract cancer
- Pages: 584-591
- First Published: 03 March 2015
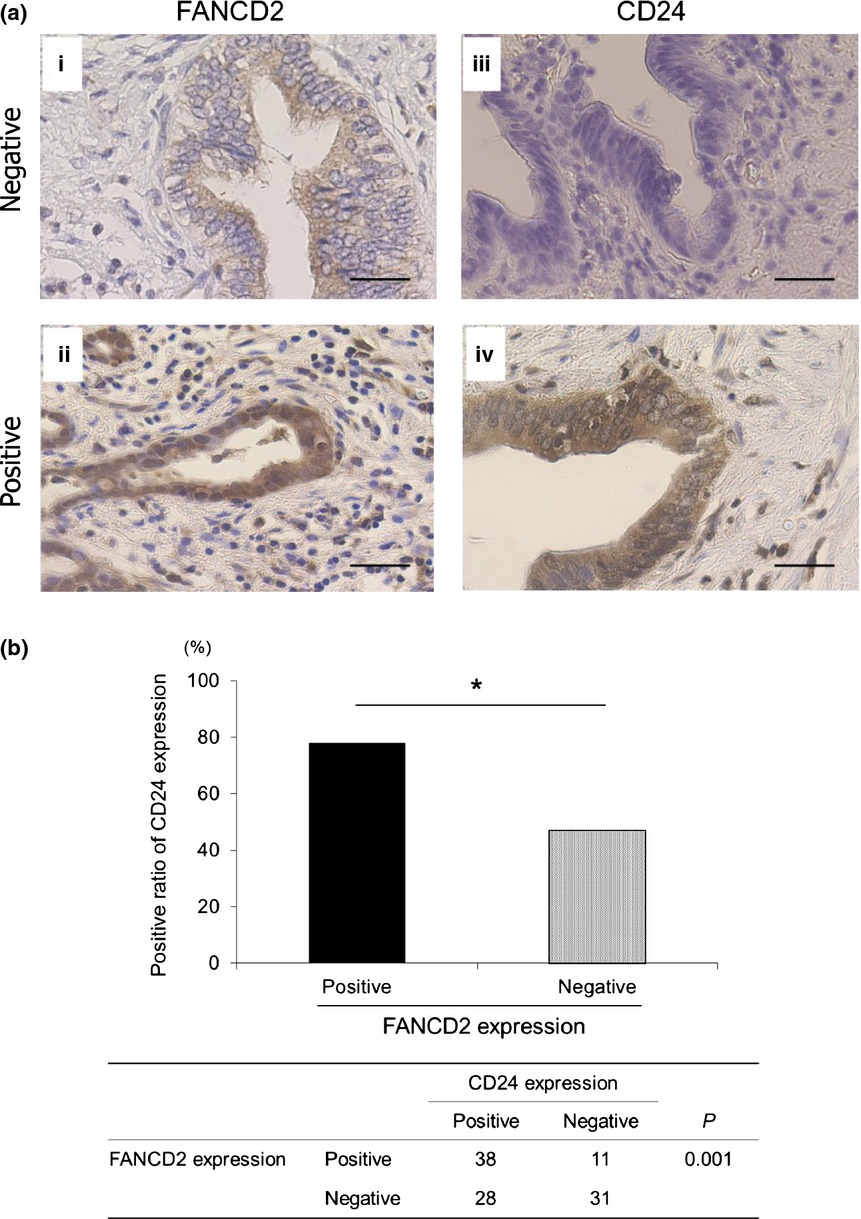
We demonstrated that up-regulation of the BRCA/Fanconi anemia pathway was one mechanism of chemo-resistance to gemcitabine. GEM exposure would lead to enrichment of the CD24+/44+ cells highly-expressing BRCA/FA in BTC, which would cause co-resistance to GEM and CDDP. Inhibiting the BRCA/FA pathway decreased the CD24+/44+ population and restored chemo-resistance in GEM resistant BTC cells.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
High expression of interleukin-11 is an independent indicator of poor prognosis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 592-597
- First Published: 20 February 2015
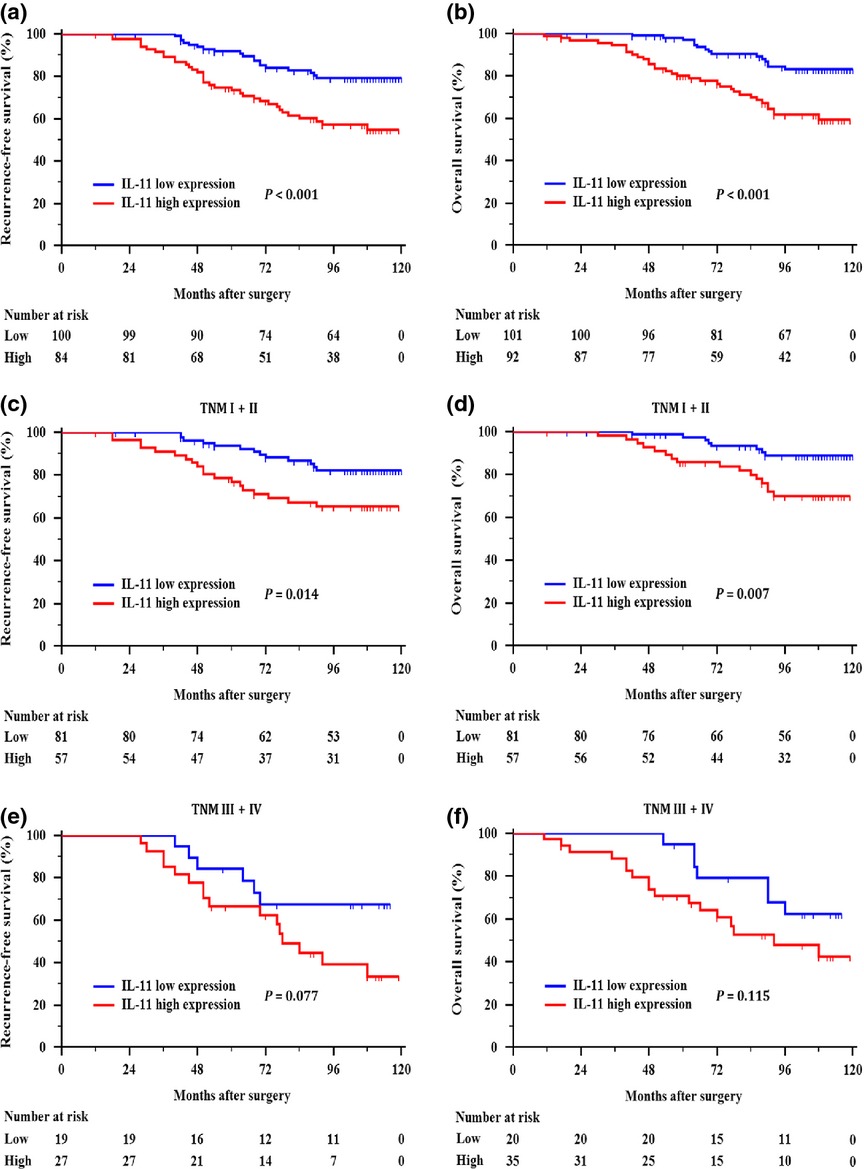
High IL-11 expression in ccRCC tissues is associated with a greater risk of recurrence and reduced survival in patients with ccRCC, especially in early-stage patients. And high IL-11 expression is an independent predictor of poor clinical outcome in patients with ccRCC. It may help identify patients who could benefit from additional treatments and closer follow-up.
Advanced human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 carriers and early-stage indolent adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma are indistinguishable based on CADM1 positivity in flow cytometry
- Pages: 598-603
- First Published: 20 February 2015
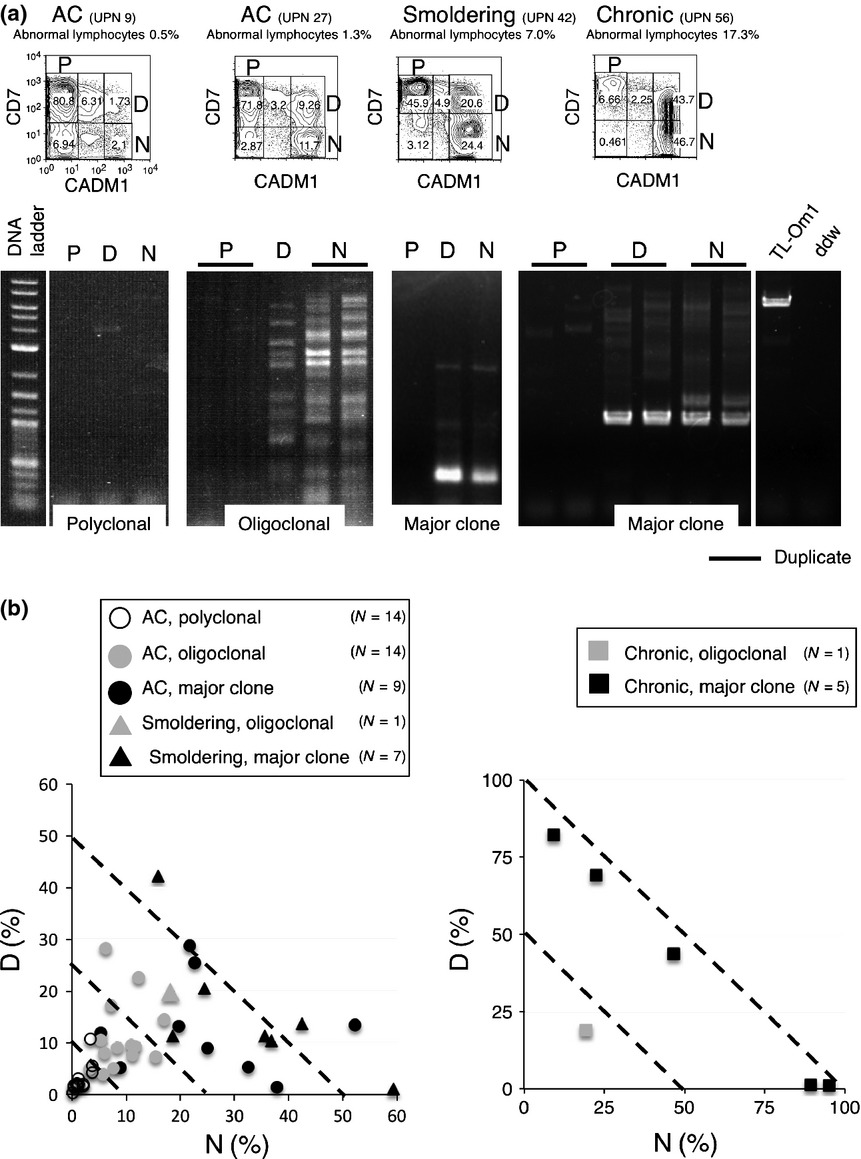
The CADM1 vs. CD7 plot (flow cytometry) for CD4+ cells from peripheral blood revealed the diversity of disease stages in asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers (AC) as well as ATL, and will help us to identify advanced AC with a similar disease status to indolent ATL patients at an early stage. Some cases of smoldering ATL and AC could not be distinguished; therefore, a new clinical category that includes these cases is warranted.
Association between serum ligands and the skin toxicity of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody in metastatic colorectal cancer
- Pages: 604-610
- First Published: 24 February 2015
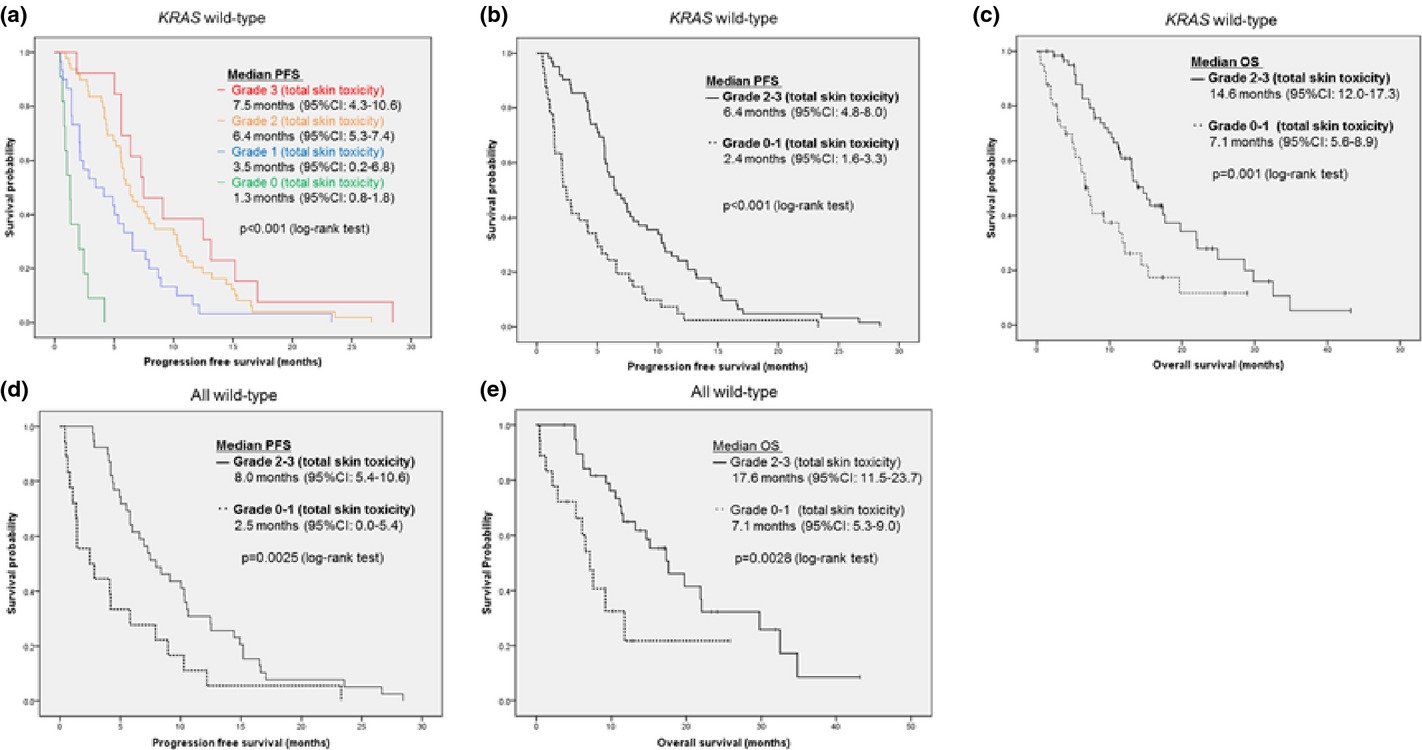
We evaluated the associtation between serum levels of ligands and grade of skin toxicity by anti-EGFR antibody treatment in metastatic clorectal cancer patients. Serum levels of HGF, EREG and AREG were inversely proportional to grades of skin toxicity as determined by the Cochran–Armitage test (P = 0.019, P = 0.047, P = 0.021, respectively). Our study indicated that serum levels such as HGF, EREG and AREG may be significant markers to predict the grade of skin toxicity and the prognosis of anti-EGFR antibody treatment.
Phase I study of tivantinib in Japanese patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Distinctive pharmacokinetic profiles from other solid tumors
- Pages: 611-617
- First Published: 25 February 2015
This would be one of the first manuscripts demonstrating that the recommended dose of an anti-cancer agent for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) could be distinct from its recommended dose for patients with other solid tumors.
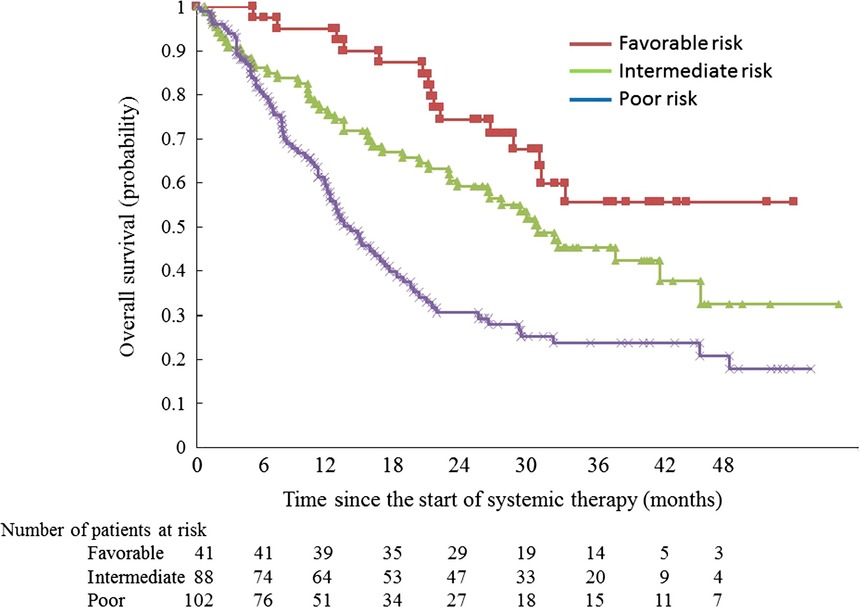
Prognosis of Japanese patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the era of molecular-targeted therapy
- Pages: 618-626
- First Published: 25 February 2015
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Enhanced antitumor effect of anti-tissue factor antibody-conjugated epirubicin-incorporating micelles in xenograft models
- Pages: 627-634
- First Published: 25 February 2015
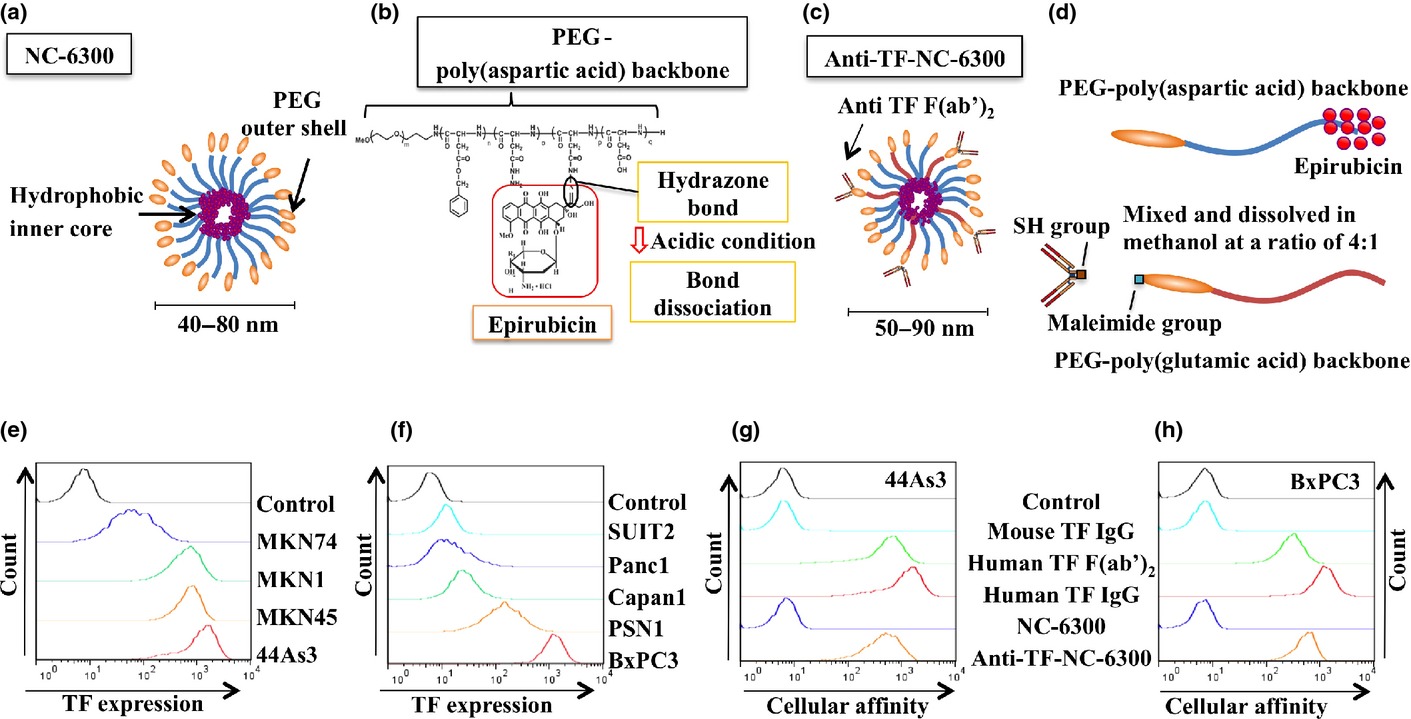
Considering its possible clinical use, our anti-TF-NC-6300 may continue to exert a high antitumor activity despite the existence of the tumor stromal barrier, since anti-TF-NC-6300 was capable of suppressing tumor growth associated with damage to the tumor vessels and the death of cancer cells in humans.
Cadmium-coordinated supramolecule suppresses tumor growth of T-cell leukemia in mice
- Pages: 635-641
- First Published: 03 March 2015
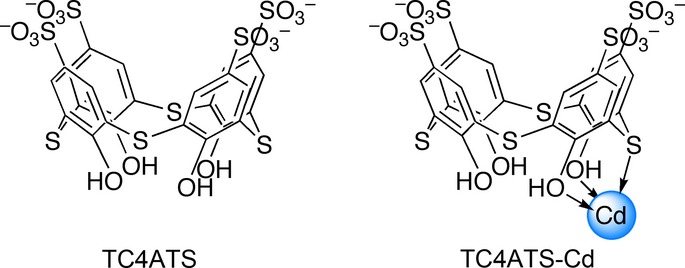
We found that thiacalixarene-cadmium complex has an anti-proliferative effect against T-cell leukemia cells, with no cytotoxicity in epithelia-derived cancer cells in vitro and minimum accumulations of cadmium in mice. In xenograft tumor model, cadmium-complex treatment significantly suppressed tumor growth of Jurkat cells in mice. These results suggest that thiacalixarene-cadmium complex may have therapeutic potential for treatment of T-cell leukemia.
GENETICS, GENOMICS AND PROTEOMICS
Epidermal growth factor receptor and AKT1 gene copy numbers by multi-gene fluorescence in situ hybridization impact on prognosis in breast cancer
- Pages: 642-649
- First Published: 20 February 2015
Prediction of desmoid tumor progression using miRNA expression profiling
- Pages: 650-655
- First Published: 24 February 2015
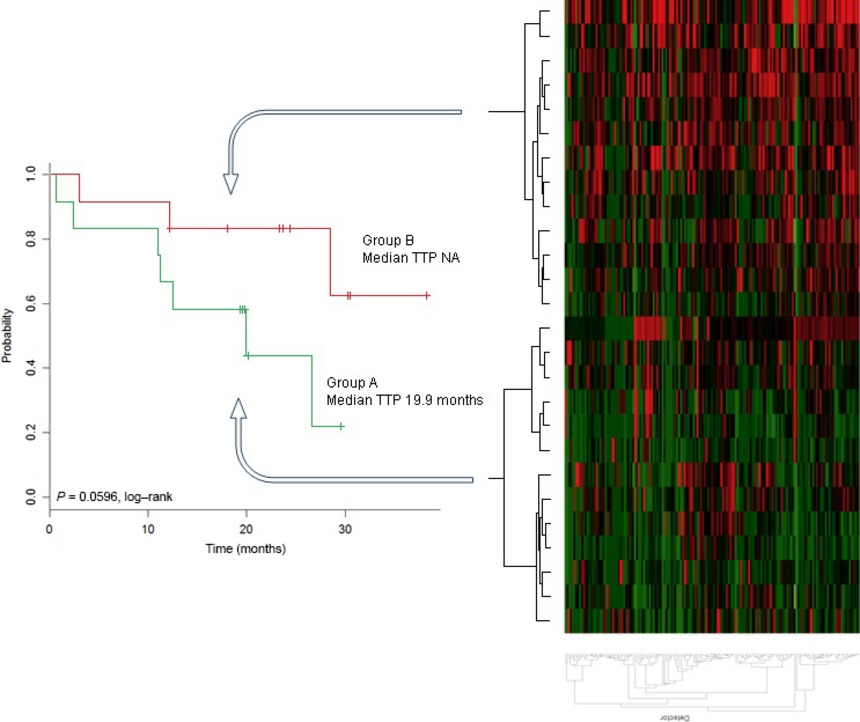
This study was conducted to define the potential predictive and/or prognostic value of a miRNA expression profile of desmoid tumors. The results bring the first demonstration of the prognostic value of miRNA profile in DT. The results were obtained in a cohort of patients included in a clinical phase II trial and validated in an independent cohort. The implication of such a discovery will be important in the management of patients with tumors particularly over-treated.
PATHOLOGY
Expression and regulatory effects on cancer cell behavior of NELL1 and NELL2 in human renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 656-664
- First Published: 02 March 2015
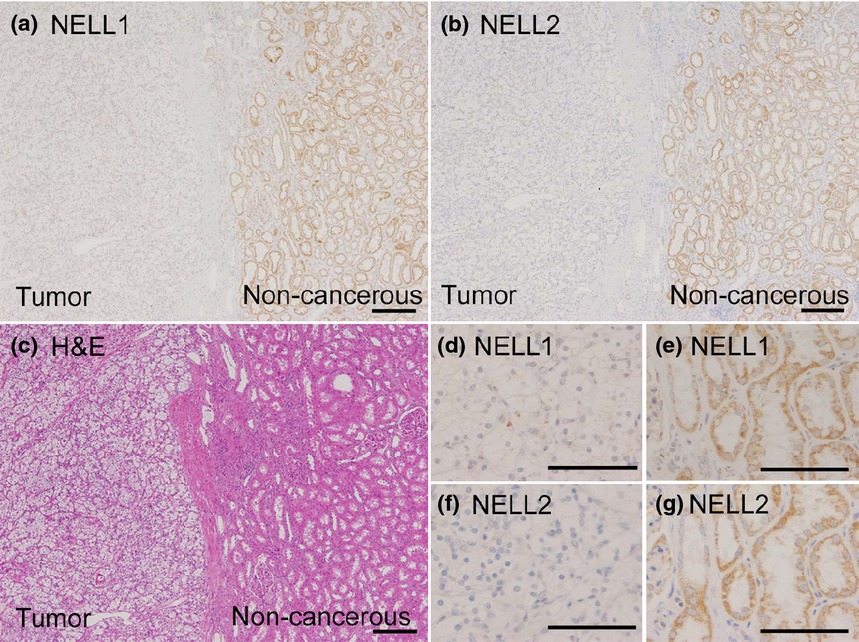
We found that the down-regulation of NELL1 and NELL2 in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is in part due to the hypermethylation of CpG islands in their putative promoter regions. Furthermore, we found that NELL1 suppresses and NELL2 partially suppresses RCC cell migration, and NELL1 further inhibits RCC cell adhesion.