Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Hedgehog pathway as a therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer. Immunohistochemical staining for Gli1 in gallbladder cancer.
- Page: March cover
- First Published: 06 March 2014
ISSUE INFORMATION
IN THIS ISSUE
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
CARCINOGENESIS
Natural variant of the Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein that lost the ability to interact with PAR1
- Pages: 245-251
- First Published: 19 December 2013
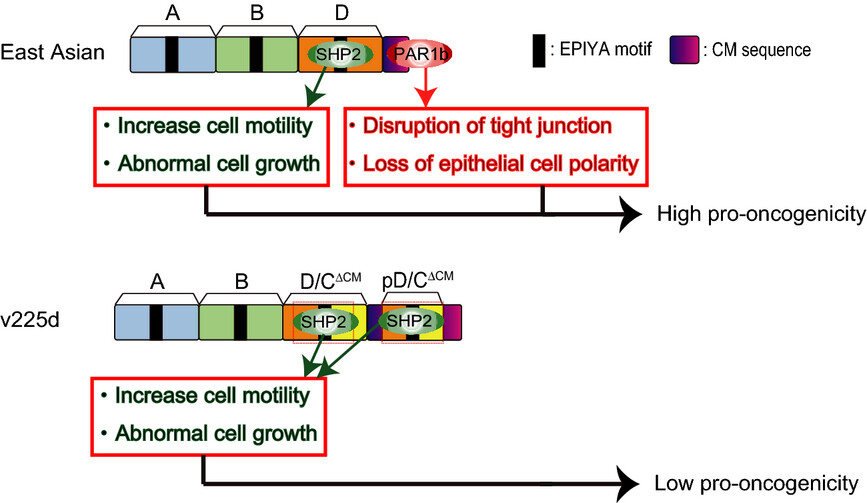
We investigated the biological activity of a natural variant of the Helicobacter pylori CagA oncoprotein that lost CM sequence. This is the first report demonstrating the presence of a natural CagA variant that cannot interact with PAR1b and therefore cannot disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Furthermore, SHP2-binding activity of the CagA variant was quite weak due to its inability to interact with PAR1b.
Anti-proliferative and apoptosis-inducing activity of lycopene against three subtypes of human breast cancer cell lines
- Pages: 252-257
- First Published: 08 January 2014
The anticancer effects of lycopene vary with subtypes of breast cancer, with the greatest inhibition observed in triple negative cells where the anticancer activity could be brought not only by an arrest of cell cycle progression at G0/G1 phase, but also by apoptosis induction. Our findings provide evidence explaining preferential preventive activity of lycopene against ER-negative breast cancer including triple negative breast cancer reported in epidemiological studies.
Genome-wide approach to identify second gene targets for malignant rhabdoid tumors using high-density oligonucleotide microarrays
- Pages: 258-264
- First Published: 13 January 2014
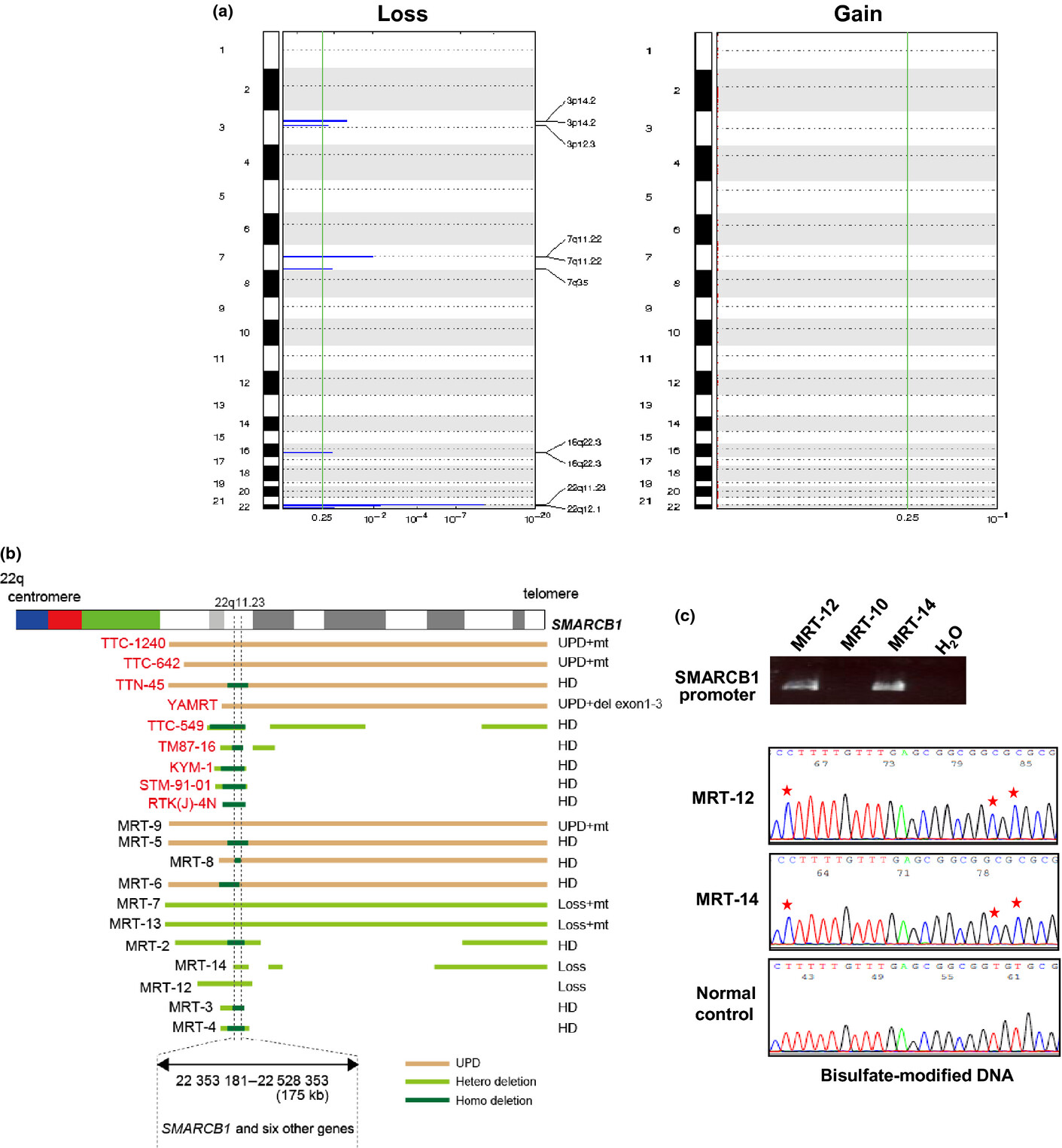
Consistent with other reports, our results illustrate the fact that SMARCB1 is the primary gene implicated in the pathogenesis of MRT. Although frequencies of recurrent genetic changes other than SMARCB1 locus were low, our findings suggest that CNTNAP2 is one of the potential second gene targets for MRT.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: MicroRNA-16 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through suppression of BCL2 and the nuclear factor-κB1/MMP9 signaling pathway
- Pages: 265-271
- First Published: 13 January 2014
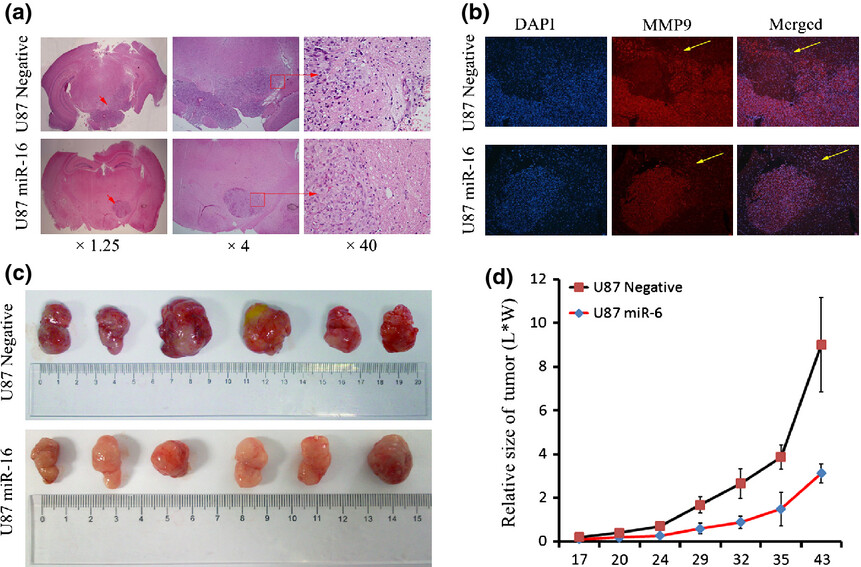
We first report that miR-16 and NF-κB1expression were inversely correlated to glioma levels in the same patient samples. We further identified the miR-16 as a negative regulator of tumor growth and invasion, both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically the tumor-suppressive role of miR-16 can be attributed to inhibition of BCL-2 and NF-kappaB1/MMP9 signaling pathways.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
CARCINOGENESIS
Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer
- Pages: 272-280
- First Published: 17 January 2014
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Mesenchymal-transitioned cancer cells instigate the invasion of epithelial cancer cells through secretion of WNT3 and WNT5B
- Pages: 281-289
- First Published: 17 December 2013
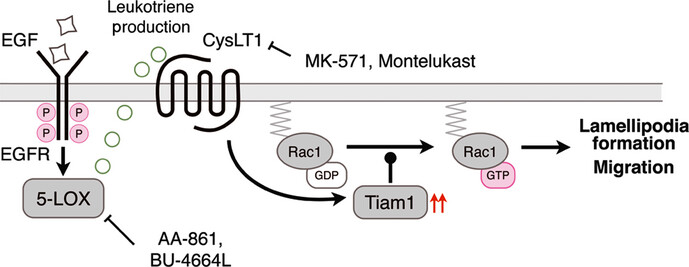
5-Lipoxygenase and cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 regulate epidermal growth factor-induced cell migration through Tiam1 upregulation and Rac1 activation
- Pages: 290-296
- First Published: 18 December 2013
Downregulation of miR-217 correlates with resistance of ph+ leukemia cells to ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Pages: 297-307
- First Published: 18 December 2013
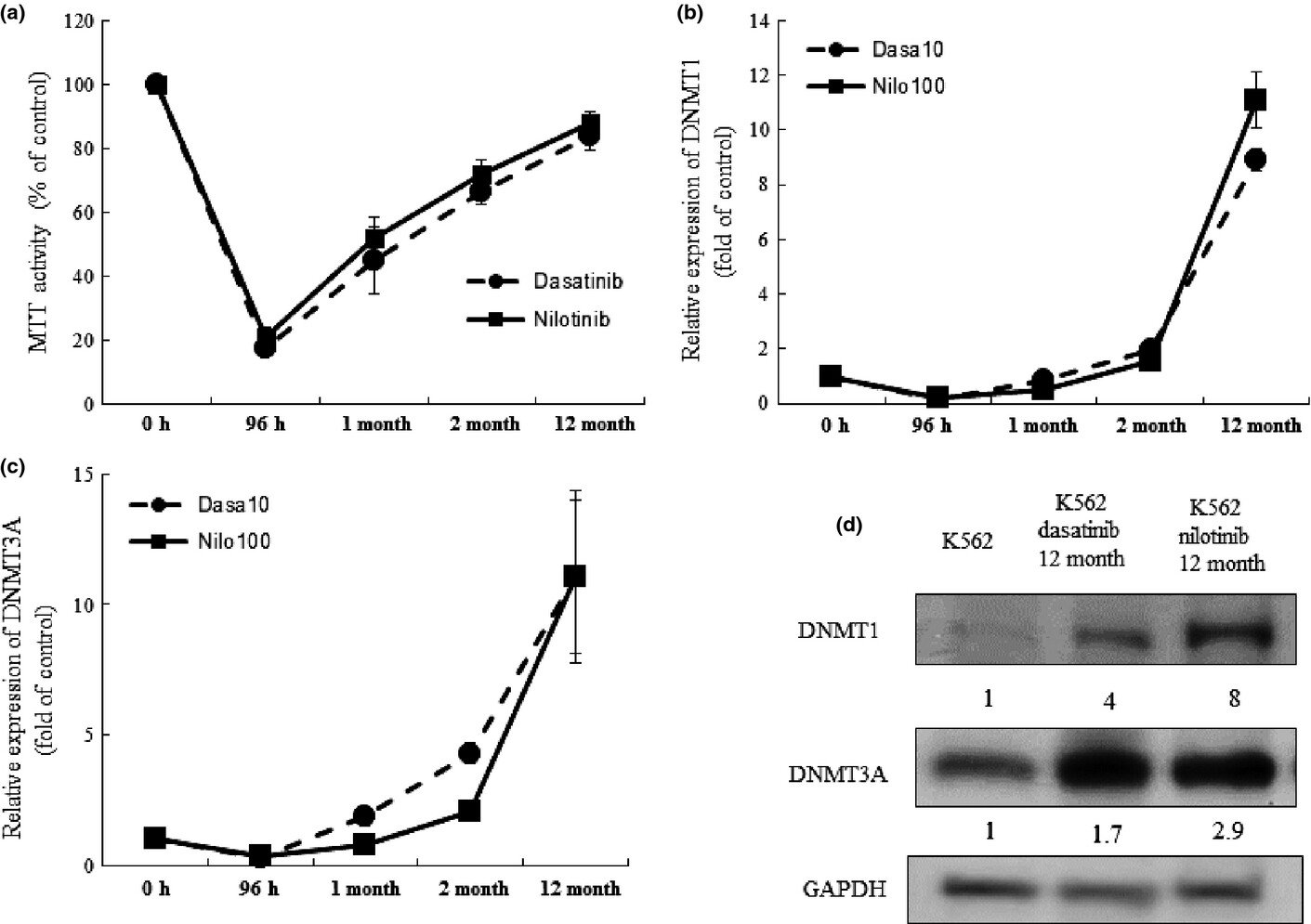
This study found that long-term exposure of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) K562 cells to BCR/ABL thyrosine kinase inhibirors (TKIs) caused drug-resistance in association with an increase in levels of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and a decrease in levels of microRNAs (miRNAs) miR-217. Ph+ leukemia cells acquire TKI-resistance via downregulation of miR-217 and upregulation of DNMT3A. Inhibition of DNMT3A by forced expression of miR-217 or 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine may be useful to prevent drug resistance in individuals who receive TKIs.
Fluorescence-lifetime molecular imaging can detect invisible peritoneal ovarian tumors in bloody ascites
- Pages: 308-314
- First Published: 23 December 2013
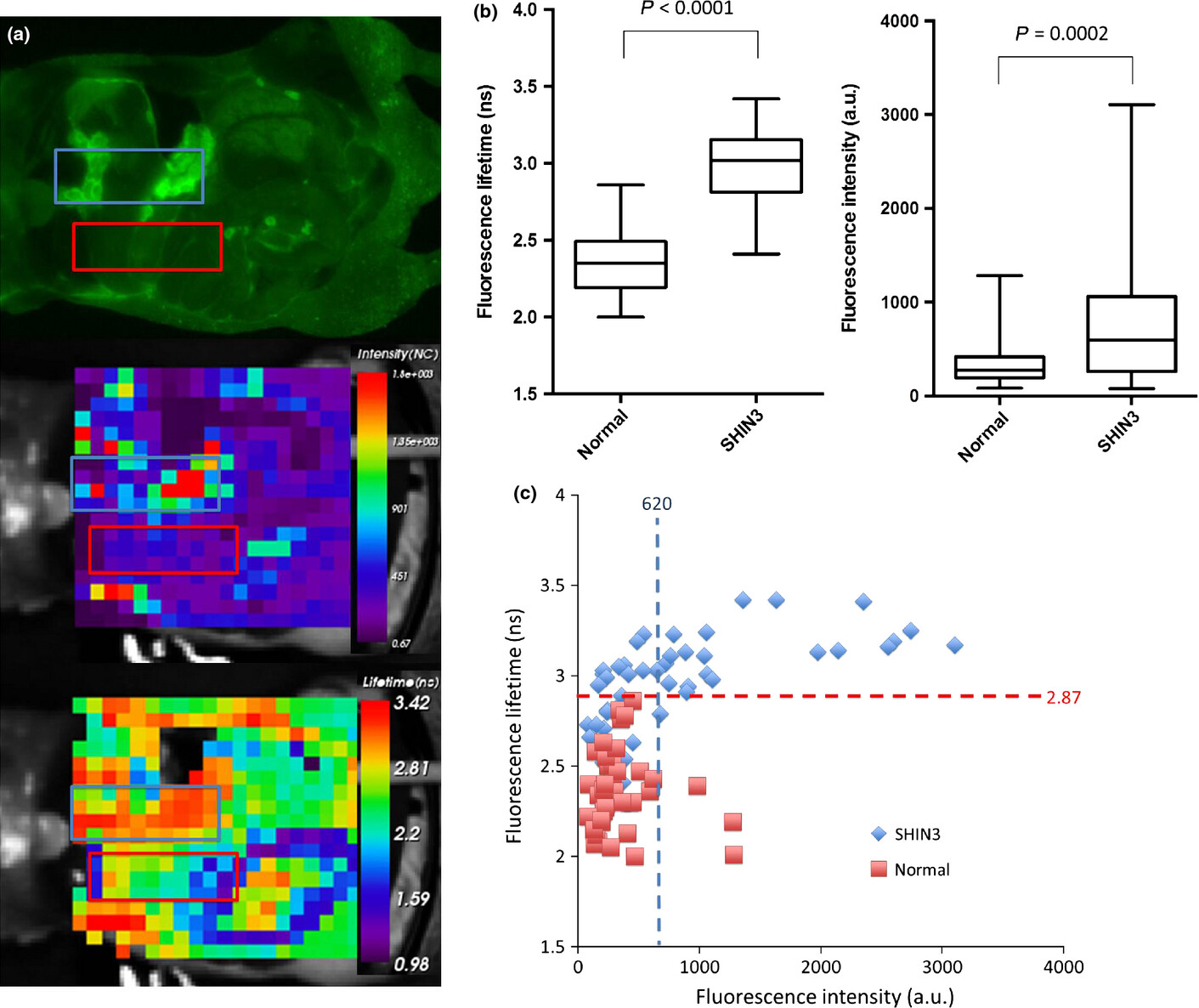
Fluorescence life time imaging (FLTI) is a new optical imaging technology for depicting cancer using molecular targeting imaging probe. FLTI can detect cancer by fluorescence lifetime even without sufficient contrast on photon intensity in fluorescence images, therefore, FLTI can be another new eye of surgeons or endoscopy physicians for finding cancer even under high auto-fluorescence background or in the bloody fluid/ascites.
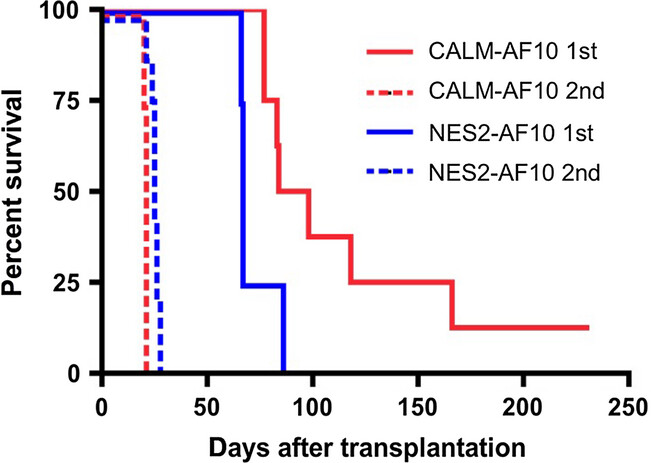
Nuclear export signal within CALM is necessary for CALM-AF10-induced leukemia
- Pages: 315-323
- First Published: 08 January 2014
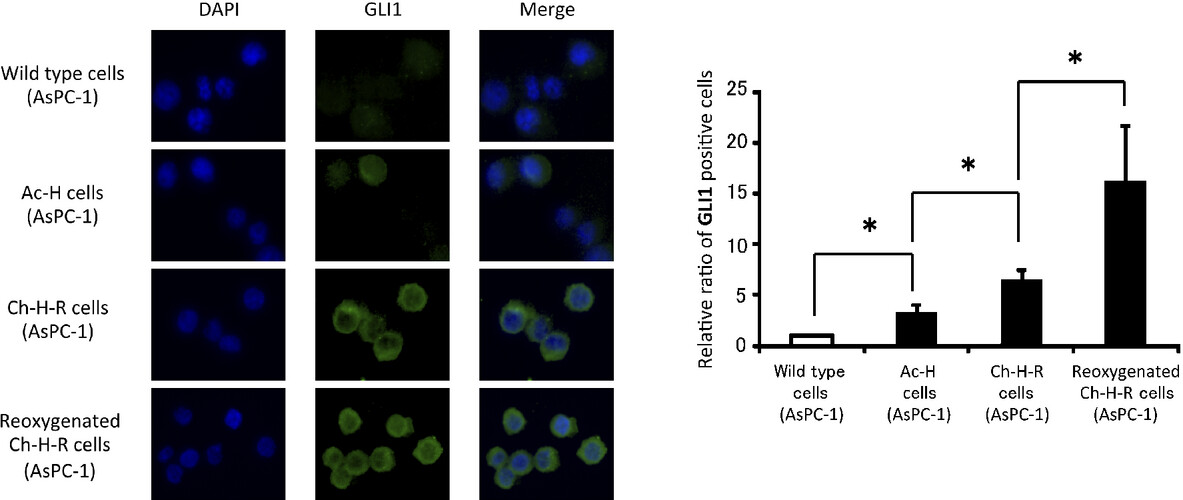
Reoxygenation from chronic hypoxia promotes metastatic processes in pancreatic cancer through the Hedgehog signaling
- Pages: 324-333
- First Published: 08 January 2014
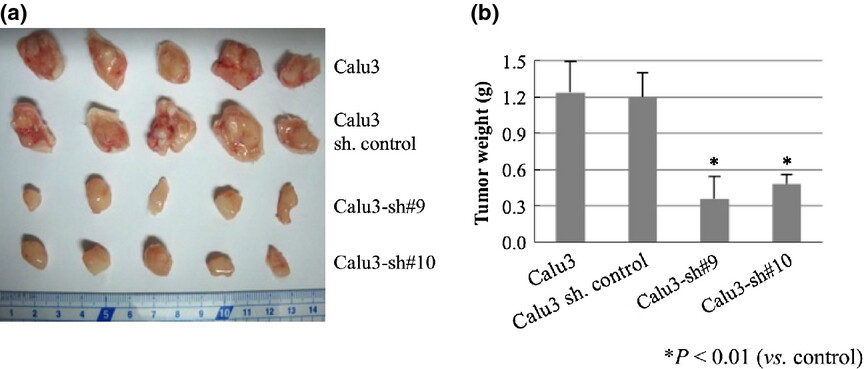
TMEPAI/PMEPA1 enhances tumorigenic activities in lung cancer cells
- Pages: 334-341
- First Published: 17 January 2014
CLINICAL RESEARCH
STAT3 gene mutations and their association with pure red cell aplasia in large granular lymphocyte leukemia
- Pages: 342-346
- First Published: 18 December 2013
SH2 domain of the STAT3 gene is frequently mutated in Asian T cell large granular lymphocyte leukemia and chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells. Pure red cell aplasia is closely associated with the mutations.
Phase I dose-escalation study of buparlisib (BKM120), an oral pan-class I PI3K inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors
- Pages: 347-353
- First Published: 10 January 2014
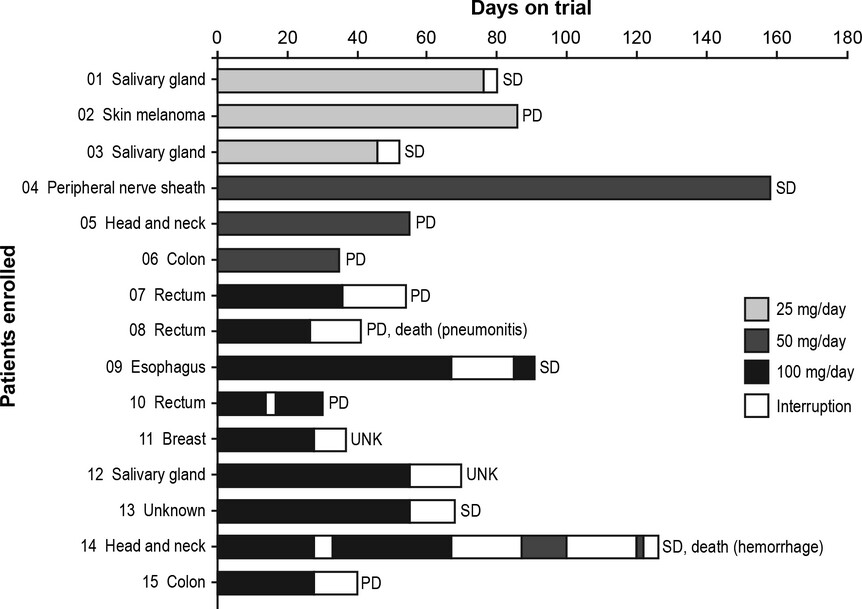
This Phase I dose-escalation study demonstrate that the pan-PI3K inhibitor buparlisib has a manageable safety profile, favorable pharmacokinetics, and has shown preliminary signs of antitumor activity in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. The recommended dose of 100 mg/day will be used in future studies of buparlisib.
Phase I study of combination chemotherapy using sorafenib and transcatheter arterial infusion with cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 354-358
- First Published: 17 January 2014
We planed a phase I study of sorafenib combined with transcatheter arterial infusion (TAI) of cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. The combination of sorafenib at 800 mg/day with TAI of cisplatin at 65 mg/m2/cycle was determined to be the recommended regimen.
CASE REPORT
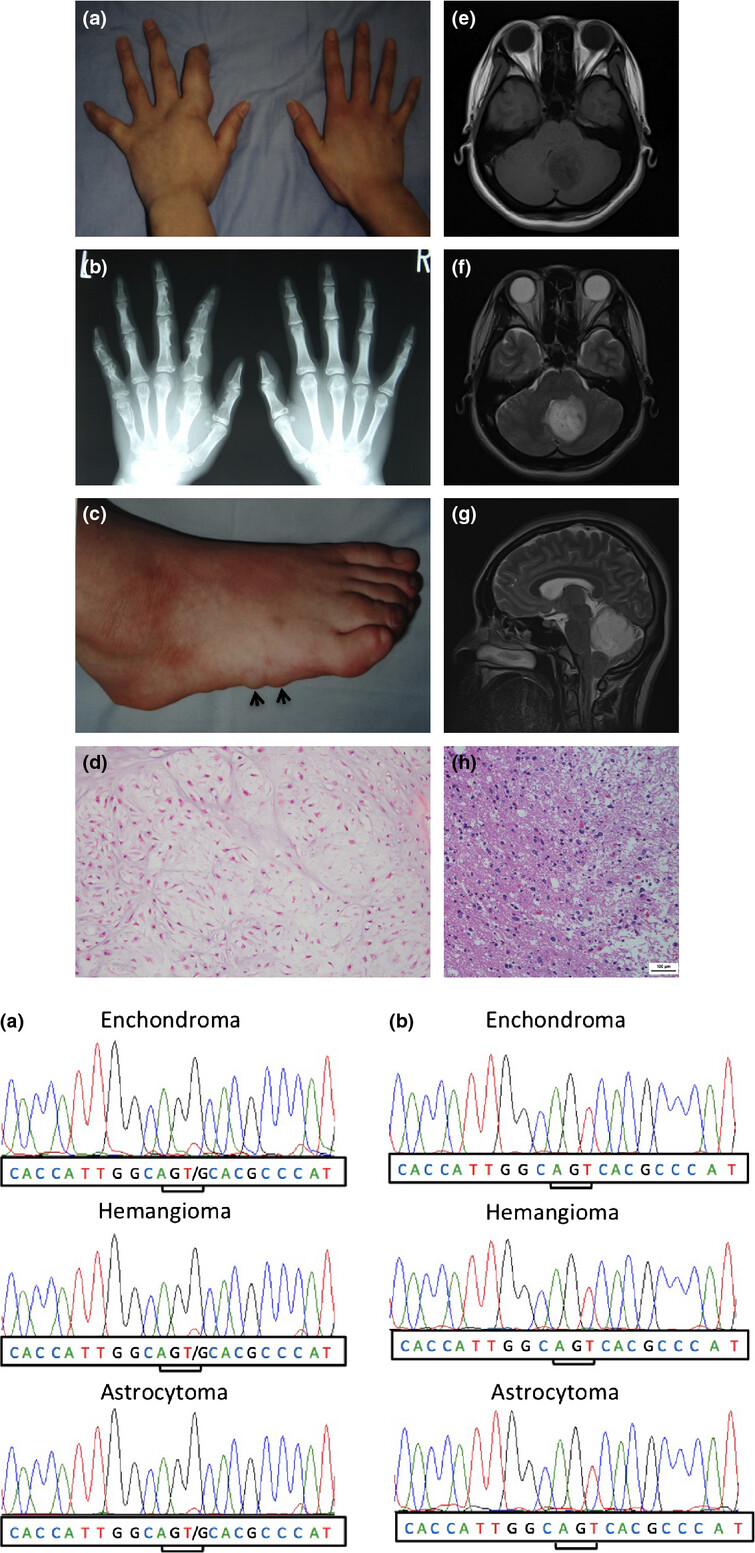
IDH2 and TP53 mutations are correlated with gliomagenesis in a patient with Maffucci syndrome
- Pages: 359-362
- First Published: 17 December 2013