Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Rapid Communications
Crystallographic characterization of the α,γ C12 helix in hybrid peptide sequences
- Pages: 504-510
- First Published: 22 July 2016
On the synthesis of cyclodextrin–peptide conjugates by the Huisgen reaction
- Pages: 511-516
- First Published: 22 July 2016
Research Articles
Sequences of stilboflavin C: towards the peptaibiome of the filamentous fungus Stilbella (= Trichoderma) flavipes
- Pages: 517-524
- First Published: 22 July 2016
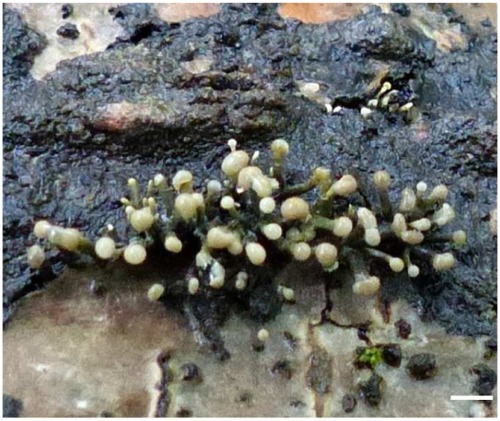

The novel stilboflavin C peptides, namely ten 16-residue and five 19-residue sequences, were isolated from submerged cultures of the fungus Stilbella flavipes CBS 146.81 (Image: the species growing on a fallen tree, white scale bar: 1 mm). These peptides contain Ser-Alaol or Ser-Leuol, which are rarely found as C-termini, as well as repetitive motifs (Leu-Aib-Gly)2,3 which have not been detected in peptaibols before.
Cyclodimerization of immunosuppressive fragment of HLA-DR molecule. Design, synthesis and ESI-MS/MS analysis
- Pages: 525-532
- First Published: 22 July 2016
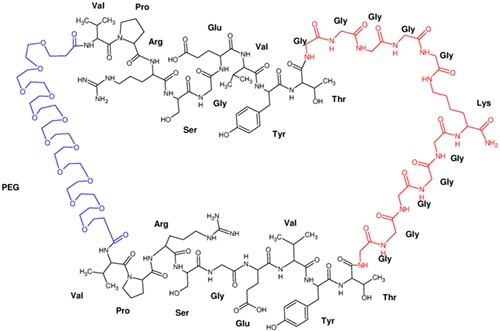
Solid phase cyclodimerization of VPRSGEVYT sequence using polyethylene glycol for head-to-head and (Gly5)2-Lys spacer for tail-to-tail cyclization resulted in a 132 atom macrocycle with enhanced immunosuppressive activity. The structure of cyclodimer was unambiguously confirmed by detailed ESI-MS/MS analysis.
Targeting the SH3 domain of human osteoclast-stimulating factor with rationally designed peptoid inhibitors
- Pages: 533-539
- First Published: 22 July 2016
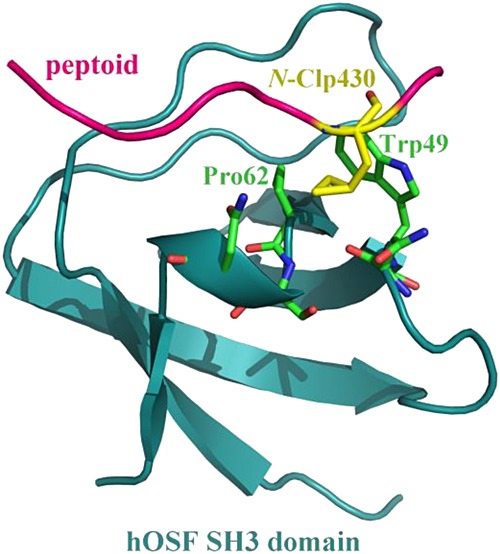
Human osteoclast-stimulating factor (hOSF) is an intracellular protein produced by osteoclasts that induces osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Here, we report rational design of the peptoid ligands of hOSF SH3 domain by integrating computational biology analysis and fluorescence binding assay. Consequently, two designed peptoid molecules with proline residue replaced separately by N-substituted amino acids N-Clp and N-Ffa are identified to have a satisfactory affinity profile towards hOSF SH3 domain.
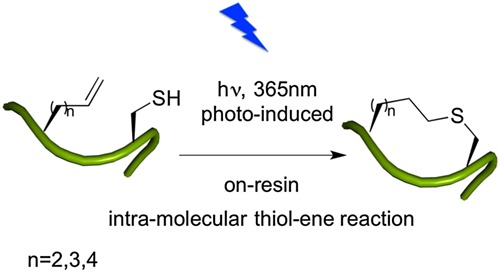
Constructing thioether-tethered cyclic peptides via on-resin intra-molecular thiol–ene reaction
- Pages: 540-544
- First Published: 05 July 2016
The impact of β-azido(or 1-piperidinyl)methylamino acids in position 2 or 3 on biological activity and conformation of dermorphin analogues
- Pages: 545-551
- First Published: 22 July 2016
Synthesis, characterization and systematic comparison of FITC-labelled GnRH-I, -II and -III analogues on various tumour cells
- Pages: 552-560
- First Published: 22 July 2016

Confocal laser scanning microscopy image of Detroit-562 human pharynx tumour cells (blue) after 5 h of incubation with 10 μM Lys8(FITC)]-GnRH-III (green).
Selectively labelled fluorescent GnRH-I, -II and -III derivatives are reliable tools for tracking and quantifying their receptor-mediated cellular uptake in vitro and able to predict the corresponding GnRH-drug conjugate tumour targeting efficiency in vivo.
We demonstrate for the first time that human pharynx tumour (Detroit-562) cells highly express GnRH-I receptors on their surface. Cellular uptake experiments with these labelled GnRH conjugates proved that the transport for each of the three GnRH analogues into Detroit-562 cells is efficiently mediated by the GnRH-I receptor.