Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Microarray analysis of circRNAs sequencing profile in exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients
- First Published: 19 November 2021
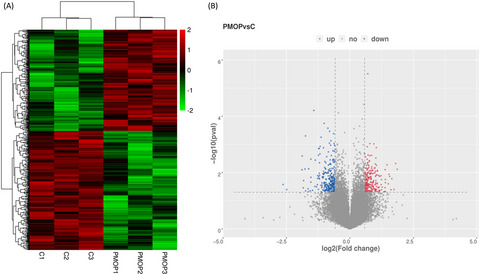
CircRNAs expression patterns. (a) Cluster analysis of circRNAs which are differentially expressed. (b) Volcano plots visualization of relative expression under two conditions. Vertical lines designate 1.5 folds (log2 scaled) up and down, respectively. Horizontal lines represent p-value = 0.05 (-log10 scaled).
Mettl3 promotes oxLDL-mediated inflammation through activating STAT1 signaling
- First Published: 26 November 2021
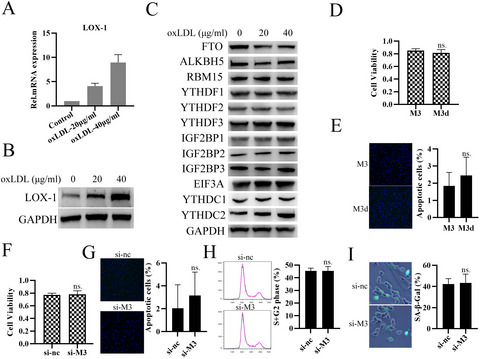
oxLDL induces LOX-1 expression and Mettl3 does not affect cell biological activity. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of LOX-1 mRNA expression in RAW264.7 cells treated with oxLDL with indicated concentrations for 24 h. (B) WB analysis of LOX-1 in RAW264.7 cells treated with oxLDL or not for 24 h. (C) WB analysis of the indicated proteins in RAW264.7 cells treated with oxLDL or not for 24 h. (D) Cell viability analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with M3 or M3d vector for 24 h. (E) Apoptosis analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with M3 or M3d vector for 24 h. (F) Cell viability analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with si-nc or si-M3 for 24 h. (G) Apoptosis analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with si-nc or si-M3 for 24 h. (H) Cell cycle analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with si-nc or si-M3 for 24 h. (I) Cell senescence analysis of RAW264.7 cells transfected with si-nc or si-M3 for 24 h.
The potential role of hsa_circ_0001079 in androgenetic alopecia via sponging hsa-miR-136-5p
- First Published: 17 November 2021
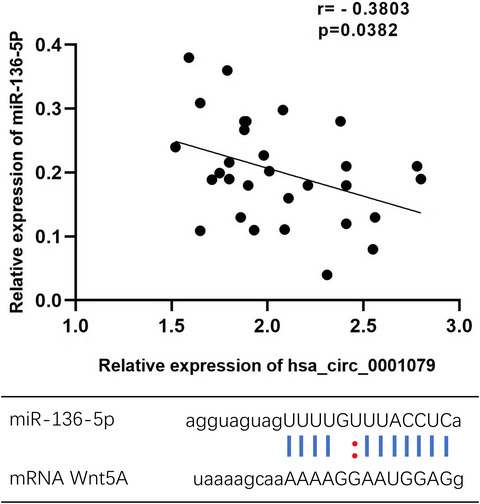
The relationship between hsa_circ_0001079 and AGA in this study suggests that hsa_circ_0001079 plays a key role in the occurrence and development of AGA. The reverse correlation and perfect binding sequence between hsa_circ_0001079 and miR-136-5p suggests that hsa_circ_0001079 might regulate Wnt5A mRNA to inhibit normal hair follicle growth through sponging adsorption of miR-136-5p and that Wnt5A also participates in multiple cellular DNA replication pathways. It is of great significance to study the expression profile of AGA circRNAs and determine novel biomarkers to provide new directions and strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of AGA.
Long non-coding RNA ANRIL interacts with microRNA-34a and microRNA-125a, and they all correlate with disease risk and severity of Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 17 December 2021

Totally, 78 PD patients and 78 age-/gender- matched controls were consecutively enrolled. Their peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples were collected and proposed for reverse-transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction to complete lncRNA ANRIL, miR-34a and miR-125a measurements. The results displayed that lncRNA ANRIL was upregulated, while miR-34a and miR-125a were downregulated in PD patients compared to controls. Furthermore, lncRNA ANRIL negatively correlated with miR-34a and miR-125ain PD patients. In addition, lncRNA ANRIL was observed to positively associate with UPDRS-I score while negatively correlate with MMSE score. While these associations were less distinct as to miR-34a and miR-125a.
Study on perinatal-related factors of maternity and newborn in parturients with intrapartum fever in part of Eastern China: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 16 November 2021
Maternal intrapartum fever is a common obstetric disease during birth process and has a serious impact on mother and child. However, corresponding study seems to be in short. A retrospective cohort study was designed to evaluate the role of inflammatory cell in patients who diagnosed with intrapartum fever (defined as temperature over 37.5℃) lived in part of Eastern China. Prepartum value of white blood cell (WBC), red blood cell (RBC), and hemoglobin (Hb) were all a little higher in febrile group than afebrile group, and postpartum WBC in afebrile group still higher while postpartum RBC and Hb were inferior to non-fever maternity. Postpartum neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and monocyte to lymphocyte ratio were all higher in fever group but not preferred overtly difference before delivery. Additionally, the comparison of WBC, RBC, Hb, platelets, neutrophils, and monocytes in prepartum and postpartum all showed significant difference. The parturition could bring about the value change of CBC and intrapartum fever might aggravate or alleviate this change. Besides, the intrapartum fever might not be caused mainly by infection and the difference between bacteria and fungus could reflect in the CBC.
REVIEW ARTICLE
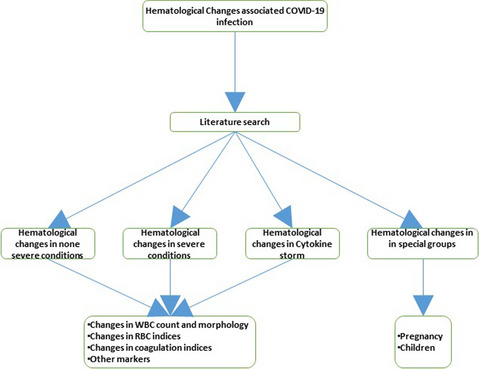
Hematological changes associated with COVID-19 infection
- First Published: 16 November 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Investigation of the quantitative detection of serum Helicobacter pylori antibody in clinical laboratories in China
- First Published: 16 November 2021
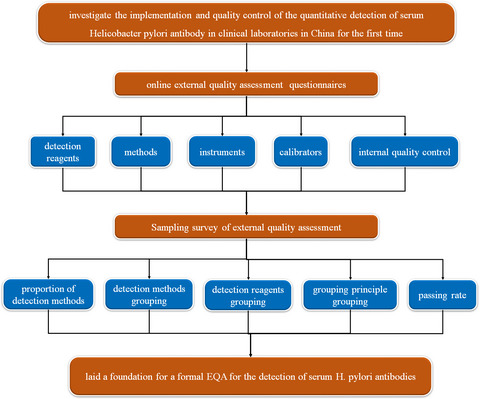
This is the first report from China where the status of quantitative detection of serum H. pylori antibody was investigated. Online questionnaires were used to collect information on the quantitative detection procedures of serum H. pylori antibody in clinical laboratories. Distributed quality control products to select laboratories and analyzed the obtained test data. This study laid a foundation for the development of a formal EQA for the detection of serum H. pylori antibodies.
LncRNA UCA1, miR-26a, and miR-195 in coronary heart disease patients: Correlation with stenosis degree, cholesterol levels, inflammatory cytokines, and cell adhesion molecules
- First Published: 01 December 2021
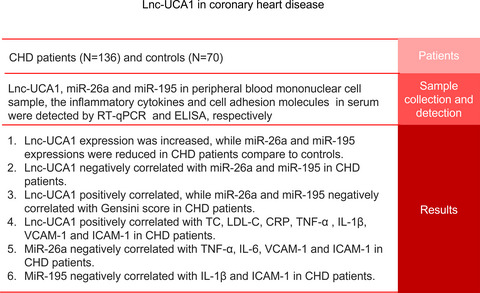
There were 136 coronary heart disease (CHD) patients and 70 age-/gender-matched controls constitutively recruited. Their peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples were collected for long noncoding RNA urothelial cancer-associated 1 (lnc-UCA1), microRNA-26a (miR-26a), and microRNA-195 (miR-195) measurement. Besides, serum samples from CHD patients were obtained for inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules measurement. Lnc-UCA1 expression was increased, while miR-26a and miR-195 expressions were reduced in CHD patients compared to controls. In CHD patients, lnc-UCA1 negatively correlated with miR-26a and miR-195. Besides, lnc-UCA1 positively correlated, while miR-26a and miR-195 negatively correlated with Gensini score. Moreover, lnc-UCA1 positively correlated with total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), while miR-26a negatively correlated with TNF-α, IL-6, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1. Also, miR-195 negatively correlated with IL-1β and ICAM-1. These findings suggest that lnc-UCA1, miR-26a, and miR-195 may serve as potential biomarkers for CHD patients’ management.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Dynamic changes of IgM and IgG antibodies in asymptomatic patients as an effective way to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection
- First Published: 16 December 2021
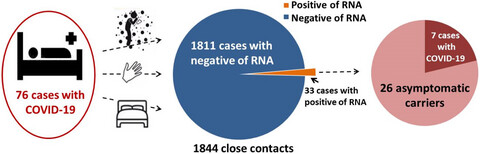
COVID-19 has become a global epidemic, close contacts and asymptomatic patients are worthy of attention. A total of 1844 people in close contact with 76 COVID-19 patients were investigated, and nasopharyngeal swabs and venous blood were collected for centralized medical quarantine observation. The IgG concentration in asymptomatic cases remained at a high level after nucleic acid turned negative. Nucleic acid combined with IgM and IgG antibody detection is a more effective way to screen asymptomatic infections.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Long non-coding RNA MIR31HG as a prognostic predictor for malignant cancers: A meta- and bioinformatics analysis
- First Published: 27 November 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Association between lipoprotein (a) and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction development
- First Published: 01 December 2021
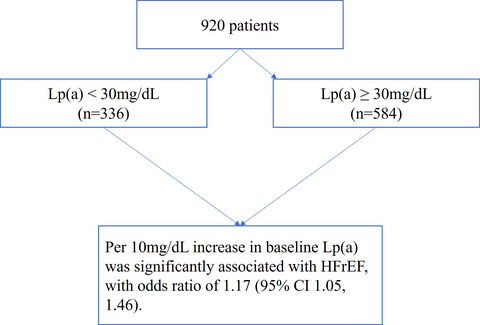
After stepwise adjusting for covariates, per 10 mg/dl increase in baseline Lp(a) remained significantly associated with HFrEF, with odds ratio of 1.17 (95% CI 1.05, 1.46). In addition, the magnitude of the association between baseline Lp(a) level and HFrEF was greater in men and in individuals with diabetes mellitus (DM) or coronary heart disease (CHD), while it was weaker in individuals treated with beta-blocker at baseline.
Expression of SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1 and its clinical prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 29 November 2021
REVIEW ARTICLE
Bacteriocins: Properties and potential use as antimicrobials
- First Published: 01 December 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Association between serum uric acid and carotid atherosclerosis in elderly postmenopausal women: A hospital-based study
- First Published: 27 November 2021
The influence of age on prostate cancer screening index
- First Published: 24 November 2021
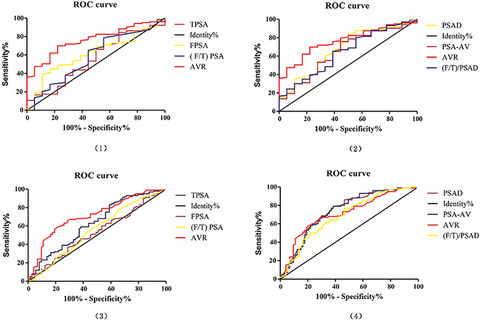
(1) and (2) show the ROC curves of clinical indicators in the diagnosis of prostate cancer when the age was ≤66 years; (3) and (4) show the ROC curves of clinical indicators in diagnosing prostate cancer when the age is >66 years. In the ≤66 years old group, the AUC of TPSA, FPSA, (F/T)PSA, PSAD, PSA-AV, AVR and (F/T)/PSAD were respectively 0.559, 0.614, 0.581, 0.679, 0.656, 0.764 and 0.644. In the >66 years old group, the AUC of TPSA, FPSA, (F/T)PSA, PSAD, PSA-AV, AVR and (F/T)/PSAD were respectively 0.629, 0.529, 0.556, 0.740 0.735, 0.712 and 0.687. In the ≤66 years old group, AVR, PSAD and (F/T)/PSAD have higher diagnostic value for PCa. In the >66 years old group, AVR, PSAD and PSA-AV have higher diagnostic value for PCa.
Development, validation, and clinical application of an FIA-MS/MS method for the quantification of lysophosphatidylcholines in dried blood spots
- First Published: 17 November 2021
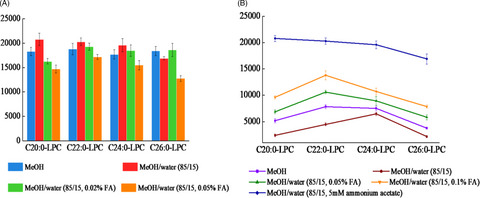
We proposed a reliable and simple flow injection analysis–tandem mass spectrometry (FIA-MS/MS)-based method using dried blood spots (DBS) for quantification of four individual LPC (C20:0, C22:0, C24:0, and C26:0). The elaborated method was successfully applied to assessment of C20:0-C26:0LPCs in 1900 Chinese neonates.
Low serum interleukin-38 levels in patients with Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- First Published: 19 November 2021

IL-38 concentrations were reduced in the Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) and Graves’ disease (GD) groups compared with those in the healthy control group (A). In the GD group, serum IL-38 concentrations were positively correlated with C-reactive protein (CRP) concentrations (B) and the white blood cell count (WBC) (C). We evaluated the diagnostic value of IL-38 concentrations and IL-38 combined with CRP concentrations for autoimmune thyroid disease using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The area under curve (AUC) was 0.7276 using IL-38 concentrations for the diagnosis of HT (D) and 0.7300 using IL-38 concentrations in combination with CRP concentrations (E). The AUC was 0.7736 (F) when IL-38 concentrations were used to diagnose GD and 0.7972 (G) when IL-38 concentrations were combined with CRP concentrations.
Late onset of type 2 diabetes is associated with mitochondrial tRNATrp A5514G and tRNASer(AGY) C12237T mutations
- First Published: 22 November 2021

In this study, we reported here the clinical, genetic and molecular features of a large Chinese pedigree with maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD). Through the application of PCR and direct sequence analysis, we identified two possible pathogenic mitochondrial tRNA mutations: tRNATrp A5514G and tRNASer(AGY) C12237T, which were localized at extremely conserved nucleotides, altered secondary structure of tRNAs and may cause the failure in tRNAs metabolism, and subsequently lead to mitochondrial dysfunctions which were involved in the pathogenesis of MIDD.
Quantitative detections of TP53 gene mutations improve the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of biliary tract cancers using droplet digital PCR
- First Published: 23 November 2021
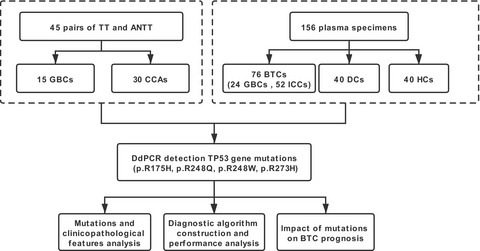
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is a rare malignancy and lack of effective diagnostic and prognostic marker. Here, we aimed to investigate the clinical implication of TP53 mutation detection in BTC using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR).TP53 gene (loci p.R175H, p.R248Q, p.R248W, and p.R273H) mutation frequencies of 45 pairs of tumor tissues (TTs) and adjacent normal tissues (ANTTs) were analyzed, respectively, using ddPCR. Meanwhile, the same detections were conducted in plasma cell-free DNA (cfNDA) of 156 subjects including BTC, disease control (DC), and healthy controls (HC). The logistic regression algorithm was established to identify BTC. The correlations between mutations and clinicopathological features as well as the effects of TP53 mutation frequency on BTC prognosis were assessed. The higher mutation of p.R175H was found in TTs compared with ANTT (p = 0.006). The mutation at p.R273H in cfDNA was also higher in BTC when compared with DC and HC (p < 0.05). The logistic algorithms combining p.R273H mutation demonstrated the higher diagnostic efficacy trend than carbohydrate antigen 19–9 (CA19-9), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in identifying BTC from DC (the area under the curves of the algorithm: 0.845, 95% CI:0.775–0.914). The median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were significantly shorter when the BTC patients harboring the p.R273H mutation (OS: p = 0.032; PFS: p = 0.046). This study revealed for the first time that the quantitative TP53 mutations using the ddPCR might serve as a potential genetic biomarker for BTC diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
Developing metabolic gene signatures to predict intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma prognosis and mining a miRNA regulatory network
- First Published: 06 December 2021
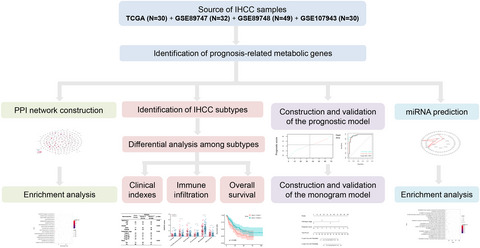
By virtue of data of 141 IHCC samples from TCGA and GEO, prognosis-related metabolic genes were selected. Then, samples were divided into two clusters which had significant differences in clinical characteristics, survival status and immune cell infiltration. Then gene signatures with prognostic independence were also identified, and the prognostic model and nomogram model were constructed accordingly to predict the prognosis. Finally, the upstream regulators were found to mediate the involvement of gene signatures in metabolic pathways.
Aberrant expression profiles and bioinformatic analysis of CAF-derived exosomal miRNAs from three moderately differentiated supraglottic LSCC patients
- First Published: 17 November 2021
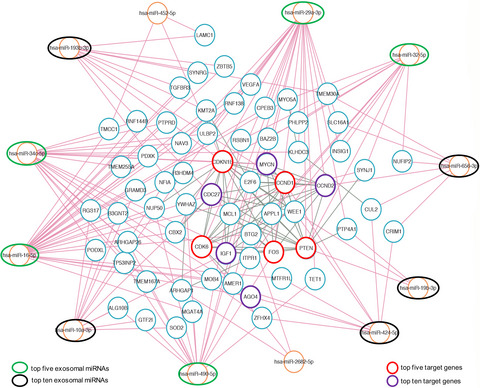
Twelve critical CAF-derived exosomal miRNAs are identified in three supraglottic LSCC patients through next-generation sequencing, which are further divided into top 5 and top 10 based on the expression level and the number of target genes. Ten critical target genes of these exosomal miRNAs are identified, which are further divided into top 5 and top 10 based on the number of upstream and downstream interacting miRNAs and target genes. Five of the top ten target genes are related to cell cycle regulation, indicating that the abnormal regulation of cell cycle plays a key role in the pathogenesis of supraglottic LSCC.
Measurement of synovium and serum dual specificity phosphatase 22 level: Their inter-correlation and potency as biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis
- First Published: 22 November 2021
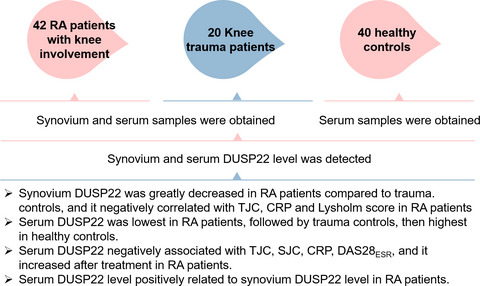
Synovium and serum samples from 42 RA patients with knee involvement underwent arthroscopy, and 20 knee trauma patients were collected; meanwhile, serum samples from 40 healthy controls were also obtained. Synovium DUSP22 level was greatly decreased in RA patients compared to trauma controls (p < 0.001), and it was negatively correlated with TJC (p = 0.040), CRP (p = 0.033), and Lysholm score (p = 0.005) in RA patients. Serum DUSP22 level was lowest in RA patients, followed by trauma controls, then highest in healthy controls (p < 0.001). Serum DUSP22 level was negatively associated with TJC (p = 0.004), SJC (p = 0.015), CRP (p = 0.011), and DAS28ESR score (p = 0.008), and it increased after treatment (p = 0.001) in RA patients. In addition, serum DUSP22 level positively related to synovium DUSP22 level in RA patients (p = 0.010).
Blood MALT1, Th1, and Th17 cells are dysregulated, inter-correlated, and correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients; meanwhile, MALT1 decline during therapy relates to treatment outcome
- First Published: 17 November 2021
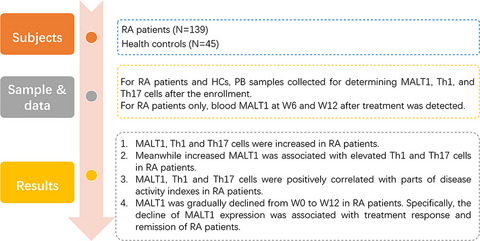
This study enrolled 139 RA patients and 45 health controls; then, blood MALT1, Th1, and Th17 cells were determined. For RA patients only, blood MALT1 at W6 and W12 after treatment was also detected. Additionally, clinical response and remission of RA patients were assessed at W12. Interestingly, MALT1, Th1, and Th17 cells were all increased in RA patients; meanwhile, increased MALT1 was associated with elevated Th1 and Th17 cells in RA patients. Besides, MALT1, Th1, and Th17 cells were positively correlated with parts of disease activity indexes in RA patients. In addition, MALT1 was gradually declined from W0 to W12 in RA patients; furthermore, the decline of MALT1 expression was associated with treatment response and remission of RA patients.
Construction of an m6A-related lncRNA pair prognostic signature and prediction of the immune landscape in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 16 November 2021
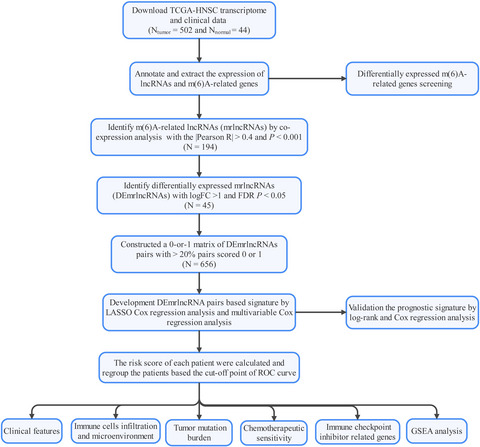
The m6A-related lncRNA pair prognostic signature was evaluated from the perspective of survival, clinicopathological features, immune cell infiltration, tumor immune microenvironment, tumor mutation burden, efficacy of chemotherapeutics, and immune checkpoint inhibitor -related genes. The m6A-related lncRNA pair signature was an efficient independent prognostic indicator and may provide a rationale for research on immunotherapeutic and chemotherapeutics strategies for HNSCC patients.
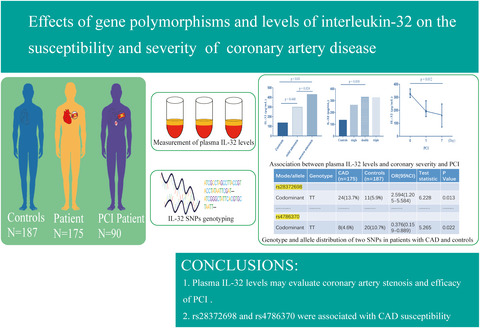
Effects of IL-32 polymorphisms and IL-32 levels on the susceptibility and severity of coronary artery disease
- First Published: 19 November 2021
Effects of dexmedetomidine on the expression profile of tsRNAs in LPS-induced acute lung injury
- First Published: 22 November 2021
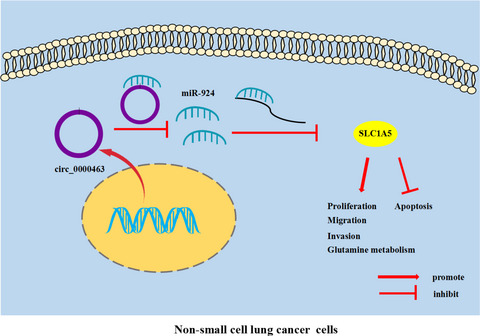
Circ_0000463 contributes to the progression and glutamine metabolism of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting miR-924/SLC1A5 signaling
- First Published: 22 November 2021
ABC typing and extracellular enzyme production of Candida albicans isolated from Candida vulvovaginitis
- First Published: 27 November 2021
Expression and prognostic significance of m6A-related genes in TP53-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer
- First Published: 23 November 2021
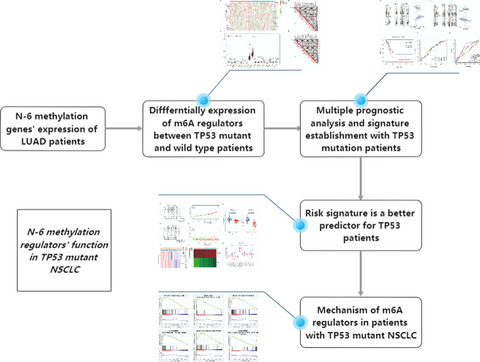
In this study, we further explored the role of m6A regulators' function in TP53-mutant lung cancer. First, we found the m6A expression differentially between TP53-mutant and wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Then, we established a risk model using multivariate regression method, and comprehensively expounded the potential role of m6A regulators in NSCLC from aspects of prognosis verification, clinical characteristics, and molecular mechanism.
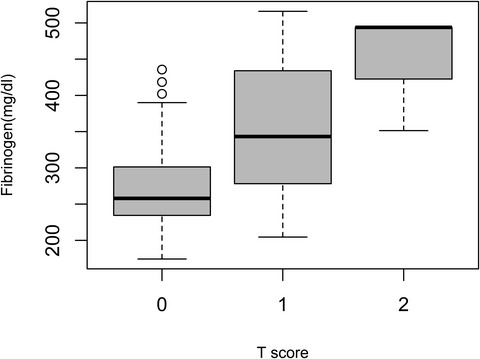
A high value of fibrinogen in immunoglobulin A nephropathy patients is associated with a worse renal tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis score
- First Published: 16 November 2021
Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants isolated from wound specimen of a tertiary care hospital in China
- First Published: 27 November 2021
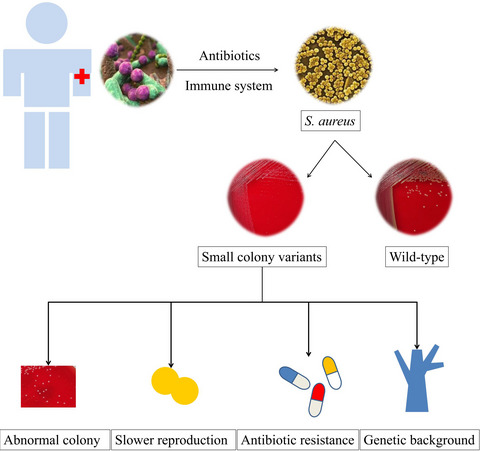
Through investigating the epidemiology and characteristics of small colony variants (SCVs) of S. aureus in wound specimens, here we found that the formation of SCVs is very rare and closely related to the usage of antibiotics. At the same time, the formation of SCVs may not be limited to specific resistance types and genetic types. Therefore, clinical laboratories should pay more attention to SCVs to facilitate effective treatment of SCVs infection.
Combination of artificial intelligence-based endoscopy and miR148a methylation for gastric indefinite dysplasia diagnosis
- First Published: 22 November 2021
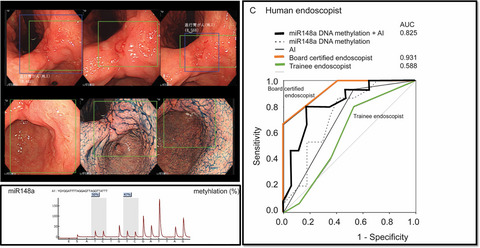
This study aimed to compare and evaluate the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of physician-performed endoscopy, AI-based endoscopy, and/or molecular markers in detecting gastrointestinal neoplasms (GIN). We believe that our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because despite the availability of both endoscopic and histologic diagnosis, differentiating between a benign and malignant lesions is still challenging; some lesions are classified indeterminately as GIN. AI diagnosis is gaining popularity because it enables the non-invasive diagnosis of the presence, site, and extent of lesions. Further, we believe that this paper will be of interest to the readership of your journal because we observed that the accuracy for GIN diagnosis from the combination of miR-148a and AI was high.
Christianson syndrome: A novel splicing variant of SLC9A6 causes exon skipping in a Chinese boy and a literature review
- First Published: 17 November 2021
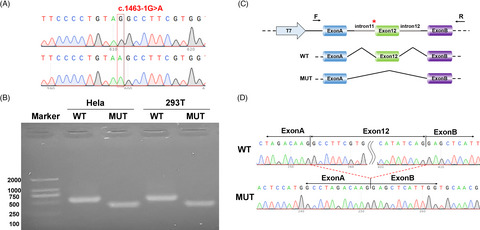
We report on a case of 3-year-old Chinese boy with Christianson Syndrome (CS) displayed the features of epilepsy, psychomotor retardation, microcephaly, low body weight, difficulty in feeding, excessive movement, attention loss, ataxia, and cerebellar atrophy. We identified a novel homozygous splicing variant [c.1463–1 (IVS11) G >A] in SLC9A6 by trio-based exome sequencing. The minigene expression in vitro confirmed the splicing variant altered a consensus splice acceptor site of SLC9A6 intron 11, resulting in skipping over exon 12. Our finding extends the catalog of pathogenic intronic mutations affecting SLC9A6 pre-mRNA splicing and provides a basis for the genetic diagnosis of CS.
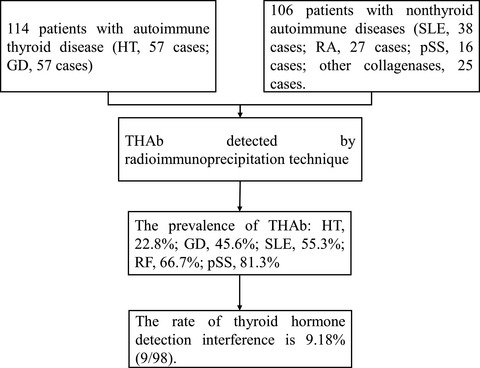
High prevalence of thyroid hormone autoantibody and low rate of thyroid hormone detection interference
- First Published: 01 December 2021
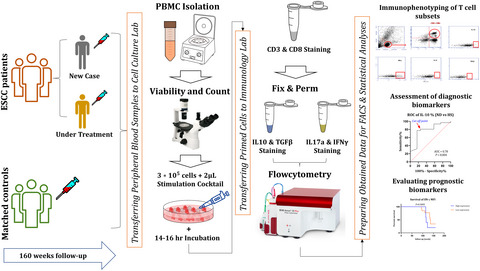
Simultaneous disruption of circulating miR-21 and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs): Prospective diagnostic and prognostic markers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC)
- First Published: 19 November 2021
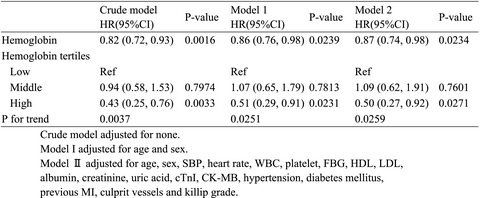
Association between serum hemoglobin and major cardiovascular adverse event in Chinese patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention
- First Published: 10 December 2021
Novel splicing-site mutation in DCAF17 gene causing Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome in a large consanguineous family
- First Published: 08 December 2021
Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome, a rare autosomal recessive disease with endocrine and neuroectodermal abnormalities including progressive sensorineural hearing loss, alopecia, mental retardation and hypogonadism resulting from mutations in the DCAF17 gene. Here we reported a large consanguineous family with multiple affected individuals showing Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome phenotypes and having a novel a splice site deletion mutation in DCAF17 gene
Significance of preoperative blood tests in the prognosis of colorectal cancer: A prospective, multicenter study from Hungary
- First Published: 23 November 2021
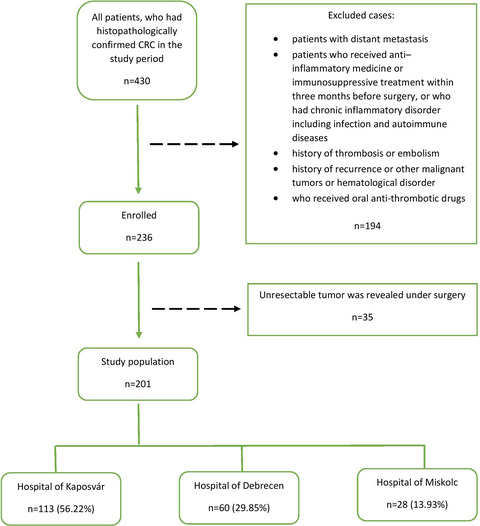
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was proved to be an independent prognostic factor for disease-free survival in patients with non-metastatic colon cancer in our Hungarian multicenter study. NLR might help to recognize the high-risk patients between patients with the same tumor-node-metastasis stage and could help with the decision on adjuvant chemotherapy. The biomarkers in preoperative blood tests are habitually evaluated, and NLR could be an inexpensive prognostic marker that can be easily assessed in clinical practice.
Association of a common genetic variant (insertion/deletion) in ACE gene with prostate cancer susceptibility in a Tunisian population
- First Published: 19 November 2021
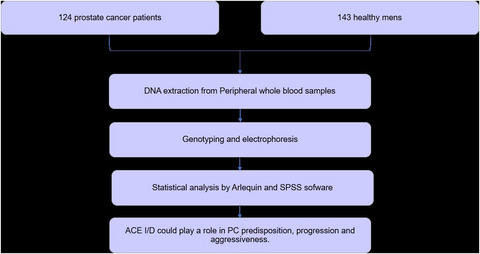
The association of insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism of the ACE gene with prostate cancer (PC) risk remains controversial. The ACE SNP rs 4646994 is likely to predispose to PC and aggressiveness in Tunisia population. This study provides valuable information for the diagnosis and prognosis of the risk of PC disease.
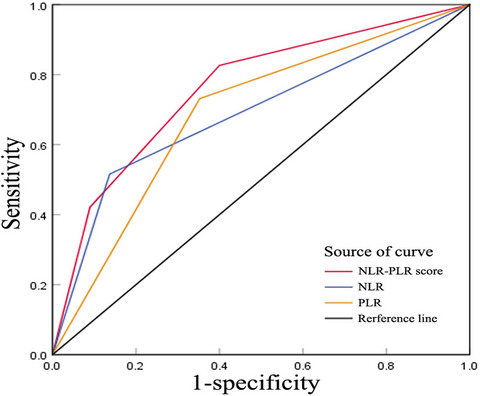
Predictive significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte for cytomegalovirus infection in infants less than 3 months: A retrospective study
- First Published: 22 November 2021
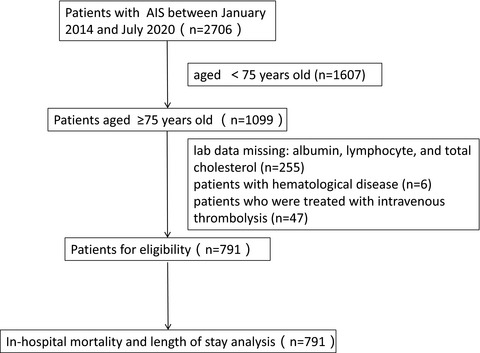
Malnutrition on admission increases the in-hospital mortality and length of stay in elder adults with acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 08 December 2021
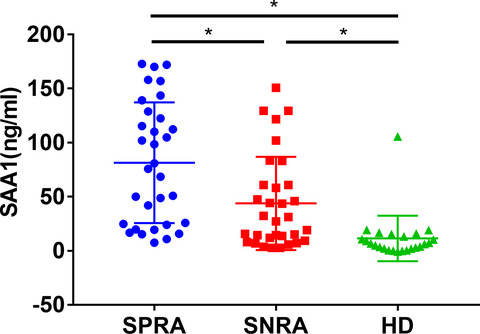
iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in sera of seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients
- First Published: 23 November 2021
A novel model based on liquid-liquid phase separation–Related genes correlates immune microenvironment profiles and predicts prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 19 November 2021

A prognostic model based on the LLPS-related genes using LASSO regression and multivariate Cox regression analyses was constructed and validated for LUSC. The risk index (RI) calculated for each patient according to the model was significantly related to patients’ prognosis and caner-related immune activities.
Neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictors of free-wall rupture in patients with acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 25 November 2021
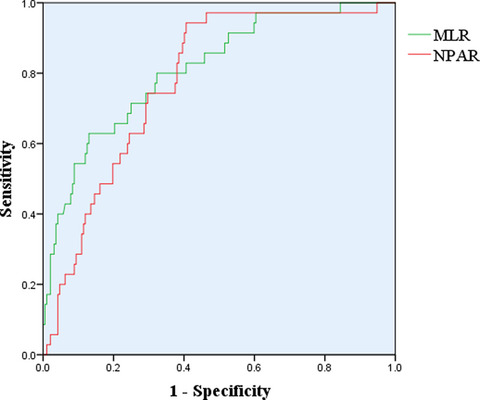
Emergency PCI and ACEI/ARB treatment were independent protective factors for for FWR patients with AMI, while the increase of MLR and NPAR were independent risk factors. What's more, NPAR and MLR are good indicators for predicting FWR. This study provides evidence for a better understanding between NPAR, MLR and FWR.
Smaller reaction volume of triplex taqman real-time reverse transcription-PCR assays for diagnosing coronavirus disease 2019
- First Published: 03 December 2021
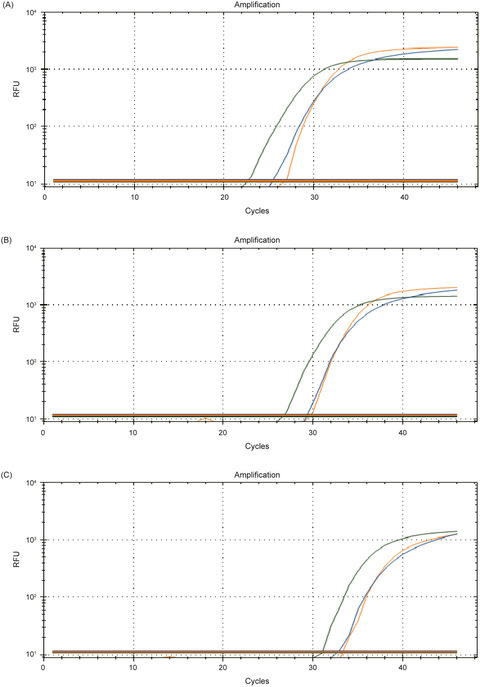
In this work, We established a bunch of triplex new TaqMan real-time PCR assays. Three sets of primers and probes (targeting the ORF1ab, N and E genes, respectively) are poorly consistent with other human coronaviruses and the human influenza virus. Surveillance of RNA-based pseudovirus demonstrated that they were identified positive with respect to SARS-CoV-2, and the established PCR assays is achievable. The assays established provides a smaller reaction volume for diagnosing COVID-19.
MicroRNA-34a in coronary heart disease: Correlation with disease risk, blood lipid, stenosis degree, inflammatory cytokines, and cell adhesion molecules
- First Published: 03 December 2021

This study enrolled 203 CHD patients and 100 patients with unexplained chest pain or suspected CHD symptoms but excluded from CHD by CAG examination as controls, then plasma samples were collected to detect miR-34a. Besides, for CHD patients only, serum samples were obtained for inflammatory cytokine and cell adhesion molecule measurement. Interestingly, miR-34a was increased in CHD patients and disclosed a good diagnostic value of CHD. Moreover, miR-34a positively correlated with hyperlipidemia, hyperuricemia, and DM in CHD patients. Furthermore, miR-34a positively associated with blood lipid (including TG, TC and LDL-C) and Gensini score in CHD patients. Additionally, miR-34a positively related to inflammation-related indexes (including CRP, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-17A) and cell adhesion molecules (including VCAM-1 and ICAM-1) in CHD patients.
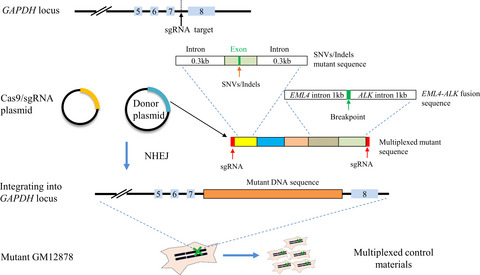
Preparation of multiplexed control materials for cancer mutation analysis by genome editing in GM12878 cells
- First Published: 23 November 2021
REVIEW ARTICLE
Predictive molecular markers for the treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 24 November 2021
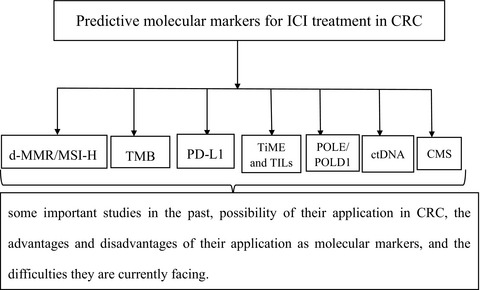
Predictive molecular markers are important tools to precise screen of patient groups who can benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors treatment. This article focused on some important predictive molecular markers for ICI treatment in colorectal cancer, which included not only some mature molecular markers such as deficient mismatch repair (d-MMR) or microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H), tumor mutational burden (TMB), programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1), and tumor immune microenvironment (TiME) or tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), but also some novel molecular markers, such as POLE or POLD1, circulating tumor DNA and consensus molecular subtypes (CMS). We have made in-depth reviews for these markers, which included some important studies in the past, possibility of their application in CRC, the advantages and disadvantages of their application as molecular markers, and the difficulties they are currently facing.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
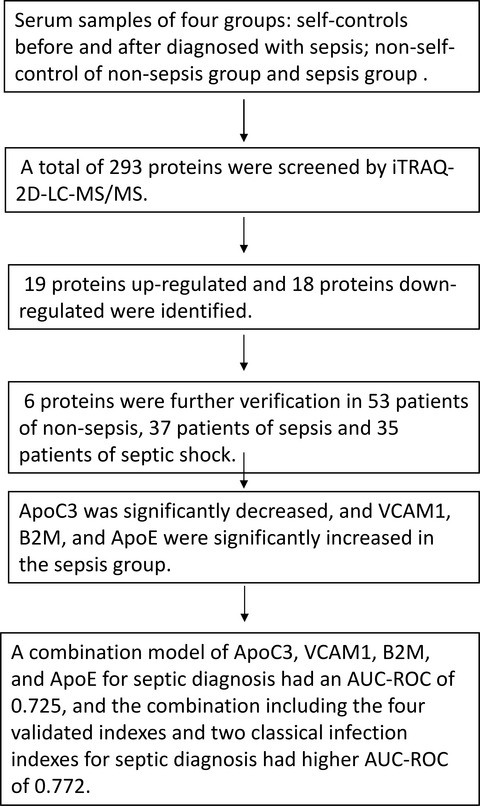
Identification of novel biomarkers for sepsis diagnosis via serum proteomic analysis using iTRAQ-2D-LC-MS/MS
- First Published: 26 November 2021
Expression changes of serum LINC00941 and LINC00514 in HBV infection-related liver diseases and their potential application values
- First Published: 26 November 2021
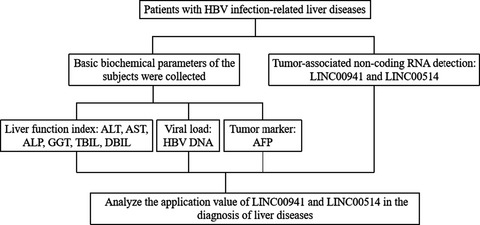
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a promising serum biomarker for disease diagnosis. However, literature on the diagnostic value of the lncRNA for liver diseases, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is scant. The present study is to detect the expression levels of LINC0094 and LINC00514 in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection-related liver diseases and evaluate their potential application in the diagnosis of liver diseases. Our results showed that serum LINC0094 and LINC00514 levels were significantly elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), liver cirrhosis (LC), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared with healthy controls, and the combined detection with alpha fetal protein (AFP) can significantly improve the diagnostic efficiency of liver diseases.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Serum exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE level for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis
- First Published: 26 November 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
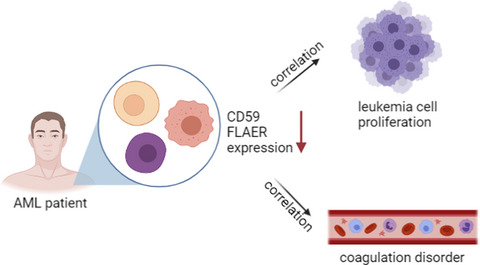
The expression and clinical significance of CD59 and FLAER in Chinese adult AML patients
- First Published: 21 December 2021
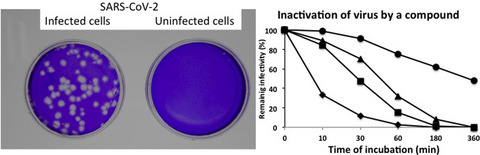
Virucidal effect of monogalactosyl diacylglyceride from a green microalga, Coccomyxa sp. KJ, against clinical isolates of SARS-CoV-2 as assessed by a plaque assay
- First Published: 27 November 2021
Evaluation of plasma circ_0006282 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in colorectal cancer
- First Published: 03 December 2021
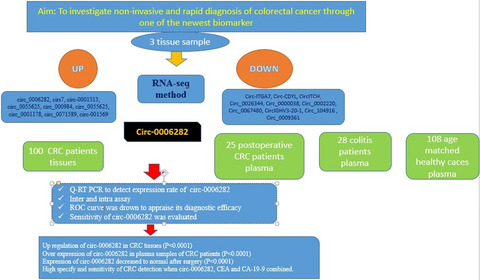
Based on RNA-sequencing results circ_0006282, cirs7, circ-0001313, circ_0055625, circ_000984, circ_0055625, circ_0001178, circ_0071589, circ-001569 were upregulated and Circ-ITGA7, Circ-CDYL, CircITCH, Circ_0026344, Circ_0000038, Circ_0002220, Circ_0067480, CircIGHV3-20-1, Circ_104916, Circ_0009361 were downregulated circRNA. Upregulation of hsa_circ_0006282 confirmed in CRC tissues and plasma samples of CRC patients in comparison to healthy controls. This expression decreased to normal after surgery. There is a high specificity and sensitivity of CRC detection when hsa_circ_0006282, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and carbohydrate antigen199 (CA199) are combined.
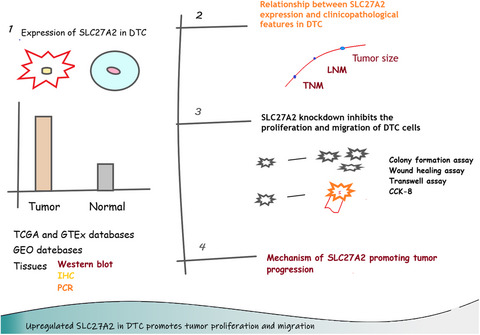
Upregulated SLC27A2/FATP2 in differentiated thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor proliferation and migration
- First Published: 02 December 2021
Diagnostic comparison between cord blood and filter paper for the screening of congenital hypothyroidism
- First Published: 03 December 2021
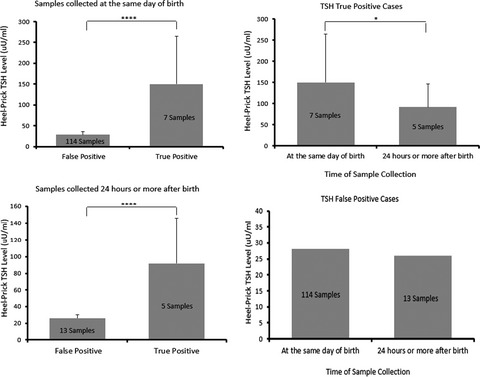
Cord blood and heel prick TSH levels are essential in diagnosing and preventing congenital hypothyroidism (CH). Out of the total screened newborn 12 were confirmed for having primary congenital hypothyroidism. 10 cases were positive for cord blood TSH (Sensitivity 75%, specificity 99.9%, and a recall rate of 0,004%) while 139 cases were positive for heel prick blood TSH (Sensitivity 100%, specificity 99.3%, and a recall rate of 0.60%). Cord blood is an alternative method to heel-prick but not with cases of prematurity.
Association between TBXT rs2305089 polymorphism and chordoma in Iranian patients identified by a developed T-ARMS-PCR assay
- First Published: 27 November 2021
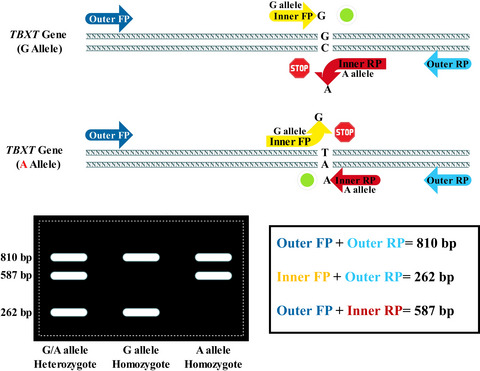
This study aimed to show whether rs2305089 polymorphism is associated with chordoma in the Iranian population. In order to detect the rs2305089, tetra-primer amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (T-ARMS-PCR) was used. In total, 19 chordoma patients and 108 normal healthy individuals were recruited and screened using T-ARMS-PCR. Besides, the results were validated by Sanger sequencing. This study demonstrated the association of TBXT rs2305089 with chordoma in an Iranian population using a simple, accurate, and cost-effective T-ARMS-PCR assay. Our results were in line with the previous studies showing that TBXT rs2305089 is associated with chordoma development. We also developed an efficient T-ARMS-PCR assay so as to determine the genotype of rs2305089.
REVIEW ARTICLES
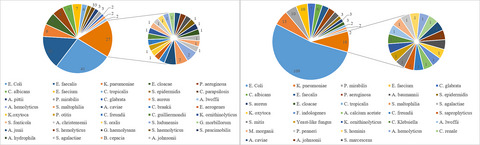
Worldwide prevalence of microbial agents’ coinfection among COVID-19 patients: A comprehensive updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 01 December 2021
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Emerging detection technologies and auxiliary analysis
- First Published: 10 December 2021
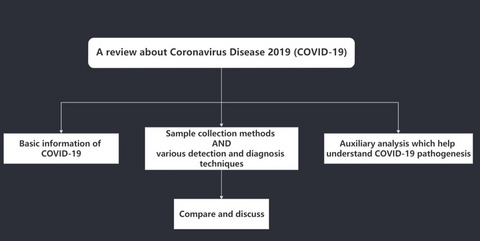
The main goal of this review was to provide a critical discussion on the development and application of these different analytical methods, which based on etiology, serology, molecular biology, as well as to compare their respective advantages and disadvantages. In addition to these methods, hematology and biochemistry, as well as auxiliary analysis based on pathological anatomy, ultrasonography, and cytokine detection, will help understand COVID-19 pathogenesis.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Circulating JNK pathway-associated phosphatase: A novel biomarker correlates with Th17 cells, acute exacerbation risk, and severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients
- First Published: 16 December 2021
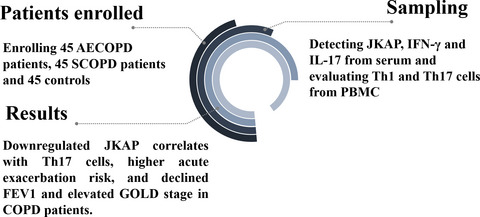
Serum from 45 AECOPD patients, 45 SCOPD patients, and 45 controls was collected for JKAP, IFN-γ, and IL-17 detection. Meanwhile, PBMC from COPD patients was collected for Th1 and Th17 cells evaluation. Subsequently, JKAP was highest in controls followed by SCOPD patients and lowest in AECOPD patients (p < 0.001). Meanwhile, downregulated JKAP correlated with declined FEV1 (%predicted) (p = 0.019) and elevated GOLD stage (p = 0.021) in AECOPD patients. Additionally, JKAP was negatively correlated with Th17 cells (p = 0.010), IFN-γ (p = 0.016) and IL-17 (p = 0.005) in AECOPD patients.
Assessing the utility of the Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampin assay for analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in patients with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis
- First Published: 01 December 2021
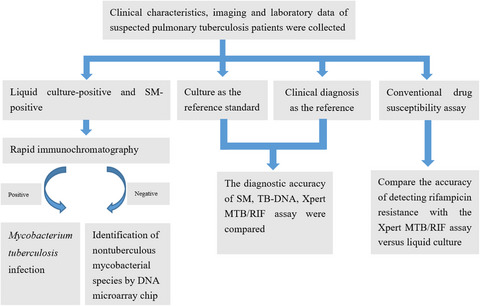
The analysis of BALF with the Xpert MTB/RIF assay provides a rapid and accurate tool for the early diagnosis of PTB. The accuracy of diagnosis was superior compared to SM and TB-DNA. Moreover, Xpert is a quick and accurate method for the diagnosis of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis and can also provide more effective guidance for the treatment of PTB or multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB).
Gender differences in the microbial spectrum and antibiotic sensitivity of uropathogens isolated from patients with urinary stones
- First Published: 02 December 2021
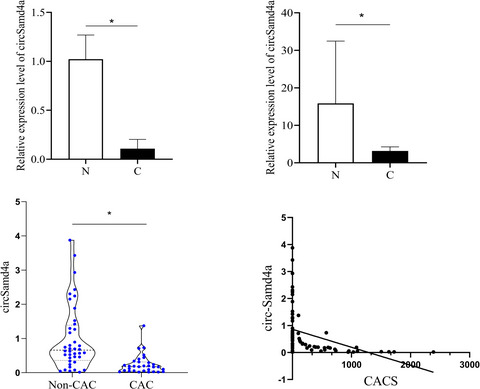
CircSamd4: A novel biomarker for predicting vascular calcification
- First Published: 29 November 2021
The possible mechanism of Hippophae fructus oil applied in tympanic membrane repair identified based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- First Published: 03 December 2021
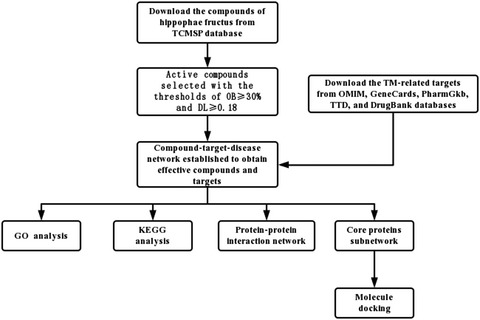
The mechanism of hippophae fructus oil in treatment of tympanic membrane perforations was explored by the technology of network pharmacology and molecular docking. Hippophae fructus oil may repair perforations by influencing the regulation of cellular oxidative stress, and the quercetin may be one of the possibly effective compounds in tympanic membrane repair. This study provided a novel idea to explore new drugs in tympanic membrane repair.
Upregulation of CD3ζ and L-selectin in antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by eliminating myeloid-derived suppressor cells with doxorubicin to improve killing efficacy of neuroblastoma cells in vitro
- First Published: 03 December 2021
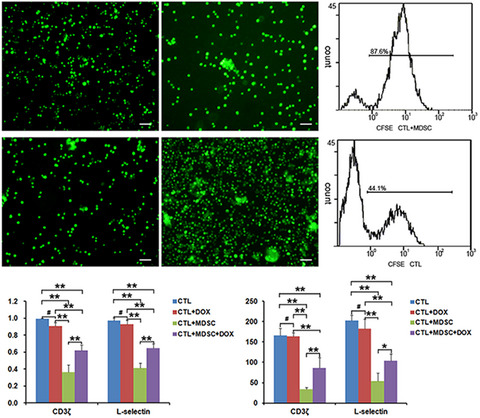
High aggregation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the tumor microenvironment of neuroblastoma results in immunosuppression and affects its therapeutic effectiveness. Targeted elimination of MDSC by doxorubicin can improve antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte killing neuroblastoma cells in vitro by upregulating the levels of cluster of differentiation 3ζ chain and L-selectin. The present study provided a novel method to enhance immunotherapeutic effects for neuroblastoma.
RETRACTION
Retraction: Long noncoding RNA XIST binding to let-7c-5p contributes to rheumatoid arthritis through its effects on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts via regulation of STAT3
- First Published: 06 December 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Comparison of Real-Q 2019-nCoV and DaAn Gene 2019-nCoV polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2
- First Published: 09 December 2021
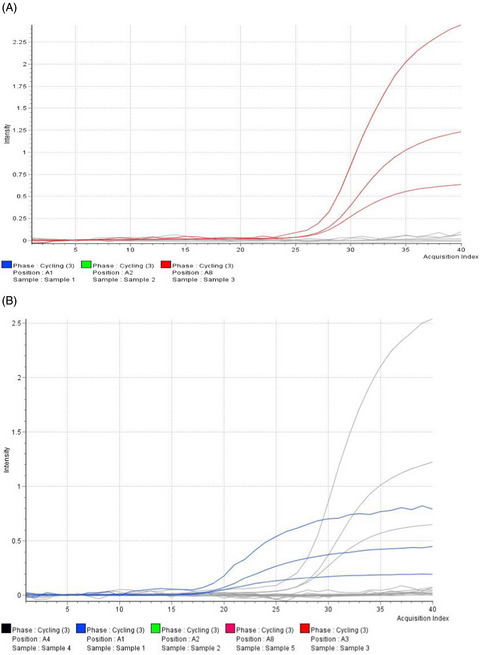
Our study compared the analytical performance characteristics of the Real-Q (BioSewoom) and Da An Gene assays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 from nasopharyngeal swab samples. A total of 48 nasopharyngeal samples were tested using the two assays. The results suggests that the two kits have an overall percent agreement of 93.2%, positive percent agreement of 83.4% and negative percent agreement of 100%.
Association between serum inflammatory parameters and the disease severity in COVID-19 patients
- First Published: 07 December 2021
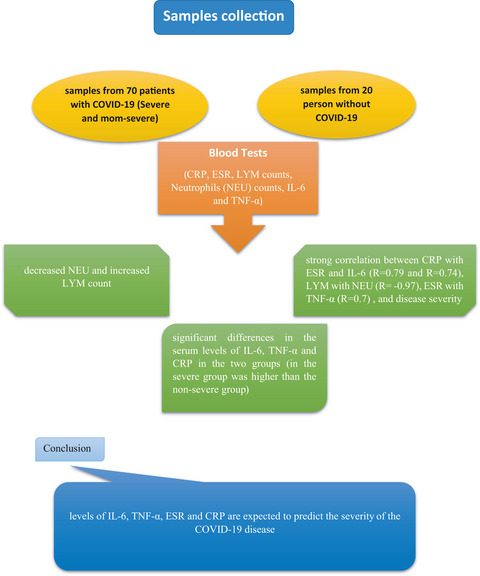
Serum inflammatory parameters were analyzed in patients with severe and non-severe COVID-19. The serum levels of LYM, CRP, IL-6, TNF-α and ESR in severe patients were significantly higher than in non-severe patients. Measurement of inflammatory markers might help clinicians monitor and evaluate the severity and prognosis of COVID-19.
Oxidative stress parameters and keap 1 variants in T2DM: Association with T2DM, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and obesity
- First Published: 03 December 2021
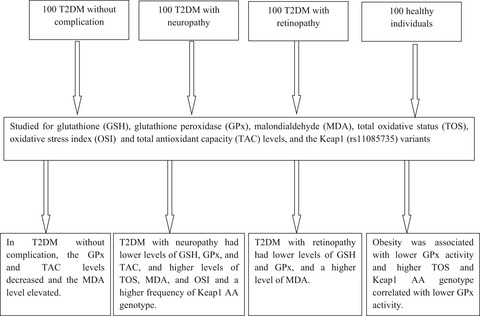
Studying 400 T2DM patients without complication indicated: In T2DM patients without complication, the GPx and TAC levels decreased and the MDA level elevated. T2DM with neuropathy had lower levels of GSH, GPx, and TAC and higher levels of TOS, MDA, and OSI and a higher frequency of Keap1 AA genotype. T2DM with retinopathy had lower levels of GSH and GPx and a higher level of MDA. Obesity-enhanced oxidative stress was associated with lower GPx activity and higher TOS and Keap1 AA genotype correlated with lower GPx activity. Reduced antioxidant system and Keap1 variants are involved in the pathogenesis of T2DM and its complications of neuropathy and retinopathy.
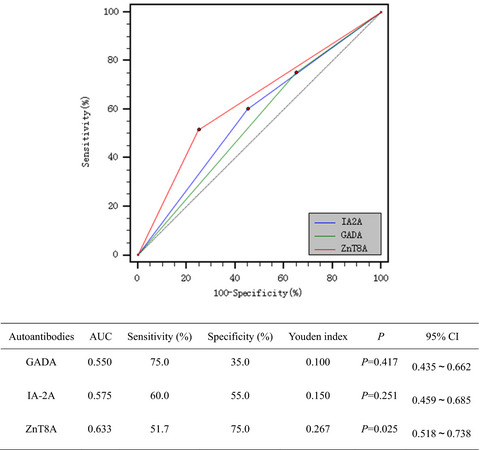
Clinical study of autoantibodies in type 1 diabetes mellitus children with ketoacidosis or microalbuminuria
- First Published: 03 December 2021
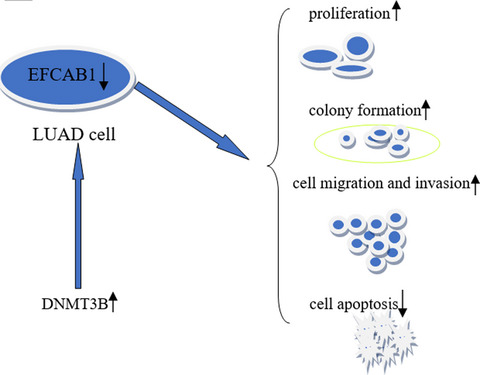
Low-level EFCAB1 promoted progress by upregulated DNMT3B and could be as a potential biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 14 December 2021
Association between the rs3802201 polymorphism of the lncRNA MIR2052HG gene and the risk of recurrent miscarriage in a Southern Chinese population
- First Published: 14 December 2021
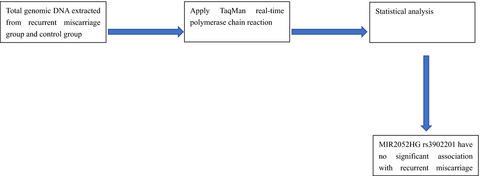
We recruited 248 women which were diagnosed with recurrent miscarriage (RM) as the RM group and included 392 age-matched healthy controls with at least two normal pregnancies and no history of miscarriage as the control group. By TaqMan method, we compared the frequency of rs3802201 between control group and current miscarriage group, and we found out that rs3802201 has no significant association with RM.
Long non-coding RNA HAGLROS promotes the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma via suppressing miR-100
- First Published: 09 December 2021
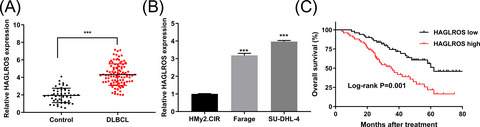
HAGLROS is upregulated in DLBCL tissues and correlated with the survival outcome of DLBCL patients. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of HAGLROS expression in DLBCL tissues (n = 100) and reactive hyperplasia of lymph nodes tissues (control, n = 51). (B) RT-qPCR analysis of HAGLROS expression in normal B-cell-immortalized cell line (HMy2.CIR) and DLBCL cell lines (Farage and SU-DHL-4). (C) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival for DLBCL patients stratified by HAGLROS expression in DLBCL tissues. ***p < 0.001. DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
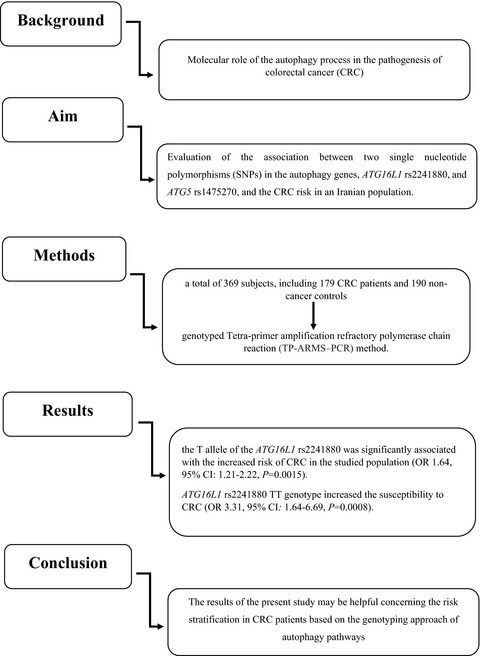
Autophagy ATG16L1 rs2241880 impacts the colorectal cancer risk: A case-control study
- First Published: 11 December 2021
Investigation of serum levels of orexin-A, transforming growth factor β, and leptin in patients with multiple sclerosis
- First Published: 11 December 2021
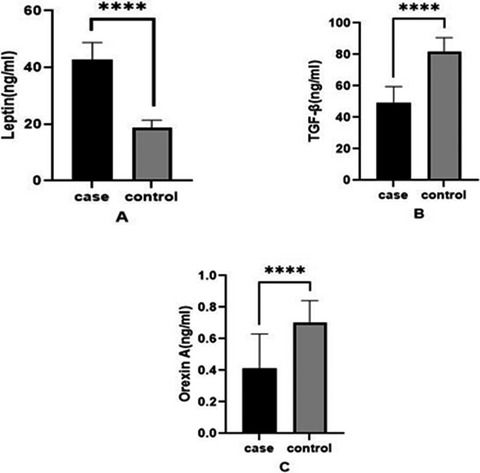
Background: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease related to various inflammatory and nutritional parameters. This study was conducted to determine the relationship between serum leptin, orexin-A, and TGF-β levels and BMI in MS patients. Methods: This cross-sectional study included 25 patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and 40 healthy controls. Serum levels of leptin, orexin-A and TGF-β were measured by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, chi-square tests, and linear regression tests. 65 volunteers, including 25 MS patients and 40 healthy individuals, were enrolled in the study. Results: The mean ages of subjects in the case and control groups were 38.04 ± 7.53 and 40.23 ± 5.88, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences between the case and control groups in sex, age, alcohol consumption, and cigarette consumption (p > 0.05). Mean serum levels of orexin-A and TGF-ss were lower in patients with MS than in healthy controls, but leptin was higher (42.8 vs. 18.9 ng/ml, p < 0.001). The relationship between BMI and serum levels of orexin-A, TGF-ss, and leptin in MS patients was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Conclusion: Our results showed that serum levels of orexin-A and TGF-P were lower. The serum level of leptin was higher in patients with MS than in healthy controls. In addition, there was no statistically significant relationship between BMI and serum levels of orexin-A, TGF-ss, and leptin in patients with MS.
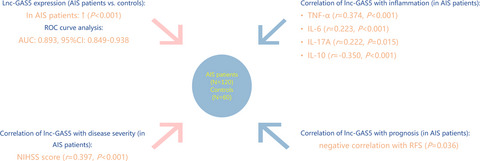
The clinical value of long noncoding RNA GAS5 in acute ischemic stroke: Correlation with disease risk, inflammation, severity, and risk of recurrence
- First Published: 17 December 2021
Development of a novel five-lncRNA prognostic signature for predicting overall survival in elderly patients with breast cancer
- First Published: 11 December 2021
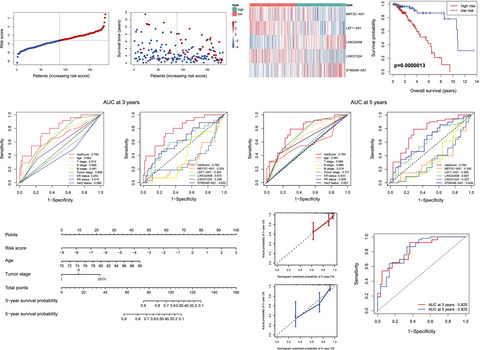
The five-lncRNA signature (including LEF1-AS1, MEF2C-AS1, ST8SIA6-AS1, LINC01224, and LINC02408) successfully divided elderly breast cancer patients into low- and high-risk groups with significantly different prognosis, and the predictive accuracy of the signature was better than all the single genes and clinical characteristics. The five-lncRNA signature was an independent prognostic factor of overall survival, and the nomogram constructed by independent prognostic factors was an accurate predictor of predicting overall survival probability.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Time course of antibody concentrations against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 among healthy hospital workers up to 200 days after their first COVID-19 vaccination
- First Published: 14 December 2021
REVIEW ARTICLE
Recent advances in methods for the diagnosis of Corona Virus Disease 2019
- First Published: 17 December 2021
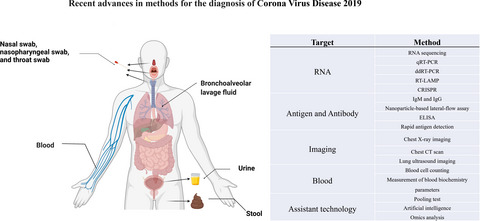
Methods for the diagnosis of COVID-19. 1. Summarizes the currently commonly used methods for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2. 2. The current gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19 is qRT-PCR. Other RNA-based methods include RNA-seq, ddRT-PCR, RT-LAMP, and CRISPR. The serological testing of antibodies (IgM and IgG), nanoparticle-based lateral-flow assay, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) can be used to enhance the detection sensitivity and accuracy. 3. The pooling test is an important public health tool to reduce cost and increase testing capacity in low-risk area, while artificial intelligence (AI) may aid to increase the diagnostic efficiency of imaging-based methods. 4. Depending on the type of samples and stages of the disease, a combination of information on patient demographics and histories, clinical symptoms, results of molecular and serological diagnostic tests, and imaging information is highly recommended to achieve adequate diagnosis of patients with COVID-19.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Detection of folate receptor-positive circulating tumor cells as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognostication, and therapeutic monitoring in breast cancer
- First Published: 17 December 2021
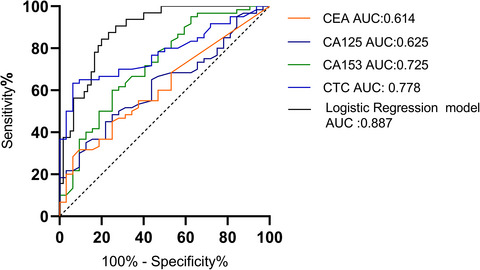
In this paper, FR+CTC was detected in peripheral blood of the patients with breast cancer with the ligand-targeted PCR. The levels of FR+CTC were significantly higher in breast cancer patients compared to healthy controls and the FR+CTC level were significantly higher in the distant metastasis and high TNM stage. The level of FR+CTC was decreased underwent the surgery in 2 weeks post-operation compared to pre-operation. The detection sensitivity and specificity of FR+CTC was higher diagnostic efficacy than other biomarkers, such as CEA, CA125, and CA153. This study showed that may be used as a potential biomarker for auxiliary diagnosis and early detection particularly combined with other biomarkers assay in breast cancer.
Comparison of IL-6 measurement methods with a special emphasis on COVID-19 patients according to equipment and sample type
- First Published: 14 December 2021
The overall analytical performance of AFIAS is acceptable. In light of the recent coronavirus pandemic, AFIAS may be an attractive tool for measuring IL-6 levels. An easy and quick method for the evaluation of IL-6 levels even in outpatient and small laboratory settings, aiding in the management of patients with COVID-19.
Accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleural effusion
- First Published: 17 December 2021