Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 112, Issue 17
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 25 July 2012

Large scale Jahn-Teller systems, such as the biologically important iron-sulfur proteins, polynuclear metal-oxide clusters, and metal ions in crystals, present a complicated dynamic problem that, in general, cannot be solved analytically. In fact, the vibronic properties of these systems have remained unknown due to the lack of efficient computational tools. On page 2957, Boris Tsukerblat, Andrew Palii, Juan M. Clemente-Juan, Alejandro Gaita-Arinõ, and Eugenio Coronado present a symmetry-adapted approach aimed at the accurate solution of this problem. The image on the cover and left illustrates an ideal system for the application of this method, the reduced mixed-valence dodecanuclear Keggin anion, in which the electronic pair is delocalized over 12 sites.
Inside Cover, Volume 112, Issue 17
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 25 July 2012

The generation procedure of the potential energy surface (PES) can, in some systems, influence the relative stability of conformers. In the case of the triatomic van der Waals molecule HeI2, presented on page 2971 by Gerardo Delgado-Barrio and coworkers, it is concluded that different procedures provide PESs of similar quality, determined by the accuracy of the available ab initio data. Confirming the results of previous experimental studies, the surface depicted on the cover shows two potential minima corresponding at the linear and T-shaped configurations with very similar welldepths.
Introduction
Introduction
- Pages: 2849-2856
- First Published: 14 July 2012

It is a great honor and privilege for the guest editors to pay tribute to the remarkable Professor Ilya G. Kaplan. One of us, E.S.K., had the privilege to be partly among Kaplan's many former graduate students and three, O.N., J.S., and J.L., have fruitfully collaborated with him. We all have been good friends of Ilya and the admirers of his work. Here, we present our tribute in a quite unusual format: a dialogue where Ilya Kaplan shares his memoirs of his path to and in science.
Full Papers
Early stage of the development of quantum chemistry without spin and its recent applications
- Pages: 2858-2867
- First Published: 18 June 2012
General ideas, on which the quantum chemistry without spin is based, are discussed. Three important applications of quantum chemistry without spin are presented in details: (1) the methods for finding the molecular spin-multiplets allowed by the Pauli principle; (2) the symmetry properties of the electron density that determined the Kohn-Sham equations in DFT; and (3) the foundations of the Pauli principle.
Complexes of C60 with cyclic oligoisothianaphthenes. A theoretical study
- Pages: 2868-2874
- First Published: 21 November 2011
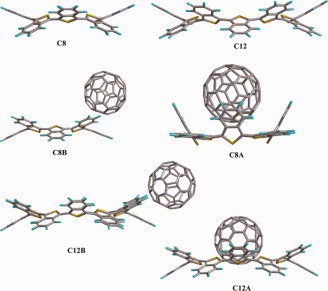
Fullerene and thiophene-based devices tend to show the greatest promise among current organic solar cell candidate materials. Recently, it was shown that 2D-macrocyclic oligothiophenes form CT complexes with C60. This article presents the first study of the alternate, low transport-gap cyclooligoisothianaphthenes with C60.
The origins and later developments of molecular orbital theory
- Pages: 2875-2879
- First Published: 23 January 2012
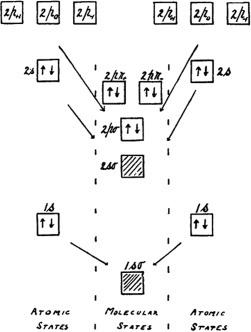
Molecular Orbital (MO) theory is the basis of almost all modern quantum mechanical calculations of the electronic structure of molecules. It has the enormous advantage of being both easy to develop into semi-empirical models and of providing ab initio calculations at simple and advanced levels, some of which have been shown to be very accurate for small molecules. Within MO theory there are well defined levels of approximation, such as the Hartree-Fock limit, that make it easy to compare calculations from different sources at several levels of approximation. This article traces the history of the development of this important tool in a quantum chemist's toolbox.
Hund's rule in the doubly excited states of the helium isoelectronic†
- Pages: 2880-2893
- First Published: 06 February 2012
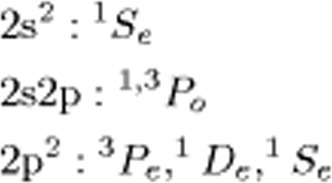
This article takes advantage of the progress that has taken place in the study of doubly excited states of two electron atomic systems in the last 30 years to examine some of the conclusions of an earlier analysis of the role of nuclear attraction vs. interelectronic repulsion differences in the determination of the multiplet structure of open shell atoms.
Some difficulties in considering rotation motion within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for polyatomic molecules
- Pages: 2894-2903
- First Published: 16 March 2012
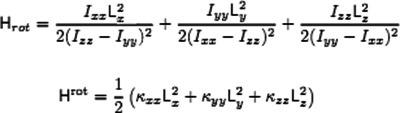
Almost 90 years after its introduction, there is still no available mathematically sound account of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation for polyatomic molecules, in which rotation can be considered as a separable motion. This could be possible to achieve considering the separation of electronic and nuclear motion in the context of a potential composed of many wells in a translationally invariant frame.
Charge transfer in composites “dielectric + metal nanoparticles”: Effect of electric and magnetic fields
- Pages: 2904-2914
- First Published: 19 March 2012
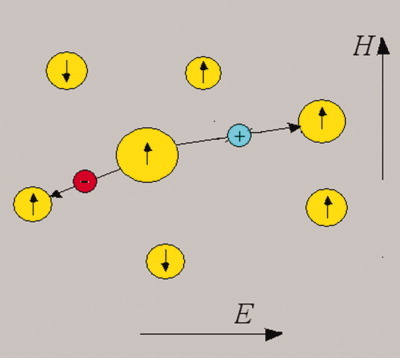
The conductivity mechanism in ferromagnetic metal nanoparticles embedded in insulator matrixes is explained in terms of electron tunneling between neighboring particles and can be divided in three regimes, corresponding to weak, strong, and super-strong applied electric fields. The dependence of the resistivity on temperature and applied voltage is significantly different for all these three modes, whereas the magnetoresistance is found to be the same in the cases of weak and super-strong electric fields.
Some spin and spin-free aspects of coulomb correlation in molecules
- Pages: 2915-2923
- First Published: 03 April 2012
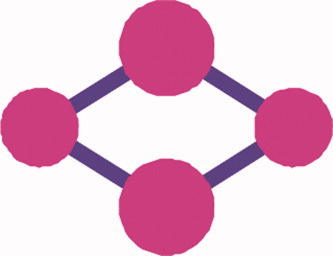
A detailed spin-component analysis of the pair electron density and the associated cumulants is provided. For the given atom A, we can define a suitable correlation measure, the spin-up spin-down correlation index KAαβ. It shows in what extent the atom A is involved into internal electron-correlation processes. The KAαβ- index may serve as a rough indicator of the instablity unstable atoms in molecule. An example of the rhombic carbon cluster C4 demonstrates a result of the proposed analysis.
Role of diffusion in the violation of the long-wave approximation in line wings
- Pages: 2924-2931
- First Published: 05 May 2012
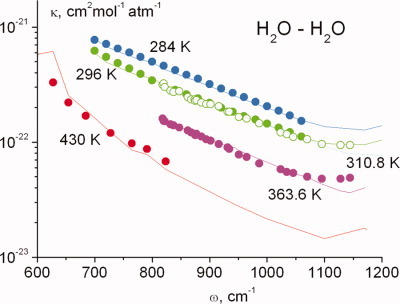
The 8–12 lm spectral interval has a fundamental role in the radiation balance of the Earth's atmosphere. The temperature dependence of water-vapor absorption coefficient in that interval is simulated in this article. As the same classical intermolecular interaction potential is used in the calculations of both the line wing absorption and the second virial coefficient of the water vapor, the relationship between the spectroscopic and thermodynamic properties is made more explicitly considered in this model.
Accurate ab initio-based double many-body expansion adiabatic potential energy surface for the 22 A′ state of NH2 by extrapolation to the complete basis set limit
- Pages: 2932-2939
- First Published: 07 April 2012
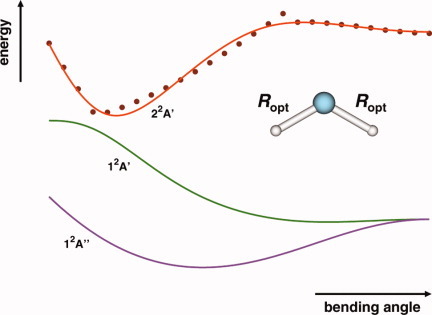
A global double-many-body expansion potential energy surface is reported for the second excited state of NH2 (22A′) from accurate ab initio electronic structure calculations. The form here reported, jointly with similar ones published elsewhere by the authors for the ground and first excited doublet electronic states, are expected to have an important role in the dynamics and kinetics of the N + H2 reaction being, therefore, recommended for such purposes.
Nonorthogonal orbitals; the Hartree–Fock–Heitler–London method and preliminary applications†
- Pages: 2940-2946
- First Published: 23 April 2012
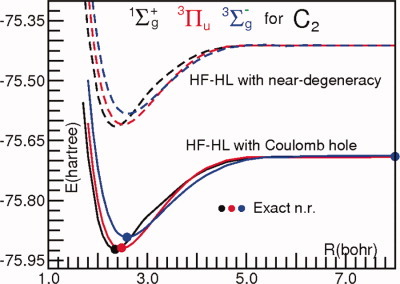
The recent Hartree-Fock-Heitler-London proposal is exposed and tested for a number of small molecules. As an example, the potentail energy curves for the ground and two excited states of C2 are reported from HF-HL computations with near-degeneracy and HF-HL computations with inclusion of the Coulomb hole functional. The equilibrium and dissociation energies are compared with the exact non relativistic, n.r., values.
Modeling absorption of the kindling fluorescent protein with the neutral form of the chromophore
- Pages: 2947-2951
- First Published: 17 April 2012
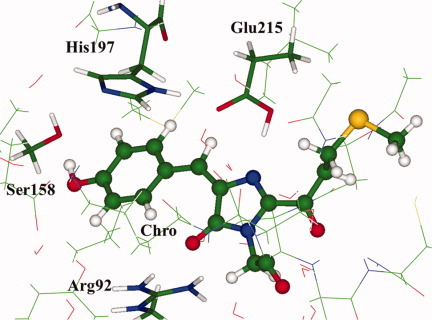
Spectral properties of the kindling fluorescent protein were modeled by computing structure and spectra of a large molecular cluster, mimicking the chromophore containing-pocket assuming the neutral form of the chromophore in the trans configuration. Evidence was provided that this protein conformation accounts for the previously unassigned absorption band at 445 nm. This study demonstrates that the properties of the amino acid residues nearest to the chromophore play a role in the shifts in the absorption spectra.
Nonadditive effects on the stability of Be3: A benchmark CASSCF + averaged quadratic coupled cluster study of the equilateral and linear symmetrical configurations
- Pages: 2952-2956
- First Published: 27 April 2012
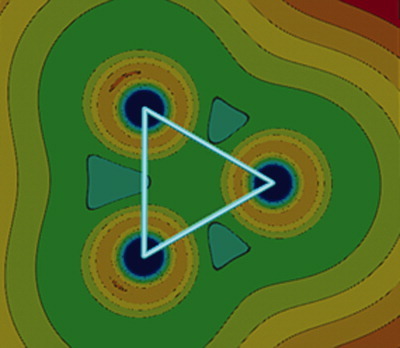
The binding energies of the linear and triangular isomers of the beryllium trimer are an order of magnitude larger than the one of the dimer. This large difference is explained in terms of very large nonadditive three-body corrections in Be3. Such nonadditive three-body terms are expected to have an even larger effect on the bonding properties of solid beryllium.
A symmetry adapted approach to the dynamic Jahn-Teller problem: Application to mixed-valence polyoxometalate clusters with keggin structure†
- Pages: 2957-2964
- First Published: 15 May 2012
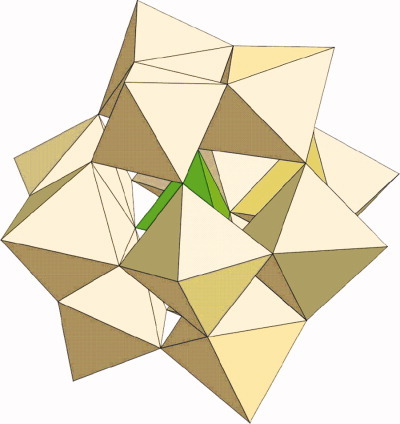
Large scale Jahn-Teller systems, especially high-nuclearity mixed-valence clusters, represent an important class of objects in molecular nanoscience. While the quantum-mechanical solution for the eigen-problem has been proposed earlier, the vibronic properties of these systems remained unknown due to the lack of efficient computational tools. Here, a symmetry-adapted approach to the dynamic vibronic problem is developed and applied to a reduced mixed-valence Keggin polyoxometalate. In this molecular metal-oxide an electronic pair is delocalized over twelve sites giving rise to a complicated vibronic problem for the spin-singlet and spin-triplet states.
Ionization and double-excitations within the framework of the G-particle-hole hypervirial equation method
- Pages: 2965-2970
- First Published: 15 May 2012
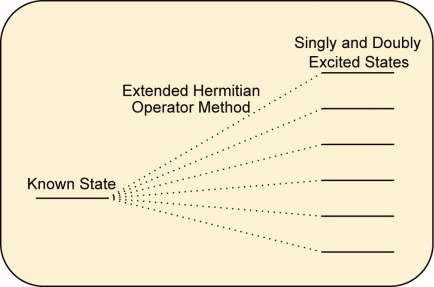
Given a well-known initial electronic state of an atom or molecule, one may obtain the spectrum of energies corresponding to its single and double excited states. This may be achieved by applying the close-form analytical expressions reported here, which constitute an extension of the well-known Hermitian Operator method.
Extended relations for the ionization energies are also reported here. In all these derivations a geminal-second-quantization algebra has been used.
HeI2 interaction potential based on an interpolation scheme†
- Pages: 2971-2975
- First Published: 29 May 2012
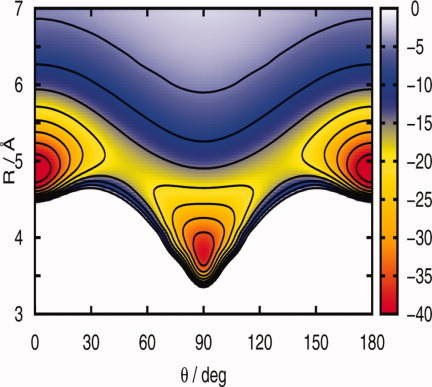
A new CCSD(T) interaction potential for the HeI2 ground state complex is constructed using the reproducing kernel Hilbert Space interpolation method. The influence of different generation procedures of the surface on the stability of the two, linear and T-shaped, isomers, and vibrational states of the cluster in comparison with the experimental measurements is also discussed.
A novel approach to coupled proton–phonon macroscopic system in H-bonded solids with strong low-barrier hydrogen bonds on the examples of KH2PO4 and KD2PO4
- Pages: 2976-2979
- First Published: 24 May 2012
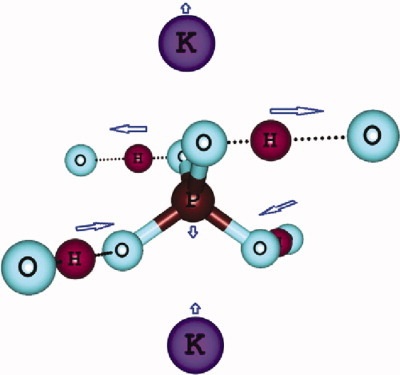
Using the heteroligand systems vibronic theory approach for KDP and its isomorphs, the pseudospin Ising model is modified to furnish the Ising parameters determined in an explicit analytical form in terms of the electronic and vibronic characteristics for PO4 units, enabling the use of quantum chemistry. The method is illustrated by the estimation of proton–phonon coupling influence on the Tc of KDP.