Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
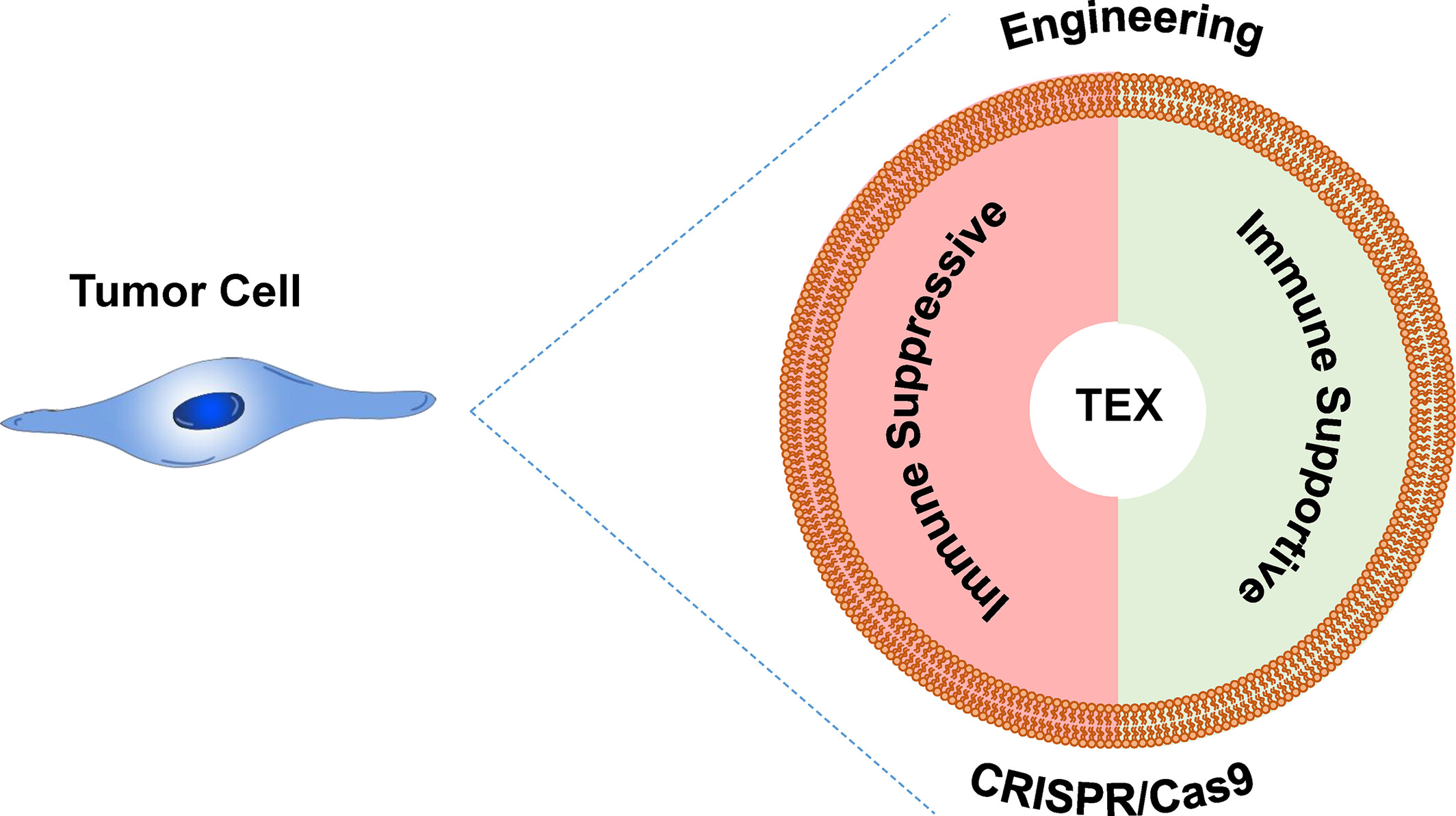
Engineered exosomes in service of tumor immunotherapy: From optimizing tumor-derived exosomes to delivering CRISPR/Cas9 system
- Pages: 898-913
- First Published: 30 October 2024
SHORT REPORT
Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Prior antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, and probiotics in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint blockade: A post-hoc analysis of the phase I/III IMpower 133 trial
- Pages: 914-919
- First Published: 05 November 2024
What's New?
First-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) typically involves administration of combined chemo-immunotherapy. ES-SCLC patients, however, also often receive other medications, including antibiotics, probiotics, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Although previous research has indicated that such medications potentially impact the prognosis of first-line treatments, the authors of the present study found no association between concomitant antibiotic, probiotic, or PPI exposure and outcomes among ES-SCLC patients treated with atezolizumab/chemotherapy. Baseline use of concomitant medications did not influence overall or progression-free survival. The findings indicate that antibiotic, probiotic, and PPI use can be considered for ES-SCLC patients receiving first-line chemo-immunotherapy.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Cancer Epidemiology
Maternal illnesses during pregnancy and the risk of childhood cancer: A medical-record based analysis (UKCCS)
- Pages: 920-929
- First Published: 13 November 2024
What's new?
Relationships between maternal illness during pregnancy and cancer risk in offspring have been investigated for decades, with inconsistent results. Here, the authors reviewed medical records to examine relationships between maternal illness in pregnancy and several types of childhood cancer. Analyses reveal associations between maternal anaemia in pregnancy and childhood acute myeloid leukaemia and certain embryonal tumours. No evidence was found, however, linking maternal infections to increased risk of childhood cancer, with the exception of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The findings warrant additional exploration of the impact of maternal anaemia, iron and vitamin deficiency in pregnancy on the pathogenesis of childhood leukaemia and embryonal tumours.
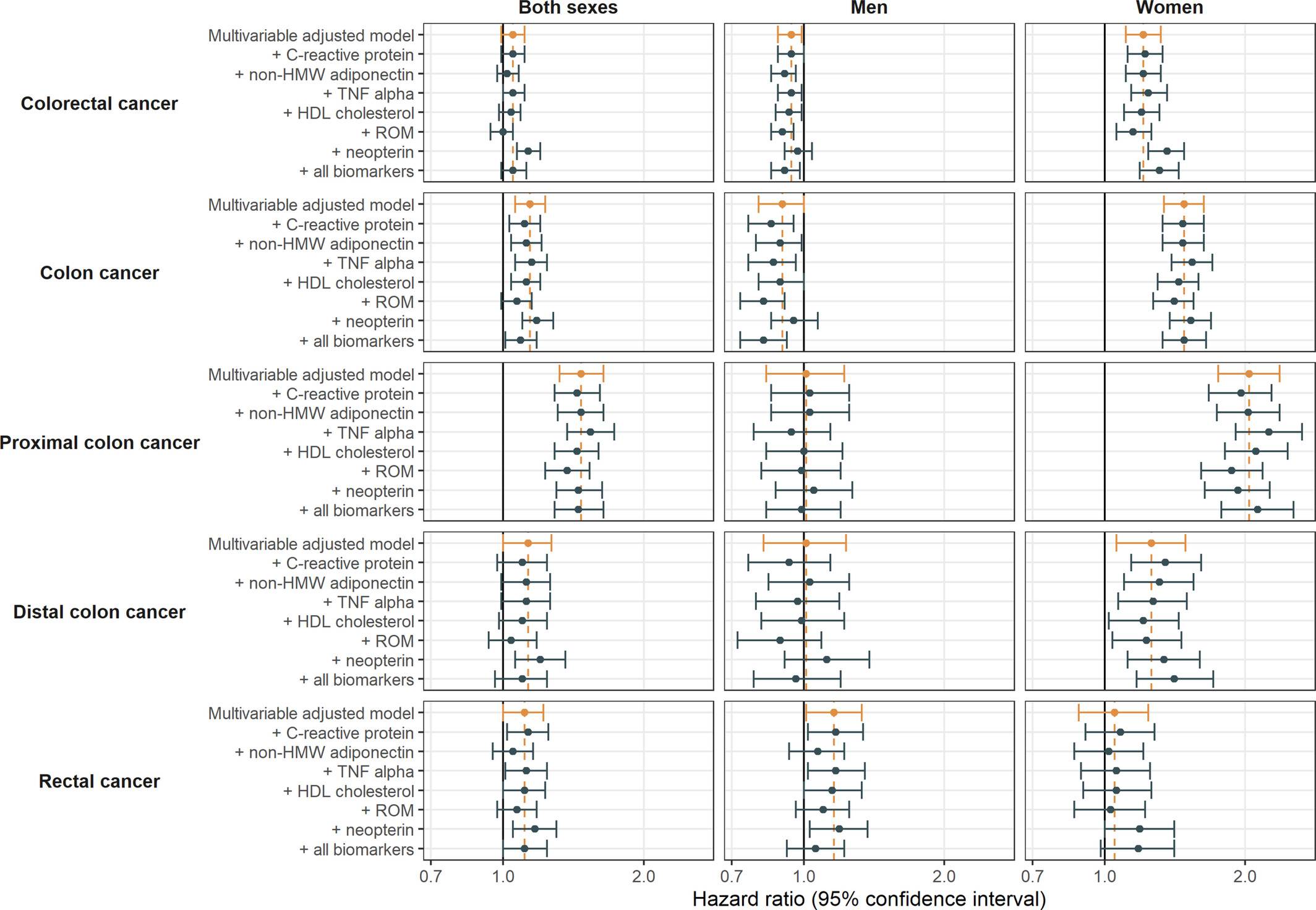
Sex- and site-specific associations of circulating lipocalin 2 and incident colorectal cancer: Results from the EPIC cohort
- Pages: 930-942
- First Published: 07 November 2024
What's New?
Chronic inflammation can lead to cancer, particularly in the colon, and a glycoprotein associated with inflammation, lipocalin-2 (LCN2), has been implicated in cancer progression. Here, using data from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition cohort (EPIC), the authors show that higher levels of circulating LCN2 are associated with an increased risk of colon cancer in women. No association was seen in men. The association was particularly pronounced in people with higher waist circumference and for cancers arising in the proximal colon.
Perturbations in the blood metabolome up to a decade before prostate cancer diagnosis in 4387 matched case–control sets from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
- Pages: 943-952
- First Published: 08 October 2024
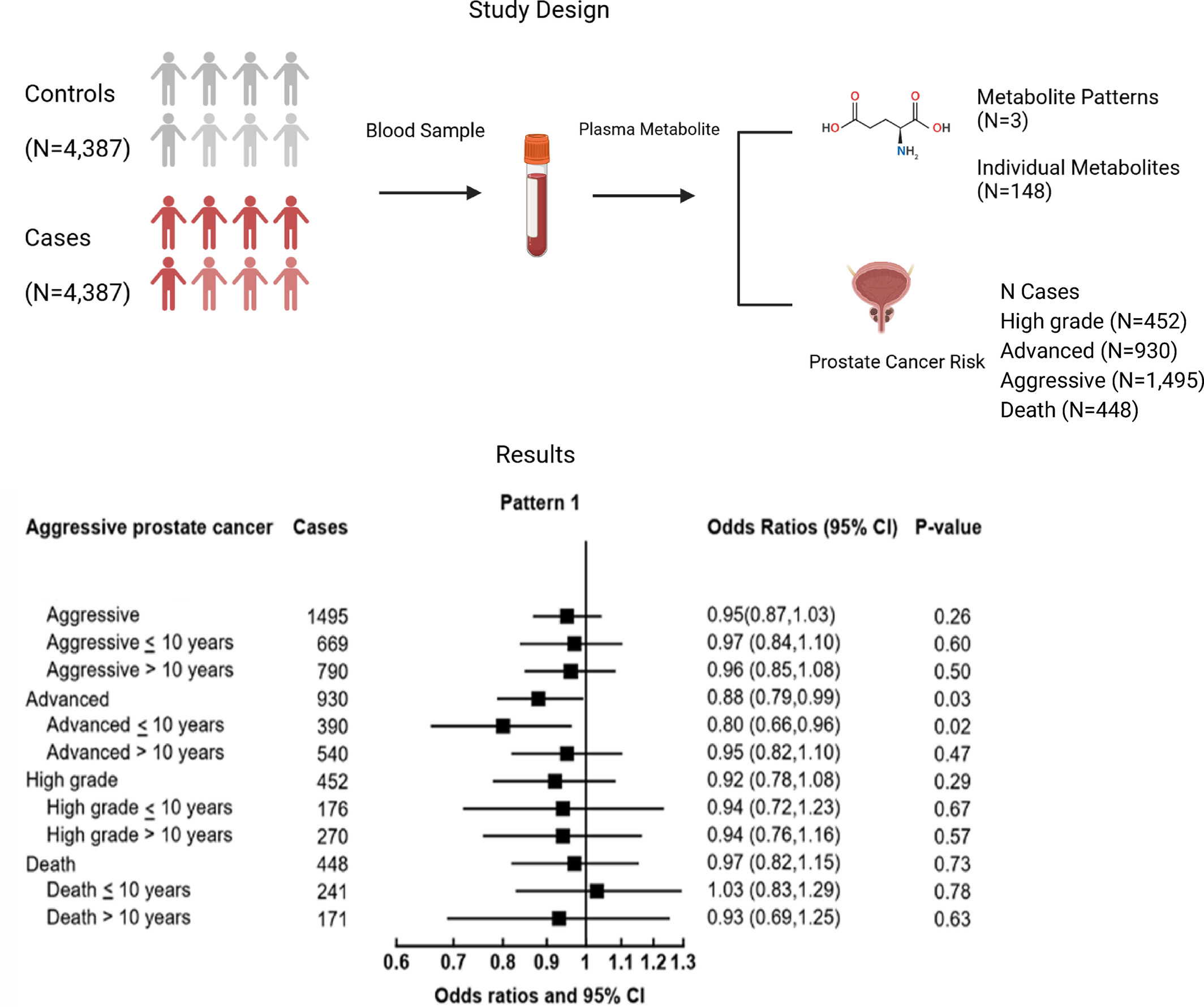
What's New?
Prostate cancer has few known risk factors, but metabolomics may provide some insight in this regard. Here, the authors measured the levels of 148 different individual metabolites, and three metabolite patterns, looking for an association with prostate cancer. They found an association between certain metabolites and a reduced risk of advanced prostate cancer when diagnosed within 10 years of blood collection. One metabolite pattern was associated with prostate cancer death. These results suggest that prostate-cancer related changes in metabolite profile may occur up to 10 years prior to diagnosis.
Development and validation of a lung cancer polygenic risk score incorporating susceptibility variants for risk factors
- Pages: 953-963
- First Published: 08 October 2024
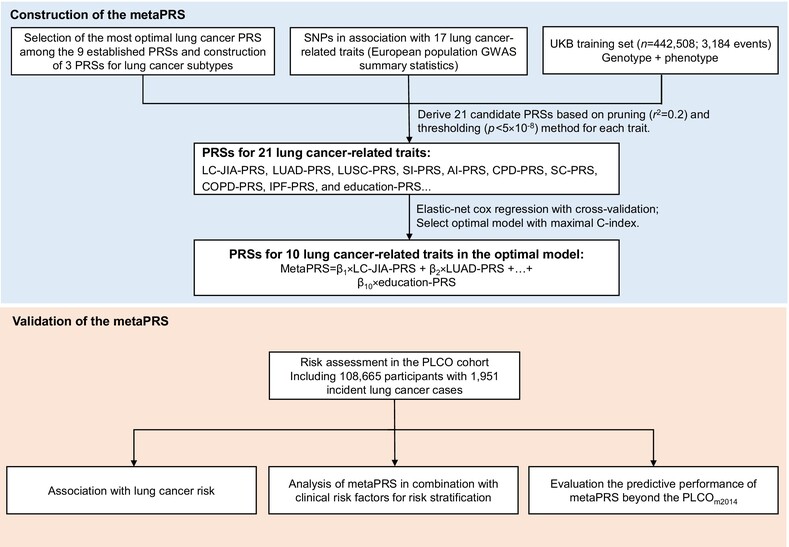
What's new?
MetaPRS, which incorporates genetic information of disease, different subtypes, and related risk factors, could provide substantively improved genomic prediction of stroke and coronary artery disease. However, no studies have attempted to use this strategy to construct PRS for lung cancer and explore its improvement in prediction performance and reclassification accuracy. Our findings suggest that metaPRS is superior to the previously reported nine PRSs of lung cancer in optimizing lung cancer prediction efficiency and risk stratification.
High malignancy rate in IgE-deficient children
- Pages: 964-968
- First Published: 06 October 2024
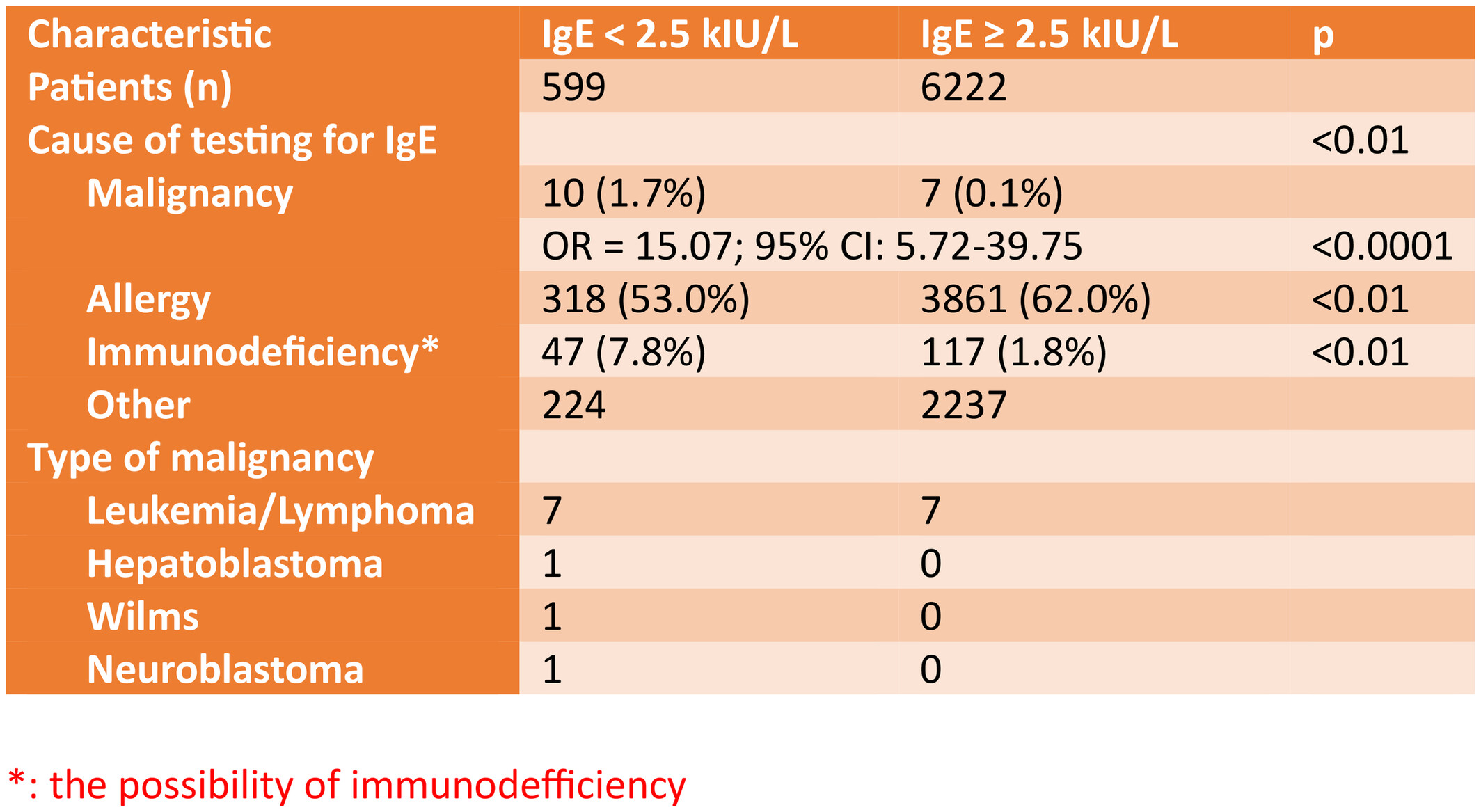
What's New?
IgE plays specific roles in the recognition and inhibition of cancer cells as well as the maintenance of a memory response to cancer. However, the association between IgE deficiency and malignancy risk remains unclear, especially in children. In this study of 6821 pediatric patients, children with low serum IgE levels were found to have a higher rate of previous malignancy. This effect was mostly observed in hematological cancers. Meanwhile, low IgE levels in patients with suspected or diagnosed immunodeficiency did not increase the prevalence of cancer in children.
Diagnostic performance of tomosynthesis plus synthetic mammography versus full-field digital mammography with or without tomosynthesis in breast cancer screening: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 969-979
- First Published: 12 October 2024
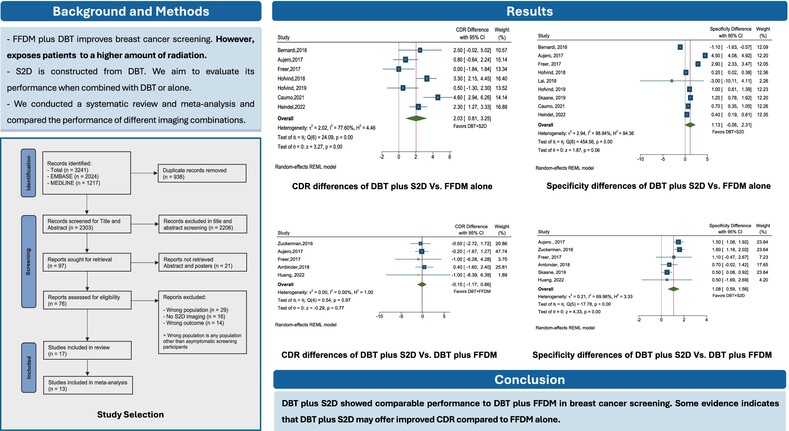
What's new?
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), when combined with full-field digital mammogram (FFDM), exhibits relatively high accuracy in breast cancer diagnosis. The combination, however, increases radiation exposure. This review evaluated the performance of DBT plus synthesized 2D (S2D), derived from reconstructed tomosynthesis images, as an alternative to DBT + FFDM. DBT + S2D was found to have a higher cancer detection rate compared to FFDM alone and exhibited superior specificity relative to DBT + FFDM. CDR, however, was similar for DBT + S2D and DBT + FFDM. DBT and S2D perform similarly to DBT combined with FFDM, while mitigating increased radiation exposure, suggesting that it is a safe and effective alternative.
Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics
Calcium sensing receptor expression is downregulated in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours via epigenetic mechanisms
- Pages: 980-992
- First Published: 23 November 2024
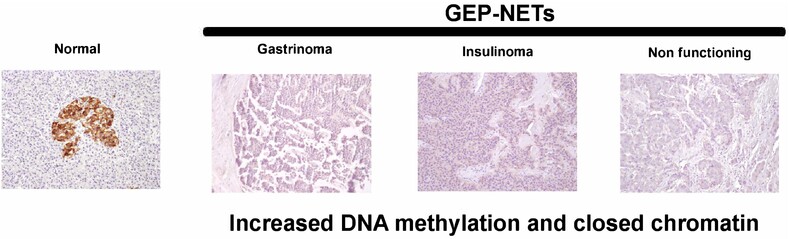
What's New?
Epigenetic regulation has been suggested to play a major role in the pathogenesis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here, the authors show in two independent cohorts that the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is down-regulated in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours and that this reduced expression is likely due to alterations in DNA methylation and chromatin organisation. Moreover, they show that transfection of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumour cell lines with CaSR decreases cell viability. The findings shed light on the specific role of CaSR as a tumour suppressor in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours.
Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Transgenic overexpression of the miR-200b/200a/429 cluster prevents mammary tumor initiation in Neu/Erbb2 transgenic mice
- Pages: 993-1004
- First Published: 06 October 2024
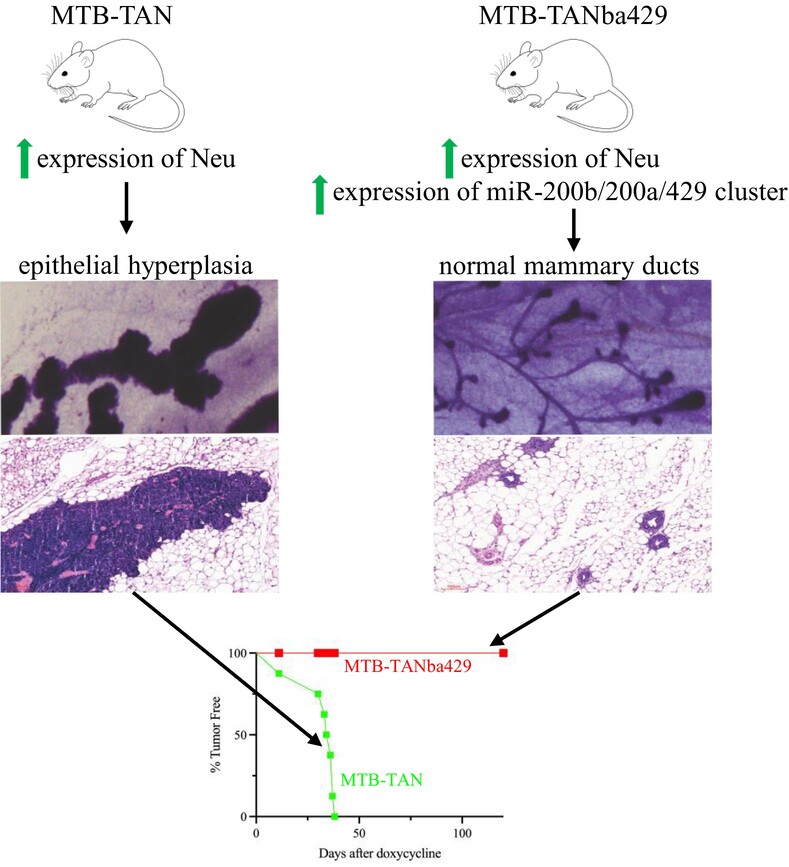
What's new?
While miR-200 s have been suggested to reduce breast cancer growth and metastasis, whether these microRNAs can prevent mammary tumor development in the first place is unknown. Using a transgenic model of HER2+ breast cancer, this study found that elevated expression of miR-200 family members in mouse mammary epithelial cells can completely prevent mammary tumor formation induced by the potent oncogene Neu, possibly through the maintenance of functional myoepithelial cells. The findings indicate that increasing miR-200 expression in mammary epithelial cells should be further explored as a potential strategy to prevent breast cancer in women.
A phase I clinical trial of sonodynamic therapy combined with radiotherapy for brainstem gliomas
- Pages: 1005-1014
- First Published: 08 October 2024
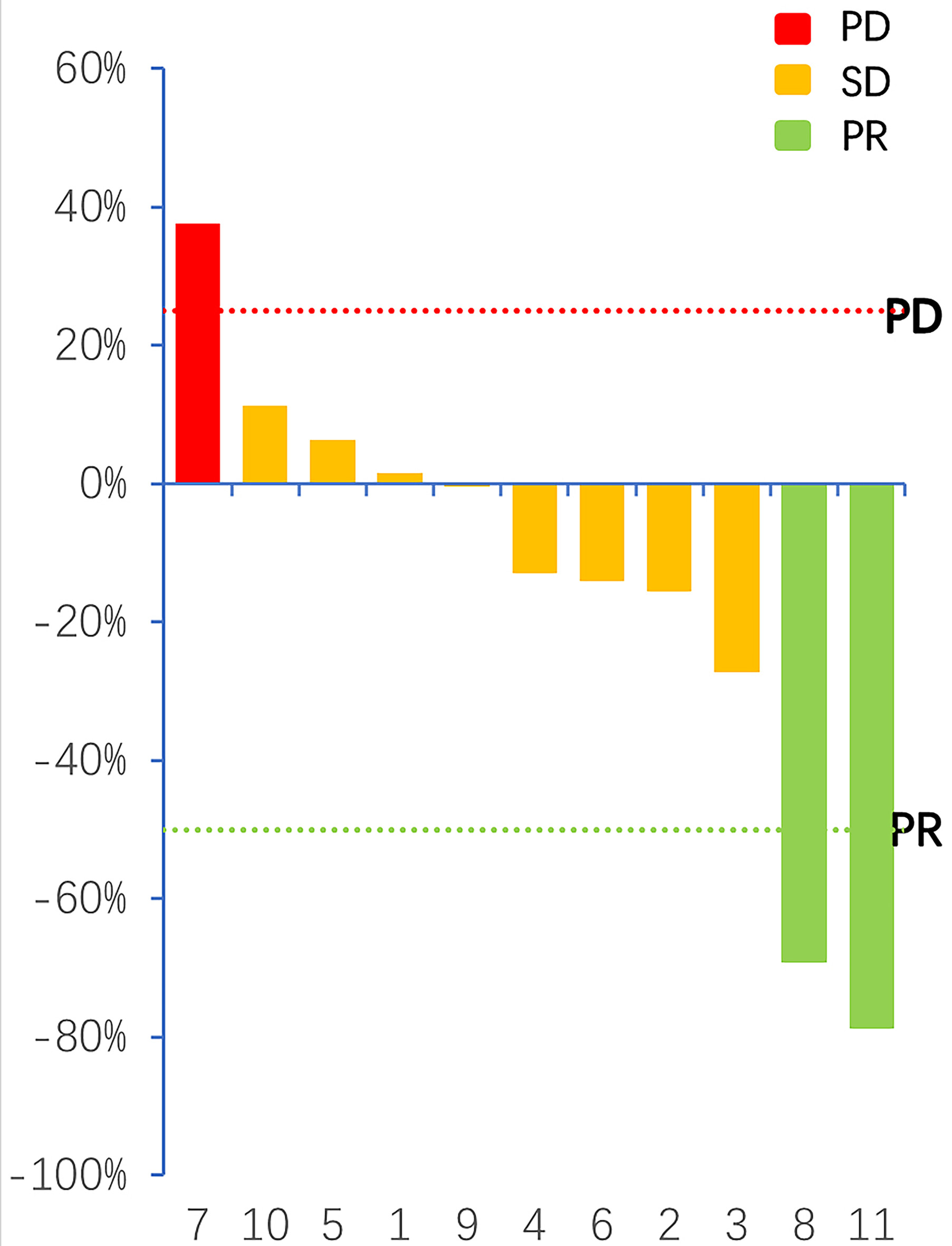
What's new?
Effective treatments for brainstem glioma (BSG) are lacking. This is partly because the brainstem regulates critical body functions, which complicates surgery, and because the blood brain barrier severely limits drug delivery. In this study, the authors investigated the safety and efficacy of sonodynamic therapy combined with radiotherapy following hematoporphyrin administration in 11 BSG patients. The combination therapy was well-tolerated, and most patients maintained stable disease. Two patients exhibited partial responses, and several experienced symptom relief to varying degrees, although no significant reduction in tumor size was observed. The findings warrant further study of combined sonodynamic therapy and radiotherapy for BSG.
Chronotherapy in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1015-1032
- First Published: 07 November 2024
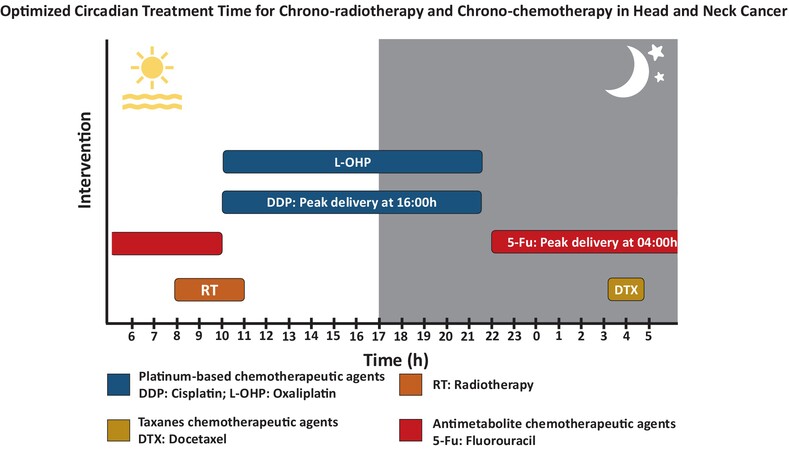
What's New?
Adverse events are common after chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Chronotherapy, which tailors treatment to the circadian rhythm, aims to reduce the frequency of adverse events and improve treatment efficacy. Here, the authors conducted a systematic review of chrono-chemotherapy and chrono-radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancer (HNC). Their analysis included 22 studies and 3366 patients. Patients who received chrono-radiotherapy had fewer instances of oral mucositis than those who received evening radiotherapy, they found; patients who received chrono-chemotherapy experienced lower overall toxicity and improved objective response rate than those who received nontime-stipulated chemotherapy.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation is an underestimated but fatal adverse event associated with blinatumomab therapy: A pharmacovigilance analysis of FAERS
- Pages: 1033-1042
- First Published: 13 November 2024
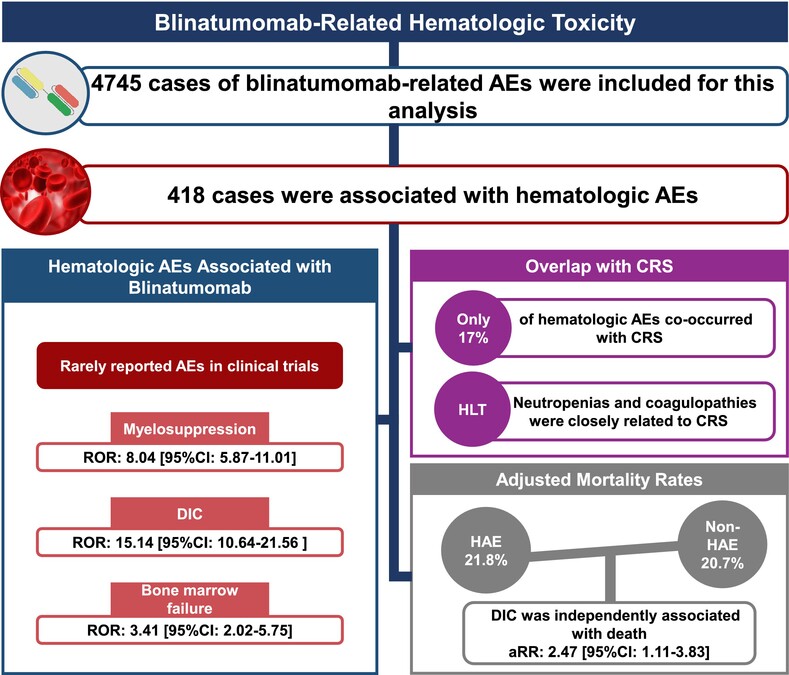
What's New?
Blinatumomab has demonstrated promising efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell hematologic malignancies. However, a comprehensive real-world study of hematologic adverse events is lacking. Harnessing the Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System from October 2014 to December 2023, this pharmacovigilance study identified three highly underestimated hematologic adverse events in clinical trials: myelosuppression, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and bone marrow failure. Notably, disseminated intravascular coagulation was independently associated with increased mortality. The findings highlight the importance of detecting early these rarely reported but severe hematologic adverse events to mitigate the risk of fatal toxicity in patients.
Infectious Causes of Cancer
The variations in the natural history of high-risk human papillomavirus infections in Chinese healthy women aged 27–45 years compared with 18–26 years: A prospective cohort study
- Pages: 1043-1054
- First Published: 13 December 2024

What's New?
Data on the natural history of high-risk human papillomavirus infection in middle-aged women compared to younger women in regions with a bimodal prevalence pattern are scarce. Here, the authors found that although women in China aged 27–45 years exhibit lower incidences of high-risk human papillomavirus infection and associated cervical lesions than younger women, this population continues to face a substantial risk of acquiring causal human papillomavirus infections that may progress to cervical lesions. The findings offer insights for shaping human papillomavirus vaccination policies in China and other regions with a second peak in human papillomavirus prevalence after the mid-twenties.
Innovative Tools and Methods
Performance of the WID-qEC test to detect uterine cancers in black women with abnormal uterine bleeding: A prospective observational cohort study in Ghana
- Pages: 1055-1064
- First Published: 10 December 2024
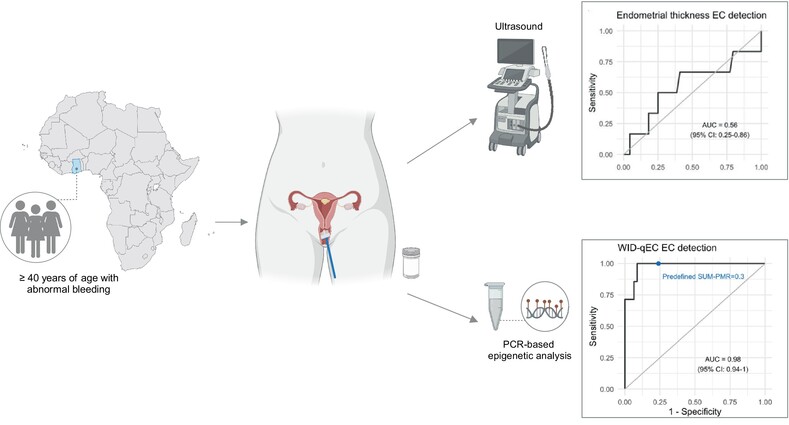
What's New?
Endometrial cancer (EC) is increasing significantly among women in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). EC detection may be improved by WID-qEC testing, a DNA methylation-based approach, though its use has been limited primarily to Caucasian populations. Here, the authors investigated the ability of WID-qEC testing to detect endometrial and cervical cancer in black women in Ghana who presented with abnormal uterine bleeding. WID-qEC testing successfully identified 100% of endometrial and cervical cancers in the study population. Utilizing simple sample collection and low-cost, high-throughput PCR-based analysis, WID-qEC is a promising tool for EC detection for all women in LMICs.
Molecular Cancer Biology
Colposcopy referrals and CIN3 detection after triage by host cell DNA methylation and/or HPV genotyping in HPV positive women with low-grade cytology from a population-based Dutch primary HPV screening trial
- Pages: 1065-1073
- First Published: 16 December 2024
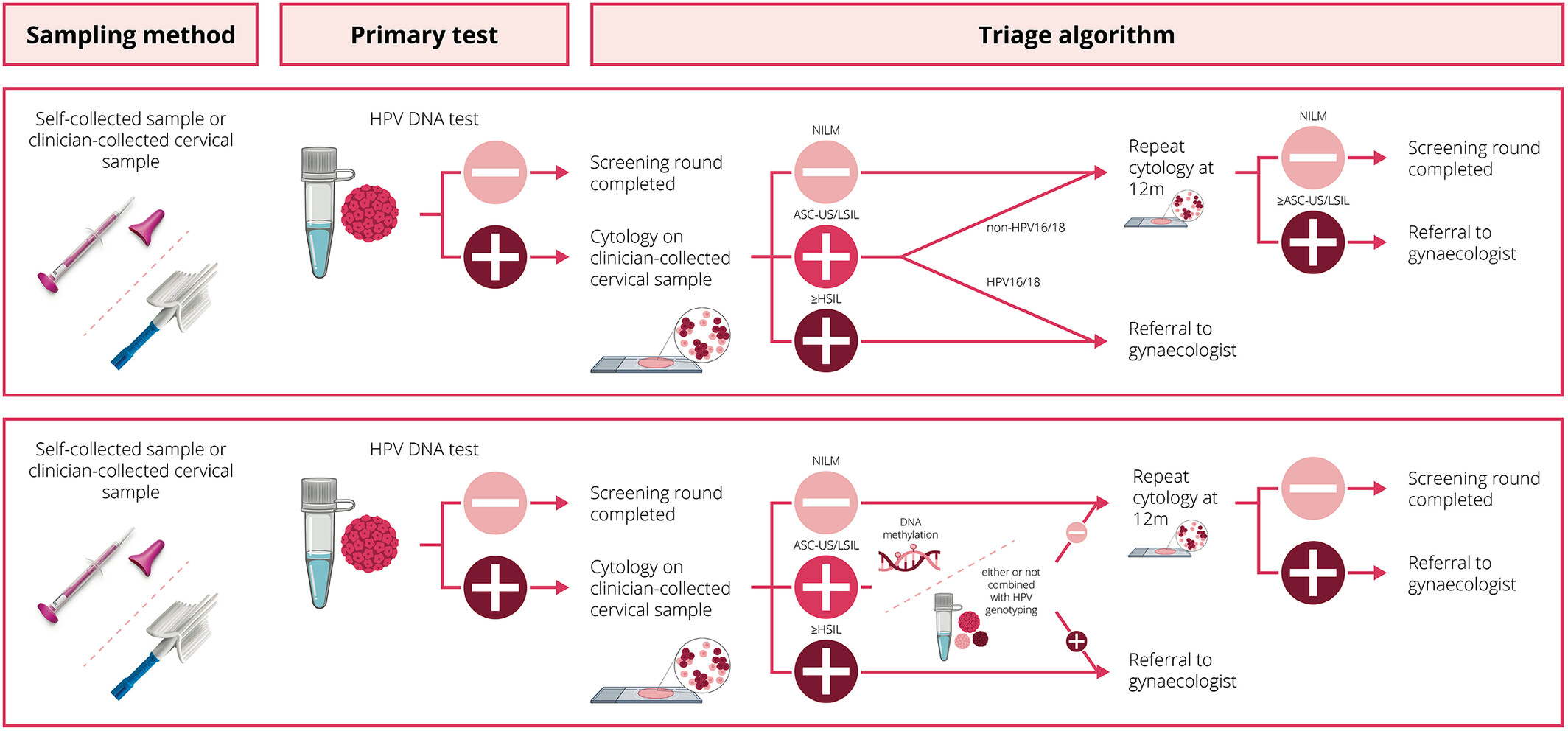
What's New?
The implementation of primary human papillomavirus (HPV)-based cervical cancer screening has led to an increase in colposcopy referrals and detection of low-grade lesions. This study examines the ability of methylation-based triage strategies, together with HPV genotyping, to improve screening efficiency in women with low-grade cytology. Analyses show that the combination of HPV16/18 genotyping and FAM19A4/miR124-2 methylation resulted in a 95% reduction in direct colposcopy referrals. As single triage tests, FAM19A4/miR124-2 or ASCL1/LHX8 methylation decreased direct referrals by 86%. The findings indicate that methylation-based triage strategies help reduce colposcopy referrals and maintain timely detection of clinically relevant lesions.
Tumor Immunology and Microenvironment
Nivolumab in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Results of Polish multicenter observational study
- Pages: 1074-1084
- First Published: 05 November 2024
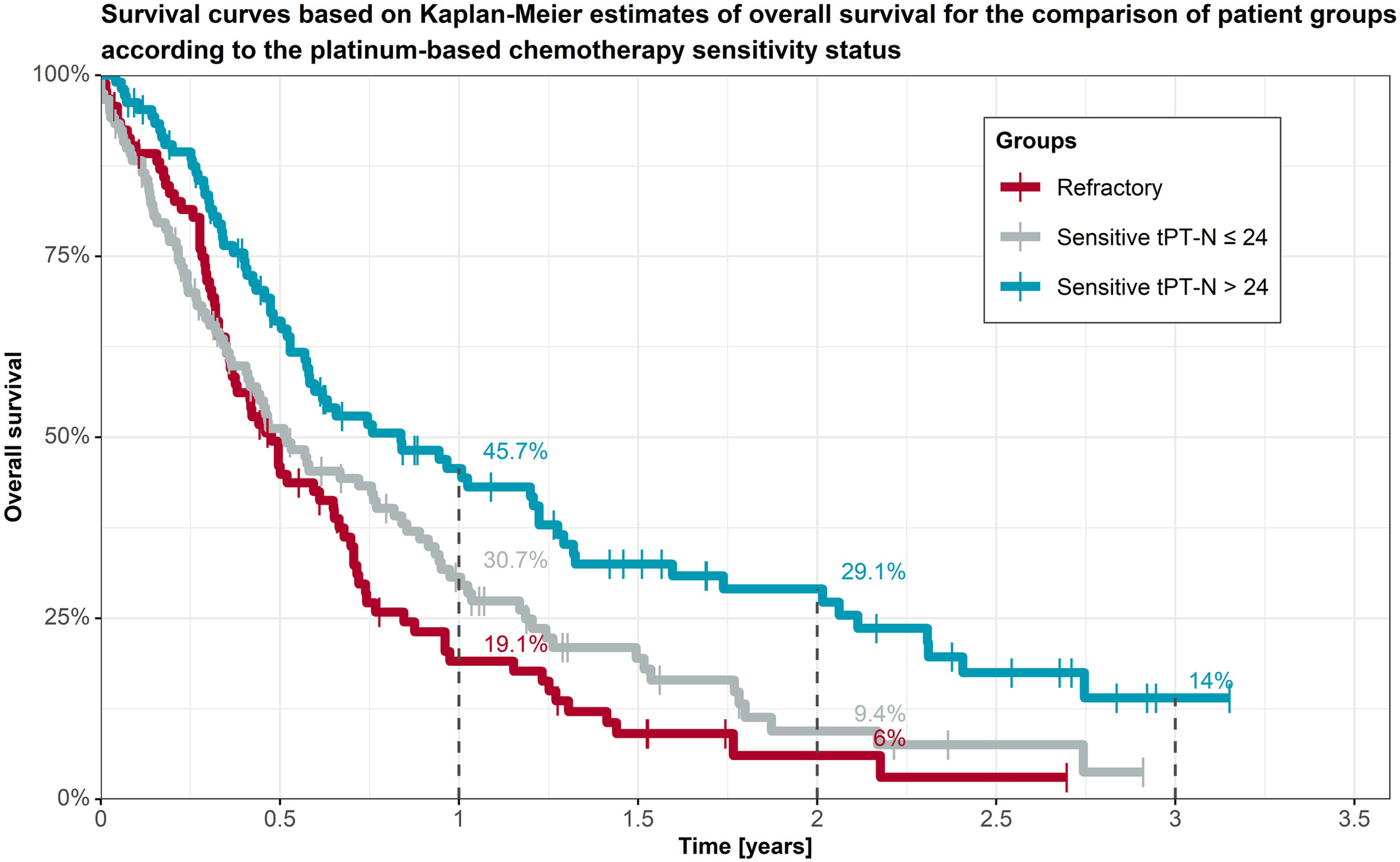
What's New?
Treatment with the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab significantly improves outcomes for patients with recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Here, the authors evaluated the efficacy of nivolumab in Polish patients with recurrent or metastatic HNSCC using real-world data. They grouped the patients according to the time between completing platinum therapy and beginning nivolumab: within 6 months, between 6 and 24 months, or after 24 months. The more time that passed before starting nivolumab, they found, the better the outcomes.
Tumor Markers and Signatures
TP53 mutations and survival in ovarian carcinoma patients receiving first-line chemotherapy plus bevacizumab: Results of the MITO16A/MaNGO OV-2 study
- Pages: 1085-1096
- First Published: 16 October 2024
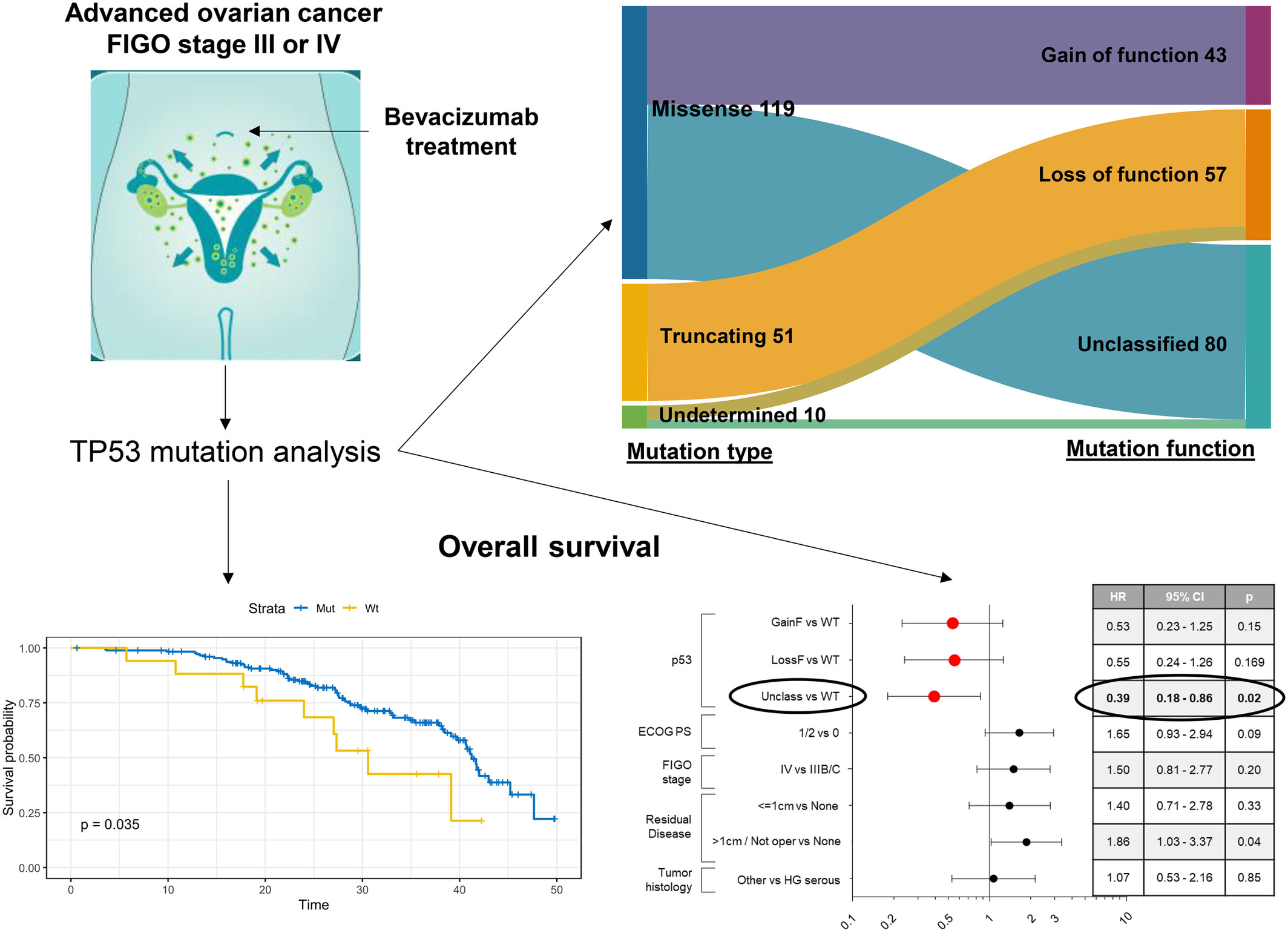
What's New?
Bevacizumab (BEV) is an effective treatment for advanced ovarian cancer, but so far, there are no known biomarkers that indicate whether a patient will respond well to the drug. Here, the authors show that missense mutations in TP53 are associated with improved overall survival in patients receiving first-line chemotherapy plus BEV for advanced ovarian cancer. Based on these results, it may be useful in future studies to test patients for TP53 mutations to assess their predictive role in BEV response.
ERRATUM
Correction to “Expression, regulation and roles of miR-26a and MEG3 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma”
- Page: E4
- First Published: 10 December 2024
EXPRESSION OF CONCERN
EXPRESSION OF CONCERN: Selective Depletion of Tumor Neovasculature by Microbubble Destruction with Appropriate Ultrasound Pressure
- Page: E5
- First Published: 27 November 2024