Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 38, Issue 30
- Page: i
- First Published: 12 October 2017

A self-consistent scheme combining the MD and DFT is employed to determine the effective charge of ionic liquid. DFT calculations are performed over snapshot configurations of MD simulations to obtain partial charges, which are used in turn for subsequent MD. This procedure is iteratively performed until the self-consistency is achieved. On page 2559 (DOI: 10.1002/jcc.24880) Ryosuke Ishizuka and Nobuyuki Matubayasi use this MD/DFT self-consistent scheme to account for the charge transfer between cation and anion in the force field for ionic liquid, leading to better description of energetics and dynamics compared to the original force field that instead employs the atomic partial charges computed in vacuum.
Issue Information
Full Papers
Effective charges of ionic liquid determined self-consistently through combination of molecular dynamics simulation and density-functional theory
- Pages: 2559-2569
- First Published: 18 July 2017
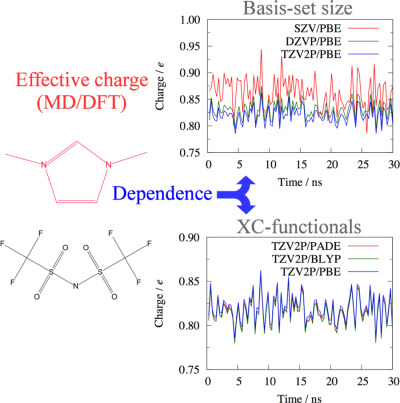
The basis set and exchange-correlation (XC) functional dependencies are shown for the effective charges of 1,3-dimethylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide (
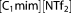 ) determined from the self-consistent scheme combining the molecular dynamics (MD) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
) determined from the self-consistent scheme combining the molecular dynamics (MD) and density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
Instanton rate constant calculations close to and above the crossover temperature
- Pages: 2570-2580
- First Published: 19 August 2017
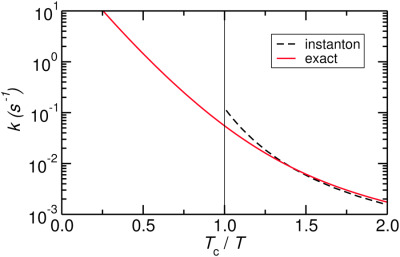
Overestimation of the rate constant k of an Eckart barrier by instanton theory close to the crossover temperature Tc compared to the analytic solution. The contribution proposes a technique to correct this overestimation which is computationally advantageous to the traditional canonical instanton approach.
Phonon spectra, electronic, and thermodynamic properties of WS2 nanotubes
- Pages: 2581-2593
- First Published: 21 August 2017
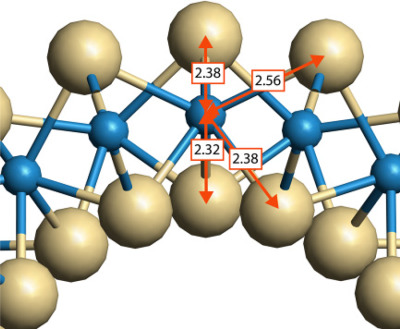
Because of many useful properties, the stability, electron, and phonon structure of bulk WS2, its monolayer, and nanotubes was a subject of extensive experimental and theoretical investigations. In this work, we perform the first-principles study of the electron and phonon band structure and thermodynamic properties of WS2 nanotubes. Temperature dependences of energy, entropy, and heat capacity of nanotubes are estimated.
Canonical orbital contributions to the magnetic fields induced by global and local diatropic and paratropic ring currents
- Pages: 2594-2604
- First Published: 18 August 2017
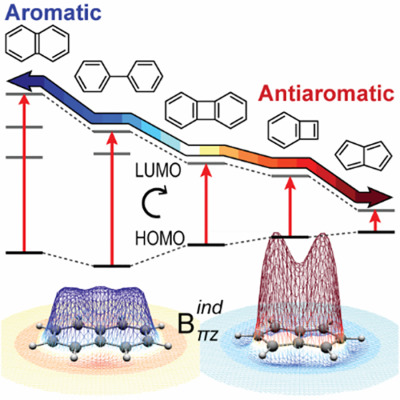
The through-space magnetic response of naphthalene, biphenyl, biphenylene, benzocyclobutadiene, and pentalene is dissected to contributions from the total π system, canonical π-molecular orbitals, and rotational HOMO→π* excitations. The characteristic pattern and topology of the magnetic field induced from global and local diatropic and paratropic ring currents are revealed. The induced magnetic field is found to be shaped from ΗΟΜΟ→π* excitations depending on the energy gap, symmetry, and nodal structure of interacting orbitals.
Evaluating electronic structure methods for accurate calculation of 19F chemical shifts in fluorinated amino acids
- Pages: 2605-2617
- First Published: 21 August 2017
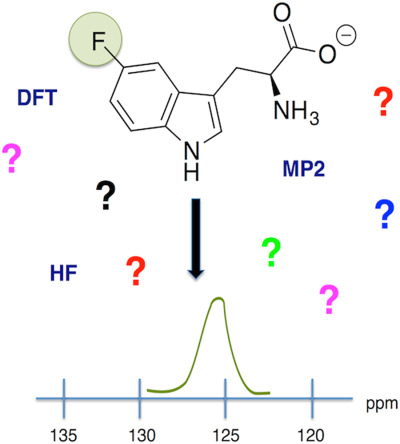
Fluorinated amino acids are used to label proteins for studies of structure, dynamics, and function. Interpreting and assigning the chemical shifts in the resulting fluorine NMR spectra of fluoro-labeled proteins is a goal of computational chemists. This article provides key information toward this aim, by evaluating the ability of numerous electronic structure methods to calculate fluorine chemical shifts of amino acids and analogues. Methods are evaluated in terms of lowest deviation from experimental values.
Automated and efficient quantum chemical determination and energetic ranking of molecular protonation sites
- Pages: 2618-2631
- First Published: 31 August 2017
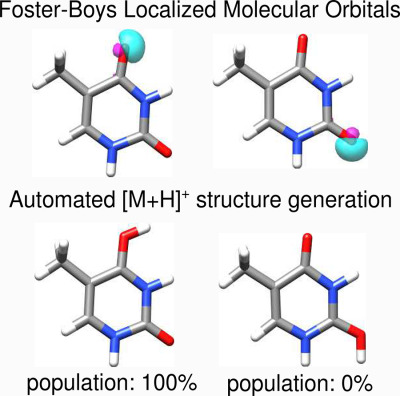
An efficient semiempirical GFN-xTB quantum chemistry method is used to automatically screen protonation sites in organic and organometallic molecules. The resulting structures are re-evaluated energetically by DFT to describe the gas phase protomer equilibrium, which is useful in the context of electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.
Efficacy of independence sampling in replica exchange simulations of ordered and disordered proteins
- Pages: 2632-2640
- First Published: 25 August 2017
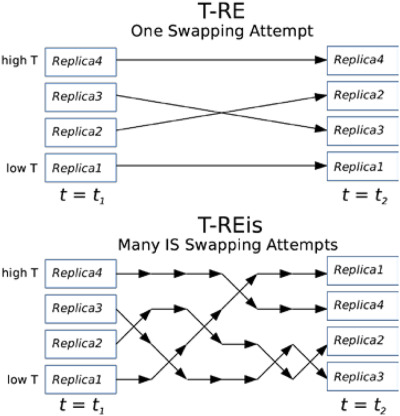
A simple extension of replica exchange (RE) involves multiple exchanges attempted at each exchange cycle with the same Metropolis criteria to enhance mixing. Automistic and coarse-grained simulations of ordered and disordered proteins are performed to critically examine if such temperature RE with independence sampling (T-REis) could improve conformational sampling. The results demonstrate that T-REis effectively increase the replica mobility in temperatures space; yet such enhanced mixing does not translate well into improved conformational sampling. The efficiency of T-RE does not appear to be limited by temperature diffusion, but by the inherent rates of spontaneous large-scale conformational re-arrangements.
Customizable de novo design strategies for DOCK: Application to HIVgp41 and other therapeutic targets
- Pages: 2641-2663
- First Published: 22 September 2017
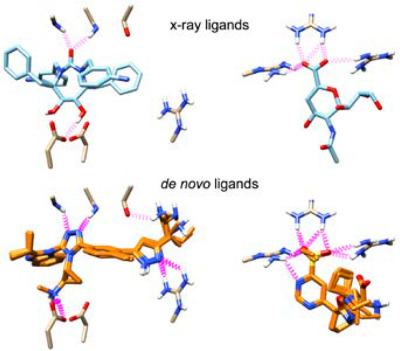
De novo design methods aim to create new molecules, from scratch, with steric and electrostatic compatibility for the target system(s). In this work, we describe development, validation, and application of a new de novo design version of the program DOCK that allows assembly of small organic molecules in a binding site using fragment libraries consisting of scaffolds, linkers, and sidechains. The results highlight the potential utility for designing new molecules against a wide variety of important protein targets.





