Edited by: Brahim Chaqour
The Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (JCCS) publishes fundamental and translational research into intercellular and intracellular signaling pathways.
We welcome research investigating how cells interact with their surrounding environment. Our published work also includes that showing altered cellular behavior contributing to pathological states and all aspects of remote cell signaling and communication. We are an open access title and the official journal of the International CCN Society.
Journal Metrics
- 7.2CiteScore
- 3.9Journal Impact Factor
Articles
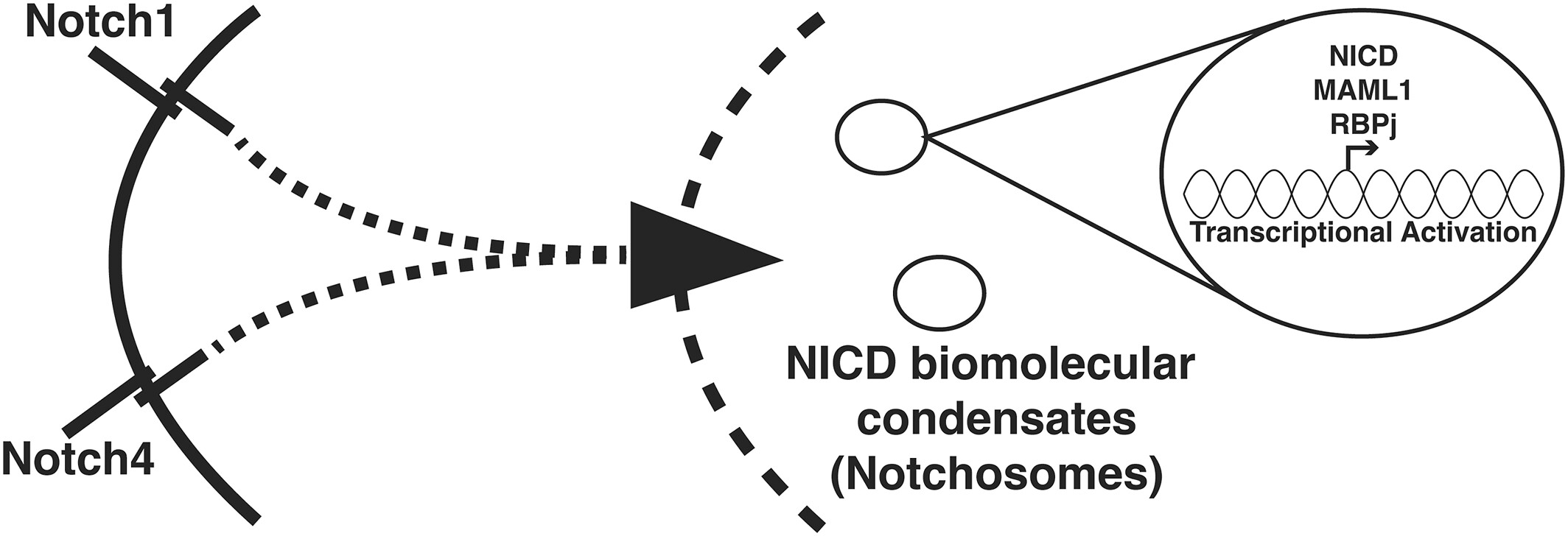
Notch NICD domains form biomolecular condensates
- 26 Jul 2025
Cancer‐associated fibroblasts‐secreted lactate promotes RNA polymerase III subunit G‐mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition in non‐small cell lung cancer by increasing m6A modification of zinc finger protein 384
- 25 Jul 2025
Graphical Abstract
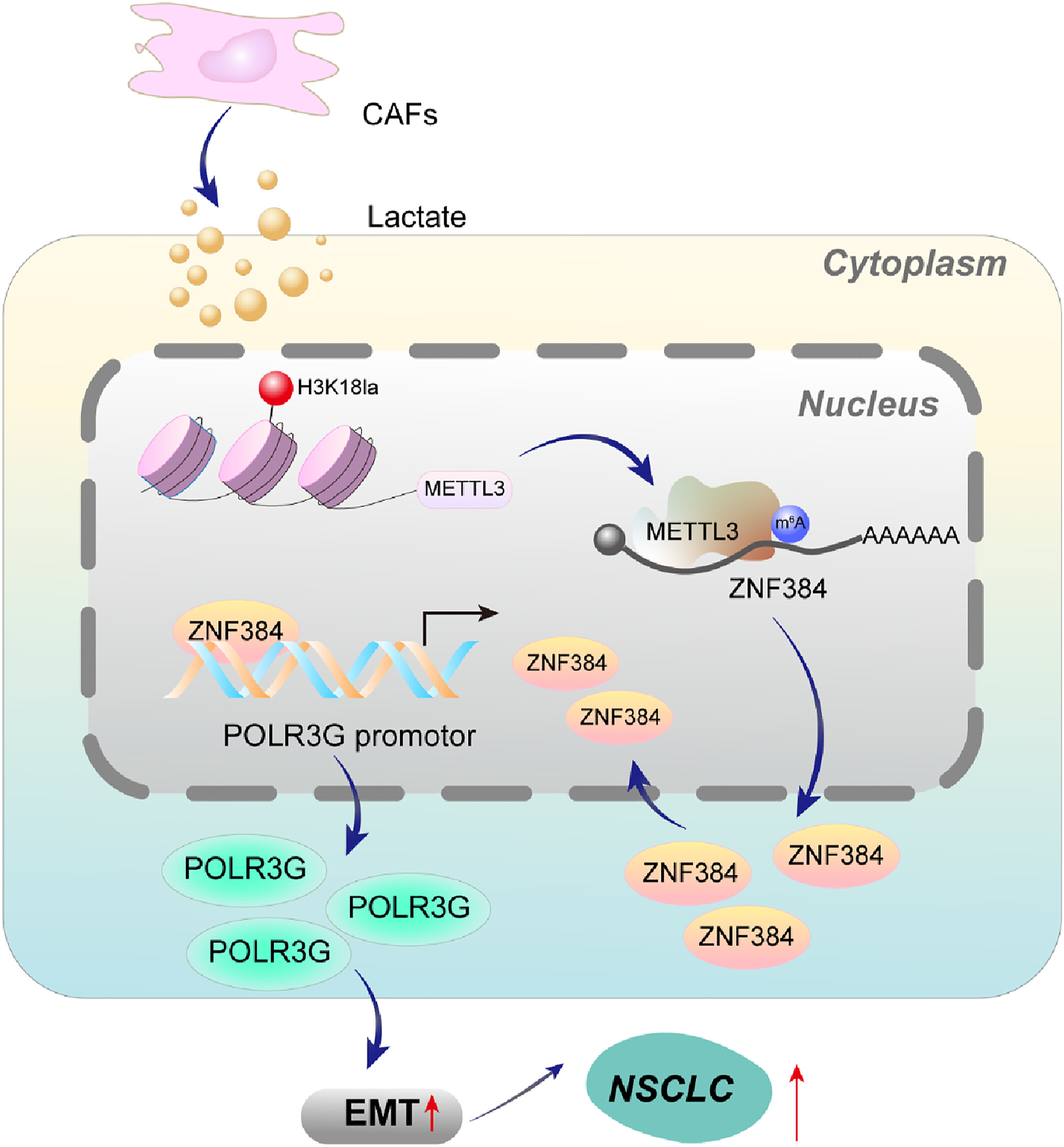
In the tumor microenvironment of non-small cell lung cancer, lactate secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances the lactylation of H3K18 within the promoter region of methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3). Furthermore, METTL3 promotes the m6A modification of zinc finger protein 384 (ZNF384) to increase its stability. The upregulation of ZNF384 transcriptionally activates polymerase III subunit G, which in turn promotes the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer cells, thereby facilitating tumor progression.
Y‐box binding protein 1 stabilizes EP300 mRNA and promotes forkhead box C1 H3K27Ac to aggravate chondrocyte injury in osteoarthritis
- 23 Jul 2025
Graphical Abstract

In this study, YBX1 binds to EP300 mRNA and enhances its stability and expression. Subsequently, EP300 binds to the FOXC1 promoter and promotes the enrichment of H3K27Ac at the FOXC1 promoter to elevate FOXC1 expression, ultimately regulating IL-1β-induced chondrocyte damage and promoting the progression of osteoarthritis.
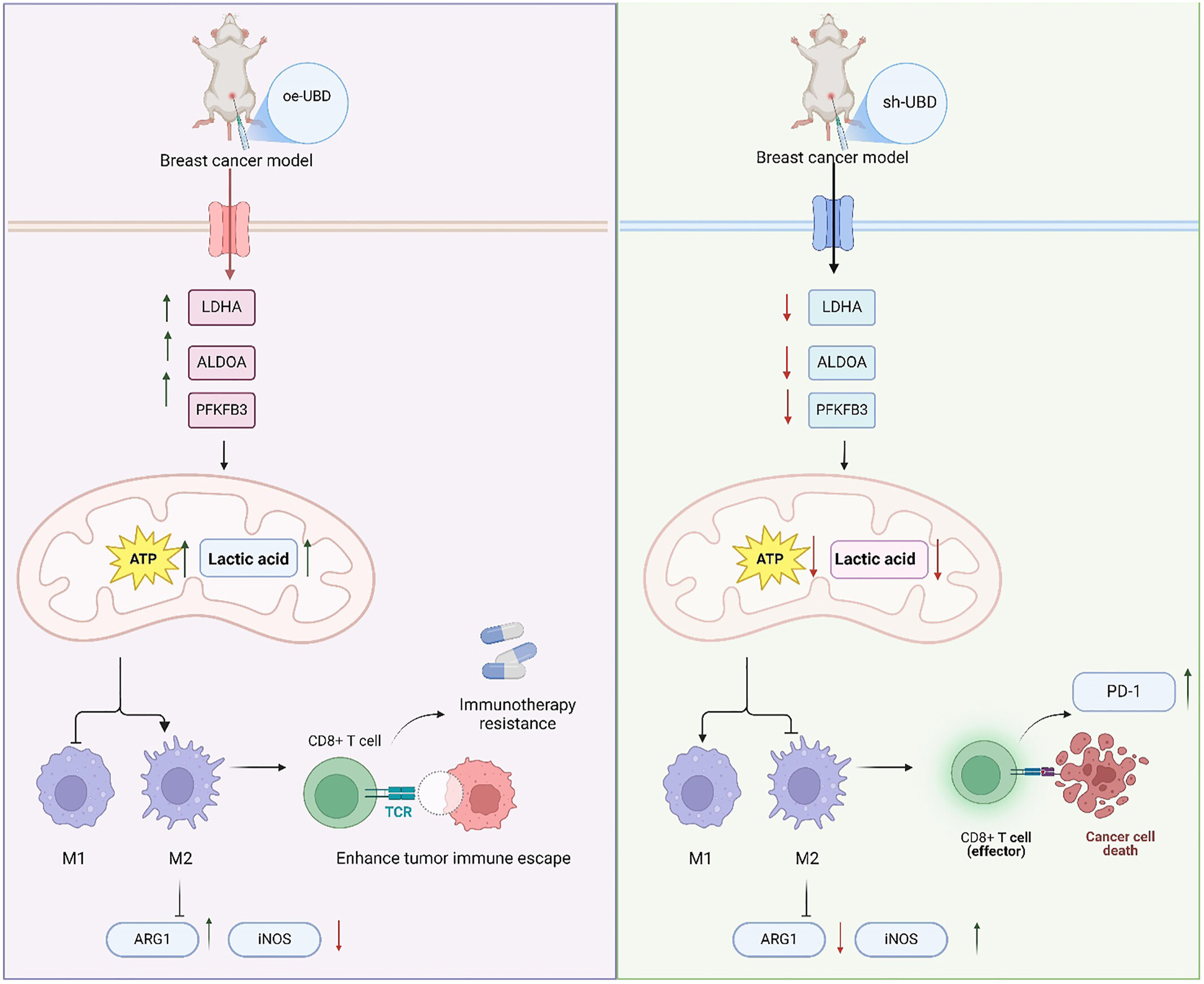
UBD‐mediated glycolytic reprogramming promotes M2 macrophage polarization in ovarian cancer immune evasion
- 21 Jul 2025
A comprehensive analysis of the relationship between inflammasomes and autophagy in human tumors: Recent developments
- 16 Jul 2025
Graphical Abstract
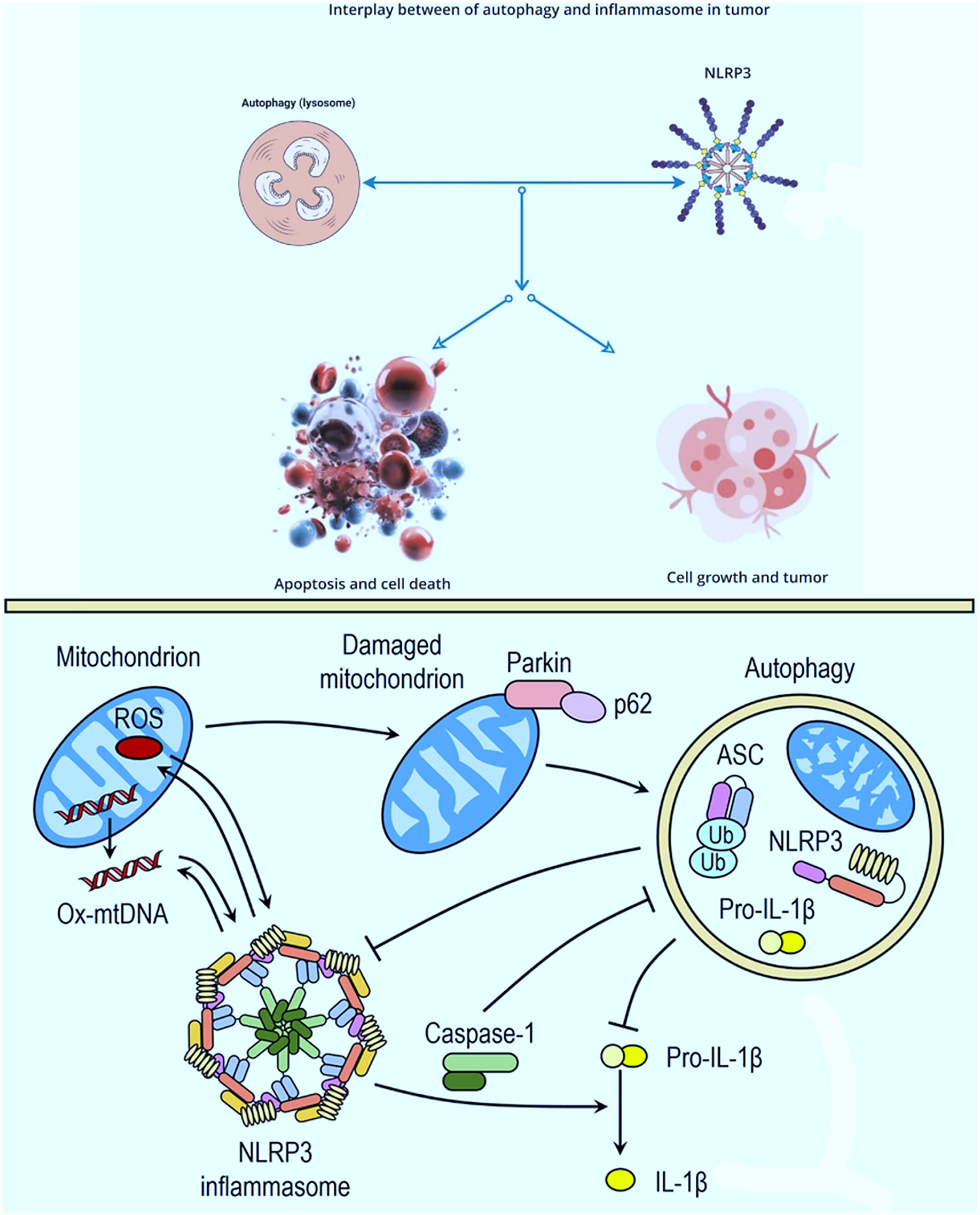
The interaction between inflammasomes and autophagy is crucial for maintaining the balance between necessary immune responses and the avoidance of excessive inflammation. Autophagy can inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by degrading endogenous activators, such as damaged mitochondria that produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), as well as by eliminating components of the inflammasome and associated cytokines. Additionally, the autophagic process plays a role in the unconventional secretion of IL-1β, thereby influencing the inflammatory response. On the other hand, the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome can also modulate the formation of autophagosomes through various mechanisms. This interplay between inflammasomes and autophagy is essential for orchestrating an appropriate host defense response while preventing detrimental inflammation.
CD99 contributes to the EWS::FLI1 transcriptome by specifically affecting FOXM1‐targets involved in the G2/M cell cycle phase, thus influencing the Ewing sarcoma genetic landscape
- Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling
- 2 Aug 2024
Graphical Abstract
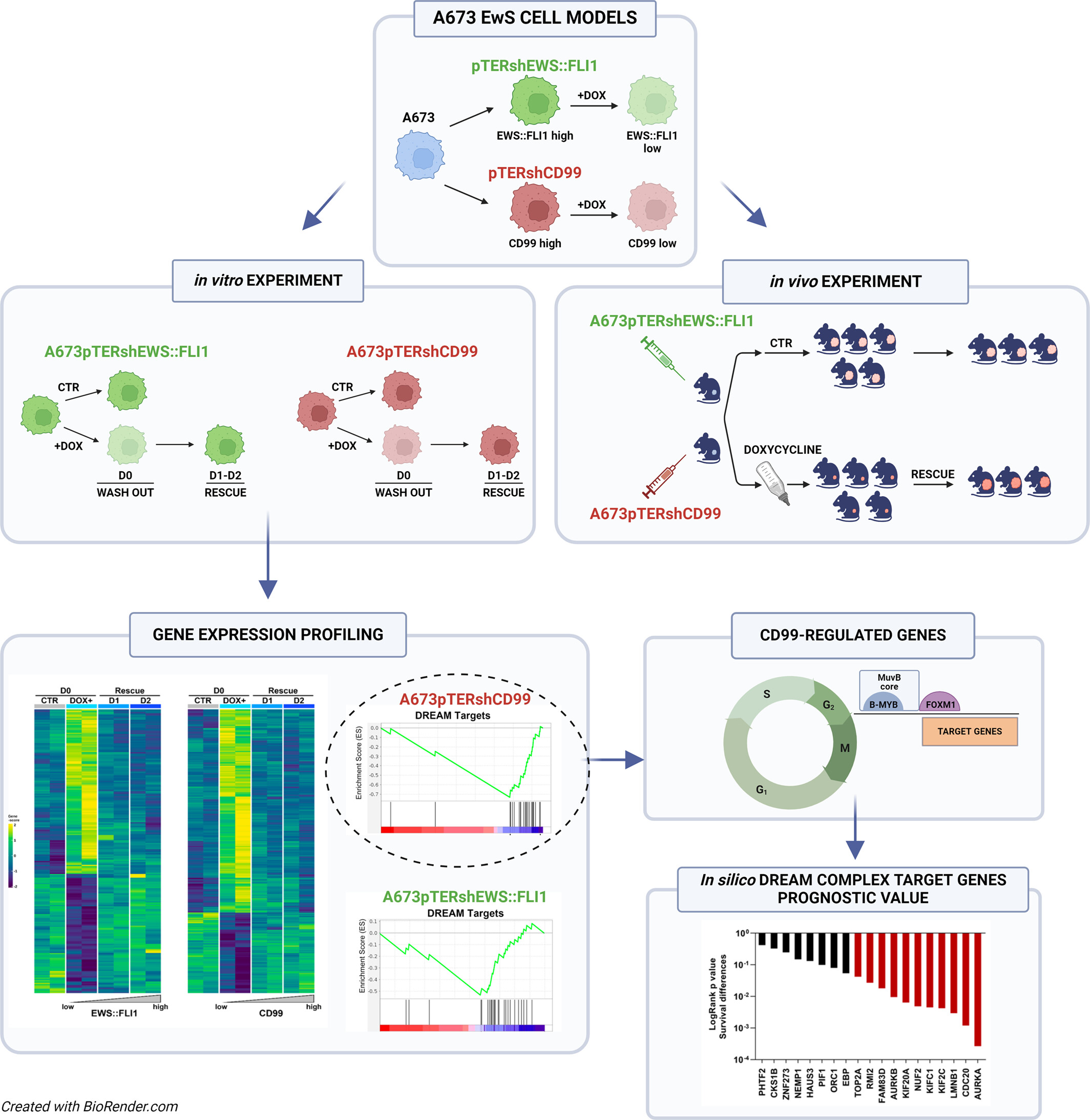
Time course analysis of differential gene expression in Ewing sarcoma experimental models with inducible expression of EWS::FL1 or CD99. The analysis revealed up-regulation of genes involved in the DREAM complex target genes either when the chimera or the CD99 antigen are inhibited. However, most of CD99-regulated genes are specifically involved in the setting of the G2/M phase of the cell cycle and are targets of the FOXM1 transcription factor. Eleven of them were found to correlate with poor prognosis in clinical samples.
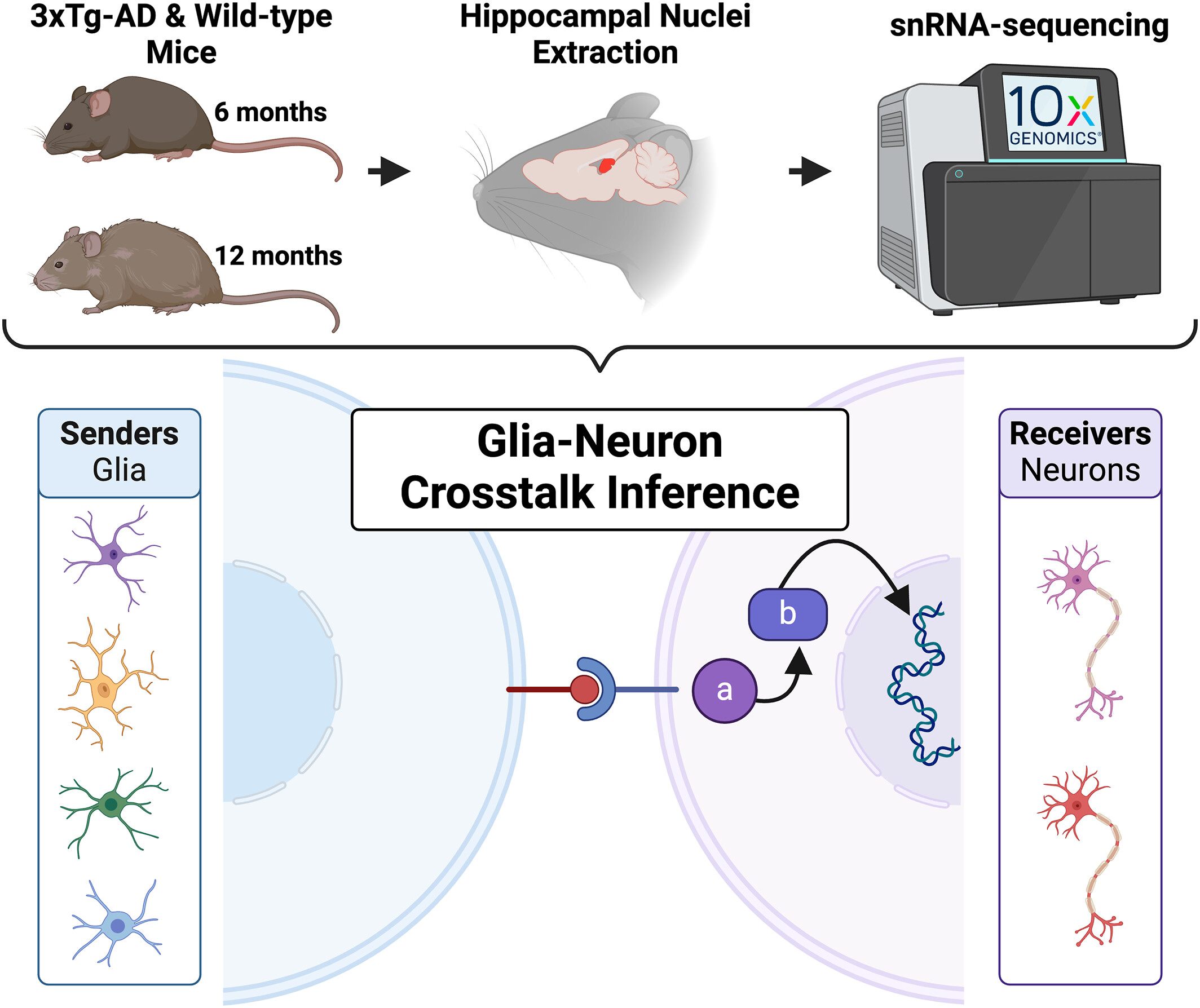
Evaluation of altered cell–cell communication between glia and neurons in the hippocampus of 3xTg‐AD mice at two time points
- Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling
- 28 Feb 2025
POSTN knockdown suppresses IL‐1β‐induced inflammation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via inhibiting the NF‐κB pathway and alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration
- Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling
- 7 May 2024
Graphical Abstract
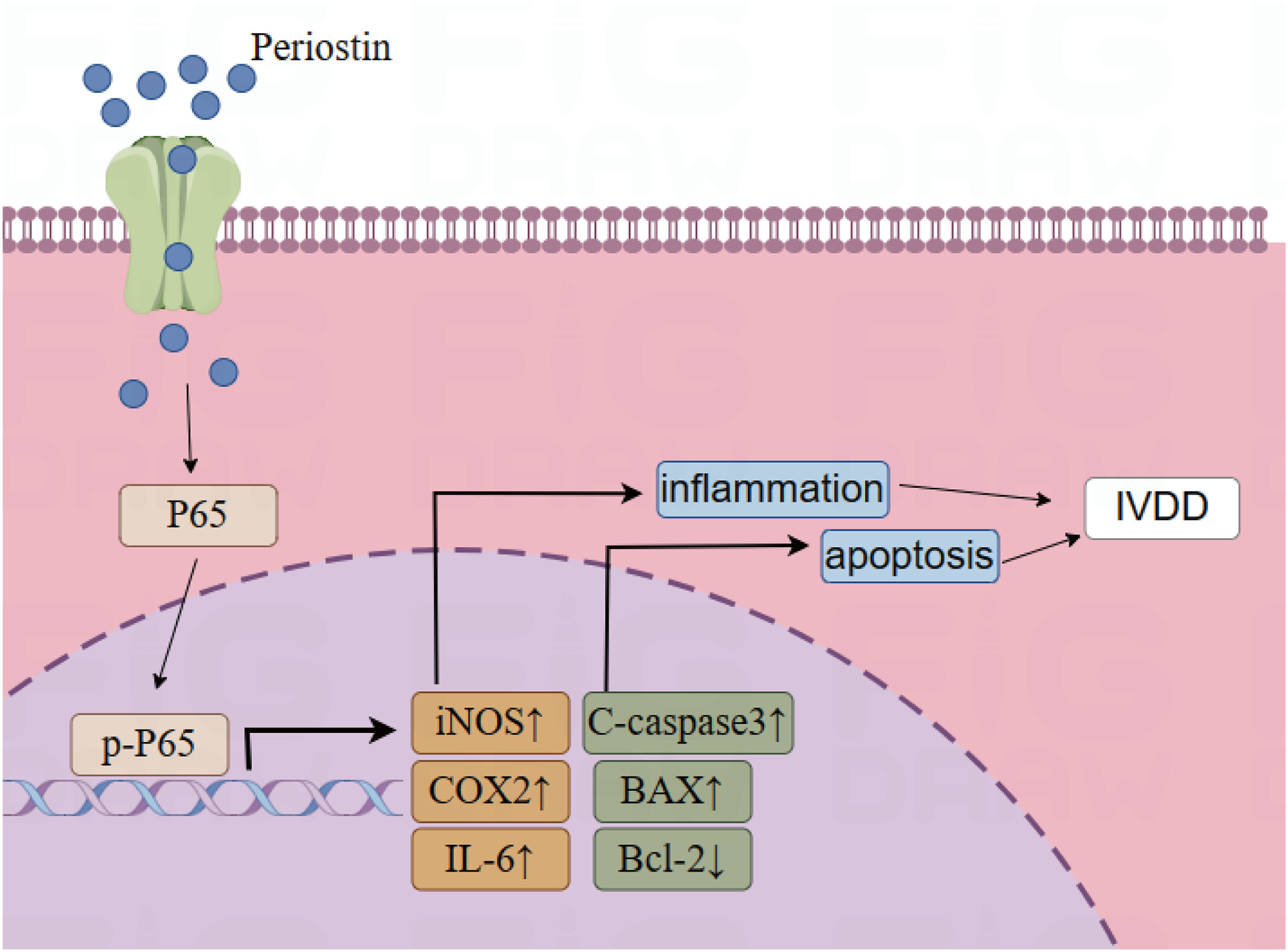
In the present experiment, the mechanism of action of POSTN on IL-1β-induced nucleus pulposus cells was investigated. Inhibition of POSTN expression can alleviate the inflammatory response and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells, and this effect is mediated by inhibiting the activity of NF-κB pathway. It is believed that our study contributes to the elucidation of the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration and raises the awareness of the role of POSTN in intervertebral disc degeneration. At the same time, a new perspective on the potential treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration is presented.
TM4SF1 is a molecular facilitator that distributes cargo proteins intracellularly in endothelial cells in support of blood vessel formation
- Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling
- 7 May 2024
Graphical Abstract
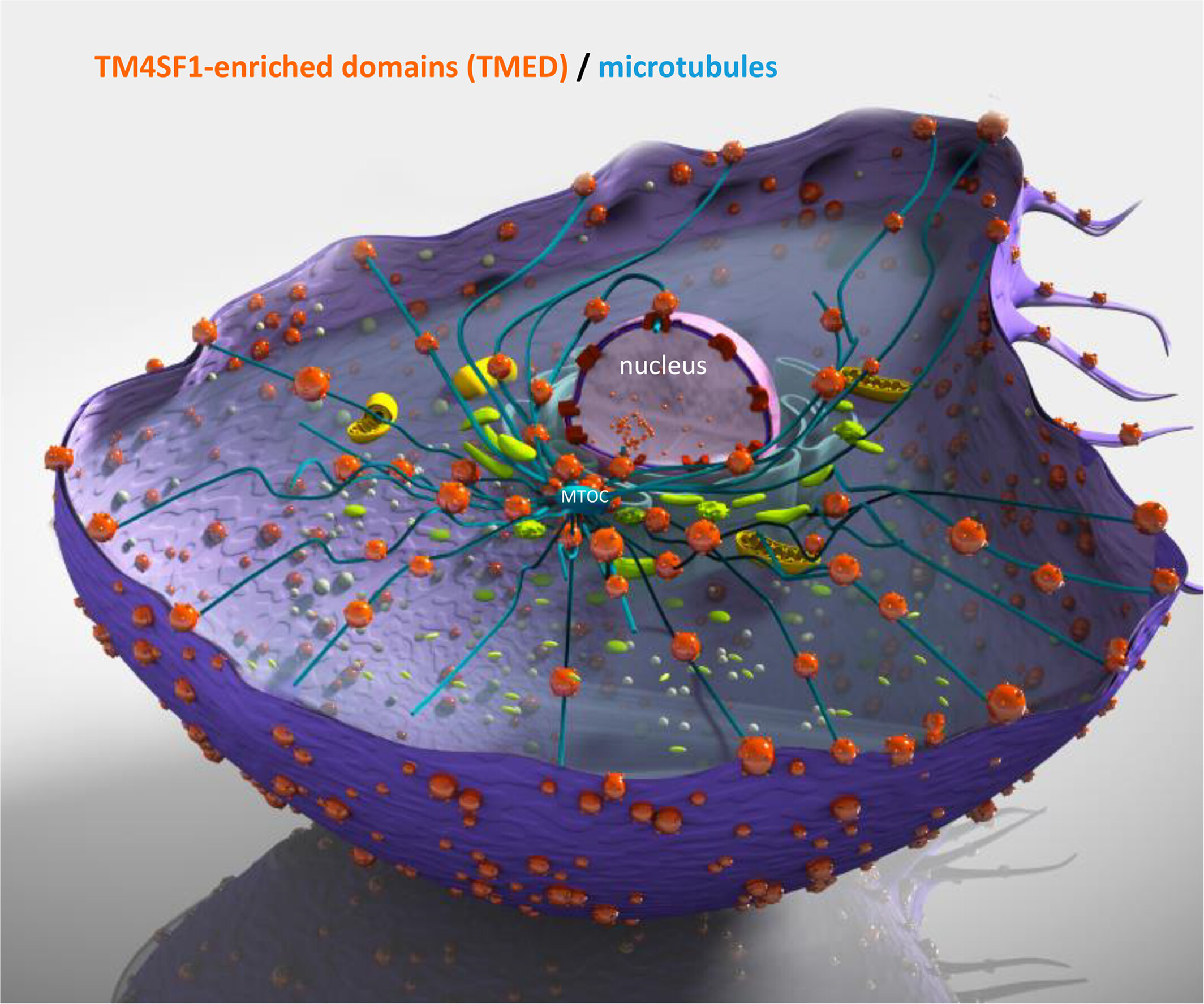
TM4SF1-enriched microdomain (TMED) are transported along microtubules to the microtubule organization center (MTOC) and then enter the nucleus via nuclear pores where TMED are being processed. This internalization mechanism delivers TMED-recruited cargo molecules for cell signaling in actively proliferating and mobile endothelial cells.
Recent issues
- Volume 19, Issue 3September 2025
- Volume 19, Issue 2June 2025
- Volume 19, Issue 1March 2025
- Volume 18, Issue 4December 2024