Edited By: Victoria Hall Moran and Rafael Pérez-Escamilla
All articles accepted from 25 July 2019 are published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License. All articles accepted before this date, were published under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License.
Journal Metrics
- 7.5CiteScore
- 2.6Journal Impact Factor
- 32%Acceptance rate
- 38 days Submission to first decision


Maternal & Child Nutrition is now Open Access!
We are pleased to announce that Maternal & Child Nutrition has now joined Wiley’s Open Access portfolio. As a result, all new submissions will be subject to an Article Processing Charge if accepted and published in the journal. For more information on the fees, please visit the Article Publication Charges page.
Articles
Adherence to the Lebanese National Dietary and Lifestyle Guidelines for Pregnancy and Its Association With Postpartum Weight Retention
- 17 July 2025
Vegetable-Related Parenting Practices, Parenting Style and Preschoolers' Vegetable Consumption: Cross-Sectional Associations and the Moderating Role of Parenting Style
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
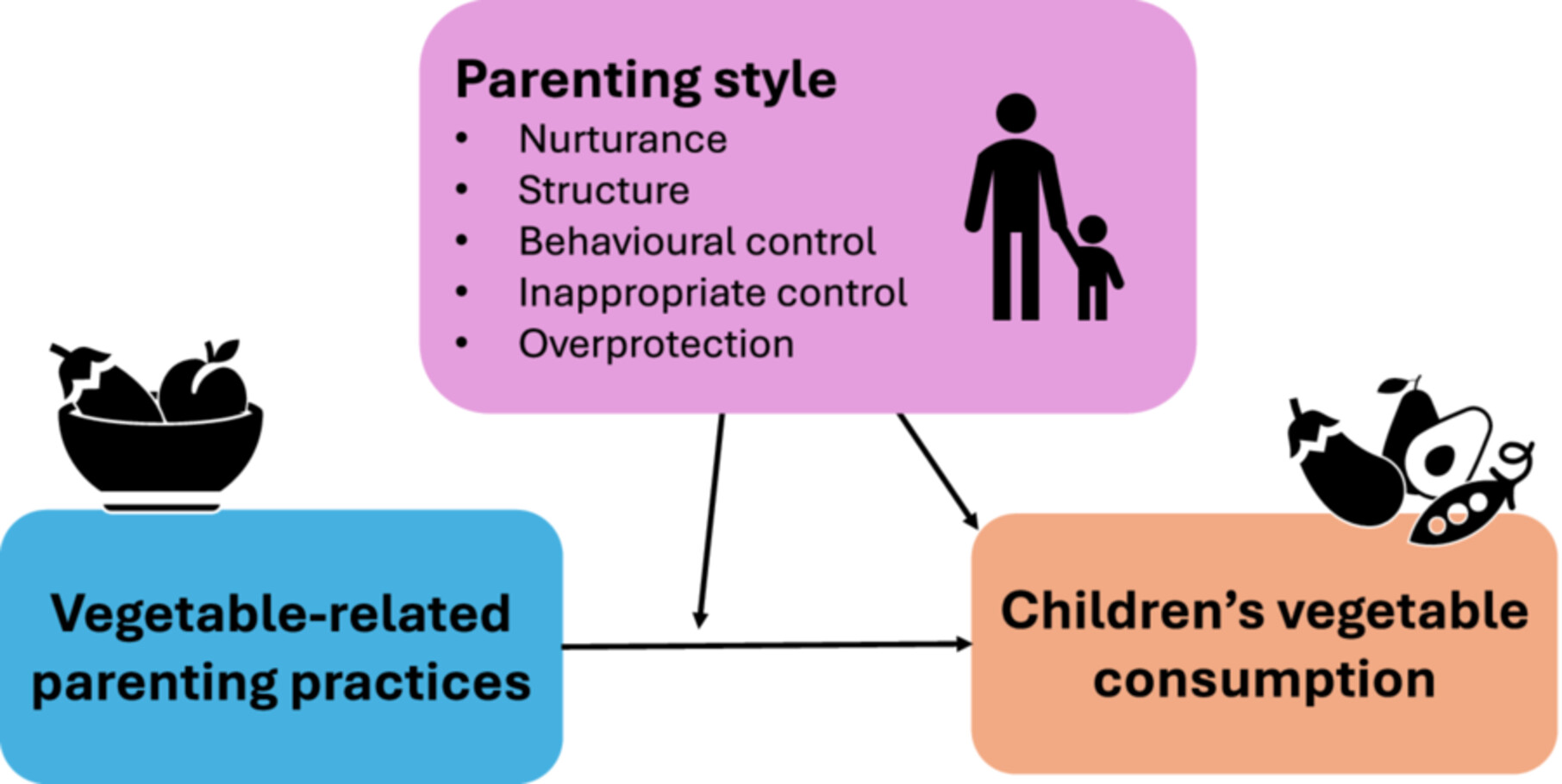
This study highlights the importance of availability/accessibility for children's vegetable consumption and identifies overprotection—a rarely studied parenting style construct—as linked to lower consumption. Two moderation effects by parenting style were also found, underscoring its role as a potential contextual factor that may influence the impact of parenting practices.
A Cross‐Sectional Association Between Serum Aflatoxin and Micronutrient Status Among Children Aged 6–24 Months in Rural Tanzania
- 15 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
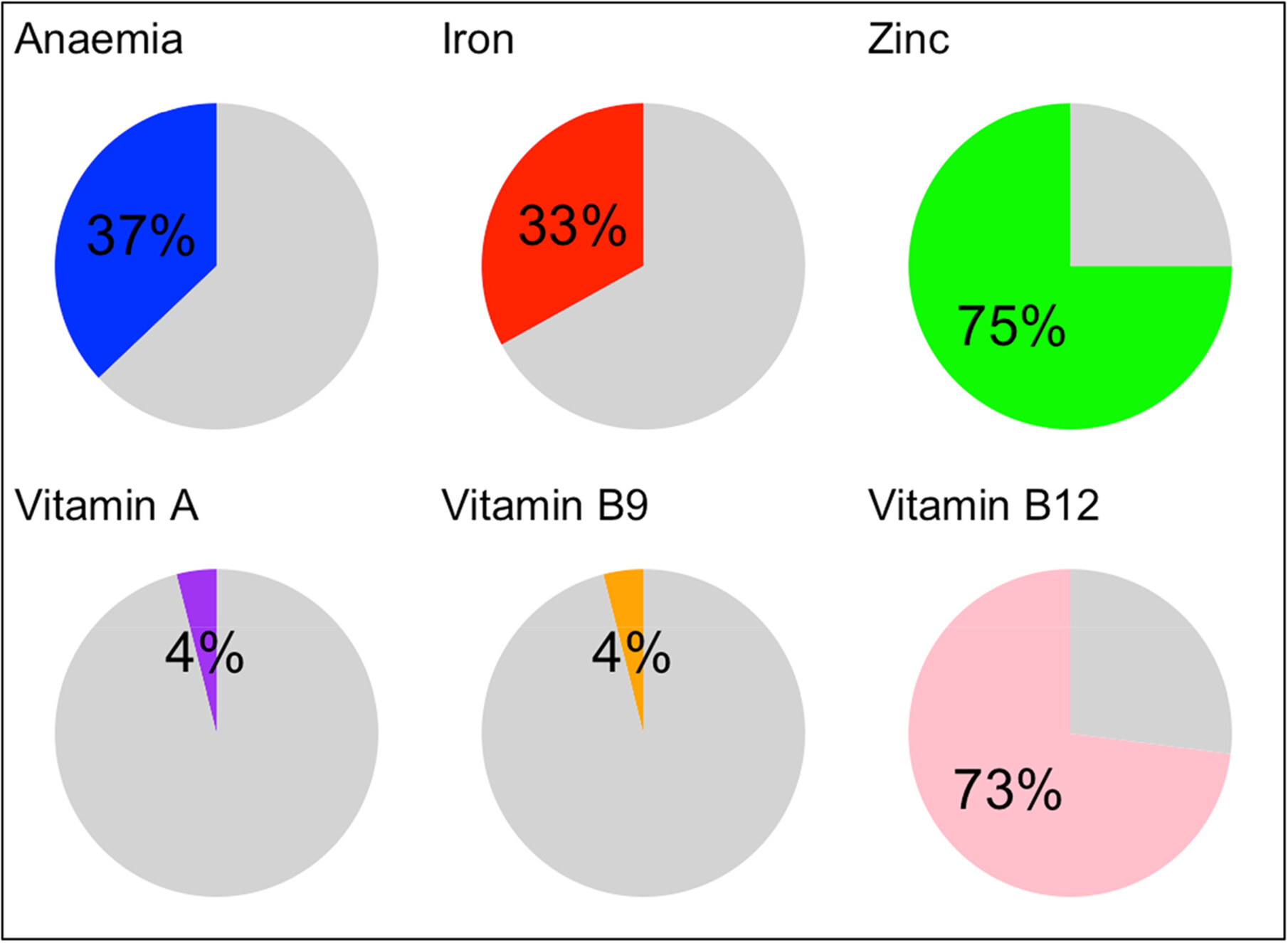
Micronutrient deficiencies and aflatoxin exposure remain high among children under five in developing countries. However, few studies have assessed the association between these factors in East Africa, particularly in agro-pastoralist societies where maize and animal foods (highly susceptible to aflatoxin contamination) are staple foods. This study found that more than two-thirds of participants were exposed to aflatoxin contamination and were deficient in zinc and vitamin B12. Children with high levels of AF-alb adducts were 40% more likely to be iron deficient than those without. Efforts should focus on improving micronutrient status and enhancing food safety by incorporating aflatoxin mitigation strategies in micronutrient interventions.
Household Food Insecurity, Growth and Development of Preschool Children: Evidence From Rural Pakistan
- 7 July 2025
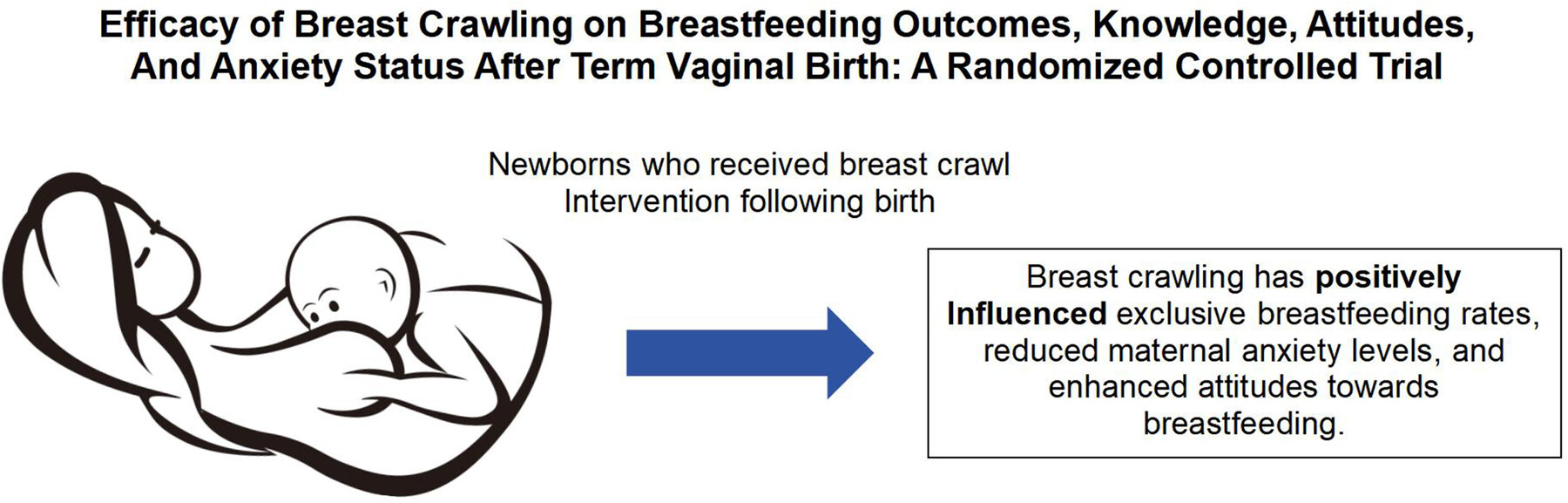
Efficacy of Breast Crawling on Breastfeeding Outcomes, Knowledge, Attitudes, and Anxiety Status After Term Vaginal Birth: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 7 July 2025
Recent issues
- Volume 21, Issue 3July 2025
- Volume 21, Issue 2April 2025
- Volume 21, Issue 1January 2025