Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Editorial
Systematic Reviews
Associations between gender and health-related quality of life in people with IgE-mediated food allergy and their caregivers: A systematic review
- First Published: 07 February 2024
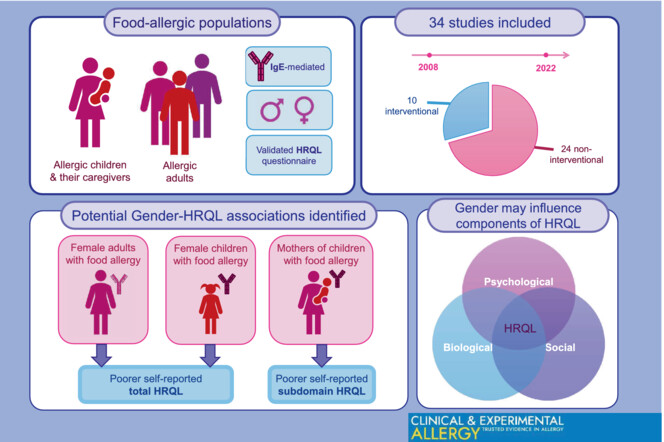
We systematically reviewed the impact of gender on health-related quality of life (HRQL) in populations with immunoglobulin-E-mediated food allergy. Females with food allergy self-report poorer baseline HRQL than males, regardless of age. Gender may impact total HRQL and subdomain HRQL in food allergy studies. However, selective reporting and narrow considerations of gender in included studies limited the strength of the findings.
Allergic diseases as risk factors for Long-COVID symptoms: Systematic review of prospective cohort studies
- First Published: 08 November 2023
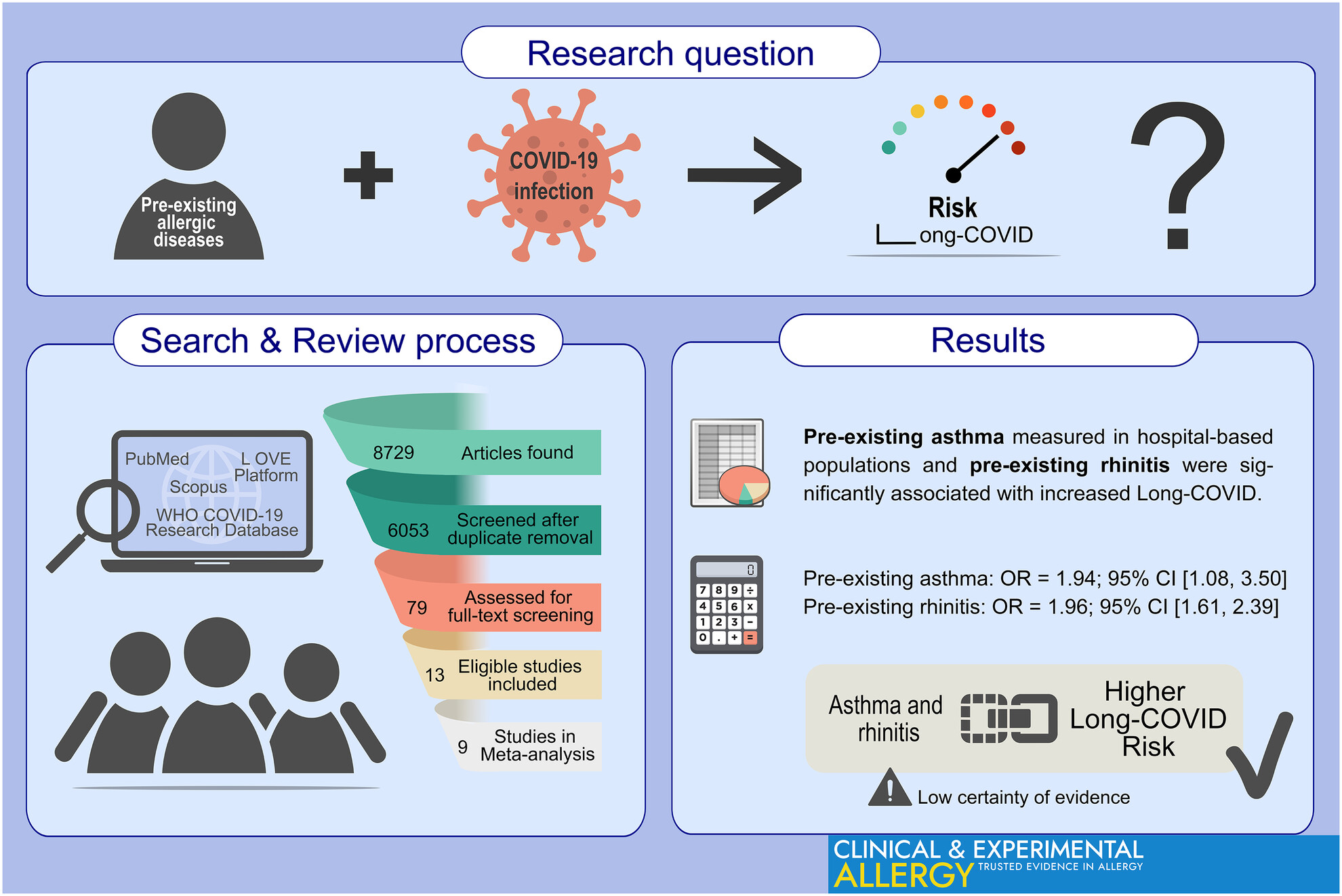
We systematically reviewed and appraised the epidemiological evidence on allergic diseases as risk factors for Long-COVID. Meta-analysis revealed that pre-existing asthma measured in hospital-based populations and pre-existing rhinitis were significantly associated with increased Long-COVID incidences. Asthma and rhinitis may increase the risk of Long-COVID but the certainty of evidence is very low. CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio
Outcomes reported in randomized controlled trials for mixed and non-IgE-mediated food allergy: Systematic review
- First Published: 07 March 2023
Review Articles
Historical and social science perspectives on food allergy
- First Published: 12 June 2023

Historians and social scientists scholars have addressed three issues related to food allergies: First, they have addressed epidemiology, including the apparent rise in the rate of food allergies and the theories proposed to explain these increases. Second, they have explored how risks related to food allergies have been constructed, understood, experienced and mitigated. Third, they have investigated the experiences of food allergy sufferers, providing qualitative insights that can deepen our understanding of food allergy.
Information needs of patients considering oral immunotherapy for food allergy
- First Published: 09 September 2022
Health-related quality of life in food and venom induced anaphylaxis and role of influencing factors
- First Published: 23 December 2022
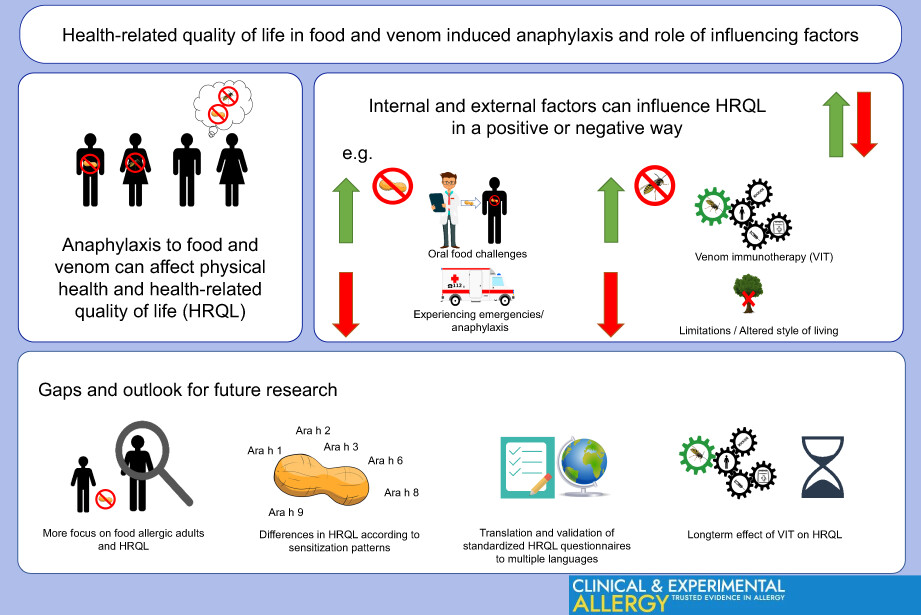
In this non-systematic narrative review, the literature on health-related quality of life (HRQL) in patients with food and venom induced anaphylaxis and the role of influencing factors was reviewed. Besides the negative influence of food or venom anaphylaxis as such, but also patient-specific and external factors can influence HRQL, for example the experience with emergencies, therapeutic interventions like venom immunotherapy (VIT) or participation in trials. Further research on HRQL is needed, especially in adult patients.
Anthropological and sociological perspectives on food allergy
- First Published: 31 August 2023
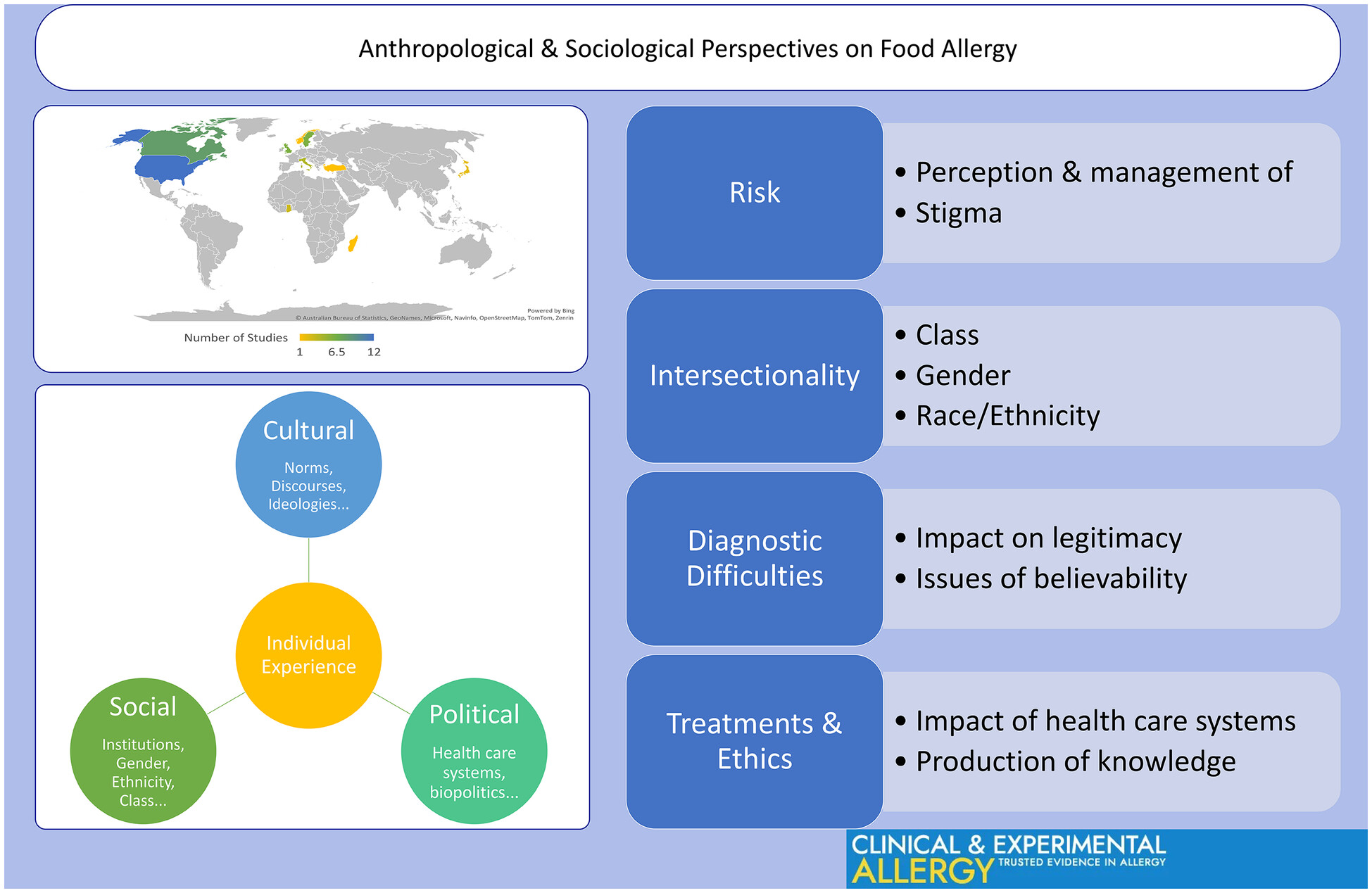
Anthropological and sociological approaches contribute to critical knowledge of how social, cultural and political factors shape the lived experience of food allergy. Research has been done on risk, intersectionality, diagnostic issues and legitimacy, and ethics in treatments. More studies are needed around the world, and incorporating anthropological and social science perspectives and methodologies in interdisciplinary research on food allergy is recommended.
Original Articles
Evaluation of measurement errors in the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) outcome
- First Published: 02 January 2024

The Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM) is a recommended score to assess eczema symptoms from a patient's perspective with a weekly recall. Patients tended to slightly underestimate their symptoms when reporting POEM with significant recall noise. Recall errors should be considered when interpreting POEM scores. More research is needed to evaluate methods to reduce poor recall (such as aide-memoirs).
Loss of smell in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease impacts mental health and quality of life
- First Published: 03 May 2022
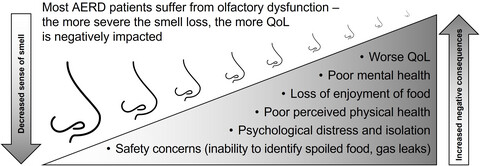
Survey responses from 853 patients with AERD demonstrate that most report diminished sense of smell/taste and 30% categorize it as a severe problem. The severity of olfactory dysfunction correlates with more psychological distress, worse general health scores, and increased negative consequences on quality-of-life. The relevance of smell loss to patients’ quality-of-life, and the safety concerns that may result from it, should be acknowledged and evaluated by clinicians caring for these patients.
Research Letters
Does proactively asking about allergens before ordering improve customer outcomes? An in-business randomised controlled trial
- First Published: 25 April 2023
Quality of life and mental well-being of adults with atopic dermatitis living in the UK
- First Published: 29 September 2022
The ability of children and families with and without nut allergy to correctly identify nuts
- First Published: 21 June 2023
Reinventing the wheal: A review of online misinformation and conspiracy theories in urticaria
- First Published: 20 October 2022
The impact of anaphylaxis on the quality of life and mental health of adults
- First Published: 06 November 2022
Child-caregiver cognitive appraisals and caregiver food allergy burden and management
- First Published: 04 June 2023
Anxiety in parents of children with IgE-mediated food allergies before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
- First Published: 07 August 2023
Educational tool for mothers of young children with food allergy: Randomised controlled trial
- First Published: 29 August 2023
Routine infant skincare advice in the UK: A cross-sectional survey
- First Published: 11 October 2023
Association between allergic conditions and school absenteeism among Indian adolescents
- First Published: 20 November 2023




