Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Attaining 15.1% Efficiency in Cu2ZnSnS4 Solar Cells Under Indoor Conditions Through Sodium and Lithium Codoping
- First Published: 18 February 2025
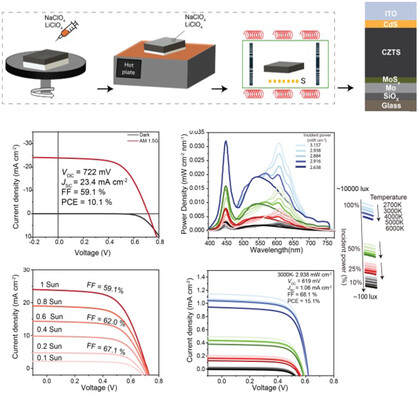
This study demonstrates that Na–Li co-doping enables Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells to achieve over 10% efficiency under AM1.5G and 15.1% under indoor light condition. The synergy of the alkali elements in enhancing grain growth and defect regulation is key to this performance, positioning Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells as a promising solution for powering Internet of Things devices in indoor environments.
A Sustainable Hydrogel-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Coupled to an Integrated Supercapacitor for Direct Indoor Light-Energy Storage
- First Published: 29 January 2025
A dye-sensitized solar cell and a supercapacitor based on xanthan gum electrolytes are coupled into a fully aqueous integrated light-harvesting and storage device. The solar cell harvests indoor light with an efficiency of 3.5%, and the integrated system achieves an overall photoelectric conversion and storage efficiency of 1.45%, ideal sustainable for low-power indoor electronics.
Comparative Study of Different Passivation Layers for n-i-p Perovskite Solar Cell for Indoor Applications
- First Published: 03 March 2025
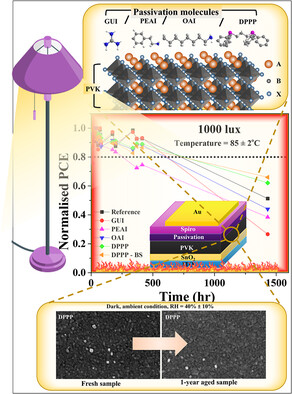
Different organic molecules, including commonly used PEAI and OAI, as well as the novel Lewis-base DPPP, are applied and compared for the passivation of perovskite films in planar, low-temperature n-i-p perovskite solar cells. This interface passivation strategy enhances both thermal stability and photovoltaic performance under indoor illumination, achieving an iPCE exceeding 34% at 1000 Lx.
Results of an International Comparison of Indoor Photovoltaic Measurements Among Seven Metrological Institutes
- First Published: 10 April 2025
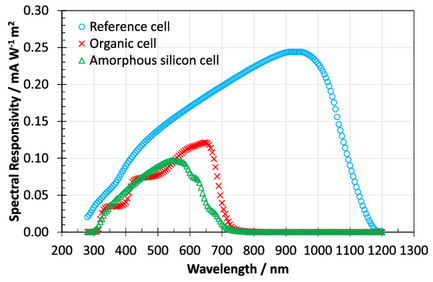
Seven National Standards Laboratories and photovoltaic (PV) testing laboratories carry out an intercomparison of indoor PVs. Three types of indoor cells are measured using three different light sources at illuminance levels 100–2000 lx. Measurements reveal notable discrepancies in short-circuit current. The reasons are analyzed and described, and recommendations for standardization are given.
Impact of Transparent Conducting Oxide on the Performance of Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells for Indoor Applications
- First Published: 14 April 2025
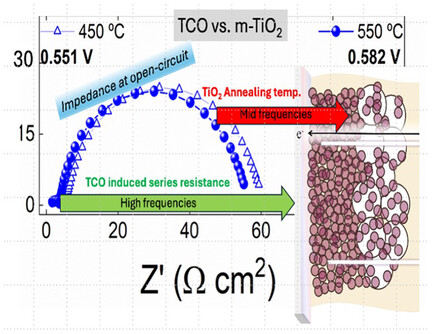
While properties like conductivity, transmittance, and morphology of the transparent conducting oxide are not especially critical for the indoor applications of dye-sensitised solar cells, it is important to ensure that the mesoporous TiO2 layer is of sufficiently high quality. Herein, the high- and mid-frequency parts of the impedance response are studied.
Bulk Passivation of Lead Halide Perovskites: The Key to High-Performance Indoor Photovoltaics at Very Low-Light Intensities
- First Published: 05 April 2025

Lead halide perovskites (LHPs) are vulnerable to performance decreasing defects that are more profound under indoor illumination, due to the reduced amount of photogenerated carriers. Utilizing sodium thioglycolate as a bifunctional bulk passivator to passivate acceptor-like defects and fill the donor-like defects leads to improved performance under low-light illumination (≤200 lux) via reduced trap-assisted recombination.
Benchmarking Inorganic Thin-Film Photovoltaics Technologies for Indoor Applications
- First Published: 27 May 2025
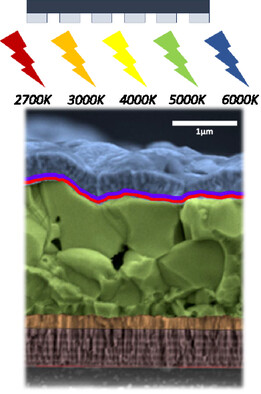
This study compares the optoelectronic performance of several technologies under relevant indoor illumination conditions using a consistent characterization methodology. The results show many devices performing well indoors, at medium irradiance, which corroborates their potential for achieving high efficiencies. However, their performance is compromised at very low irradiance due to unoptimized device shunt resistance.
The Roles of Ion Migration on Perovskite Solar Cell Operational Stability at Various Illumination Intensities
- First Published: 01 June 2025
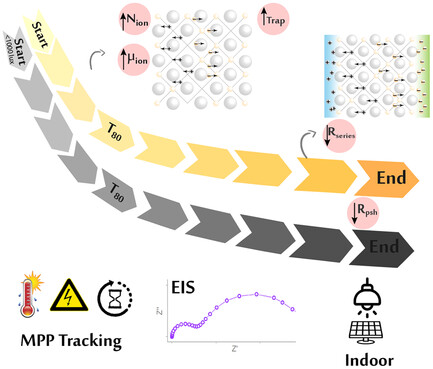
Impedance spectroscopy was measured at incrementing times during maximum power point stability tests of perovskite solar cells. An increased ionic density and mobility was identified as first signs of degradation, affecting the recombination mechanisms and shunt current leakage. Performance decay magnifies at low illumination due to the drastic decrease of the perovskite shunt resistance.




