Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
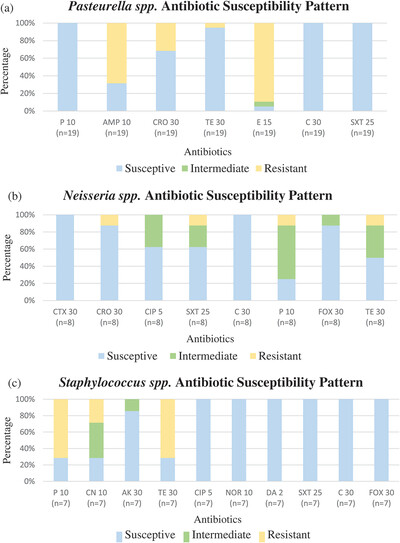
Oral flora of domestic cats in Hong Kong: Identification of antibiotic-resistant strains
- First Published: 15 December 2022
Characterization, distribution, antimicrobial resistance and resistance risk factors in staphylococci isolated from cats from 2001 to 2014
- First Published: 10 September 2018
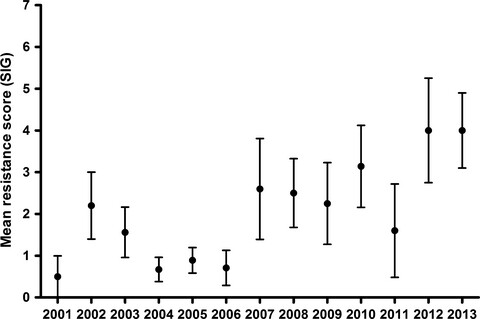
This retrospective study characterized the identity and antibiotic resistance profiles of staphylococci isolated from cats between 2001 and 2014. The results demonstrate a high and increasing prevalence of multi-drug antibiotic resistance and an increasing prevalence of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus intermedius group bacteria isolated from cats during this time.
Prevalence of most common human pathogenic Campylobacter spp. in dogs and cats in Styria, Austria
- First Published: 22 January 2018
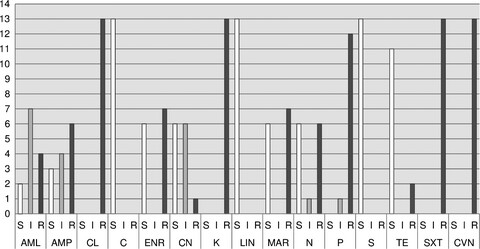
The aim of this study was to determine the frequency of occurrence of most common human pathogenic Campylobacter species in dogs and cats in Styria, Austria. Results show a very low proportion of C. spp.-positive samples (5.9%) in microbiological culture with Campylobacter jejuni as the most common type. Furthermore, the ratio of C. species between young and adult, as well as healthy and diarrhoeic animals, was analysed. There is a higher prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in kittens and in diarrhoeic animals in this study. Finally, the obtained strains of Campylobacter jejuni for antibiotic sensitivity testing to assess the resistance situation. Several antibiotics display high resistance rates.
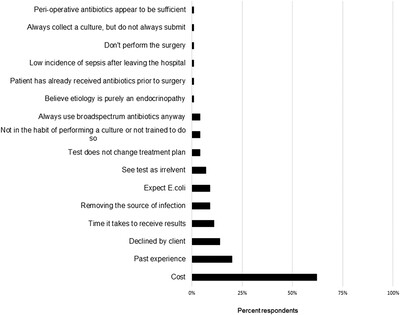
Antimicrobial use in the surgical treatment of canine pyometra: A questionnaire survey of Arizona-licensed veterinarians
- First Published: 13 April 2023
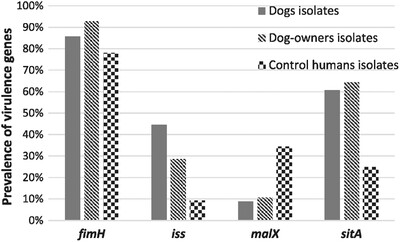
Identification of faecal Escherichia coli isolates with similar patterns of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes in dogs and their owners
- First Published: 12 October 2022
Multidrug resistant Enterococcus faecium isolate from cholangitis/cholecystitis in a dog
- First Published: 13 May 2022
Anti-microbial resistance of Salmonella isolates from raw meat-based dog food in Japan
- First Published: 25 January 2022
The current study's objective was to determine the prevalence of Salmonella contamination in RMBD for dogs and the antimicrobial resistance profiles of these isolates. Therefore, the incidence of Salmonella contamination in RMBD for dogs currently sold in Japan was surveyed. Salmonella was detected in seven of the 60 raw food samples.
Prevalence of coagulase-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in dogs in Bangladesh
- First Published: 23 December 2021
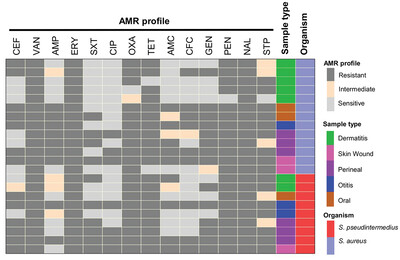
The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP) have a significant health impact on occupational people and pet owners. Although the occurrence of MRSA and MRSP in humans and animals has been reported in many other countries, the information on the magnitude of S. aureus and S. pseudintermedius infection in dogs in Bangladesh and their antimicrobial resistance pattern is limited, if not absent. This manuscript, for the first time, describes the circulation of mecA gene bearing S. pseudintermedius in dogs in Bangladesh.
Prospective study evaluating the incidence of bacteraemia and bacteruria in afebrile and febrile neutropaenic dogs undergoing chemotherapy
- First Published: 14 November 2016
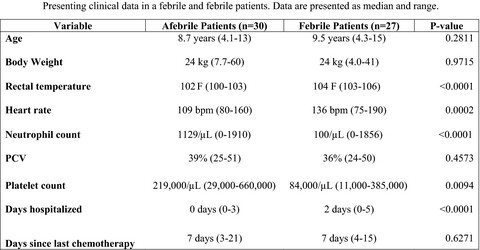
The incidence of bacteraemia in 55 neutropaenic dogs undergoing chemotherapy was found to be 12.3%. The incidence in febrile and afebrile groups was not significantly different. Of positive blood cultures, 42.9% were multi-drug–resistant organisms highlighting the value of blood cultures in this patient population.
Do post-surgical multiresistant urinary infections occur in horses? Case of unilateral pyelonephritis caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing bacteria as a complication of cystotomy
- First Published: 19 July 2023
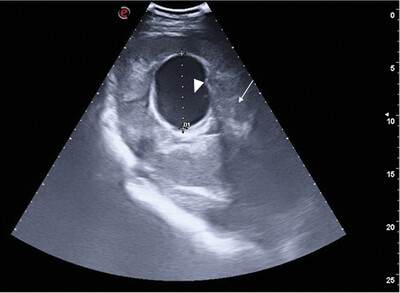
An 11-year-old Swedish warmblood gelding was diagnosed with a cystolith which was removed by cystotomy. Seven days after surgery the horse presented with pyrexia, dullness, and colic due to a right-sided pyelonephritis caused by an ESBL-producing Enterobacter cloacae complex bacteria with resistance against beta-lactams, aminoglycoside, and trimethoprim-sulfonamide classes. Treatment included prolonged oral antimicrobials according to susceptibility testing results (enrofloxacin), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, fluid therapy and gastric ulcer prophylaxis. The horse recovered successfully although unilateral renal scarring occurred.
Retrospective evaluation of association between perioperative antimicrobial protocol and complications following elective equine synovial endoscopy
- First Published: 17 February 2021
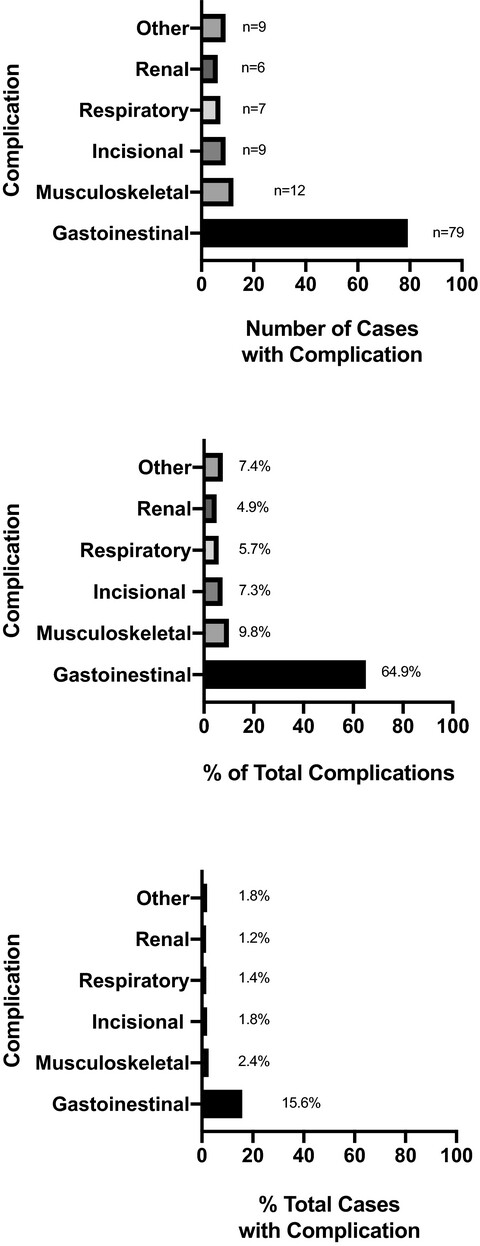
Prophylactic perioperative antimicrobial protocols in equine practice deserve periodic reconsideration due to increased antimicrobial resistance. Prolonged antimicrobial usage beyond the time of surgery was unnecessary to prevent septic synovitis following synovial endoscopy in this case population and was furthermore associated with an increased risk of gastrointestinal complications.
Emergence of the resistance-nodulation-division efflux pump tmexCD3-toprJ3 gene confers resistance to tigecycline in Pseudomonas juntendi and Proteus terrae isolated from a pig farm in China
- First Published: 21 September 2022
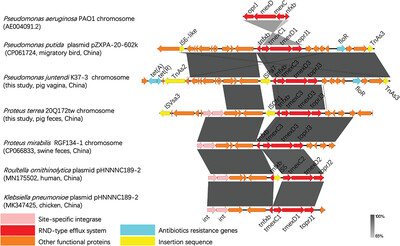
This is the first report of the emergence of the tmexCD3-toprJ3 gene in Pseudomonas juntendi and Proteus terrae isolated from a pig farm in China. The tmexCD3-toprJ3 efflux pump cluster conferred multidrug resistance, including resistance to tigecycline, demonstrating pathogenicity and transmission.
Characteristics of Aerococcus viridans isolated from porcine fetuses in Korean farms
- First Published: 24 February 2021
An efficient cephalosporin stewardship programme in French swine production
- First Published: 08 February 2021
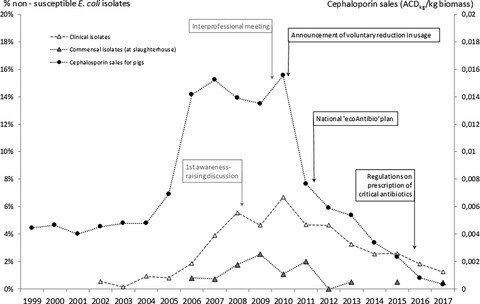
This study details success conditions of an antimicrobial stewardship program in animal agriculture. Based on data provided by complementary and independent monitoring tools, success could be assessed on both usage and resistance. Results highlight the strong relationship between cephalosporins usage and resistance in pig production, supporting a containment perspective through usage restriction.
Characterization of multidrug and heavy metal resistance of carbapenemases producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from poultry samples in Bangladesh
- First Published: 30 May 2023
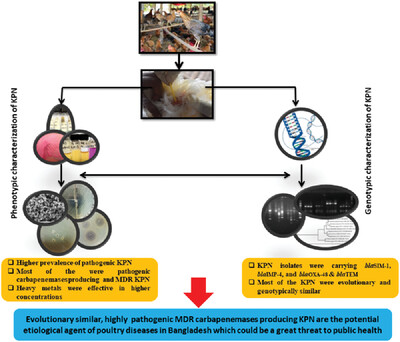
Increasing numbers of carbapenemase-producing, multidrug-resistant, highly pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae pose a serious risk to the health of people and poultry in Bangladesh. To reduce the prevalence Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in poultry which have harbored beta-lactamase genes and quinolone resistance genes, a combination of antibiotics such as doripenem, meropenem, cefoxitin, and polymyxin B is recommended, followed by the use of readily available heavy metals Cr>Co>Cu>Zn beyond their toxic metal. Antibiotics such as ampicillin, doxycycline, tetracycline, gentamycin, and ciprofloxacin have already lost their typical efficacy against the isolates examined, therefore we must be cautious when using them to treat bacterial diseases in poultry.
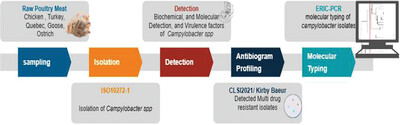
Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, virulence gene profile and molecular typing of Campylobacter species isolated from poultry meat samples
- First Published: 17 October 2022
Isolation, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Salmonella isolated from poultry farms in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- First Published: 19 February 2022
Salmonellosis is an infectious and economically important disease of humans and animals caused by different Salmonella species.
Molecular detection and antibiotyping of multi-drug resistant Enterococcus faecium from healthy broiler chickens in Bangladesh
- First Published: 16 November 2021
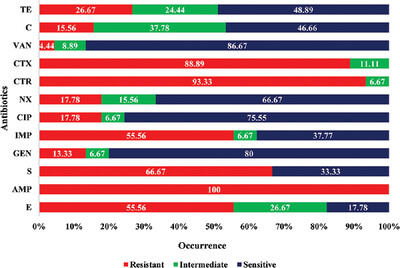
This is the first study in Bangladesh to detect multidrug-resistant (MDR) and multiple antibiotic-resistant (MAR) Enterococcus faecium along with their corresponding resistance genes from healthy broilers. Our findings indicated that faecal materials of broilers harbour a high level of MDR and MAR E. faecium and multiple antibiotic resistance genes in those isolates. The results obtained from our study show severe health risks to both animals and humans.
Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli in broiler chickens, farmworkers, and farm sewage in Bangladesh
- First Published: 02 November 2021
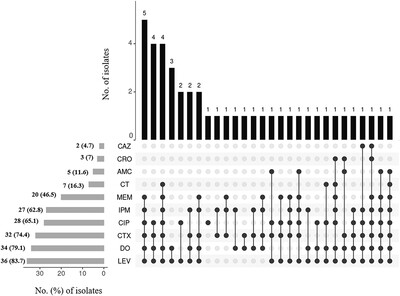
Winter season, absence of specific shoes for staff, and use of antibiotics without veterinarian's prescription were the significant risk factors of MDR-E. coli infection in broiler chickens.
A very high resistance of the E. coli isolates against levofloxacin (81.6%), doxycycline (78.1%), cefotaxime (78.1%), and ciprofloxacin (70.2%) was observed.
Similar pattern of resistance phenotype of E. coli was observed among broiler chickens, farm workers, and farm sewage, and about 76% of the isolates demonstrated multidrug resistance.
Antimicrobial resistance profiling and burden of resistance genes in zoonotic Salmonella isolated from broiler chicken
- First Published: 02 October 2021
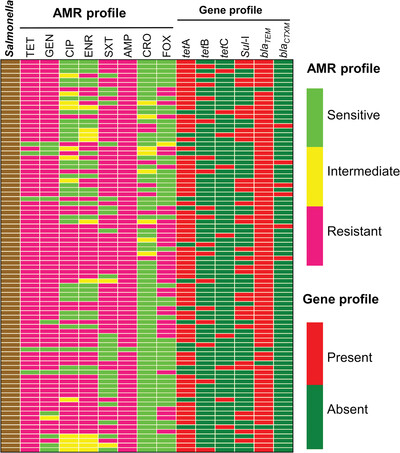
This cross-sectional study was aimed to investigate the zoonotic Salmonella strains circulating in the broiler farm environment with their detailed antimicrobial resistance profiling. Out of the 350 samples, prevalence of Salmonella was 24% and multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella was 94%. There is a great risk to secure healthy poultry products due to the circulation tetA, tetB, tetC, blaTEM, blaCTX-M and Sul-I antimicrobial resistance genes in these MDR zoonotic Salmonella.