Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
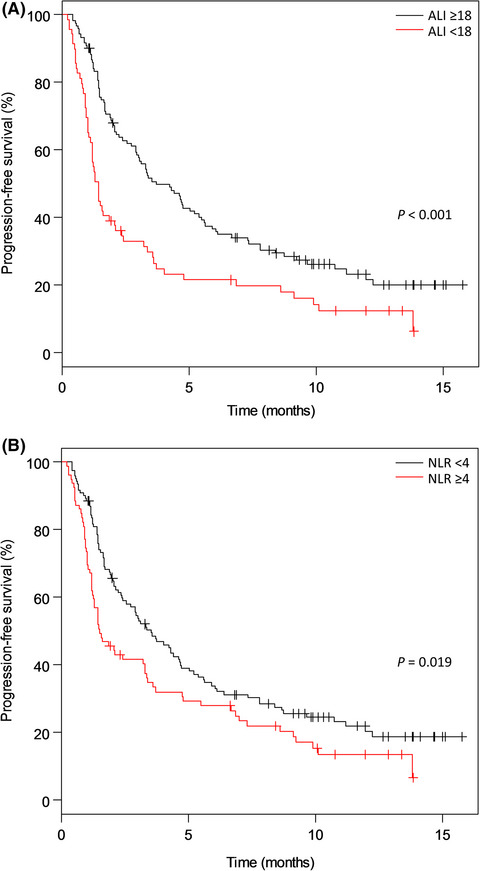
Pretreatment advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) for predicting early progression in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 18 November 2017
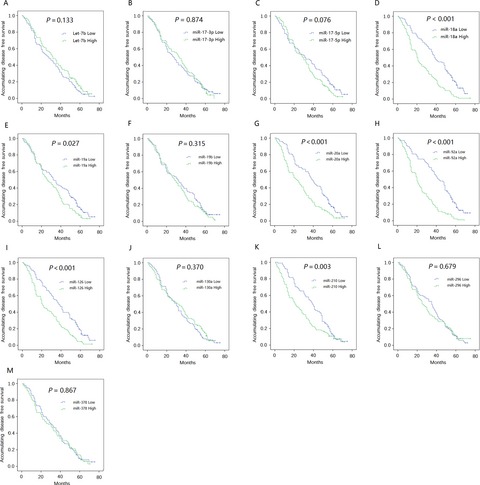
High circulating miR-18a, miR-20a, and miR-92a expression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 21 December 2017
Thromboembolic and bleeding complications during oral anticoagulation therapy in cancer patients with atrial fibrillation: a Danish nationwide population-based cohort study
- First Published: 19 May 2017
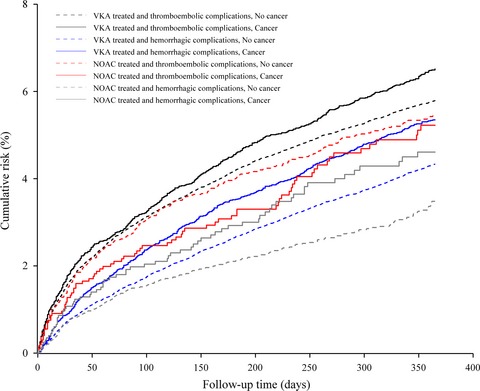
Since both atrial fibrillation and cancer are common, any increased risk of complications among patients treated with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) or non-VKA oral anticoagulants (NOACs) may have major public health implications. This study found that the absolute risks of thromboembolic or bleeding complications were nearly the same in patients with and without cancer who redeemed prescriptions for VKAs or NOACs.
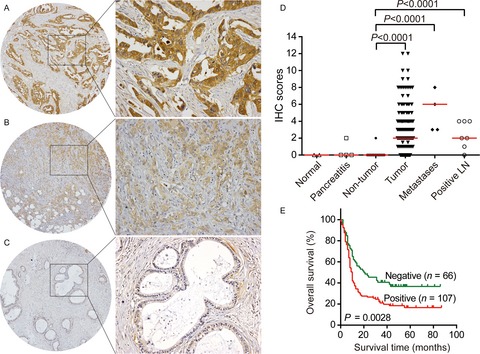
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in combination with CD8+ TILs density in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 23 November 2017
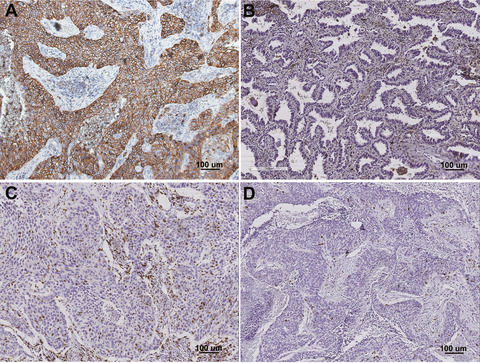
Combination of PD-L1 and CD8+ TILs density may suggest impressive prognostic value in NSCLC patients instead of PD-L1 alone. Less than half of patients with resected NSCLC experienced inconsistent PD-L1 expression between primary and metastatic lesions, and significance of PD-L1 expression in a single-biopsy specimen in advanced NSCLC may be overestimated in clinical practice.
Global circular RNA expression profile of human gastric cancer and its clinical significance
- First Published: 23 May 2017
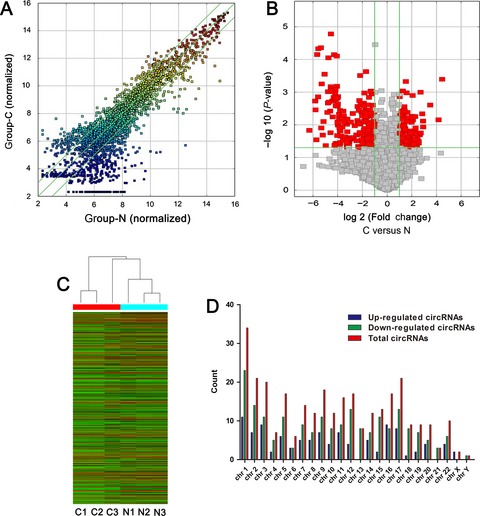
A total of 308 circRNAs, including 107 (34.74%) up-regulated and 201 (65.26%) down-regulated circRNAs, were found significantly aberrantly expressed in gastric cancer tissues. The hot-point chromosomes were chr1, chr2, chr3, chr9, and chr17. Some circRNAs including hsa_circ_0014717 can stably exist in human body fluid, and has the potential to be used as novel biomarkers for the screen of high-risk gastric cancer patients.
Automated home monitoring and management of patient-reported symptoms during chemotherapy: results of the symptom care at home RCT
- First Published: 30 January 2017
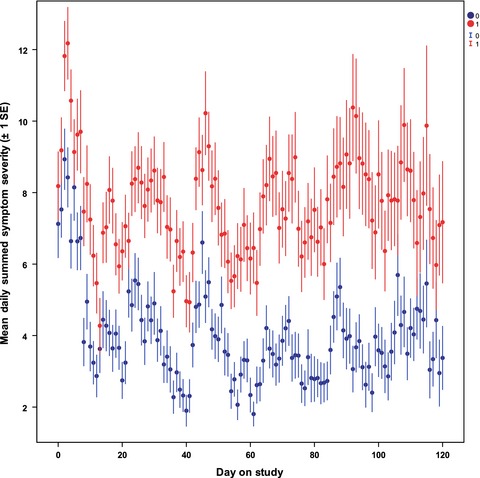
We tested an automated system to decrease symptom burden during chemotherapy. Results are reported for a randomized controlled trial of Symptom Care at Home, an automated symptom monitoring and management system that included automated self-management coaching coupled with oncology provider alerts about poorly controlled symptoms at home. Study-based nurse practitioners provided telephone follow-up utilizing a symptom care decision support system to intensify symptom care. The trial results clearly demonstrate that the intervention significantly improves symptom outcomes.
Original Research
Elevated glypican-1 expression is associated with an unfavorable prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 24 April 2017
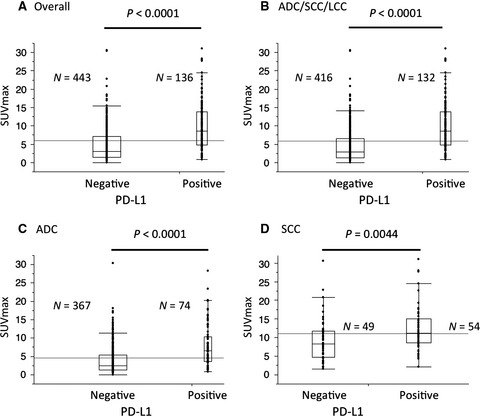
Metabolic characteristics of programmed cell death-ligand 1-expressing lung cancer on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Cancer Biology
Original Research
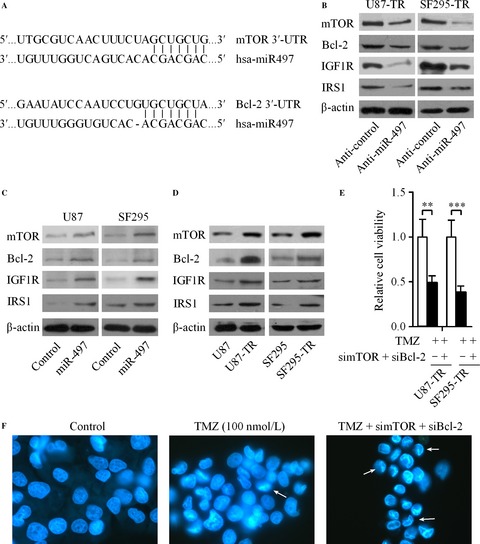
Up-regulation of miR-497 confers resistance to temozolomide in human glioma cells by targeting mTOR/Bcl-2
- First Published: 08 January 2017
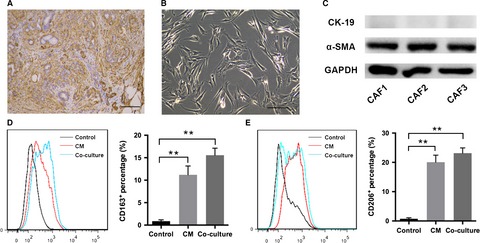
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote M2 polarization of macrophages in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 18 January 2017
Upregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration
- First Published: 15 January 2017
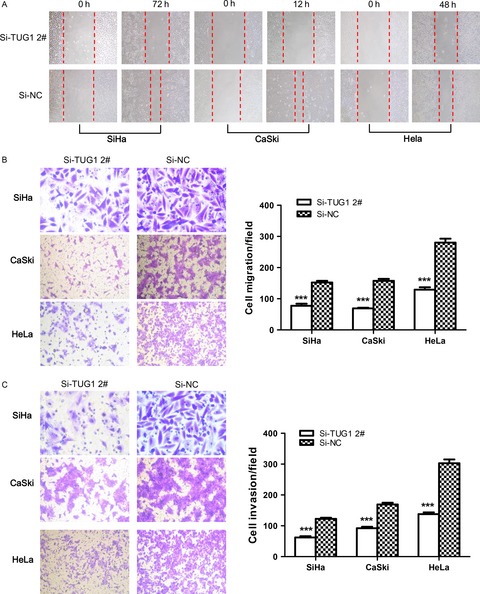
LncRNA TUG1 expression was significantly upregulated in cervical cancer and correlated with tumor size, international federation of gynecology and obstetrics (FIGO) stage, cell differentiation, and lymph node metastasis. Knockdown of TUG1 expression in cervical cancer cells inhibited cell proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis. Knockdown of TUG1 expression inhibited migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells via the mechanism of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
A Comparison of ddPCR and ARMS for detecting EGFR T790M status in ctDNA from advanced NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance
- First Published: 20 December 2016
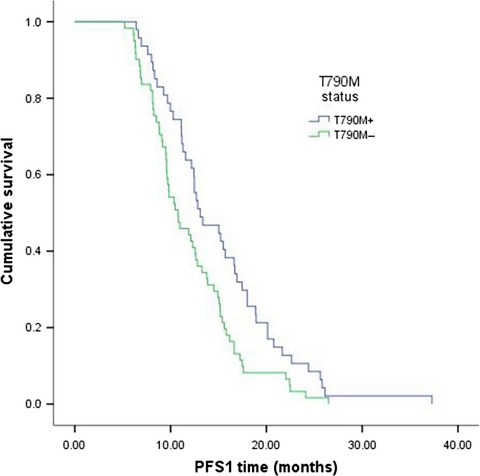
Our study demonstrates the feasibility and sensitivity of detecting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M status in plasma samples from NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance. The ddPCR assay detecting in plasma ctDNA T790M may provide an alternative method in some situations. Patients with acquired T790M mutation at the time of progression have gradual progression compared to those without T790M mutation. And T790M-positive patients have better clinical outcomes to EGFR-TKIs than T790M-negative patients.
Peripheral blood clinical laboratory variables associated with outcomes following combination nivolumab and ipilimumab immunotherapy in melanoma
- First Published: 22 February 2018
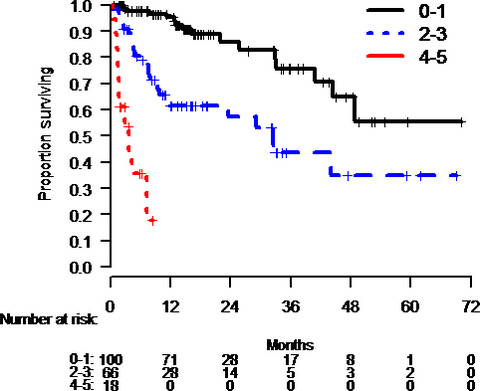
The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab is a highly effective treatment for patients with melanoma, and little is known about the patients who do the best after treatment. For the first time, we report basic clinical laboratory variables which are associated with overall survival following treatment.
Cancer Biology
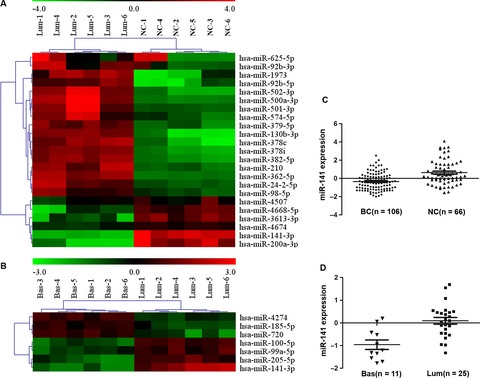
Downregulation of miRNA-141 in breast cancer cells is associated with cell migration and invasion: involvement of ANP32E targeting
- First Published: 21 February 2017
Original Research
A comprehensive genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA expression profile in hepatocellular carcinoma
- First Published: 18 October 2017
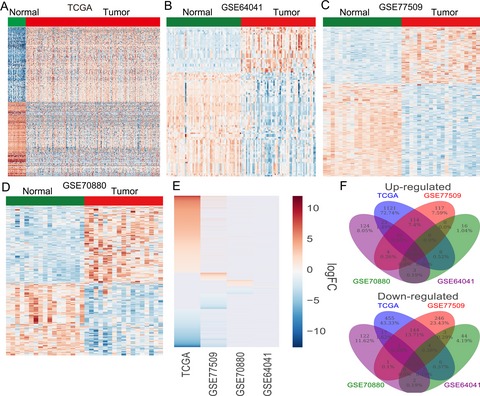
lncRNAs are emerging as critical regulators that are involved in the development and progression of cancers in humans. We comprehensively investigated lncRNA expression profiling in HCC and normal tissues; these findings may provide a valuable resource to further identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets of HCC.
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
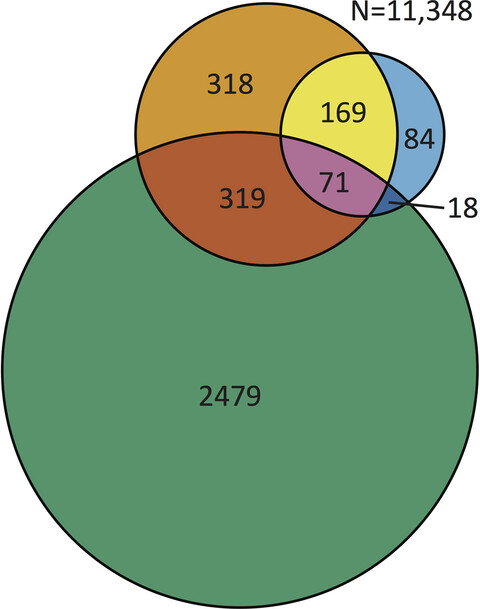
Microsatellite instability status determined by next-generation sequencing and compared with PD-L1 and tumor mutational burden in 11,348 patients
- First Published: 13 February 2018
Cancer Prevention
Environmental factors, seven GWAS-identified susceptibility loci, and risk of gastric cancer and its precursors in a Chinese population
- First Published: 21 February 2017
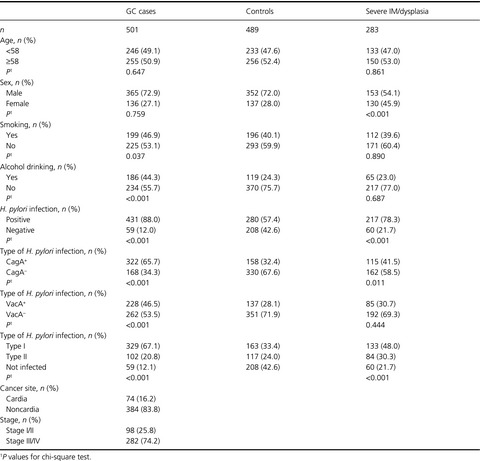
The gene–environment interaction has increased gastric cancer (GC) risk. Seven susceptibility loci identified by genome-wide association studies (GWASs) suggest that genetic factors play a role in gastric carcinogenesis. Meanwhile, Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, smoking, and drinking are also important environmental factors for gastric cancer. To explore the role of gene–environment interactions in gastric carcinogenesis, study findings of the relationship between the seven susceptibility loci and their potential interactions with H. pylori infection, smoking, and drinking in risk of GC, and severe intestinal metaplasia (IM)/dysplasia have been inconclusive. A total of 1273 subjects in a Chinese population were recruited and genotyping were carried out with competitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) method. Unconditional logistic regression was applied to model the associations between genetic polymorphisms and disease risk. Effect modifications by H. pylori infection, smoking, and drinking were evaluated. We found PSCA rs2294008/rs2976392 showed a significant interaction with H. pylori infection in risk of GC on a multiplicative scale. Meanwhile, PRKAA1 rs13361707 had an additive interaction with H. pylori infection. SLC52A3 rs13042395 showed interaction with drinking in risk of GC. Moreover, three SNPs, MUC1 rs4072037, ZBTB20 rs9841504, and PRKAA1 rs13361707 were associated with precancerous gastric lesions of severe IM/dysplasia. Our data suggest that genetic predisposition identified in the GWASs, may interact with environmental risk factors, especially for H. pylori infection and alcohol consumption to increase the risk of GC.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
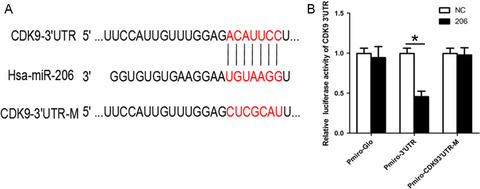
miR-206 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting CDK9
- First Published: 21 September 2017
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
An inflammatory biomarker-based nomogram to predict prognosis of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an analysis of a prospective study
- First Published: 10 November 2016
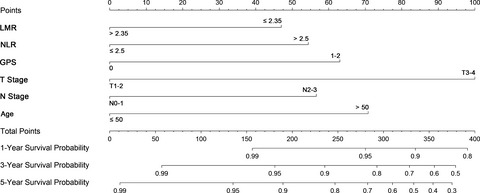
Pretreatment Glasgow prognostic score (GPS), NLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), LMR of 388 nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients who were recruited prospectively in the 863 Program No. 2006AA02Z4B4 were assessed. After multivariate analysis of the 249 patients of the development set, age, T stage, N stage, and GPS, NLR, LMR appeared to be independent prognostic factors of 5-year disease-specific survival (DSS), and a nomogram was established to predict the DSS based on these factors. The model was validated in 139 patients of the validation set.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
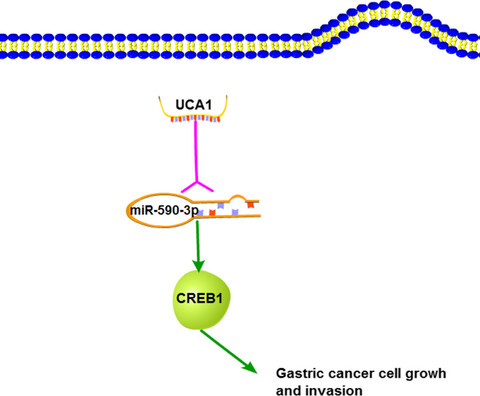
UCA1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting CREB1 sponging to miR-590-3p
- First Published: 08 March 2018