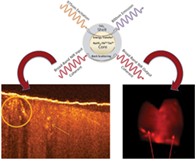
TiO2-coated fluoride nanoparticles for dental multimodal optical imaging
Abstract
Core-shell nanostructures associated with photonics techniques have found innumerous applications in diagnostics and therapy. In this work, we introduce a novel core-shell nanostructure design that serves as a multimodal optical imaging contrast agent for dental adhesion evaluation. This nanostructure consists of a rare-earth-doped (NaYF4:Yb 60%, Tm 0.5%)/NaYF4 particle as the core (hexagonal prism, ~51 nm base side length) and the highly refractive TiO2 material as the shell (~thickness of 15 nm). We show that the TiO2 shell provides enhanced contrast for optical coherence tomography (OCT), while the rare-earth-doped core upconverts excitation light from 975 nm to an emission peaked at 800 nm for photoluminescence imaging. The OCT and the photoluminescence wide-field images of human tooth were demonstrated with this nanoparticle core-shell contrast agent. In addition, the described core-shell nanoparticles (CSNps) were dispersed in the primer of a commercially available dental bonding system, allowing clear identification of dental adhesive layers with OCT. We evaluated that the presence of the CSNp in the adhesive induced an enhancement of 67% scattering coefficient to significantly increase the OCT contrast. Moreover, our results highlight that the upconversion photoluminescence in the near-infrared spectrum region is suitable for image of deep dental tissue.