Remission spectrometry for blood vessel detection during stereotactic biopsy of brain tumors
Corresponding Author
Niklas A. Markwardt
- [email protected]
- +49 89 4400 74880 | Fax: +49 89 4400 74864
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
This manuscript is part of the inaugural thesis of Niklas Markwardt to be submitted at the Medical Faculty of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Munich.
Corresponding author: e-mail: [email protected], Phone: +49 89 4400 74880, Fax: +49 89 4400 74864
Search for more papers by this authorHerbert Stepp
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGerhard Franz
Department of Applied Sciences and Mechatronics, Munich University of Applied Sciences, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorRonald Sroka
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAdrian Rühm
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Niklas A. Markwardt
- [email protected]
- +49 89 4400 74880 | Fax: +49 89 4400 74864
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
This manuscript is part of the inaugural thesis of Niklas Markwardt to be submitted at the Medical Faculty of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, Munich.
Corresponding author: e-mail: [email protected], Phone: +49 89 4400 74880, Fax: +49 89 4400 74864
Search for more papers by this authorHerbert Stepp
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGerhard Franz
Department of Applied Sciences and Mechatronics, Munich University of Applied Sciences, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorRonald Sroka
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAdrian Rühm
Laser-Forschungslabor, LIFE Center, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Department of Urology, University Hospital of Munich, Munich, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Stereotactic biopsy is used to enable diagnostic confirmation of brain tumors and treatment planning. Despite being a well-established technique, it is related to significant morbidity and mortality rates mostly caused by hemorrhages due to blood vessel ruptures.
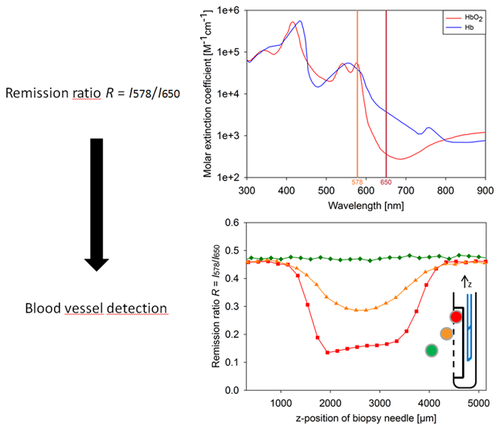
This paper presents a method of vessel detection during stereotactic biopsy that can be easily implemented by integrating two side-view fibers into a conventional side-cutting biopsy needle. Tissue within the needle window is illuminated through the first fiber; the second fiber detects the remitted light. By taking the ratio of the intensities at two wavelengths with strongly differing hemoglobin absorption, blood vessels can be recognized immediately before biopsy sampling.
Via ray tracing simulations and phantom experiments, the dependency of the remission ratio R = I578/I650 on various parameters (blood oxygenation, fiber-to-vessel and inter-fiber distance, vessel diameter and orientation) was investigated for a bare-fiber probe. Up to 800–1200 µm away from the probe, a vessel can be recognized by a considerable reduction of the remission ratio from the background level. The technique was also successfully tested with a real biopsy needle probe on both optical phantoms and ex-vivo porcine brain tissue, thus showing potential to improve the safety of stereotactic biopsy.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201600193-sup-0001-author-biographies.pdfPDF document, 164.8 KB | Author Biographies |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. Malone, J. Yang, D. L. Hershman, J. D. Wright, J. N. Bruce, and A. I. Neugut, World neurosurgery 84 (4), 1084–1089 (2015).
- 2M. L. Goodenberger and R. B. Jenkins, Cancer Genet 205 (12), 613–621 (2012).
- 3Q. T. Ostrom, L. Bauchet, F. G. Davis, I. Deltour, J. L. Fisher, C. E. Langer, M. Pekmezci, J. A. Schwartzbaum, M. C. Turner, K. M. Walsh, M. R. Wrensch, and J. S. Barnholtz-Sloan, Neuro Oncol 16 (7), 896–913 (2014).
- 4H. Ohgaki, Methods Mol Biol 472, 323–342 (2009).
- 5M. Weller, R. Stupp, G. Reifenberger, A. A. Brandes, M. J. van den Bent, W. Wick, and M. E. Hegi, Nat Rev Neurol 6 (1), 39–51 (2010).
- 6S. Eigenbrod, R. Trabold, D. Brucker, C. Erös, R. Egensperger, C. La Fougere, W. Göbel, A. Rühm, H. A. Kretzschmar, J. C. Tonn, J. Herms, A. Giese, and F. W. Kreth, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 156 (8), 1427–1440 (2014).
- 7C. W. Brennan, R. G. Verhaak, A. McKenna, B. Campos, H. Noushmehr, S. R. Salama, S. Zheng, D. Chakravarty, J. Z. Sanborn, S. H. Berman, R. Beroukhim, B. Bernard, C. J. Wu, G. Genovese, I. Shmulevich, J. Barnholtz-Sloan, L. Zou, R. Vegesna, S. A. Shukla, G. Ciriello, W. K. Yung, W. Zhang, C. Sougnez, T. Mikkelsen, K. Aldape, D. D. Bigner, E. G. Van Meir, M. Prados, A. Sloan, K. L. Black, J. Eschbacher, G. Finocchiaro, W. Friedman, D. W. Andrews, A. Guha, M. Iacocca, B. P. O'Neill, G. Foltz, J. Myers, D. J. Weisenberger, R. Penny, R. Kucherlapati, C. M. Perou, D. N. Hayes, R. Gibbs, M. Marra, G. B. Mills, E. Lander, P. Spellman, R. Wilson, C. Sander, J. Weinstein, M. Meyerson, S. Gabriel, P. W. Laird, D. Haussler, G. Getz, and L. Chin, Cell 155 (2), 462–477 (2013).
- 8J. S. Smith, A. Perry, T. J. Borell, H. K. Lee, J. O'Fallon, S. M. Hosek, D. Kimmel, A. Yates, P. C. Burger, B. W. Scheithauer, and R. B. Jenkins, J Clin Oncol 18 (3), 636–645 (2000).
- 9N. A. Markwardt, N. Haj-Hosseini, B. Hollnburger, H. Stepp, P. Zelenkov, and A. Rühm, J Biophotonics, doi: 10.1002/jbio.201500195 (2015).
- 10S. A. Prahl, Optical Absorption of Hemoglobin, tabulated data compiled from various sources (1999), http://omlc.ogi.edu/spectra/hemoglobin.
- 11A. V. Kulkarni, A. Guha, A. Lozano, and M. Bernstein, J Neurosurg 89 (1), 31–35 (1998).
- 12M. J. McGirt, G. F. Woodworth, A. L. Coon, J. M. Frazier, E. Amundson, I. Garonzik, A. Olivi, and J. D. Weingart, J Neurosurg 102 (5), 897–901 (2005).
- 13R. Dammers, I. K. Haitsma, J. W. Schouten, J. M. Kros, C. J. Avezaat, and A. J. Vincent, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150 (1), 23–29 (2008).
- 14M. Nishihara, T. Sasayama, H. Kudo, and E. Kohmura, The Kobe journal of medical sciences 56 (4), E148–E153 (2011).
- 15A. A. Shakal and E. A. Mokbel, J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 75 (3), 177–182 (2014).
- 16D. Kondziolka, A. D. Firlik, and L. D. Lunsford, Neurol Clin 16 (1), 35–54 (1998).
- 17R. Grossman, S. Sadetzki, R. Spiegelmann, and Z. Ram, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147 (6), 627–631 (2005).
- 18J. Gilsbach, M. Mohadjer, and F. Mundinger, Acta Neurochir (Wien) 89 (1–2), 77–79 (1987).
- 19K. Wardell, S. Hemm-Ode, P. Rejmstad, and P. Zsigmond, Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 94 (1), 1–9 (2016).
- 20W. Göbel, D. Brucker, Y. Kienast, A. Johansson, G. Kniebühler, A. Rühm, S. Eigenbrod, S. Fischer, M. Goetz, F. W. Kreth, A. Ehrhardt, H. Stepp, K. M. Irion, and J. Herms, Opt Express 20 (24), 26117–26126 (2012).
- 21A. Goyette, J. Pichette, M. A. Tremblay, A. Laurence, M. Jermyn, K. Mok, K. D. Paulsen, D. W. Roberts, K. Petrecca, B. C. Wilson, and F. Leblond, Opt Lett 40 (2), 170–173 (2015).
- 22J. Pichette, A. Goyette, F. Picot, M. A. Tremblay, G. Soulez, B. C. Wilson, and F. Leblond, Biomed Opt Express 6 (11), 4238–4254 (2015).
- 23K. Wardell, P. Blomstedt, J. Richter, J. Antonsson, O. Eriksson, P. Zsigmond, A. T. Bergenheim, and M. I. Hariz, Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85 (6), 279–286 (2007).
- 24K. Wardell, P. Zsigmond, J. Richter, and S. Hemm, Neurosurgery 72 (2 Suppl Operative), 127–140; discussion 140 (2013).
- 25 Directive 2006/25/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 April 2006 on the minimum health and safety requirements regarding the exposure of workers to risks arising from physical agents (artificial optical radiation) (19th individual Directive within the meaning of Article 16(1) of Directive 89/391/EEC) < http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:02006L0025-20140101&from=EN>
- 26S. C. Gebhart, W. C. Lin, and A. Mahadevan-Jansen, Phys Med Biol 51 (8), 2011–2027 (2006).
- 27A. N. Yaroslavsky, P. C. Schulze, I. V. Yaroslavsky, R. Schober, F. Ulrich, and H. J. Schwarzmaier, Phys Med Biol 47 (12), 2059–2073 (2002).
- 28T. J. Beck, W. Beyer, T. Pongratz, W. Stummer, R. Waidelich, H. Stepp, S. Wagner, and R. Baumgartner, in: Proc. SPIE, Photon Migration and Diffuse-Light Imaging, 2003.
- 29R. Michels, F. Foschum, and A. Kienle, Opt Express 16 (8), 5907–5925 (2008).
- 30N. Bosschaart, G. J. Edelman, M. C. Aalders, T. G. van Leeuwen, and D. J. Faber, Lasers Med Sci 29 (2), 453–479 (2014).
- 31A. Rühm, W. Göbel, R. Sroka, and H. Stepp, Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 11 (3), 307–318 (2014).
- 32V. Tuchin,
Tissue Optics – Light Scattering Methods and Instruments for Medical Diagnosis
(SPIE, Bellingham,
Washington, USA,
2015), pp.
247–294.
10.1117/3.1003040 Google Scholar
- 33I. J. Bigio and S. Fantini, Quantitative Biomedical Optics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2016), pp. 229ff., esp. Fig. 8.2.
- 34C. Mansouri and N. H. Kashou, Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009, 1457–1460 (2009).
- 35L. Wang and H.-I. Wu, Biomedical Optics: Principles and Imaging (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007), pp. 98–99.
- 36B. W. Pogue and M. S. Patterson, J Biomed Opt 11 (4), 041102 (2006).
- 37M. Nitzan, A. Romem, and R. Koppel, Medical devices 7, 231–239 (2014).
- 38K. H. Shelley, Anesthesia and analgesia 105 (6 Suppl), S31–S36 (2007).
- 39J. Allen, Physiological measurement 28 (3), R1–R39 (2007).
- 40A. S. Echiadis, V. P. Crabtree, J. Bence, L. Hadjinikolaou, C. Alexiou, T. J. Spyt, and S. Hu, Physiological measurement 28 (8), 897–911 (2007).
- 41K. H. Shelley, D. Tamai, D. Jablonka, M. Gesquiere, R. G. Stout, and D. G. Silverman, Anesthesia and analgesia 100 (3), 743–747 (2005).
- 42G. E. Nilsson,
E. G. Salerud,
N. O. T. Strömberg, and
K. Wardell,
Laser Doppler perfusion monitoring and imaging.
Biomedical Photonics Handbook
(editor: Tuan Vo-Dinh): Chapter 15
(CRC Press Boca Raton,
Florida, USA,
2003), pp.
15.1–15.24
10.1201/9780203008997.ch15 Google Scholar
- 43I. Fredriksson, C. Fors, and J. Johansson, Laser Doppler Flowmetry – a Theoretical Framework, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Linköping University (2007), www.imt.liu.se/bit/ldf/ldfmain.html.
- 44A. Hagen, D. Grosenick, R. Macdonald, H. Rinneberg, S. Burock, P. Warnick, A. Poellinger, and P. M. Schlag, Opt Express 17 (19), 17016–17033 (2009).