Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Perspectives on liquid biopsy for label-free detection of “circulating tumor cells” through intelligent lab-on-chips (View 3/2020)
- First Published: 22 September 2020

In article number 20200034, Pietro Ferraro and co-workers emphasize that early detection in cancer diseases is a key issue. The current state of the art of technology could allow a great opportunity for this purpose, to develop systems for detecting circulating cancer cells (CTC) in the blood. The challenge is to recognize and classify cancer cells and detect them non-invasively through a lab-on-chip device as they flow. Single-cell holographic phase contrast tomography offers the possibility in the real world to detect CTC in a label-free mode by means of morphological analyzes when combined with artificial intelligence (AI). The cover summarizes and depicts the main concepts and the technological ingredients necessary to achieve such an ambitious goal, namely the recognition and sorting of cells, 3D-imaging by microscope and complete morphological analysis of 3D-phase-contrast tomograms by AI tools.
INSIDE FRONT COVER
Inside Front Cover: CRISPR-Cas system for biomedical diagnostic platforms (View 3/2020)
- First Published: 22 September 2020

In article number 20200008, Wenguo cui and co-workers demonstrate clustered short palindrome repeats with regular intervals, abbreviated as CRISPR, functions as a self-defense system for prokaryotes, detecting particular pathogenic nucleic acid, interfering with the functions of exoteric DNA and protecting them against foreign invaders. The CRISPR-Cas system is a prokaryotic immune system that confers resistance to foreign genetic elements such as those present within plasmids and phages that provides a form of acquired immunity. RNA harboring the spacer sequence helps Cas (CRISPR-associated) proteins recognize and cut foreign pathogenic DNA. Pathogens especially with the characteristic of infection have become one of serve diseases which threatens people with health and living quality in metropolis like Shanghai, a world-famous cosmopolitan city. Over the last two decades, remarkable achievement has been made considering the development of CRISPR-Cas system based diagnostic methods and engineering these modules to suit or enable various pathogens detection. All told, it opened a new window in the clinical laboratory with remarkable convenience, sensitivity and specificity, and has the potential for not only pathogen detection during daily practice or pandemic, such as novel coronavirus disease outbreak in 2019, but also cancer and genetic diseases.
INSIDE BACK COVER
Inside Back Cover: Granular hydrogels for 3D bioprinting applications (View 3/2020)
- First Published: 22 September 2020

In article number 20200060, Ziyi Yu and co-workers describe how current challenges of the three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting could be addressed by using granular hydrogels. Granular hydrogels are shear thinning and seal-healing, enable higher printing performance and the creation of better physiological conditions for hetero-cellular constructs. Recent advances in the use of jamming transition of granular hydrogels represent a potential paradigm shift in the 3D bioprinting. This cover art shows the use of granular hydrogels for supporting baths and bioinks in the extrusion-based 3D bioprinting.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Emerging nanobiomaterials against bacterial infections in postantibiotic era
- First Published: 08 August 2020
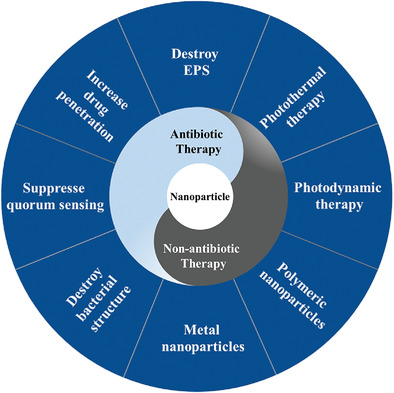
Nanomaterials, with outstanding performance including size effect, specific physicochemical property, and easy modification, show immense potential as enhancers or therapeutic agents to treat bacterial infections with antibiotic resistance. In this review, the authors have summarized the underlying causes of antibiotic resistance. Subsequently, the promising therapeutic strategies by using nanomaterials to treat bacterial infections with severe antibiotic resistance are summarized and discussed.
Perspectives on liquid biopsy for label-free detection of “circulating tumor cells” through intelligent lab-on-chips
- First Published: 27 August 2020
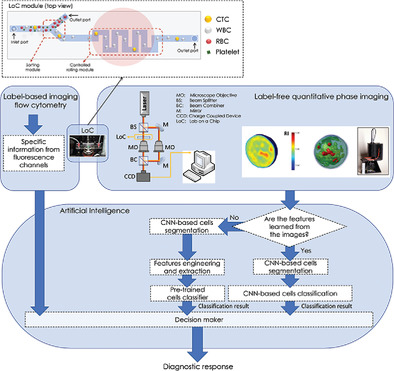
The most promising approach to liquid biopsy has its roots in the smart integration between label-free quantitative phase microscopy, accurate manipulation of microfluidic streams, and artificial intelligence. Lab-on-a-chip devices with embedded imaging functions can now rely on robust deep learning architectures to generate accurate classification results from single-cell analysis of blood flows. Flow engineering allows sorting and controlling the rotation of blood components, thus permitting added-value high-throughput tomographic inspection of circulating tumor cells.
Materdicine: Interdiscipline of materials and medicine
- First Published: 16 July 2020
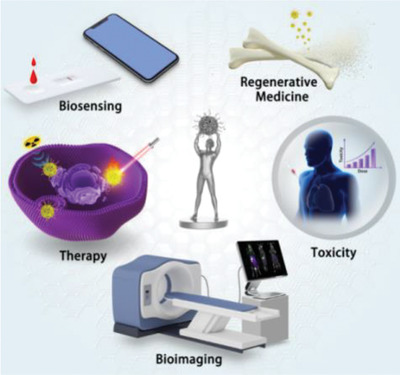
This review proposes and highlights the perspective of materdicine, providing a deep discussion on the rational design, construction, and application of versatile biomaterials/medmaterials with unique physiochemical property and specific biological effects for disease diagnosis and treatment from a broad perspective, especially on nanoscale biomaterials.
Leveraging metal oxide nanoparticles for bacteria tracing and eradicating
- First Published: 04 August 2020
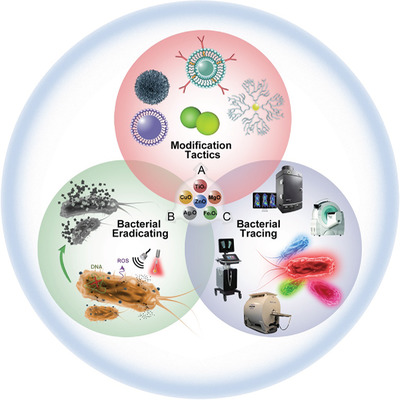
In the antimicrobial stewardship, metal oxide nanoparticles receive great attention due to their distinctive performance for bacterial tracing and eradicating. In this review, the authors examine a critical analysis of antimicrobial mechanisms, physicochemical characteristics, and modification strategies for metal oxide nanoparticles. The diagnosis of metal oxide nanoparticles for bacterial infections, coupled with their potential for bacterial theranostics, has been highlighted.
Recent advances in theranostic agents based on natural products for photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy
- First Published: 25 July 2020
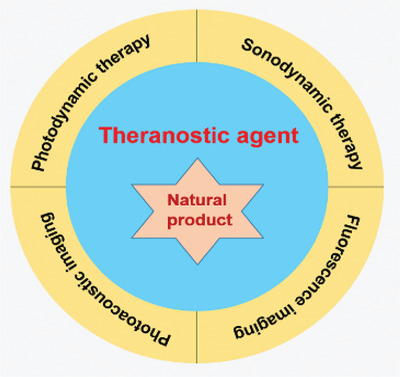
In this review, the authors summarize recent advances in theranostic agents for natural products categorized as porphyrins, perylenequinone, curcumin, and others. Some representative examples of disease diagnosis in fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging and disease treatment in PDT/SDT are introduced. Potential limitations and future perspectives of these natural products for theranostic agents are also discussed.
CRISPR-Cas system for biomedical diagnostic platforms
- First Published: 25 July 2020
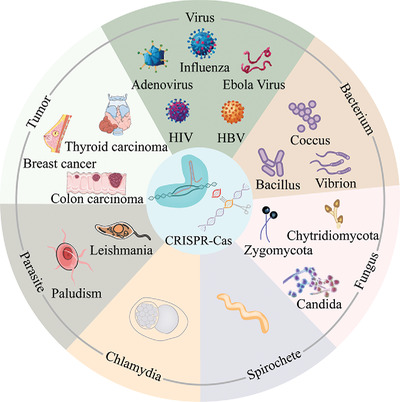
CRISPR-Cas–based diagnostic tests have been the frontline of various pathogenic factors detection including virus, bacterium, fungus, spirochete, chlamydia, and parasite, during daily practice or pandemic, as well as have the potential to screen for carcinogenic mutations and genetic diseases. The CRISPR-Cas–based diagnostics open a new window in the clinical laboratory with remarkable convenience, sensitivity, and specificity, bringing forth revolutionized diagnostic development.
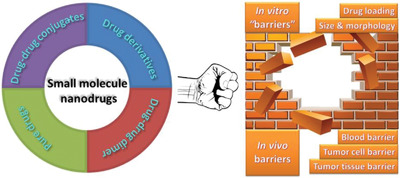
Engineering small molecule nanodrugs to overcome barriers for cancer therapy
- First Published: 26 July 2020
MINI-REVIEWS
Magnetic iron oxide nanomaterials: A key player in cancer nanomedicine
- First Published: 21 July 2020
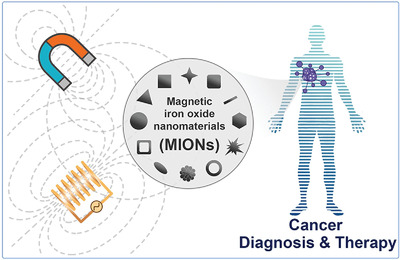
Magnetic iron oxide nanomaterials (MIONs) belong to the most widely studied candidates for cancer nanomedicine because of their biocompatibility, abundant raw materials, and especially, their diverse physicochemical properties and biological effects. This mini review presents an up-to-date overview of MIONs-based cancer nanomedicines with an emphasis on bioimaging and therapy.
Swimming nanorobots for opening a cell membrane mechanically
- First Published: 21 July 2020
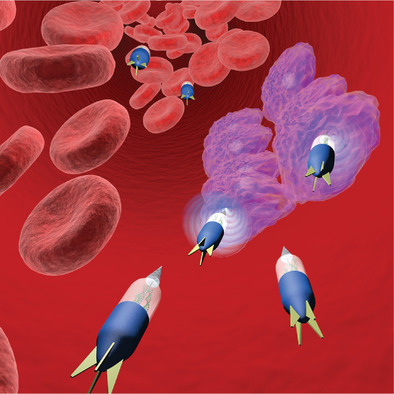
Swimming nanorobot is a powerful technique to actively pass through various biological barriers. Swimming nanorobots capable of mechanically opening the cell membrane are reviewed, because the cell membrane is a key biological barrier for various biomedical applications ranging from drug delivery to artificial insemination.
Granular hydrogels for 3D bioprinting applications
- First Published: 15 July 2020
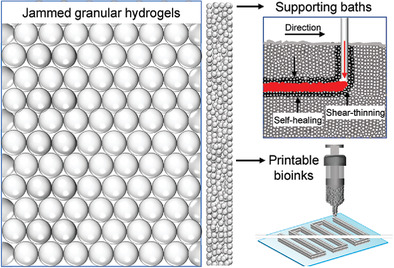
Granular hydrogels are the conglomerations of micrometer-sized hydrogel particles with impressive properties such as biocompatible, self-healing, and shear-thinning. In this review, the authors discuss how current challenges of three-dimensional (3D) bioprintings could be addressed by using granular hydrogels, acting as either novel supporting baths or printable bioinks.