Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
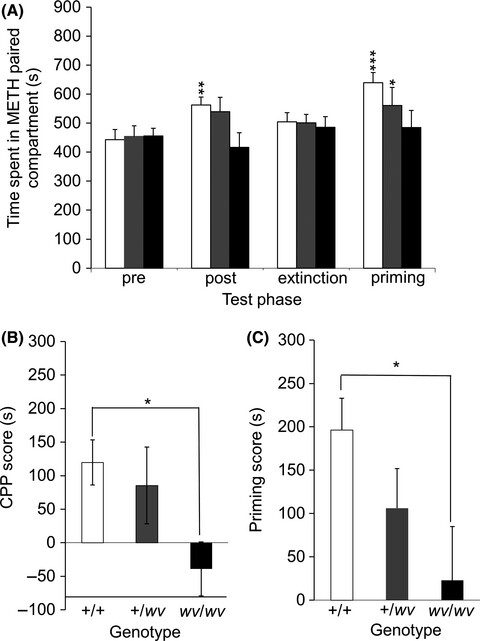
Absence of methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference in weaver mutant mice
- Pages: 324-331
- First Published: 19 August 2020
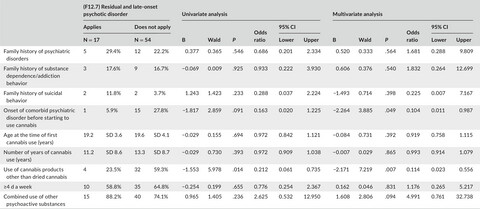
Risk factors for the onset of dependence and chronic psychosis due to cannabis use: Survey of patients with cannabis-related psychiatric disorders
- Pages: 332-341
- First Published: 07 September 2020
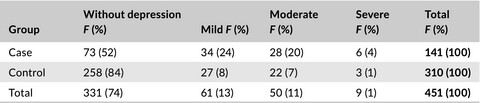
Validity of self-reporting depression in the Tabari cohort study population
- Pages: 342-347
- First Published: 19 September 2020
Noradrenaline enhances the excitatory effects of dopamine on medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons in rats
- Pages: 348-354
- First Published: 08 September 2020
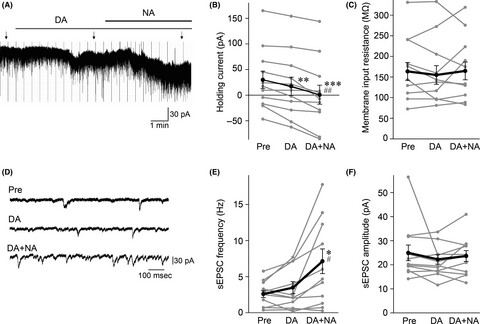
Our previous studies showed that exposure to acute restraint stress enhanced cocaine-induced conditioned place preference (cocaine-CPP). The present study revealed that noradrenaline enhanced the excitatory effects of dopamine on medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) pyramidal neurons in rats. Noradrenaline released by restraint stress exposure may cooperate with dopamine to stimulate dopamine-responsive neurons in the mPFC, thereby causing the stress-induced enhancement of cocaine-CPP.
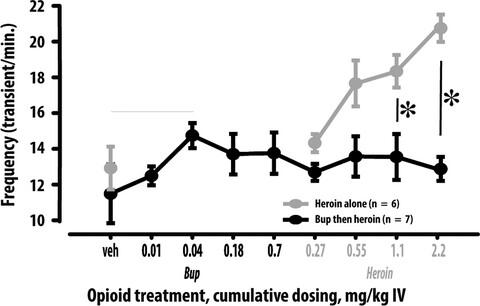
Buprenorphine is a weak dopamine releaser relative to heroin, but its pretreatment attenuates heroin-evoked dopamine release in rats
- Pages: 355-364
- First Published: 15 September 2020
High-dose antipsychotic drug use as a predictor for readmission of inpatients with borderline personality disorder: A retrospective chart review in a Japanese psychiatric hospital
- Pages: 365-370
- First Published: 10 October 2020
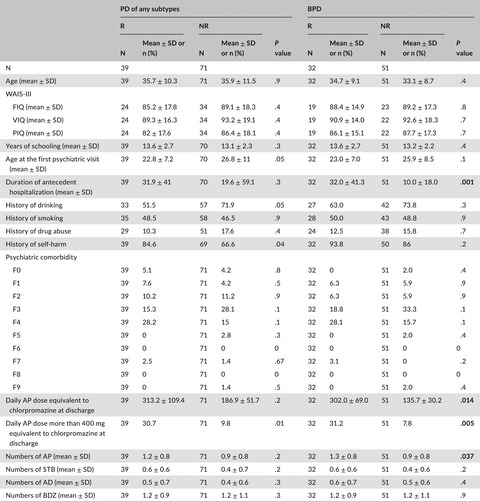
There is limited available information regarding predictors associated with repetitive admission of patients with BPD. This study aimed to evaluate predictors associated with readmission of inpatients with BPD. 1. Multivariate logistic regression analyses revealed that the use of antipsychotics equivalent to >400 mg of chlorpromazine at discharge was associated with readmission within 1 year. 2. High-dose antipsychotic drug use at discharge may be a risk factor for readmissions.
Visually cued fear conditioning test for memory impairment related to cortical function
- Pages: 371-375
- First Published: 21 October 2020
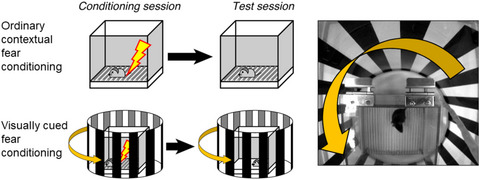
The visual stimulus of moving gratings could be distinguished from still gratings by mice, and moving gratings were related to footshock. The defect obtained here by low-frequency grating in MDGA1 deficient mice might reflect that the coarse gratings are less detectable in visual perceptions of the schizophrenic brain.
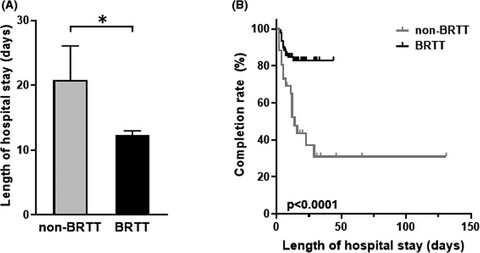
Retrospective analysis of heroin detoxification with buprenorphine in a psychiatric hospital in Japan
- Pages: 376-382
- First Published: 27 October 2020
CASE REPORTS
Non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder successfully treated with the combination of ramelteon and suvorexant in a case of autism spectrum disorder
- Pages: 383-387
- First Published: 29 September 2020
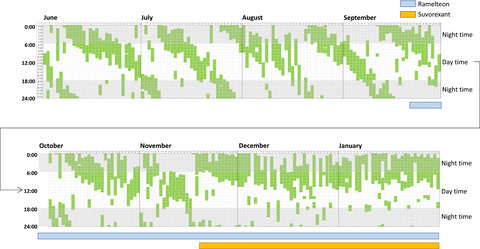
We present a case in which the combination therapy of ramelteon and suvorexant was effective for a patient with autism spectrum disorder with non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder (N24SWD) owing to social withdrawal. Here, we discussed the pharmacological mechanism of the combination of ramelteon and suvorexant as a possible therapeutic strategy for patients with N24SWD.
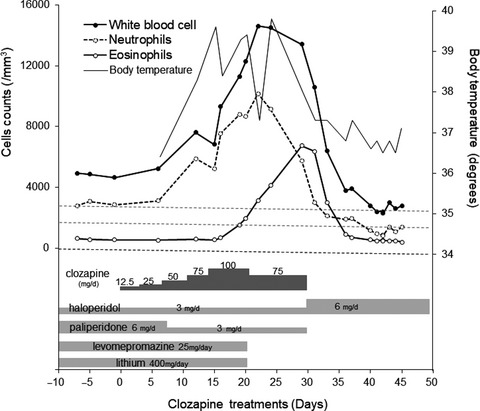
Clozapine-associated severe eosinophilia following lithium rebound neutropenia: A case report
- Pages: 388-391
- First Published: 19 September 2020
MICRO REVIEW
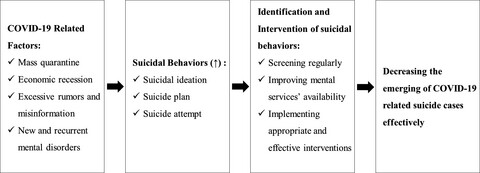
Raising awareness of suicide prevention during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 392-395
- First Published: 06 October 2020
MICRO REPORTS
Forskolin rapidly enhances neuron-like morphological change of directly induced-neuronal cells from neurofibromatosis type 1 patients
- Pages: 396-400
- First Published: 10 October 2020
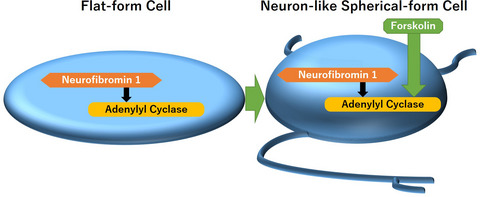
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is highly comorbid with neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and learning disorder, and underlying mechanisms have not been well clarified. We herein showed that forskolin, an AC activator, rapidly enhances neuron-like morphological change of directly induced-neuronal (iN) cells from NF1 patients. The present pilot data using the direct conversion technology indicate that forskolin or AC activators may have therapeutic effects on the growth of neuronal cells in NF1 patients.
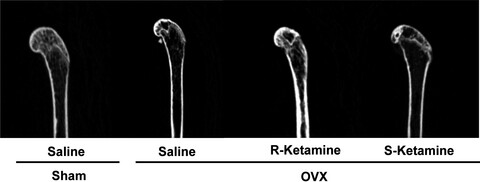
Decreased bone mineral density in ovariectomized mice is ameliorated after subsequent repeated intermittent administration of (R)-ketamine, but not (S)-ketamine
- Pages: 401-406
- First Published: 19 August 2020
Neuropsychological characteristics of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder without intellectual disability
- Pages: 407-411
- First Published: 30 August 2020
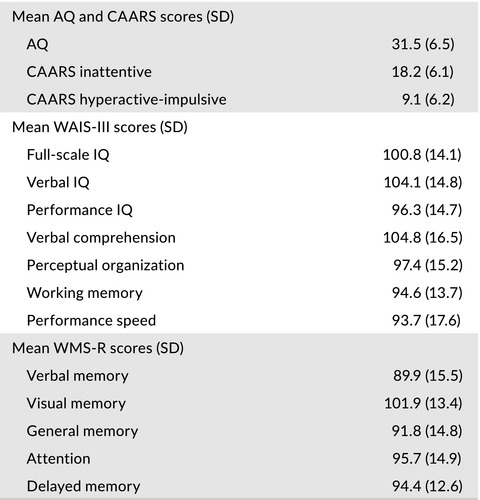
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Third Edition (WAIS-III) and Wechsler Memory Scale—Revised (WMS-R) of 30 adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were examined. The verbal intelligence quotient was significantly higher than the performance intelligence quotient in the WAIS-III and the performance intelligence quotient was significantly correlated with the visual memory and attention scores of the WMS-R. Adults with ADHD have comparatively high verbal comprehension and social knowledge, while their information processing ability and visual-motor coordination are relatively weak.
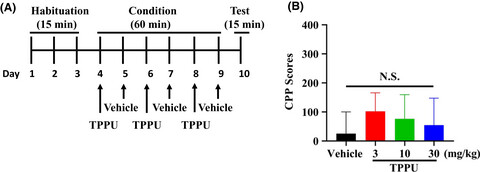
Lack of rewarding effects of a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU in mice: Comparison with morphine
- Pages: 412-416
- First Published: 07 September 2020
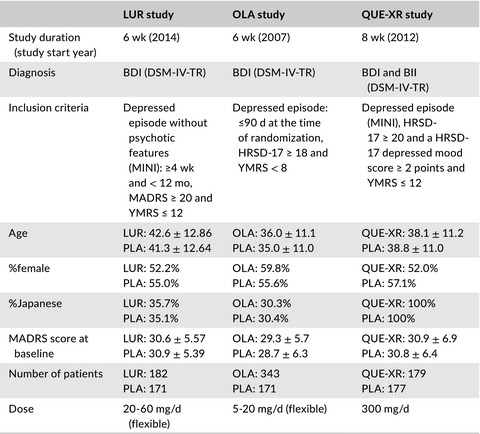
Lurasidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine extended-release for bipolar depression: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of phase 3 trials in Japan
- Pages: 417-422
- First Published: 09 September 2020
Use of the Illumina EPIC methylation array for epigenomic research in the crab-eating macaque (Macaca fascicularis)
- Pages: 423-426
- First Published: 10 October 2020
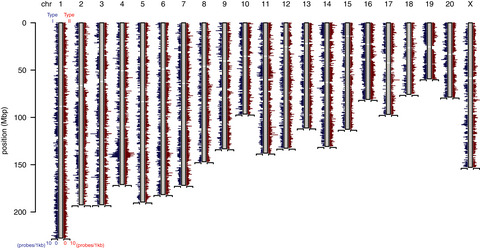
Epigenetic research in the non-human primates, such as crab-eating macaque, will be important to understand the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Among the methylation array probes for human genome, the probes that can reliably measure DNA methylation levels of the crab-eating macaque are reported.