Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image: Role of pressure in flow-induced shish-kabab in binary blend of long- and short-chain Polyethylenes
- First Published: 25 March 2020

Polymer Crystallization Research in China
In article e10008, Xi-Xi Zhang and colleagues studied the formation of shish-kebabs induced by flow under pressure in a binary blend of long- and short-chain polyethylene. The results of their experiments indicated a synergetic effect between pressure and long-chain on the formation of shish-kebab after flow. Under pressure, flow-induced oriented chains or chain segments were greatly reserved, without fast relaxation. The probability of these oriented microstructures to develop into shishes was elevated by pressure, especially for long chains with natural slower reptation dynamics. Therefore, shish-kebab structures would be generated by flow easily with the coexistence of high pressure and long polymer chains. (DOI: 10.1002/pcr2.10059)
Conjugated polymer single crystals and nanowires
- First Published: 18 March 2019
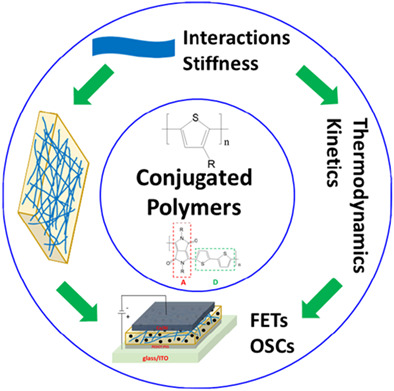
Conjugated polymers have many potential applications for preparation of organic optoelectronic devices. The structural features of conjugated polymers can be divided into two aspects: interchain interactions and backbone stiffness. Here, the authors review the preparation, structure, and device performance of conjugated polymer single crystals and nanowires. The purpose of this review is to summarize the research status of conjugated polymer single crystals and nanowires, as well as to note the difficulties in growing donor-acceptor conjugated polymer crystals.
Recent advances in crystallization and self-assembly of polypeptoid polymers
- First Published: 01 April 2019
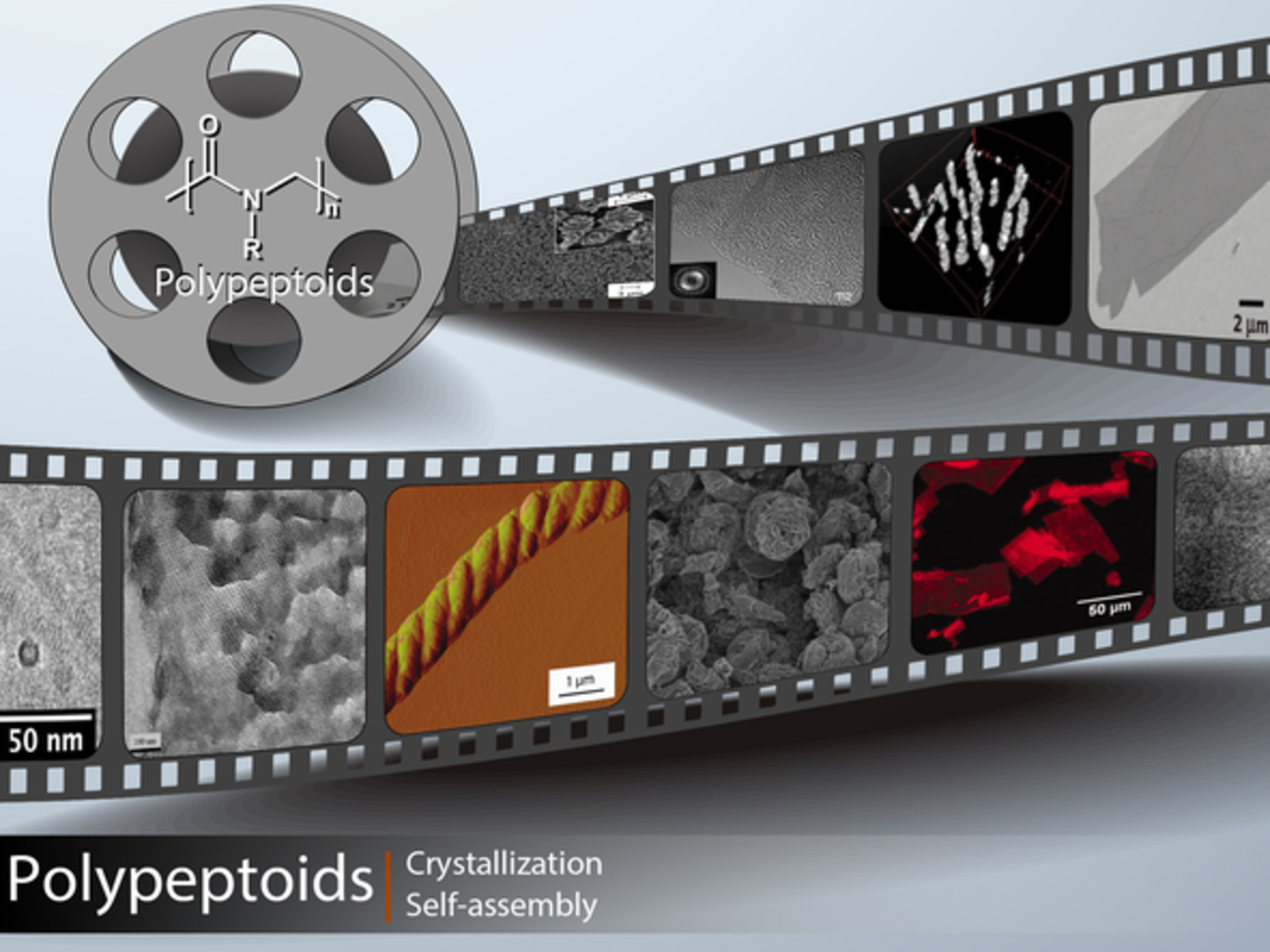
Polypeptoids represent a class of peptidomimetic polymers in which the substituent position is on the nitrogen atom instead of the α-carbon. The absence of intense inter- and intra-chain interactions allows for the high solubility and conformational flexibility of polypeptoid polymers. The modular and step-wise synthesis enables precise control of monomer sequences and chain architectures of polypeptoids, affording an ideal platform to fully explore crystallization and self-assembly of peptidomimetic polymers.
Interfacial effects on crystallization behavior of polymer nanocomposites with polymer-grafted nanoparticles
- First Published: 17 April 2019
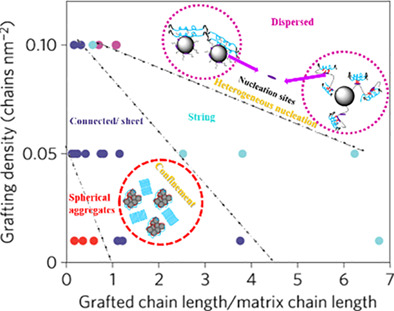
Polymer-grafted nanoparticles (PGNPs) have been increasingly explored in polymer nanocomposites (PNCs) with semi-crystalline polymers as the interfacial characteristics (e.g., conformation and segmental dynamics) can be controllable and tunable to tailor the crystallization behavior, which modifies the properties and hence determines the applications of PNCs. Two aspects that are central to optimizeing and predicting the promised properties of PNCs with PGNPs are discussed. These include (a) the factors that affect the polymer-nanoparticle interaction and (b) how they influence the crystallization properties.
Promoted stereocomplex formation and two-step crystallization kinetics of poly(l-lactic acid)/poly(d-lactic acid) blends induced by nucleator
- First Published: 15 January 2019
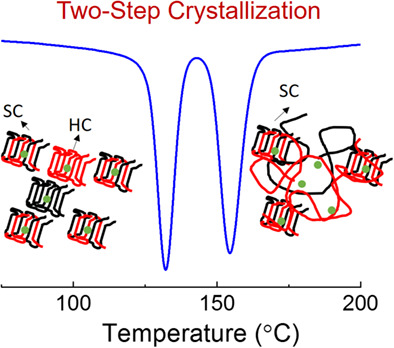
This study provides a simple yet efficient method to promote the stereocomplex (SC) crystallization of high-molecular-weight poly(l-lactic acid)/poly(d-lactic acid) (PLLA/PDLA) blends by adding a series of SC-type nucleators, that is, p-xylene bisalkyl urea compound. Because of the accelerated SC crystallization, nucleator-containing PLLA/PDLA blend exhibits unique two-step crystallization kinetics caused by the sequential formations of SCs and homocrystallites during crystallization.
Role of pressure in flow-induced shish-kabab in binary blend of long- and short-chain Polyethylenes
- First Published: 12 February 2019
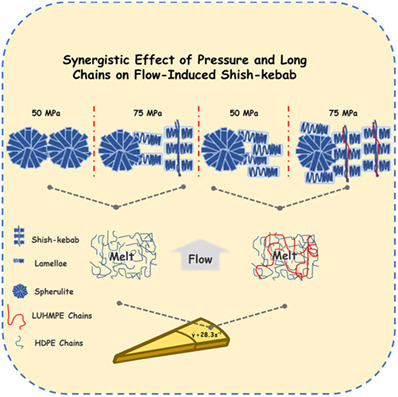
There is a synergistic effect between applied pressure and long polyethylene chains on flow-induced shish-kebab. At 50 MPa, no shish-kebab can be found in polyethylene short-chains (PE) and long−/short-chain blends (LUHMPE/PE). Whereas, at 75 MPa, shish-kebab structures are abundant in the LUHMPE/PE blends at the shear rate of 28.3 s−1, which is ascribed to the stabilizing effect of pressure on shear-induced long chains.
Formation and evolution of shish-kebab structure during hot stretching in gel-spun ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers with high concentration gel solution
- First Published: 21 February 2019
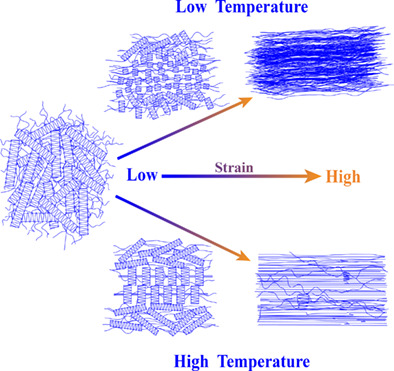
Formation and evolution of shish-kebab crystals of gel-spun ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers from high concentration gel solution during hot-stretching process were studied by in situ small-angle X-ray scattering and wide-angle X-ray diffraction measurements, differential scanning calorimetry, and scanning electron microscopy.
The structure transformation of pre-oriented polylactic acid film during uniaxial stretching at room temperature
- First Published: 22 May 2019