Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Influence of OCT3 and MATE2 Genetic Polymorphisms in Poor Response to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- First Published: 31 July 2024
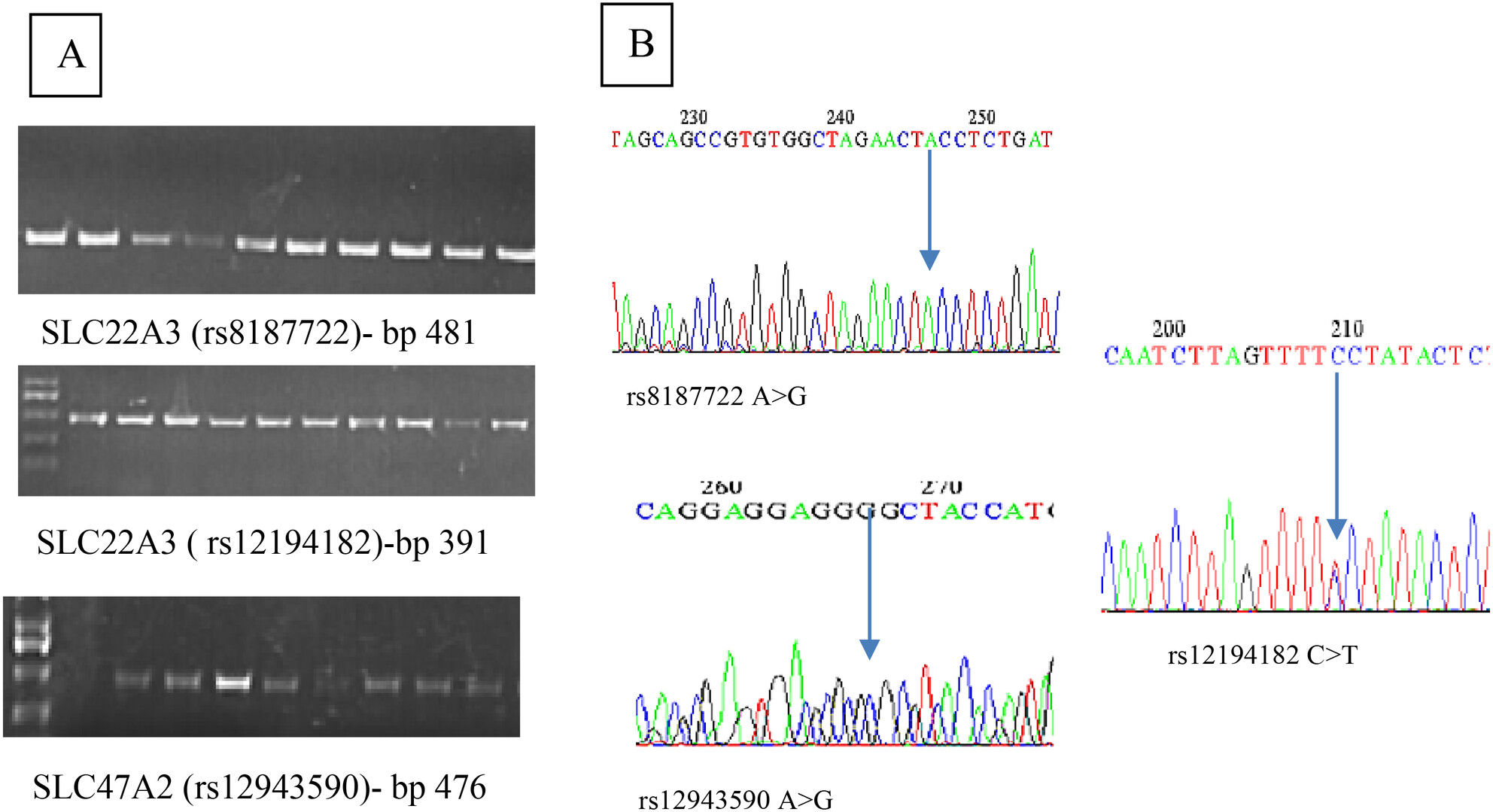
The genotypes of the rs12943590 variants of SLC47A2 showed no significant variance to the patient's response to metformin. The genotypes of the rs12194182 variants of SLC22A3 showed no significant variance to the patient's response to metformin. The genotypes of the rs8187722 variants of SLC22A3 showed no significant variance to the patient's response to metformin.
Daily Physical Activity Does Not Contribute to Differences in Muscle Oxidative Capacity Between Overweight and Obesity
- First Published: 14 August 2024
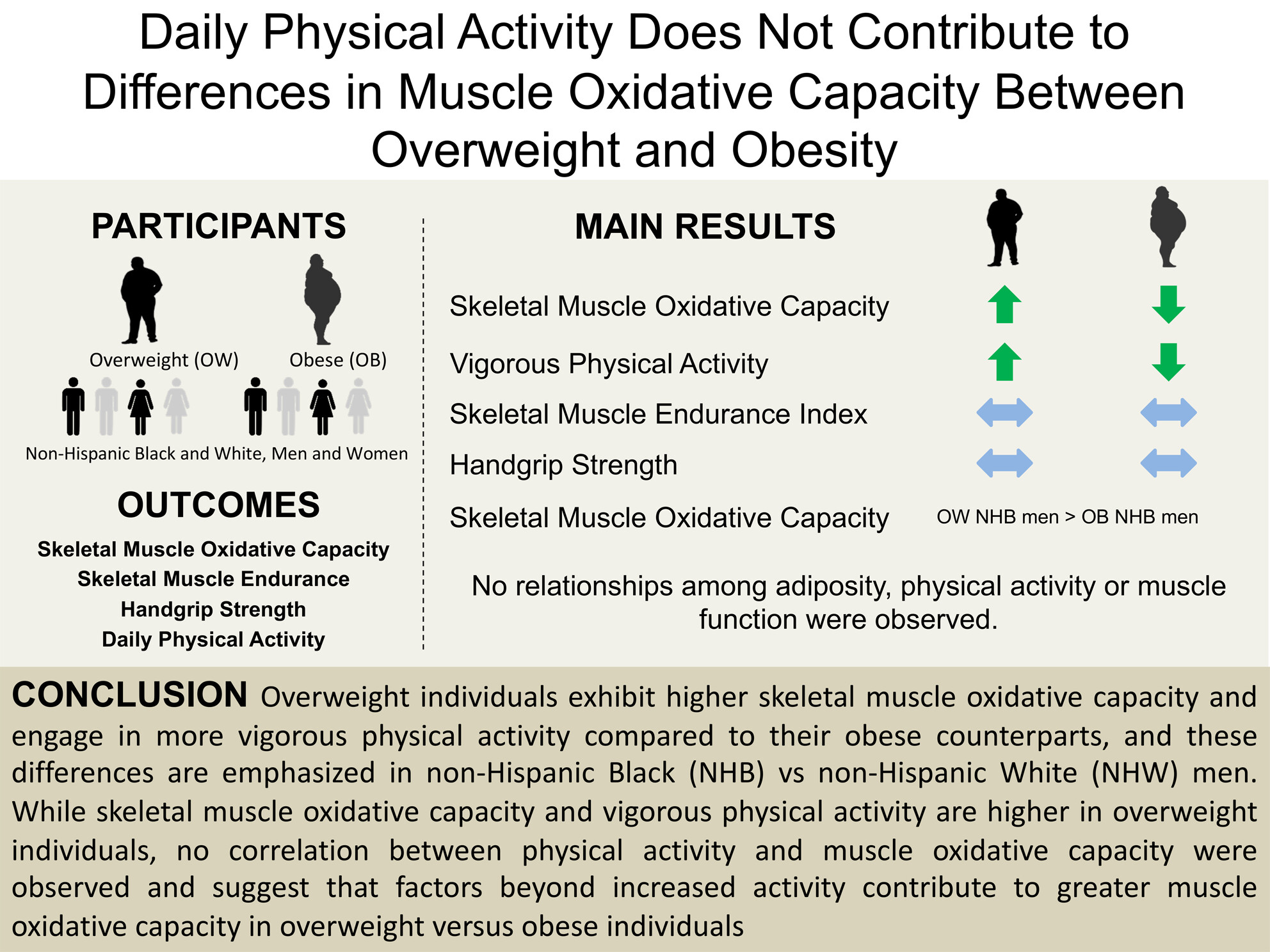
Overweight individuals exhibit higher skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and engage in more vigorous physical activity compared to their obese counterparts. No correlation between physical activity and muscle oxidative capacity were observed and suggest that factors beyond increased activity contribute to greater muscle oxidative capacity in overweight versus obese individuals.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
- First Published: 15 August 2024
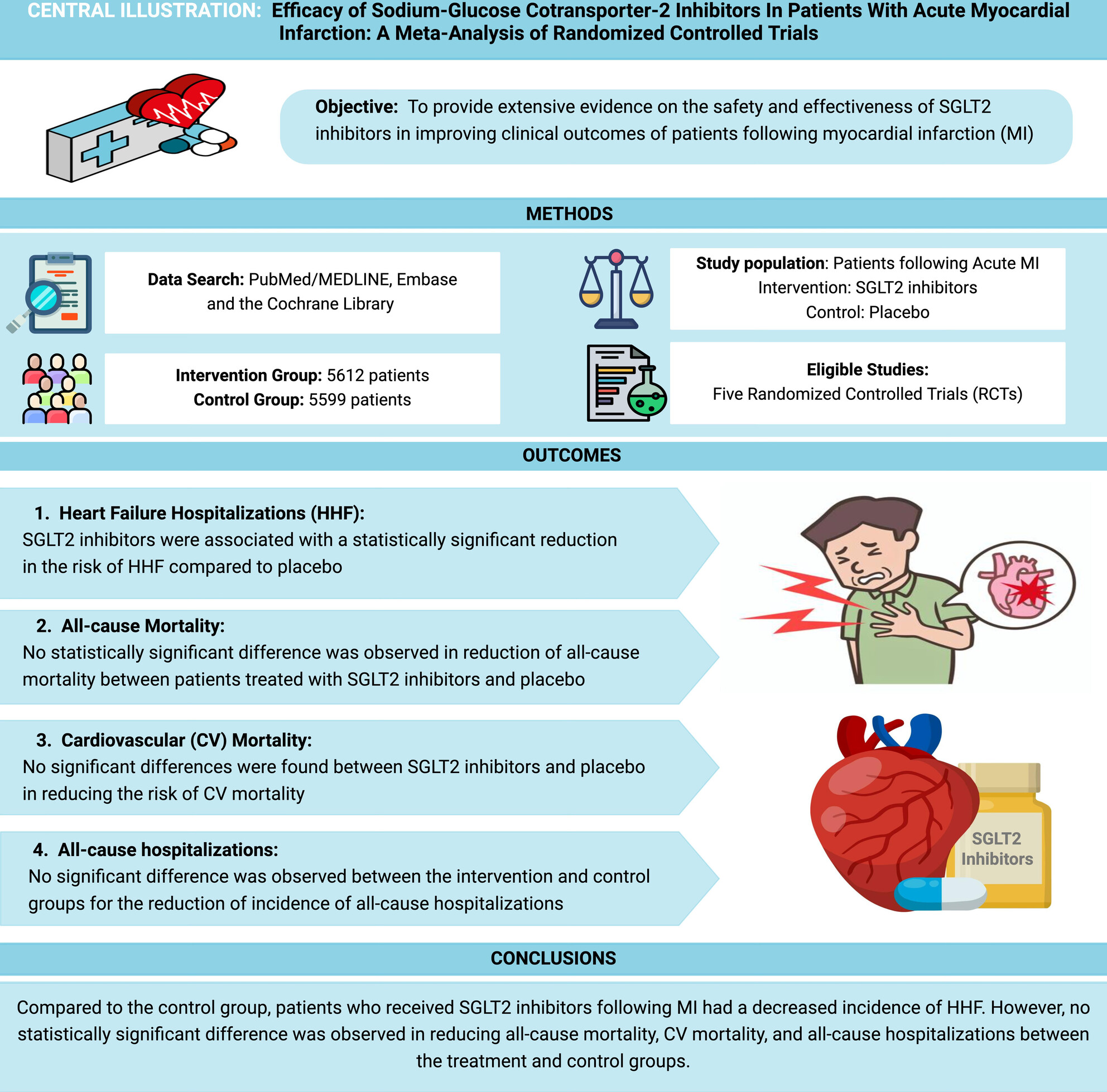
This meta-analysis of 11,211 patients demonstrates the efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors in reducing hospitalisations for heart failure in patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction. The risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality and all-cause hospitalisations remained comparable across the treatment and control groups.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
L-DOPA Test in the Diagnosis of Childhood Short Stature: Evaluation of Growth Hormone Peaks Over Time
- First Published: 30 August 2024
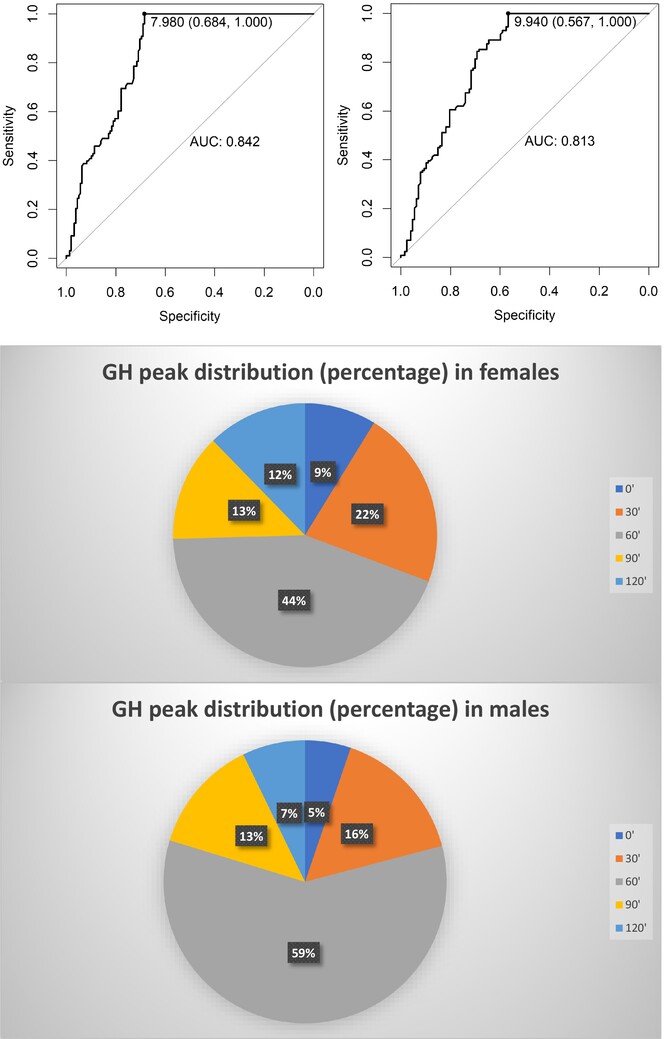
In childhood growth hormone deficiency (GHD) diagnosis is based on auxological assessment and biochemical provocative tests. We analysed the L-DOPA provocative test, evaluating GH peaks distribution over time and examining in detail the 120-min time, to assess the possibility of length reduction. We noticed that omitting 120-min time reduces test specificity, especially with GHD cut-off at 10 ng/mL.
Utility of Adrenal Vein Sampling With and Without Ultra-Low Dose ACTH Infusion in the Diagnostic Evaluation of Primary Aldosteronism
- First Published: 29 August 2024
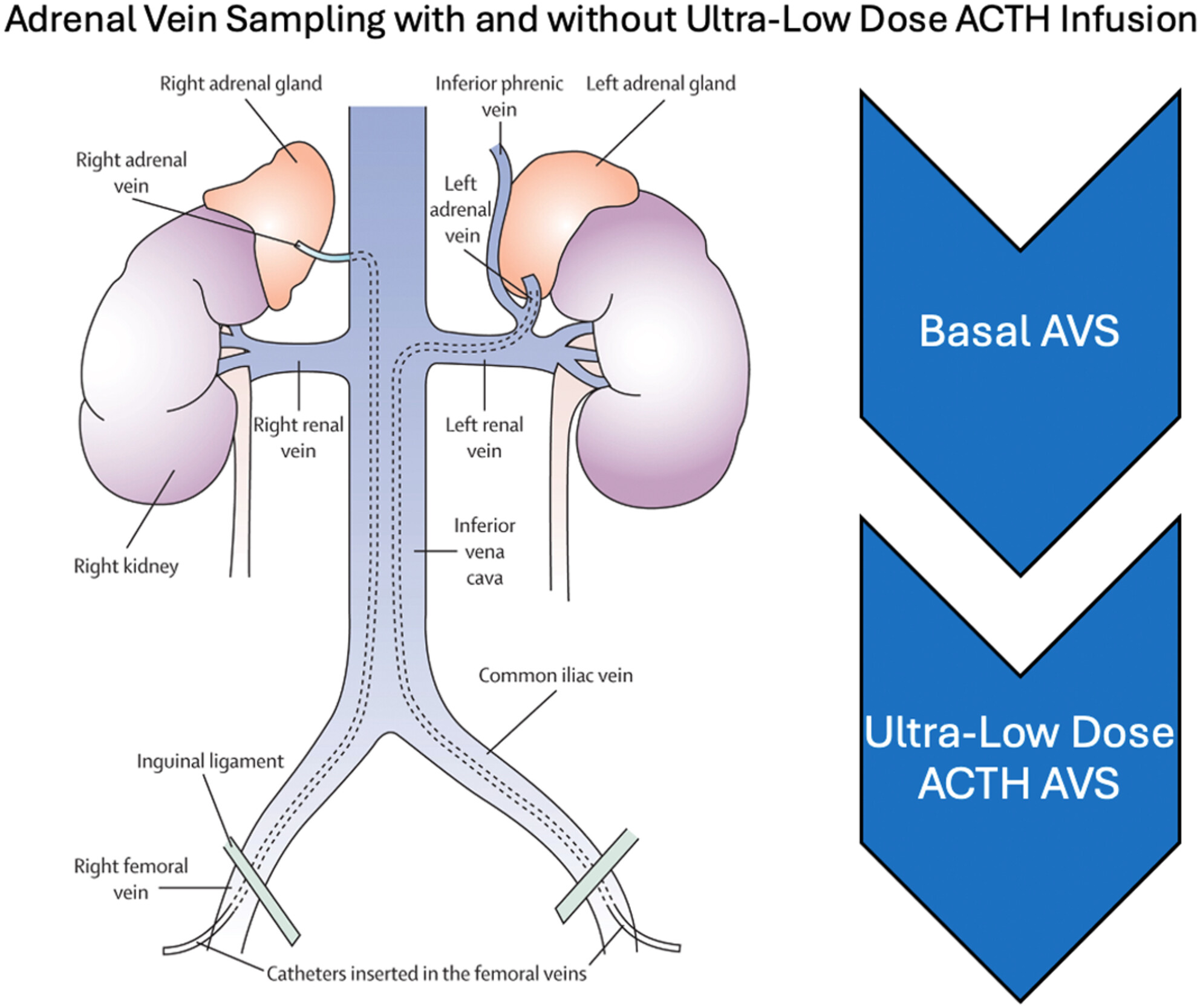
- AVS performed with ultra-low dose ACTH may mask lateralisation and does not obviate the need for non-ACTH AVS.
- Combined AVS with and without ultra-low dose ACTH can improve the diagnostic yield of the procedure, identifying additional cases of surgically remediable unilateral PA (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 296).
Enhanced Insulin Secretion Through Upregulation of Transcription Factors by Hydroalcoholic Extract of Securigera securidaca Seeds in Diabetic Animal Model
- First Published: 05 September 2024
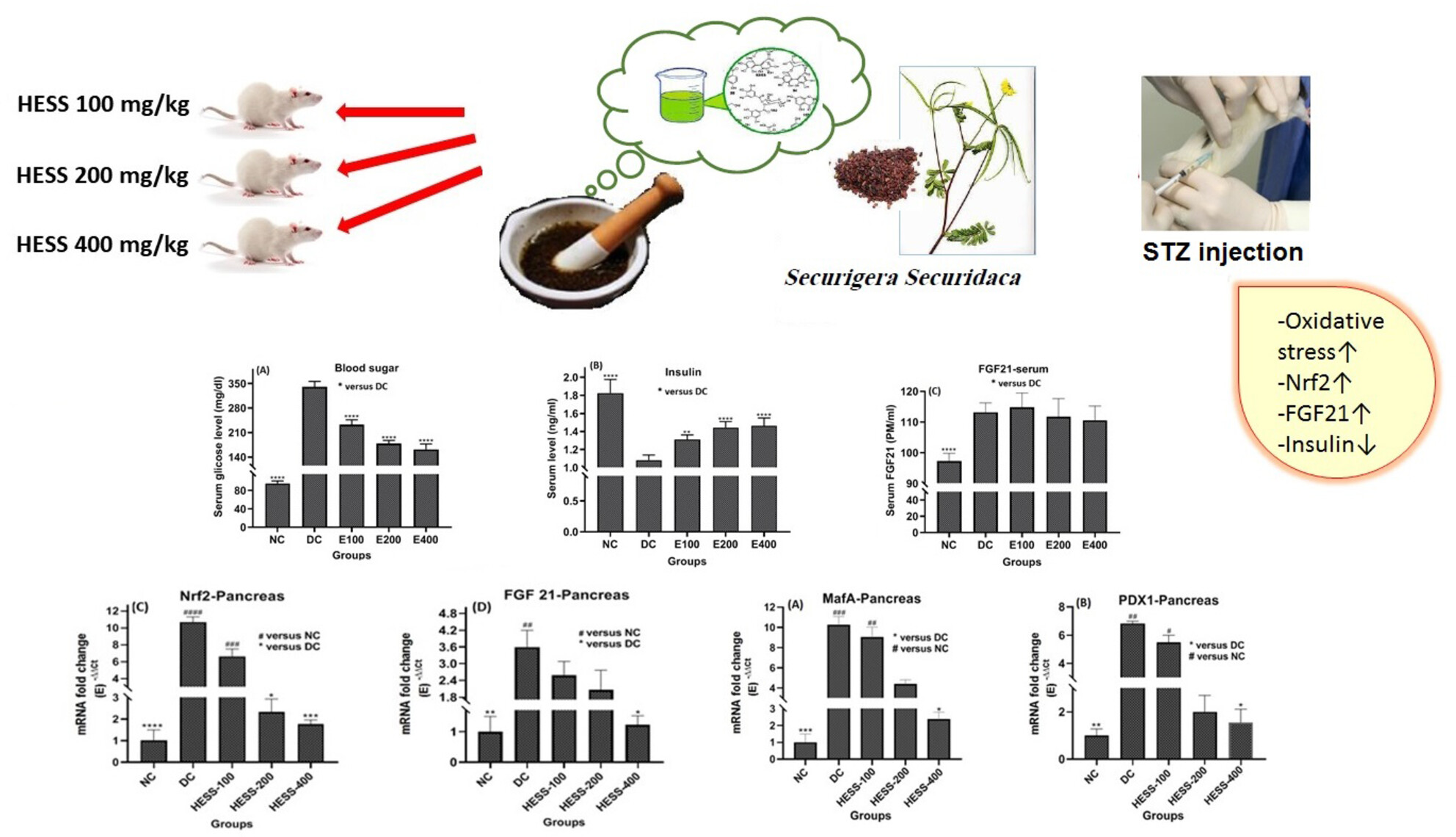
In the previous study, researchers observed an increase in insulin secretion in diabetic mice treated with STZ following treatment with hydroalcoholic extract of Securigera securidaca (HESS) seeds. This study focused on the relationship between the antioxidant properties of HESS at different doses and changes in the pancreatic tissue of diabetic mice, as well as the expression of genes that affect insulin secretion. It was found that HESS increases insulin secretion by reducing oxidative stress and tissue damage, as well as modulating the expression of genes related to insulin transcription factors PDX-1 and MafA. It was concluded that Securigera securidaca could be considered a good supplement alongside hypoglycemic medications for diabetic patients.