Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with hyperthyroidism attending a hospital endocrine clinic—A retrospective study
- First Published: 28 November 2018
Gonadal function and testicular histology in males with Prader-Willi syndrome
- First Published: 30 October 2018
Diabetes mellitus induced by somatostatin analogue therapy is not permanent in acromegalic patients
- First Published: 05 October 2018
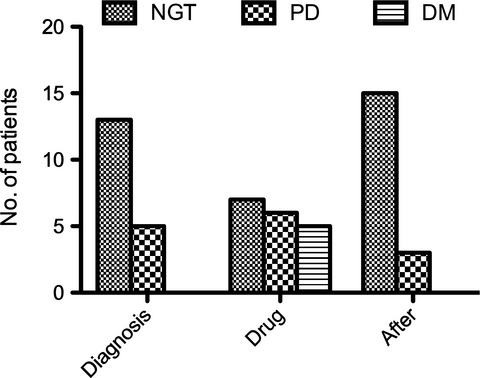
Therapy with somatostatin analogues in acromegalic patients may lead to the development of diabetes mellitus. Glycaemic alterations that develop during efficacious therapy with somatostatin analogues revert after drug withdrawal and cure of acromegaly with pituitary adenomectomy. In acromegalic patients with controlled disease, changes in glycaemic status induced by somatostatin analogues are not permanent.
Efficacy and safety of liraglutide added to insulin therapy in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 02 November 2018
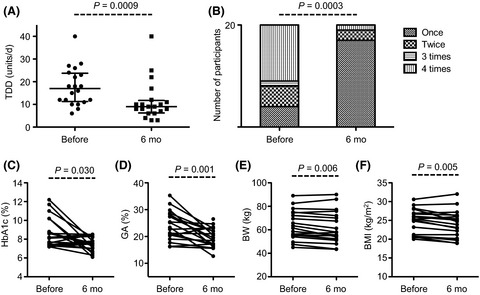
This study aimed to evaluate whether liraglutide added to insulin therapy safely improved glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes patients older than 65 years. We found that, in addition to safely improving glycaemic control, Lira administration also reduced body weight in elderly T2D patients undergoing insulin therapy.
Real-world GLP-1 RA therapy in type 2 diabetes: A long-term effectiveness observational study
- First Published: 19 November 2018
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on hypoglycaemia in brittle diabetic patients with decreased endogenous insulin secretion
- First Published: 01 December 2018
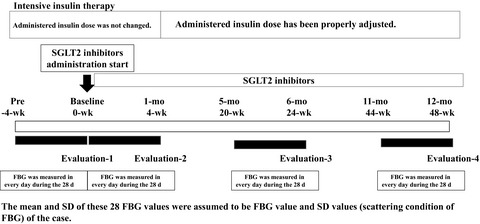
We conducted a study that targeted diabetic patients with a marked decline in endogenous insulin secretion and whose fasting blood glucose remains unstable even after receiving intensive insulin therapy. We verified the effect of SGLT2I add-on therapy on fasting blood glucose. As a result, high blood glucose values dropped, and the number of these events also decreased, but low blood glucose values did not drop any further, and the number of its occurrences increased. Despite this, the incidence of subjective hypoglycaemia reportedly decreased.
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor plus pioglitazone vs pioglitazone alone in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- First Published: 15 November 2018
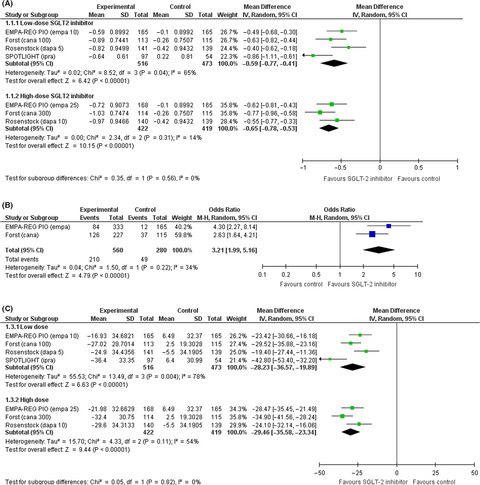
Compared to pioglitazone alone, SGLT-2 inhibitor plus pioglitazone improved glycemic control, reduced body weight and lowered blood pressure. The risks of death, hypoglycemia, and urinary tract infection were not different between active and control groups although genital tract infection was more frequently seen in SGLT-2 inhibitor group.
Estimation of magnesium level in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its correlation with HbA1c level
- First Published: 02 November 2018
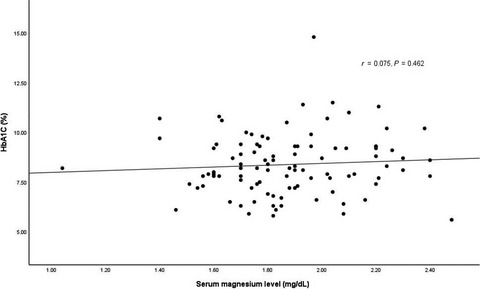
Hypomagnesaemia is linked to poor control of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The aim of this study was to measure serum magnesium level and the correlation of magnesium level with HbA1c. The majority of the patients had a normal level of magnesium (95.0%); however, most of them had uncontrolled blood glucose (82.0%). The study showed that the serum magnesium level and HbA1c are not significantly correlated (P = 0.462).
Progression of glucose-lowering diabetes therapy in TECOS
- First Published: 22 December 2018
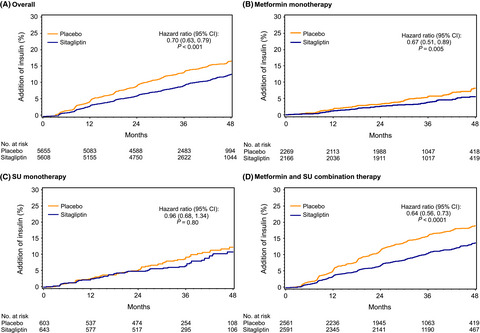
The TECOS study assessed the impact of sitagliptin compared to placebo on cardiovascular outcomes in 14 671 participants with type 2 diabetes over a median duration of 3 years. During the study, diabetes therapy was intensified in 25.2% of participants, most commonly by the addition of a sulfonylurea or insulin. A delay in the progression to insulin was observed in sitagliptin-treated participants who entered the study on metformin or metformin/sulfonylurea treatment
Tier 3 specialist weight management service and pre-bariatric multicomponent weight management programmes for adults with obesity living in the UK: A systematic review
- First Published: 25 October 2018
Although NHS England has recommended a multidisciplinary weight management services (MWMS -Tier 3 services) for patients requiring specialized management of obesity, including bariatric surgery, clinical and measurable health-related outcomes from these services remains fragmented. This systematic review of services in the UK for the management of patients with morbid obesity prior to bariatric surgery involved 19 studies (N = 11 735 patients). We report that Tier 3 and MWMPs have a short to mid-ranged positive effect on obese patients (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) living in the UK regarding accumulated reduction in weight, glycaemic control, BP and with subtle improvements in physical activity.