Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
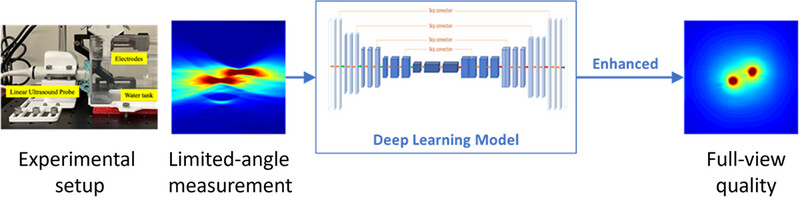
Enhanced Electroacoustic Tomography with Supervised Learning for Real-time Electroporation Monitoring
- Pages: 110-118
- First Published: 22 September 2024
Clinical results of definitive radiotherapy for local recurrent kimura disease in the head and neck after surgery: A retrospective study
- Pages: 119-125
- First Published: 21 August 2024
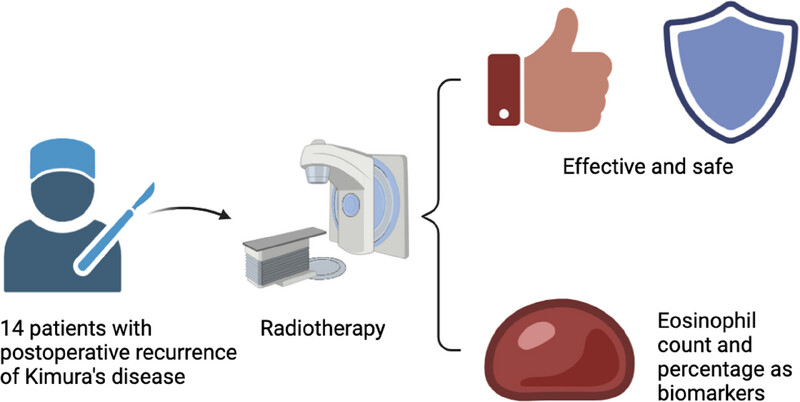
The graphic on the left represents definitive radiotherapy for selected patients with local recurrence of kimura disease in the head and neck after surgery.
The figure on the right is divided into upper and lower parts. The upper part
The graph is divided into upper and lower parts. The upper part
- Use a shield (for safety) and a thumbs-up icon (for efficacy).
- Text below the icon: “Radiation therapy is effective and safe for recurrent Kimura disease.”
- The lower half includes blood drop icons representing biomarkers.
- Add text: “Peripheral blood eosinophil count and percentage are reliable biomarkers.”
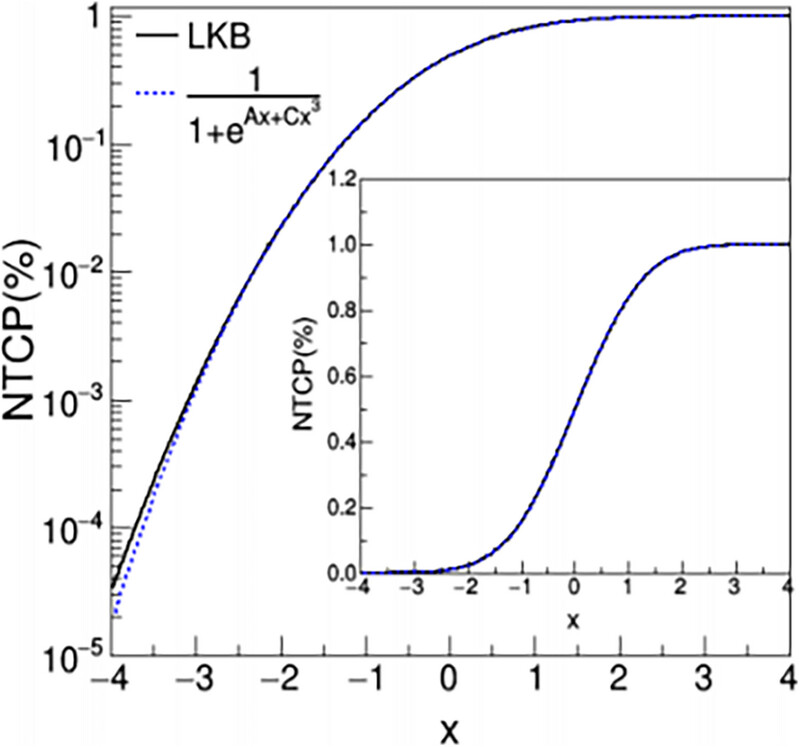
A new formula for calculating normal tissue complication probability
- Pages: 126-131
- First Published: 19 September 2024
Investigating the method of selection of background pixel values for the calibration of EBT-XD film dosimetry
- Pages: 132-137
- First Published: 11 August 2024
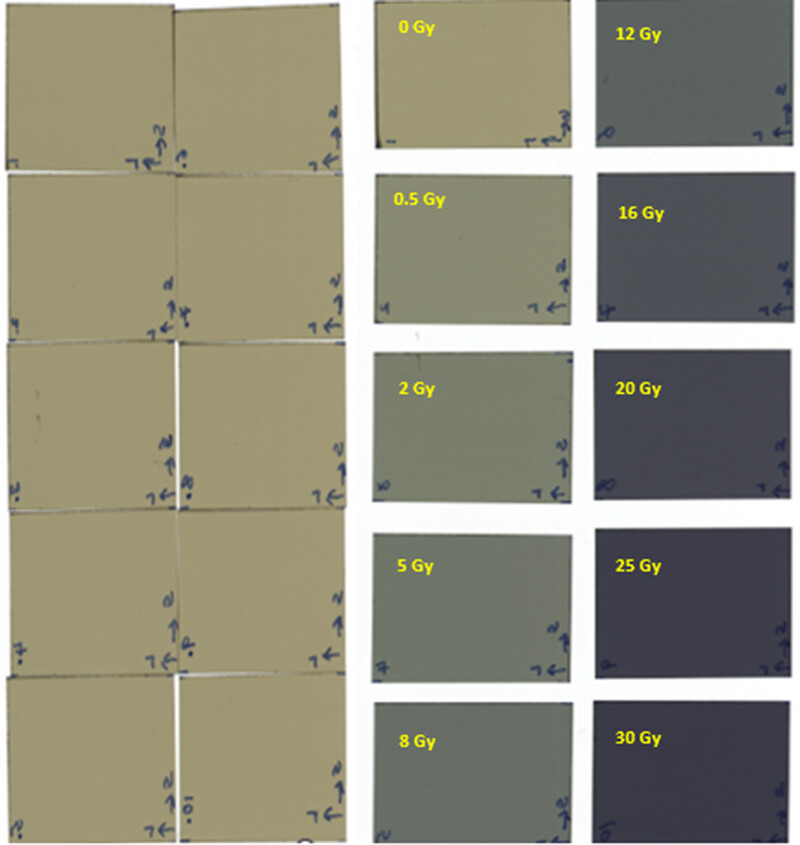
Film Exposure: Film exposure was conducted immediately after linac reference dosimetry. Film irradiation was performed using the Elekta Infinity linac with a 6 MV x-ray beam energy. SSD was set to 100 cm, and the field size was opened to 10 cm×10 cm. Films were placed at a 5 cm depth in the slab phantom. Since MUs were obtained from the same setup through the TPS, there was no need to keep the films at a water-equivalent depth in the slab phantom. A Farmer-type ion chamber was placed at the bottom of the phantom to monitor any unusual output fluctuations in the linac. The chamber was positioned well below the depth of the film to avoid any perturbation that might affect the film dose. The films were exposed to doses of 0 (control), 0.5, 2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 20, 25, and 30 Gy.
REVIEW
NUT carcinoma of the head and neck: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 138-144
- First Published: 01 September 2024
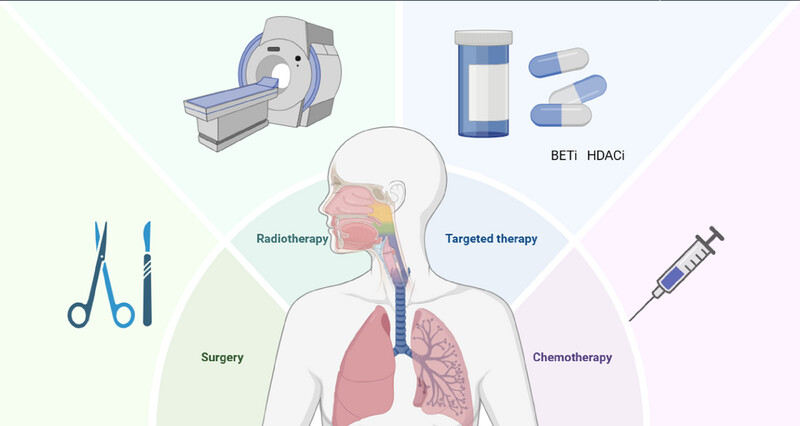
Therapies in NUT carcinoma.
A comprehensive treatment approach is recommended for NUT carcinoma including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and occasionally surgical resection. Importantly, Bromodomain and Extraterminal motif (BET) inhibitors and histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are regarded as novel potential therapies .
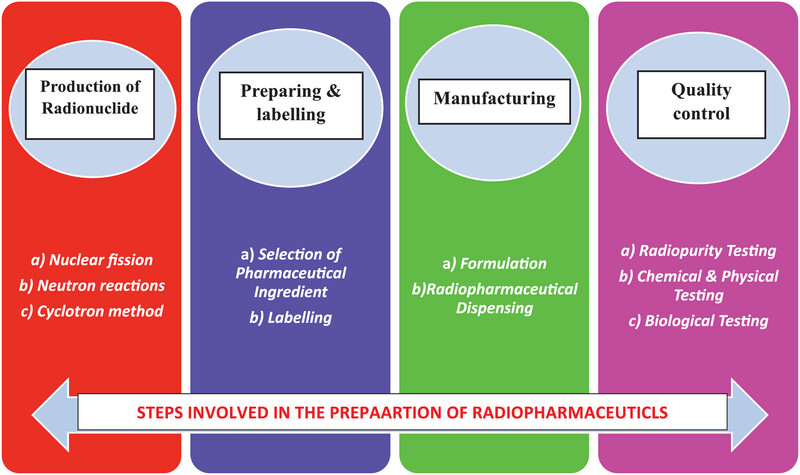
Revolutionizing cancer treatment: The role of radiopharmaceuticals in modern cancer therapy
- Pages: 145-152
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Research progress of cardiotoxicity caused by radiotherapy in breast cancer
- Pages: 153-158
- First Published: 21 September 2024
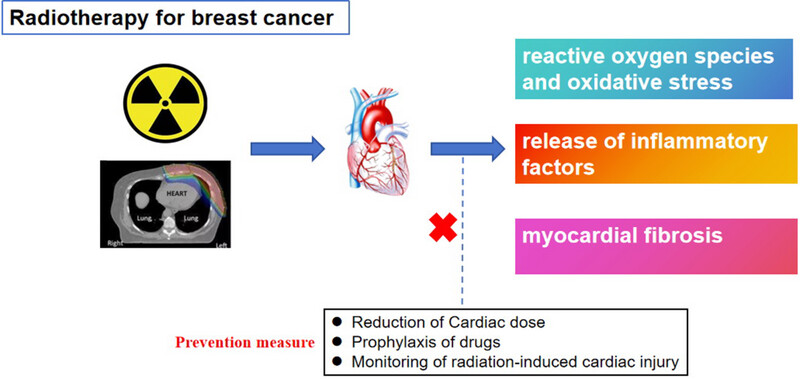
Breast cancer has surpassed lung cancer as the most common type of malignancy worldwide. Treatments for breast cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, endocrine therapy, immunotherapy, and hyperthermia. Radiotherapy plays an important role in breast cancer treatment. Patients with early breast cancer can have longer survival after combined treatment, but cardiotoxicity caused by radiotherapy may affect long-term prognosis. This article reviews cardiac damage caused by radiotherapy in breast cancer.
CASE REPORT
Treatment of Sinonasal Teratocarcinosarcoma: A case report
- Pages: 159-163
- First Published: 21 July 2024
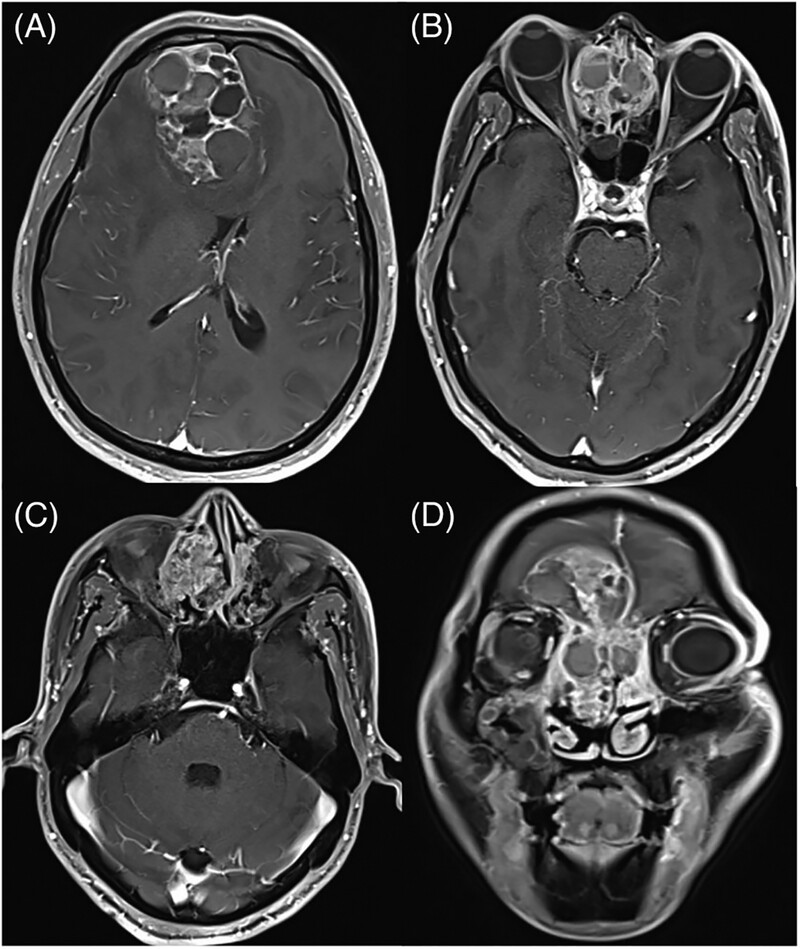
Sinonasal teratocarcinosarcoma (SNTCS) is a rare malignancy characterized by a highly aggressive nature. It mainly arises in the ethmoidal or maxillary sinus. SNTCS has a poor prognosis, with a mean survival at 2 years of 55%. Here, we present a case of advanced SNTCS successfully treated with surgery followed by chemoradiotherapy plus targeted therapy and review the published literature on this rare entity.