Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ALLERGY, RHINOLOGY, AND IMMUNOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
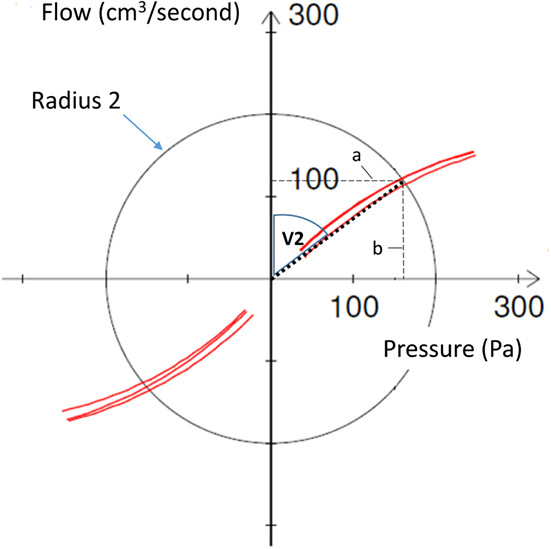
Active anterior rhinomanometry: A study on nasal airway resistance, paradoxical reactions to decongestion, and repeatability in healthy subjects
- Pages: 1136-1145
- First Published: 29 September 2023
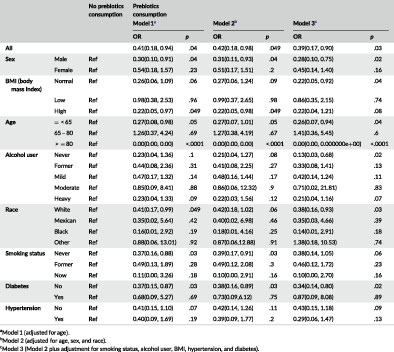
The relationship between prebiotic intake and allergic rhinitis
- Pages: 1146-1153
- First Published: 03 October 2023
COMPREHENSIVE (GENERAL) OTOLARYNGOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
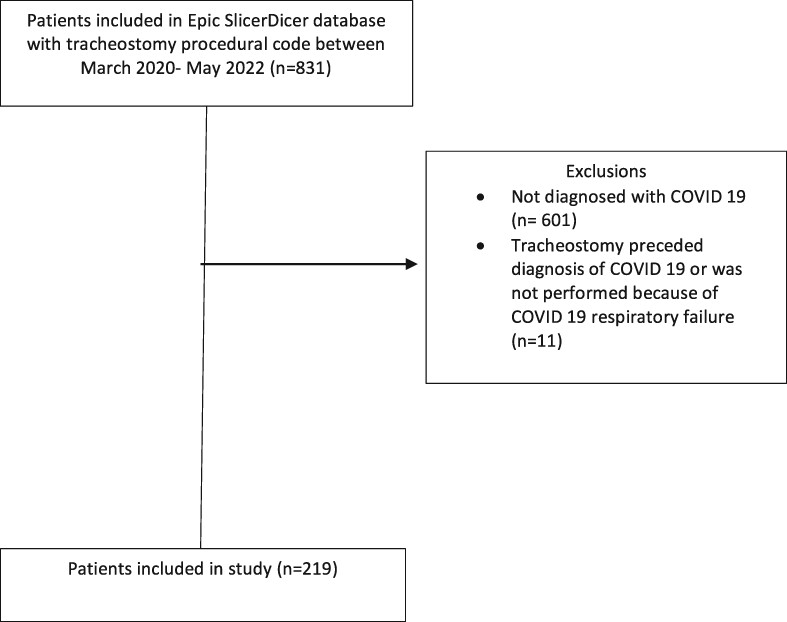
A retrospective analysis of COVID-19 tracheostomies: Early versus late tracheostomy
- Pages: 1154-1158
- First Published: 16 August 2023
Simulation-based workshop for emergency preparedness in otolaryngology
- Pages: 1159-1168
- First Published: 24 August 2023
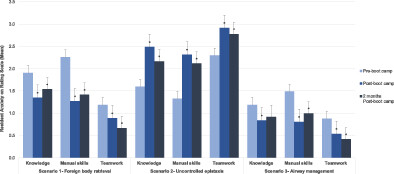
This study evaluated the outcomes of a hands-on simulation-based course designed to enhance junior OHNS residents' preparedness in managing otolaryngologic emergencies. The course led to significant reductions in anxiety and increases in confidence among participants, particularly in the areas of foreign body retrieval and airway management which were simulation-based stations; however, confidence decreased and anxiety increased for the lecture-only epistaxis station. The study suggests that simulation-centered training can be effective in improving residents' skills and confidence in critical procedures, benefiting patient safety.
Airway management during unusual tracheal stenosis: A clinical feasibility trial
- Pages: 1169-1177
- First Published: 02 September 2023
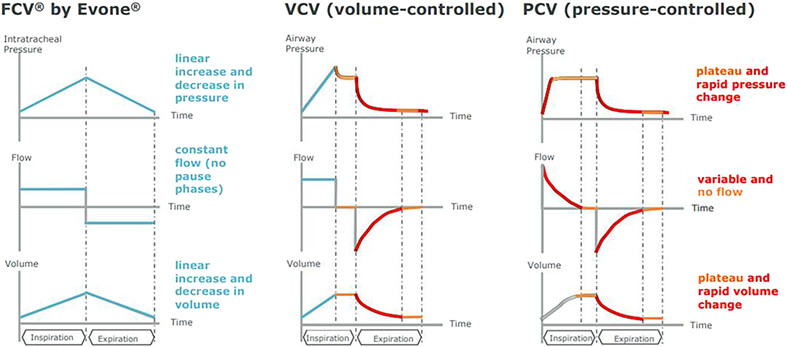
This study demonstrates the feasibility of using Tritube with FCV in patients with unusual subglottic posterior location tracheal stenosis, undergoing laryngotracheal surgery. Tritube provides a good surgical field and FCV provides highly adequate ventilation, especially in patients with compromised lung mechanics.
Gadolinium as a contrast agent for infusion sialograms in patients with iodine allergy
- Pages: 1178-1183
- First Published: 18 September 2023
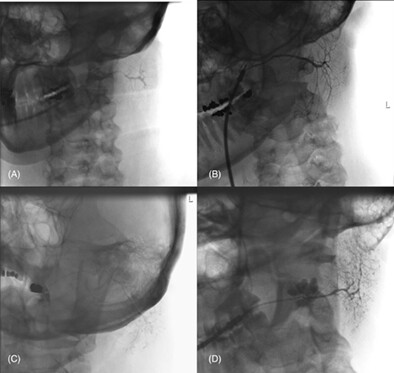
We describe the use of a gadolinium-based contrast agent as an alternative agent for digital infusion sialogrpahy in patients with iodine allergies. Our investigation demonstrates gadolinium, compared to iodine-based agents, as an adequate alternative for use in infusion sialography for patients with iodine allergies, supporting the precautionary use of gadolinium as an acceptable contrast agent for the diagnostic and therapeutic benefits in sialography.
Promoting gender diversity in the editorial boards of major otorhinolaryngology journals: A call for inclusion and equal representation
- Pages: 1184-1188
- First Published: 16 October 2023
FACIAL PLASTICS AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Predicting synkinesis caused by Bell's palsy or Ramsay Hunt syndrome using machine learning-based logistic regression
- Pages: 1189-1195
- First Published: 25 August 2023
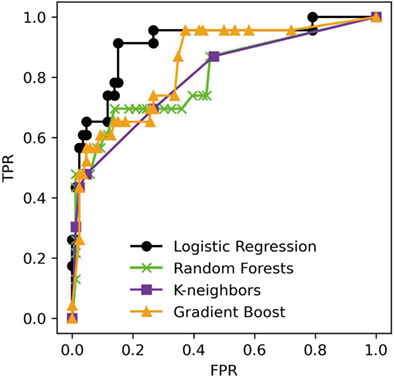
This study compared the accuracy of machine learning (ML) algorithms (logistic regression [LR], random forest, k-nearest neighbor, and gradient-boosting decision tree) to predict facial synkinesis resulting from Bell's palsy or Ramsay Hunt syndrome using early post-onset parameters against conventional statistics-based LR. Results showed that ML-based LR has potential and comparable reliability to predict synkinesis probability. AUCs ranged from 0.711 to 0.910 for the different algorithms and parameters.
Modified individualized titanium mesh in orbital floor reconstruction for preventing exposure
- Pages: 1196-1202
- First Published: 04 September 2023
HEAD AND NECK, AND TUMOR BIOLOGY
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Multidisciplinary care improves outcomes for patients with carotid body paragangliomas—The UCLA experience
- Pages: 1203-1209
- First Published: 23 August 2023
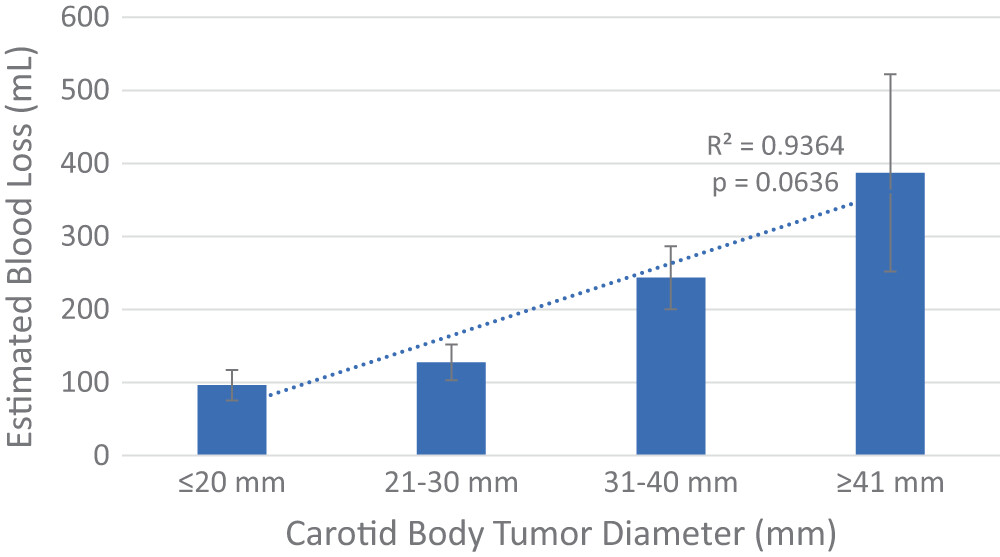
Carotid body tumors can be managed effectively by single surgical specialties with similar outcomes between vascular surgery and OHNS. In larger, higher grade tumors, however, a combined vascular and OHNS approach had lower incidence of postoperative cranial nerve injuries when compared to single specialty resections, despite a larger EBL.
Free-flap volume correlates with body mass index in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1210-1216
- First Published: 16 August 2023
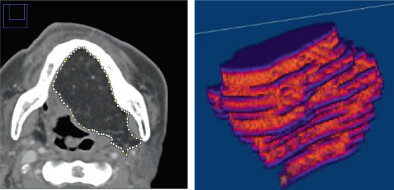
Reconstructed tongue flap volume (RTFV) correlates with body mass index (BMI) in patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. In addition, flap type and BMI, but not age or sex, were factors affecting RTFV. Maintaining good nutritional status, with BMI as an indicator, is crucial to avoid loss of RTFV.
REVIEW
Survival after induction chemotherapy in locoregional advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1217-1225
- First Published: 19 August 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
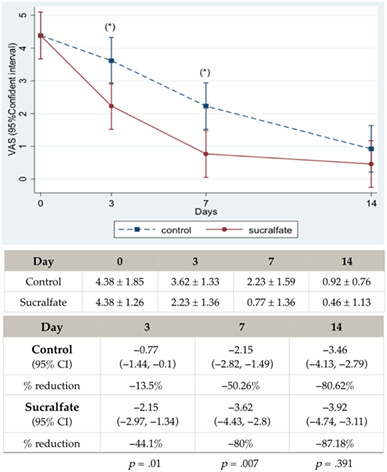
Effectiveness of Sucralfate comparing to normal saline as an oral rinse in pain reduction and wound healing promotion in oral surgery
- Pages: 1226-1232
- First Published: 24 August 2023
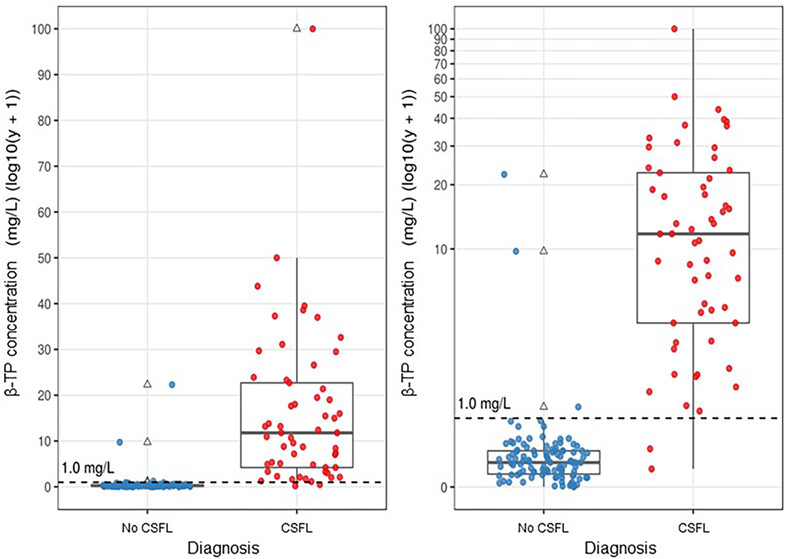
Cut-off value for β-trace protein (β-TP) as a rapid diagnostic of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak detection
- Pages: 1233-1239
- First Published: 31 August 2023
HEALTH POLICY AND OUTCOMES
REVIEW
Enhanced recovery after surgery, current, and future considerations in head and neck cancer
- Pages: 1240-1256
- First Published: 04 September 2023
Since it's conception, enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols have continued to push for comprehensive and evidence based postsurgical care to improve patient outcomes. Head and neck oncology is one of the newest fields to develop a protocol. Due to the complexity of this patient population and their postsurgical needs, a multidisciplinary approach is needed to facilitate recovery while minimizing complications. This article summarizes current and future principles in head and neck ERAS protocols.
EDITORIAL
How to publish a lot—The sequel to writing
- Pages: 1257-1258
- First Published: 25 August 2023
LARYNGOLOGY, SPEECH AND LANGUAGE SCIENCE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
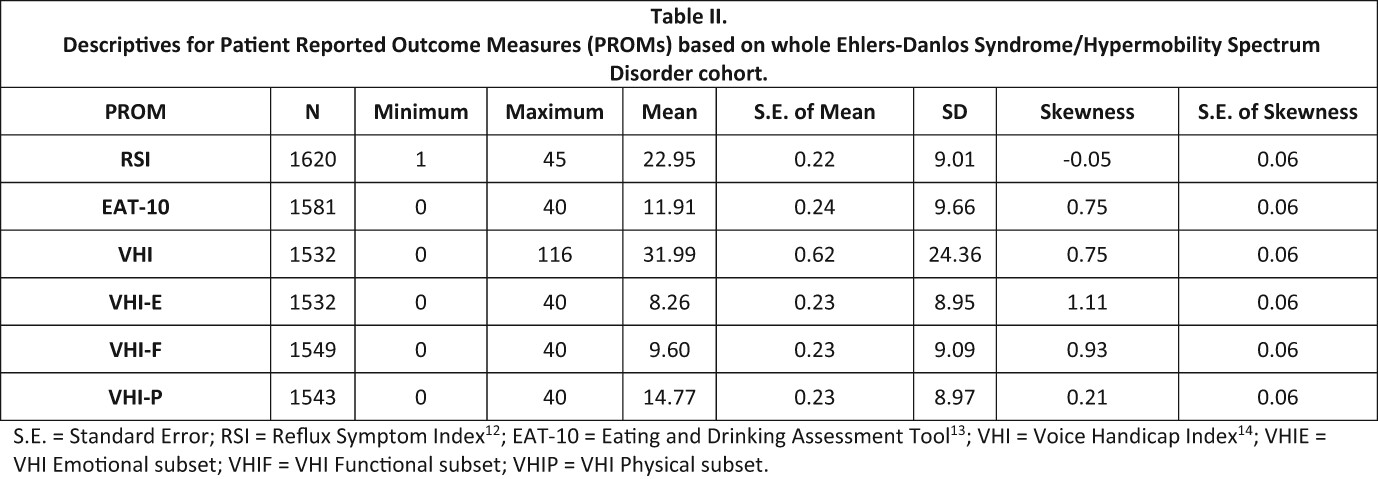
Self-reported throat symptoms in Ehlers–Danlos syndromes and hypermobility spectrum disorders: A cross-sectional survey study
- Pages: 1259-1264
- First Published: 18 September 2023
Clinician accuracy in identifying essential laryngeal landmarks on swallowing fluoroscopy
- Pages: 1265-1271
- First Published: 29 July 2023
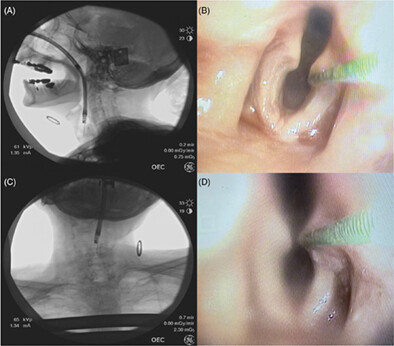
The study investigated the accuracy of clinicians and trainees in identifying essential laryngeal landmarks on videofluoroscopic swallow studies (VFSS). A single human cadaver was used to verify the location of laryngeal structures under fluoroscopy, and participants were asked to identify 18 structures on unmarked fluoroscopic images. The results showed that overall accuracy was low, with an average rate of correct identification at less than 50%, and there were no significant differences in accuracy between clinicians and trainees or between speech-language pathologists and physicians. The study suggests that more training is needed to improve clinicians' ability to identify essential anatomical structures on VFSS.
Late laryngeal dysfunction in head and neck cancer survivors
- Pages: 1272-1278
- First Published: 31 July 2023
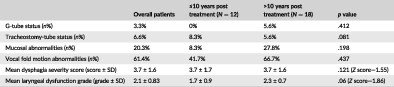
We describe laryngeal dysfunction in a cohort of long-term HNC survivors. This sequelae of long-term damage to the larynx included swallowing dysfunction, voice change, chronic cough, vocal fold motion abnormalities and mucosal changes. There was a weak correlation between time since treatment and laryngeal dysfunction, and overall, late laryngeal dysfunction in this population contributes to significant morbidity and is difficult to treat.
Voice outcomes in high-grade Reinke's edema: Comparing microflap excision and microdebrider surgery
- Pages: 1279-1287
- First Published: 19 August 2023
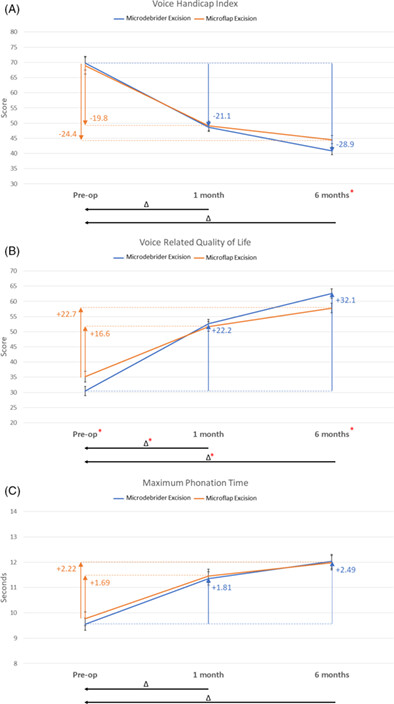
We compared patient outcomes in patients who had microflap or microdebrider excision surgeries for Reinke's edema (RE). Both microflap excision and microdebrider excision for high-grade RE lesions resulted in significant improvement in Voice Handicap Index-30, Voice-Related Quality Of Life, and mean phonation time at 1-month and 6-months postoperatively with the microdebrider excision group scoring statistically significantly better at 6-months in comparison to the microflap group. Overall, the results support the use of both surgical modalities for treating high-grade RE patients.
Somatic anxiety in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux
- Pages: 1288-1293
- First Published: 16 August 2023
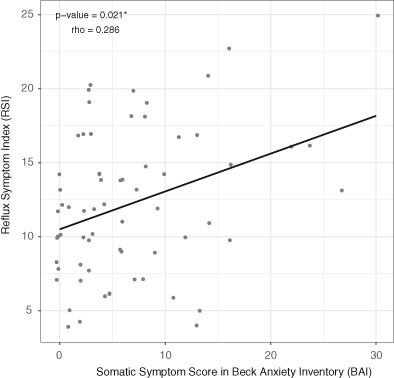
Patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) had more severe somatic anxiety than healthy individuals. Somatic anxiety symptoms were more frequent than subjective anxiety symptoms in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR). The somatic anxiety symptoms were correlated with LPR-related symptoms in patients with LPR. The somatic anxiety symptoms such as trembling hands, shaky, difficulty in breathing, and faint symptoms were statistically associated with LPR. Those somatic anxiety symptoms may represent physiological arousal of patients with LPR.
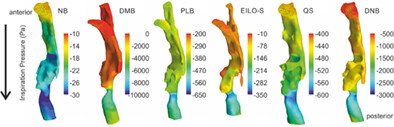
Computational fluid dynamics of upper airway aerodynamics for exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction: A feasibility study
- Pages: 1294-1303
- First Published: 19 August 2023
Platelet-rich plasma in treatment of scar, atrophy, and sulcus: Short- and long-term results
- Pages: 1304-1311
- First Published: 05 September 2023
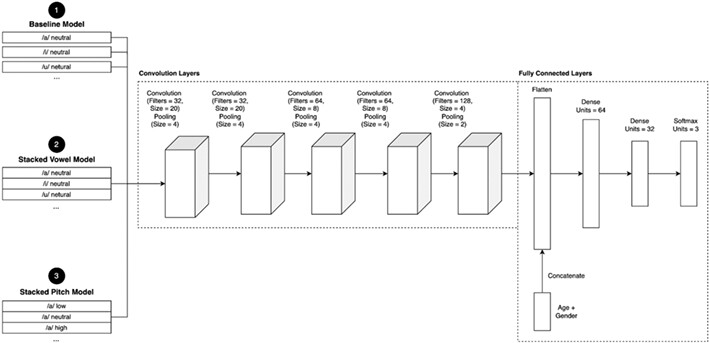
End-to-end deep learning classification of vocal pathology using stacked vowels
- Pages: 1312-1318
- First Published: 31 August 2023
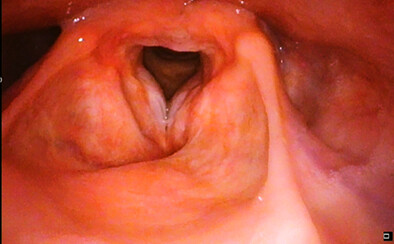
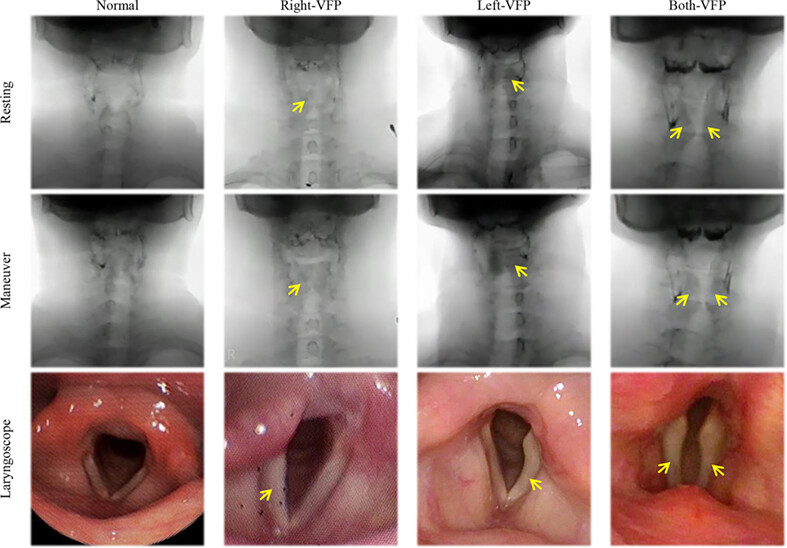
Assessment of vocal fold movement through anterior–posterior view of videofluoroscopic swallowing study
- Pages: 1319-1323
- First Published: 07 September 2023
Risk factors for postoperative vocal fold fibrosis following microlaryngeal surgery
- Pages: 1324-1327
- First Published: 13 September 2023
Extended partial laryngectomy with functional preservation using the rotational crico-thyrotracheopexy
- Pages: 1328-1336
- First Published: 19 September 2023
OTOLOGY, NEUROTOLOGY, AND NEUROSCIENCE
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
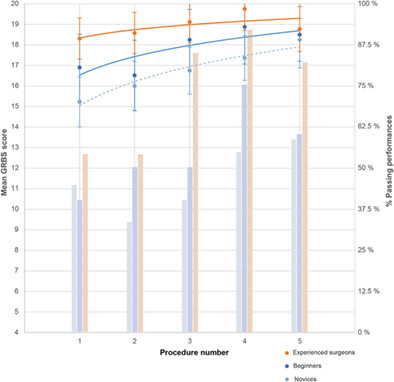
Binocular microscopes versus exoscopes: Experiences and performance in simulated otologic surgery
- Pages: 1337-1344
- First Published: 03 August 2023
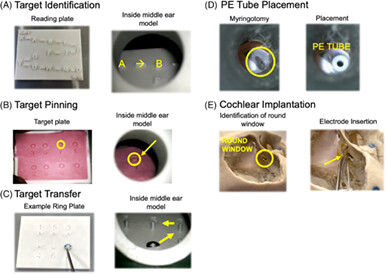
Our study prospectively compares the exoscope to the traditional binocular operative microscope (OM). We tested 29 participants, 14 medical students and 15 residents. Overall performance, predefined errors and time to task completion, was better with the OM. Subjectively, on effort required and ease of use the two systems were rated similarly by participants.
REVIEW
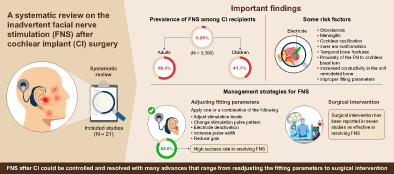
Risk factors and management strategies of inadvertent facial nerve stimulation in cochlear implant recipients: A systematic review
- Pages: 1345-1356
- First Published: 12 September 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Gathering validity evidence for a 3D-printed simulator for training of myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion
- Pages: 1357-1364
- First Published: 16 August 2023
Association between depression and tinnitus in US adults: A nationally representative sample
- Pages: 1365-1375
- First Published: 21 August 2023
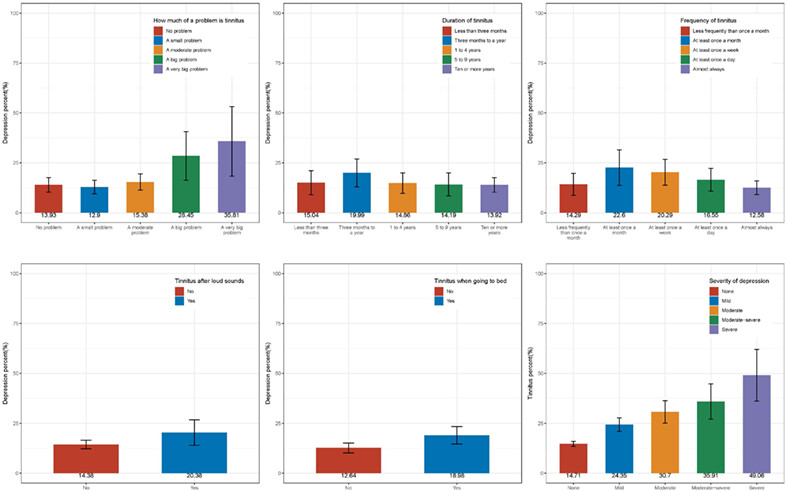
This study used data from the NHANES to examine the link between tinnitus and depression among US adults. It found that tinnitus was associated with a higher risk of depression, even after adjusting for other factors. The study suggested that psychological factors should be considered in the treatment of tinnitus.
REVIEW
Bell's palsy in pregnancy: A scoping review of risk factors, treatment and outcomes
- Pages: 1376-1383
- First Published: 14 August 2023
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
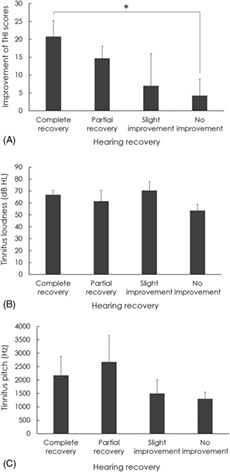
Tinnitus characteristics in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss and acute tinnitus
- Pages: 1384-1389
- First Published: 11 August 2023
Electrical stimulation of cochlear implant promotes activation of macrophages and fibroblasts under inflammation
- Pages: 1390-1400
- First Published: 07 September 2023
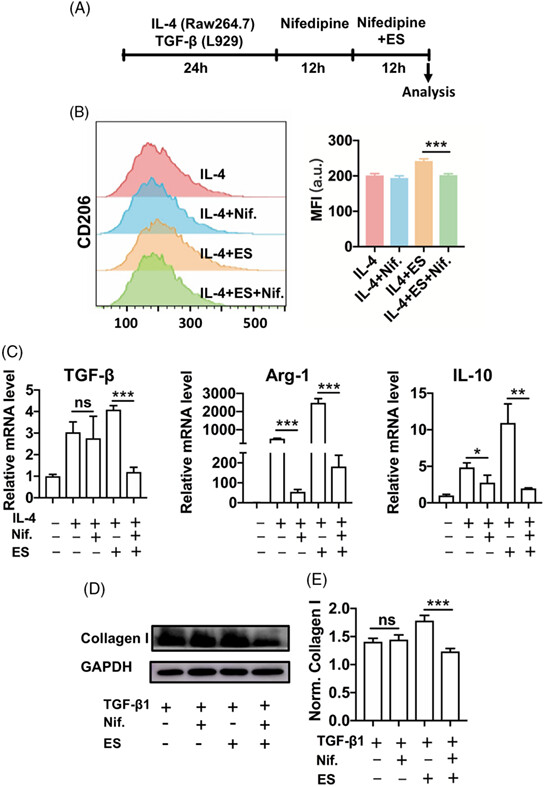
We assessed the effects of electrical stimulation of cochlear implant on postimplantation inflammation and fibrosis. We observed that electrical stimulation of cochlear implant promoted the activation of macrophages and fibroblasts under inflammation. This suggests that the cochlear implant needs to be activated after the acute inflammation has subsided and the subsequent electrical stimulation process is also needed to suppress chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
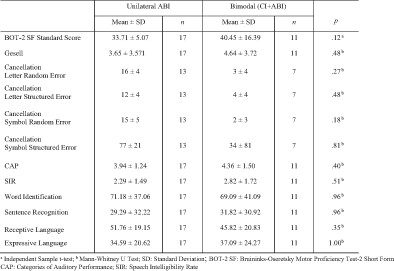
Unimodal versus bimodal auditory stimulation in inner ear malformations: Cognitive, language, and motor performance
- Pages: 1401-1409
- First Published: 18 September 2023
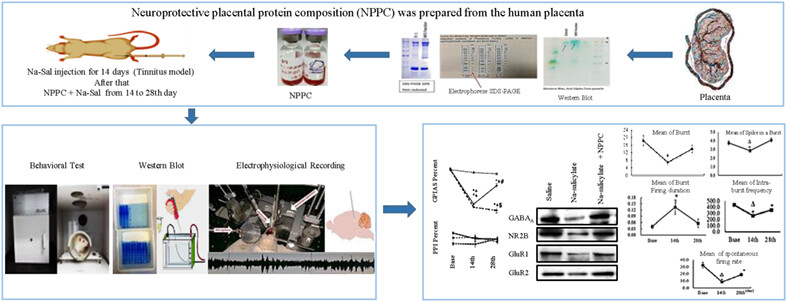
Electrophysiological and molecular changes following neuroprotective placental protein administration on tinnitus-induced rats
- Pages: 1410-1420
- First Published: 03 October 2023
PEDIATRICS AND DEVELOPMENT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
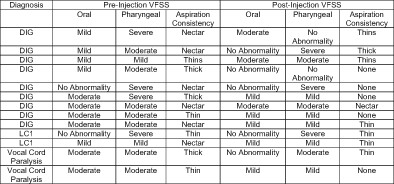
Interarytenoid injection outcomes in pediatric feeding disorders
- Pages: 1421-1427
- First Published: 16 August 2023
Establishment of novel immortalized middle ear cell lines as models for otitis media
- Pages: 1428-1435
- First Published: 28 August 2023
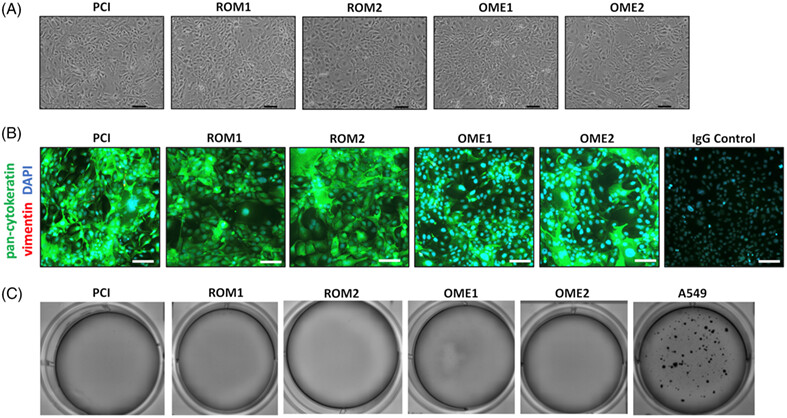
Otitis media (OM) is a common condition in children and poses a significant public health burden, but only a single immortalized human middle ear epithelial (MEE) cell line exists for its study. We generated and characterized five new middle ear cell lines from pediatric patients with non-inflamed MEE, recurrent OM, or OM with effusion and demonstrated differences in their baseline inflammatory cytokine expression and response to stimulation with an OM-relevant pathogen and cytokines. Immortalized MEE lines retained the cytokine expression and responsiveness of their tissues of origin and differences between non-OM versus OM and pediatric versus adult cultures, supporting their value as novel in vitro culture models for OM.