Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine
Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Allelic and genotype frequencies of major CYP2B6 polymorphisms in the Pakistani population
- First Published: 18 February 2021
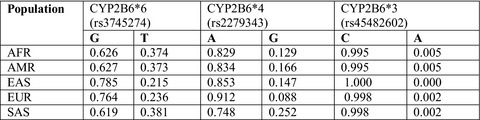
This study shows that a significant portion of the Pakistani population possesses at least one abnormal activity allele of the CYP2B6 gene, especially the frequency of the CYP2B6*6 variant is significant enough in the Pakistani population to be given an important consideration when drugs metabolized by this enzyme are prescribed.
Phenylketonuria in Portugal: Genotype–phenotype correlations using molecular, biochemical, and haplotypic analyses
- First Published: 19 January 2021

The present study identify and characterize the variants underlying PKU in affected individuals in the Portuguese PKU/HPA cohort. Biochemical data, haplotic analysis and genetic findings performed in 223 patients diagnosed through the Portuguese Neonatal Screening Program (PNSP) is presented. The information obtained will improve the diagnostic applicability of mutational analysis and the capacity to predict the evolution of the disease.
Vanishing white matter: Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B model and the impact of missense mutations
- First Published: 12 January 2021
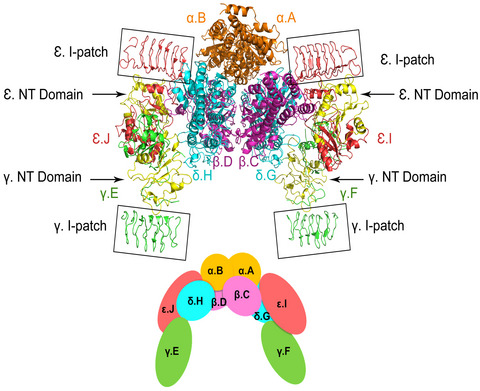
Vanishing white matter (VWM) is a clinically highly variable leukodystrophy, caused by recessive mutations in eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B)-subunit genes, mostly missense mutations. To gain insight into the strong genotype-phenotype correlation, we severity-graded 97 missense mutations using information from a clinical natural history study, created a new human eIF2B model structure by in silico modeling, and assessed mutated residues for location in subunits, eIF2B complex, and functional domains, and for information on biochemical activity. We demonstrated that mutations associated with (ultra-)severe disease mostly affect amino acids with pivotal roles in complex formation and eIF2B function, while mutations on the external eIf2B surface are mostly associated with mild phenotypes, probably because of minor functional effects. Therapies for VWM are emerging and reliable mutation-based phenotype prediction is required for propensity score matching for trials and individualized therapy decisions.
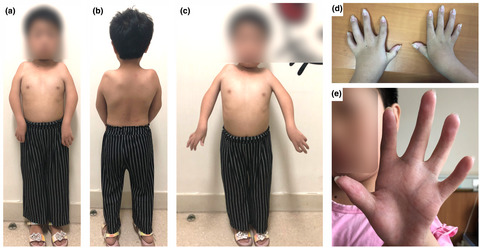
BMPR1B gene in brachydactyly type 2–A family with de novo R486W mutation and a disease phenotype
- First Published: 24 January 2021
Netherton syndrome caused by compound heterozygous mutation, c.80A>G mutation in SPINK5 and large-sized genomic deletion mutation, and successful treatment of intravenous immunoglobulin
- First Published: 16 January 2021
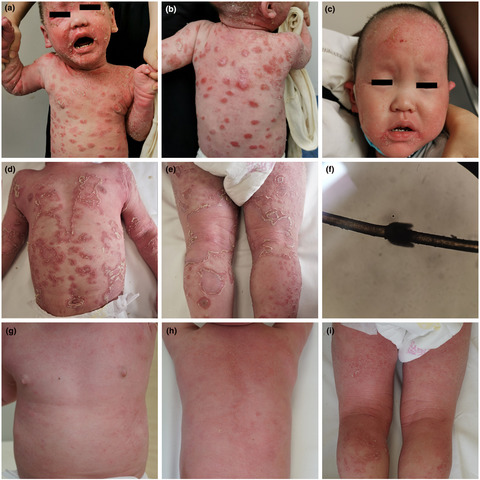
- We report the detection of compound heterozygous mutations, c.80A>G mutation in SPINK5 gene in one allele and the ~275 Kb large-sized deletion mutation in another allele in a 3-year-old boy with Netherton syndrome.
- After the intravenous immunoglobulin therapy, eruptions were improved remarkably in this patient with Netherton syndrome.
Gene correction of the CLN3 c.175G>A variant in patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells prevents pathological changes in retinal organoids
- First Published: 26 January 2021
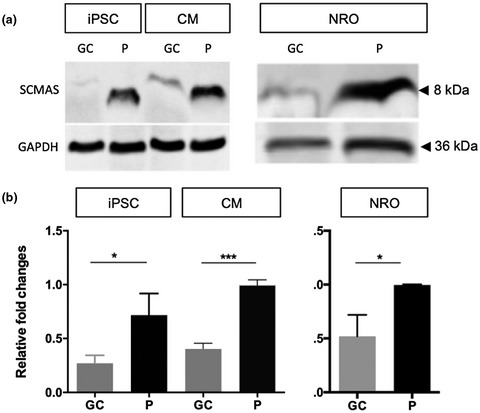
In this paper, we examined the phenotype of retinal organoids derived from a patient with non-syndromic CLN3 disease. We showed that accumulation of subunit C of mitochondrial ATPase occurs in patient retinal cells and cardiomyocytes, and could be prevented by gene correction. Additionally, we demonstrated that novel CLN3 transcripts are expressed in the human retina.
A novel Xp11.22–22.33 deletion suggesting a possible mechanism of congenital cervical spinal muscular atrophy
- First Published: 29 January 2021
Characteristic facial features and cortical blindness distinguish the DOCK7-related epileptic encephalopathy
- First Published: 20 January 2021
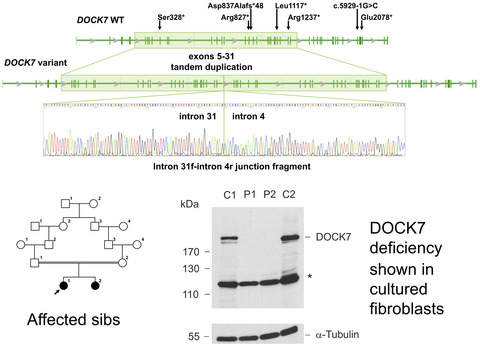
DOCK7 deficiency causes a syndromic form of epileptic encephalopathy. Five children were previously reported. We report the disease outcome in two adult patients. All patients display biallelic truncating variants including a novel intragenic tandem duplication DOCK7 deficiency shown in cultured fibroblasts.
Whole exome sequencing reveals a biallelic frameshift mutation in GRXCR2 in hearing impairment in Cameroon
- First Published: 02 February 2021
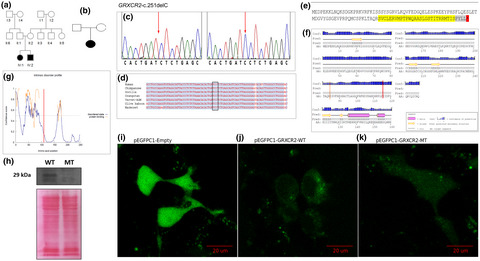
We used whole exome sequencing (WES) to investigate the pathogenic and likely pathogenic (PLP) variants in 10 individuals with HI, from four multiplex families from Cameroon, two of which were previously unresolved with a targeted gene enrichment (TGE) panel of 116 genes. All PLP variants previously identified with TGE were replicated. In one previously unresolved family, we found a homozygous frameshift PLP variant in GRXCR2 (OMIM: 615762), GRXCR2-c.251delC (p.Arg84 frameshift), in two affected siblings; and additionally, in 1/80 unrelated individuals affected with non-syndromic hearing impairment (NSHI). The GRXCR2-c.251delC variant introduced a premature stop codon, leading to truncation and loss of a zinc-finger domain. Fluorescence confocal microscopy tracked the wild-type GRXCR2 protein to the cellular membrane, unlike the mutated GRXCR2 protein. This study confirmsGRXCR2 as a HI-associated gene.
The Rh blood group system and its role in alloimmunization rate among sickle cell disease and sickle thalassemia patients in Iran
- First Published: 06 February 2021
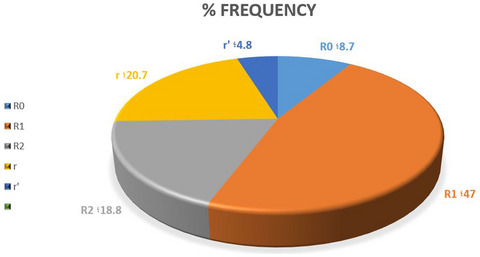
- The alloimmunization is the problem in 9.6% of sickle cell disease (SCD) and sickle thalassemia patients.
- The increase in the rate of alloimmunization was due to Rh alloantibodies.
- The Rh genotypes were different among sickle cell disease and sickle thalassemia patients than other populations and R1r′ and R0R1 genotypes were limited to our population.
Negotiating political power and stigma around fragile X Syndrome in a rural village in Cameroon: A tale of a royal family and a community
- First Published: 05 February 2021
In this paper, we present the findings of an ethnographic study in the community of a patient who received a genetic diagnosis for FXS in Cameroon. This study builds on data from 28 participants of a royal family and 58 from the community who participated in 20 in-depth interviews and nine focus group discussions. We outline the stereotyping labels used for the family and its children with Fragile X Syndrome and describe the stigma-power dynamic between the community members and the royal family. First, most villagers use less-stigmatizing terms to address FXS children from the chieftaincy because of their position in society. Second, due to their social position, the royal family uses their status to negotiate marriages with community members.
Identification and characterization of six β-crystallin gene mutations associated with congenital cataract in Chinese families
- First Published: 17 February 2021
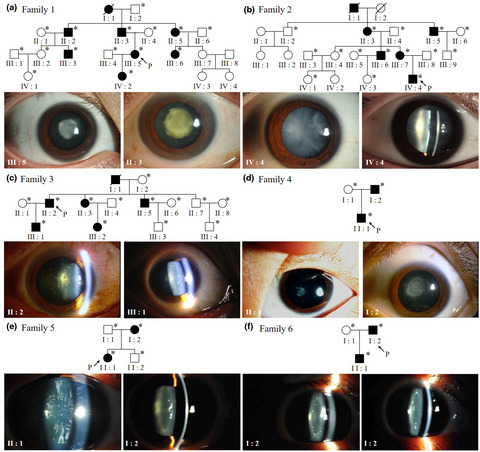
A total of 53 participants (23 affected and 30 unaffected) from six unrelated Chinese families were recruited. Cataract phenotypes covered nuclear, total, posterior polar, pulverulent, snowflake-like, and zonular. Through targeted exome sequencing, six new mutations in four β-crystallin genes were revealed which included five missense mutations CRYBB1 p.Q70P, CRYBB2 p.E23Q, CRYBB2 p.A49V, CRYBB2 R188C, CRYBA4 p.M14K, and one splice mutation CRYBB3 c.75+1 G>A.
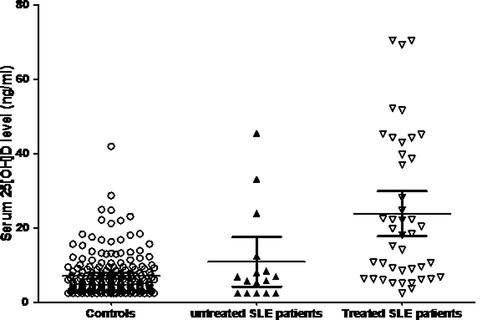
Vitamin D status and CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphism in Tunisian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
- First Published: 17 February 2021
CLINICAL REPORTS
Novel compound heterozygous variants of TBXAS1 presenting with Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia treated with steroids
- First Published: 17 February 2021
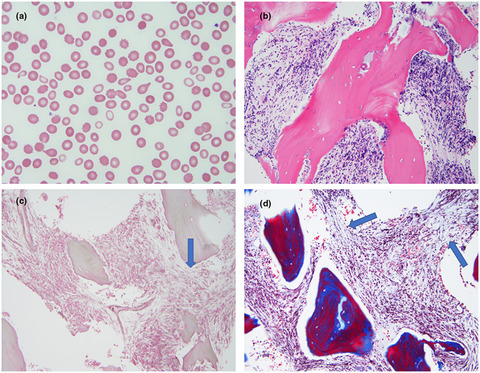
We report three Caucasiion siblings from non-consanguineous parents with novel compound heterozygous variants of TBXAS1 presenting with phenotypes of GHDD. Patient 1 and 2 are identical twins, who presented with red blood cell transfusion dependent normocytic anemia and thrombocytopenia with bone marrow fibrosis and cortical bone thickening of long bones on plain radiograph. Patient 3 is their sister with normal blood counts but cortical bone thickening on radiograph who has not required any treatment. These three cases illustrate the variable clinical expressivity of the GHDD from two-compound heterozygous pathogenic variants of TBXAS1.
Duplication of 9p24.3 in three unrelated patients and their phenotypes, considering affected genes, and similar recurrent variants
- First Published: 17 January 2021
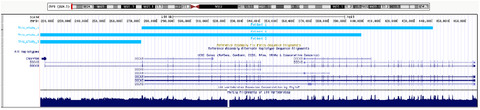
We describe three unrelated patients with autism spectrum disorders and intellectual disabilities / developmental delay who are carriers of the 9p24.3 duplication including DOCK8 and KANK1. Clinical features of duplication are similar as 15q11.2 and 16p11.2 changes. We compared clinical features of patients with dupication 9p24.3, 15q11.2 and 16p11.2.
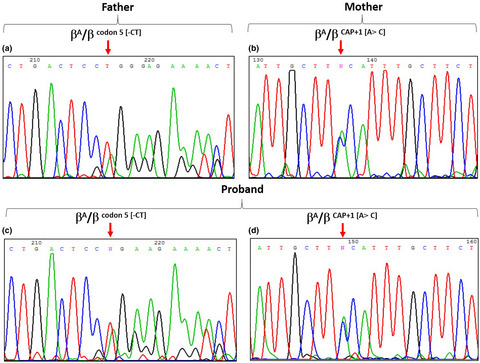
A rare gene variation cap +1 (A>C) (HBB: c. −50A>C) associated with codon 5 (-CT) (HBB: c.17_18delCT) mutation in Syrian family
- First Published: 24 January 2021
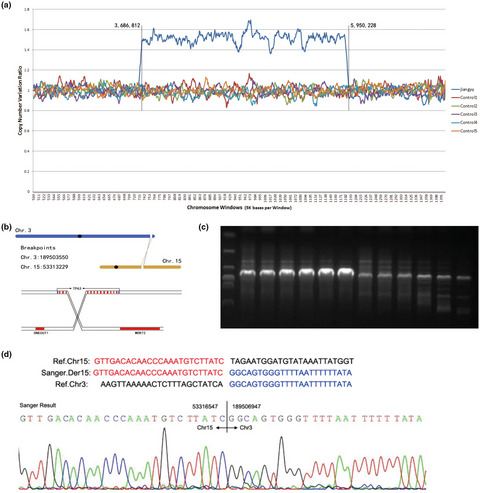
Whole genome sequencing reveals translocation breakpoints disrupting TP63 gene underlying split hand/foot malformation in a Chinese family
- First Published: 20 January 2021
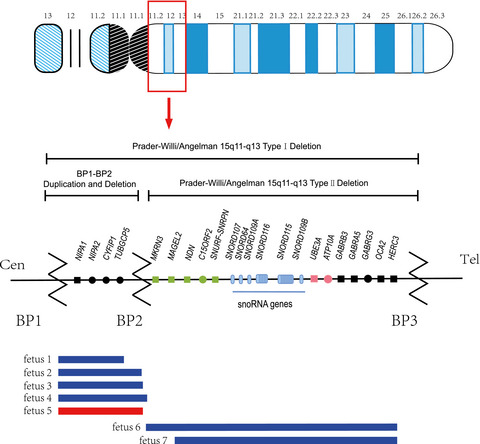
A report on seven fetal cases associated with 15q11-q13 microdeletion and microduplication
- First Published: 04 February 2021
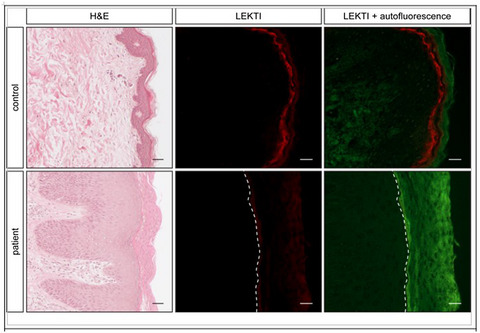
A novel SPINK5 donor splice site variant in a child with Netherton syndrome
- First Published: 03 February 2021
Clinical and genetic characterization of autosomal recessive stickler syndrome caused by novel compound heterozygous mutations in the COL9A3 gene
- First Published: 11 February 2021
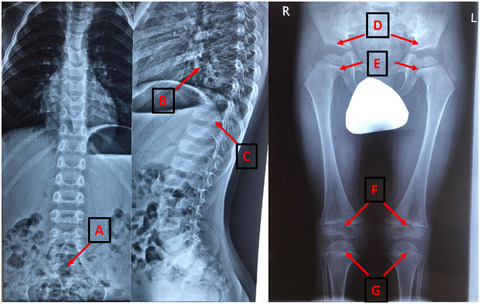
We describe a novel case of autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome caused by two undescribed loss of function mutations in the COL9A3 gene. Our patients have the more severe phenotype that included severe sensorineural hearing loss, high myopia, vitreoretinal degeneration, mild spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, and early-onset arthropathy of the lower limbs.