Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLES
EdgePlace: Availability-aware placement for chained mobile edge applications
- First Published: 16 August 2018
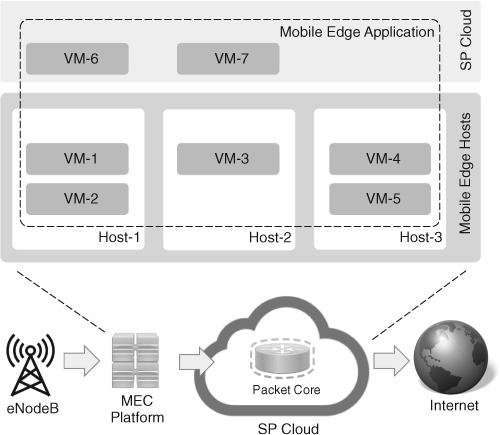
We propose a novel model to track the availability and cost impact from placement policy changes of the mobile edge applications. We formulate our model as a stochastic programming problem along with a heuristic algorithm called EdgePlace. Our model is able to find their sweet points with the consideration of both resource cost and application availability, which is vital in a less robust MEC environment.
A collaborative mobile edge computing and user solution for service composition in 5G systems
- First Published: 19 June 2018
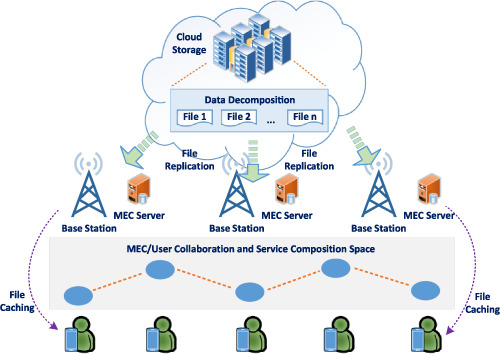
This article envisions a real-time framework that lies at the edge of the network, comprising MEC and user devices for fast composite service delivery in 5G systems. The solution decomposes cloud data into a set of files and services which are then replicated to MEC nodes. Files and services are further cached onto user mobile devices for faster access. Nodes advertise their services onto the collaborative Edge/user space, where services are delivered either composite or un-rendered according to users' requests.
Subcarriers assignment scheme for multiple secondary users in OFDMA-based IEEE 802.22 WRAN: A game theoretic approach
- First Published: 23 August 2018
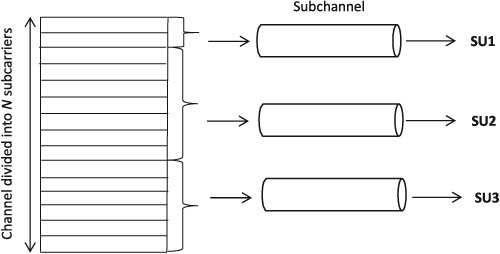
This work considered mapping or assignment of sub-carriers to the multiple unlicensed secondary users in the OFDMA and cognitive radio based IEEE 802.22 wireless regional area networks. Instead of allocating sub-carriers randomly, non-cooperative game among the secondary users is played and a fair distribution of sub-carriers has been done by achieving the Nash Equilibrium.
Reinforcement learning–based QoS/QoE-aware service function chaining in software-driven 5G slices
- First Published: 31 July 2018
A lightweight QoS information collector based on LLDP, which works in a piggyback fashion on the southbound interface of the SDN controller. A deep Q-network (DQN)-based orchestration agent is designed to support SFC. The agent takes into account the QoE and QoS as key aspects to formulate the reward so that it is expected to maximize QoE while respecting QoS constraints.
EdgeCloudSim: An environment for performance evaluation of edge computing systems
- First Published: 06 August 2018
In this paper, a new simulator tool called EdgeCloudSim streamlined for the edge computing scenarios is proposed to decrease the barriers. EdgeCloudSim builds upon CloudSim to address the specific demands of edge computing research and support the necessary functionalities. To demonstrate the capabilities of EdgeCloudSim, an experiment setup based on different edge architectures is simulated.
Balancing QoS and power consumption in programmable 5G infrastructures
- First Published: 16 May 2018

User mobility and the need for small latency and close proximity are expected to result in large fluctuations in workload and utilization at the network edge, evantually leading to large energy inefficiency. Boosting the usage of power-saving mechanisms and balancing efficiency with QoS is the only viable road for sustainable and cost-effective 5G infrastructures.
Batch-based security-aware spectrum sharing with simultaneous assignment decisions in time-critical IoT networks with cognitive radio capabilities
- First Published: 04 May 2018
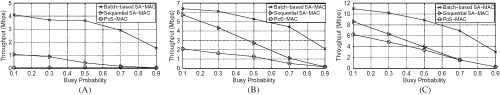
Cognitive radio (CR) is considered as a key enabling communication technology that offers efficient wireless connectivity to Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Security attacks can severely degrade the performance of CR-based IoT (CRIoT). Unlike most of previous security-aware channel assignment solutions that conduct the channel assignment sequentially, our solution simultaneously provides secured distributed channel- assignment decisions for multiple CRIoT link (batching method). Simulation results reveal that our solution significantly improves network performance compared to previous security-aware schemes.
Composing network service chains at the edge: A Resilient and adaptive software-defined approach
- First Published: 02 August 2018
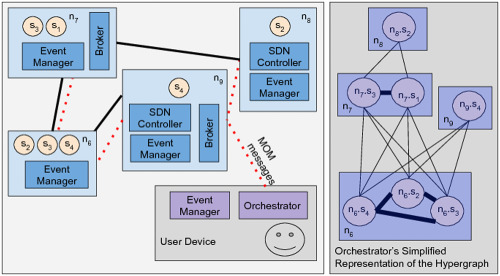
As network services are often latency sensitive, network service chaining (NSC) needs to be carried out maintaining proximity to the user, as well as among the services composing the NSC. In this paper, we present the design of a resilient and adaptive framework, following an approach inspired by software-defined networking (SDN), for the remote users to construct network service chains (NSCs) in the mobile and edge computing (MEC) environments, abiding by various user policies.
Exploring microservices for enhancing internet QoS
- First Published: 21 June 2018
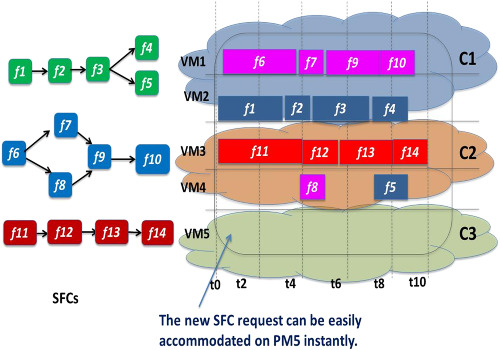
In this work, we aim to bridge this gap between the industry and the academia and discuss different microservice deployment, discovery, and communication options for service providers as a means to forming complete service chains. In addition, we address the problem of scheduling microservices across multiple clouds, including microclouds for efficient Mobile Edge Computing (MEC).
Enabling green computing in cloud environments: Network virtualization approach toward 5G support
- First Published: 29 May 2018
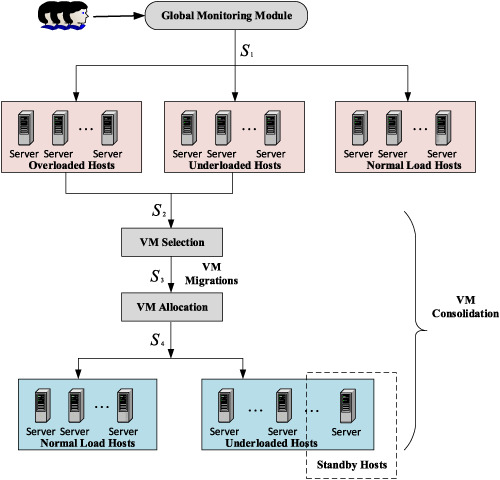
Virtualization technology allows dynamic leasing of server capabilities as services such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. The proliferation of these services among the users led to the establishment of large-scale cloud data centres, which consume an enormous amount of electrical energy and results into high-metered bill cost and carbon footprint. In this paper, we propose three heuristic models namely Median Migration Time, Smallest Void Detection and Maximum Fill that can reduce energy consumption with minimal variation in SLAs negotiated.
E2ARC: Energy-efficient adaptive resource block allocation with low complexity in device-to-device communication
- First Published: 30 October 2018
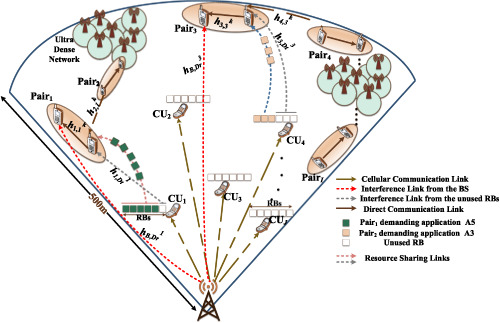
An adaptive resource block (RB) mechanism has been proposed for a D2D communication network in the fifth-generation cellular networks to achieve the objective of green communication and term as E2ARC. As a result of adaptive RB allotment, which is performed stochastically, a high degree of fairness is achieved with enhanced energy efficiency and reduced complexity.




