Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Use of aminoglycoside antibiotics in equine clinical practice; a questionnaire-based study of current use
- Pages: 279-288
- First Published: 24 October 2020
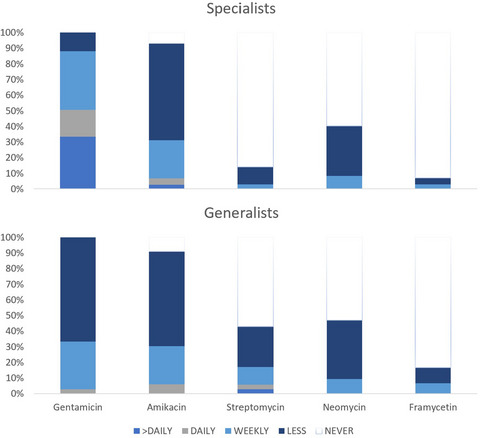
Gentamicin is the most important and commonly used aminoglycoside used in equine practice, although commonly used for conditions outside its marketing authorisation. Amikacin is the aminoglycoside most commonly used by the intra-articular or regional route. Dosing of aminoglycosides used in clinical practice could be enhanced through wider use of therapeutic drug monitoring.
Surveillance assessment for veterinary biocidal products in Korea: A laboratory investigation
- Pages: 289-296
- First Published: 27 October 2020
Three highly hazardous pesticides (coumaphos, dichlorvos and methomyl) and 10 active ingredients (abamectin, amitraz, chlorpyrifos-methyl, cypermethrin, cyromazine, fipronil, fluvalinate, muscamone, pyriproxyfen and trichlorfon) deviated from the stated concentrations. Thus, management plans should be established to distribute compliant veterinary drugs by post-distribution quality control, such as planning inspection.
CASE REPORTS
Surgical excision of a malignant metastatic melanoma located in a skeletal muscle of the lateral thorax of a horse
- Pages: 297-302
- First Published: 29 September 2020
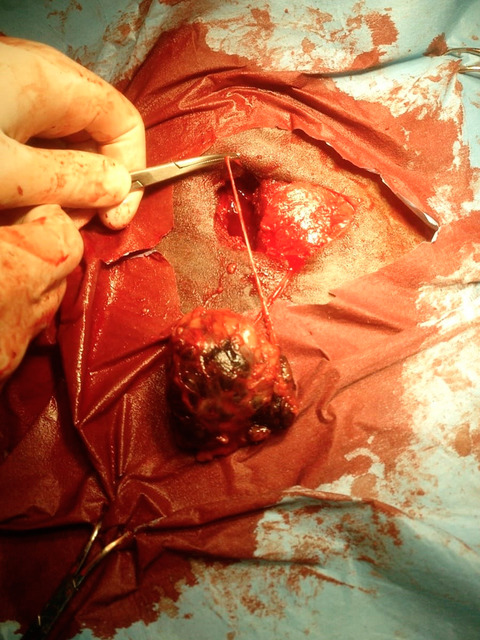
A 20-year-old grey Warmblood gelding was referred for evaluation of a large, rapidly growing, thoracic mass. Histopathology of the distant thoracic mass confirmed the diagnosis of malignant metastatic melanoma. Surgical excision of the metastatic melanoma was performed and considered successful, with no gross evidence of tumour reoccurrence.This report proposes surgical excision as a treatment option for distant malignant metastatic melanocytic masses in skeletal muscle.
First case report on the occurrence of Trypanosoma evansi in a Siam B Mare in Kelantan, Malaysia
- Pages: 303-309
- First Published: 07 November 2020
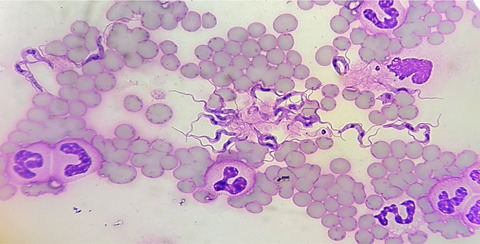
This first positive Surra case in Siam B mare in Kelantan, Malaysia, that is bordering Thailand confirms the increasing concern of transboundary infections. Thin blood smear and examination revealed the presence of Trypanosoma sp., and it was confirmed as T. evansi through molecular identification. Histopathology revealed that the horse developed a neurological form of the disease, besides the detection of the protozoa in heart, spleen and kidney tissue.
REVIEWS
Characterization of potential superspreader farms for bovine tuberculosis: A review
- Pages: 310-321
- First Published: 16 September 2020
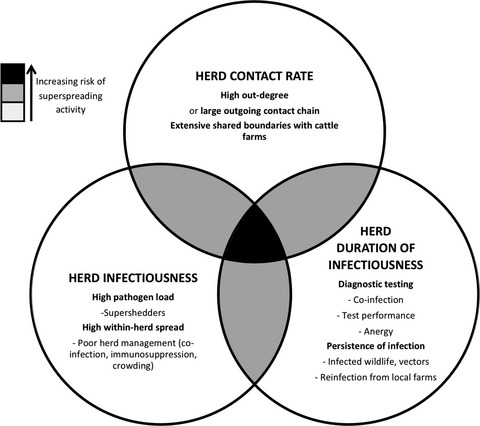
In the epidemiology of bovine tuberculosis (bTB) in Great Britain, a minority of ‘superspreader farms’ might make disproportionate contributions to the maintenance and spread of infection. A minority of farms act as trading hubs that greatly augment connections in trading networks, herd infectiousness might be increased by the presence of supershedding individuals, and herd infectiousness might be prolonged due to undetected infections or repeated local transmission, via wildlife or fomites. Targeting control methods on putative superspreader farms might yield disproportionate benefits in controlling endemic bovine tuberculosis in Great Britain.
Coronaviruses in farm animals: Epidemiology and public health implications
- Pages: 322-347
- First Published: 25 September 2020
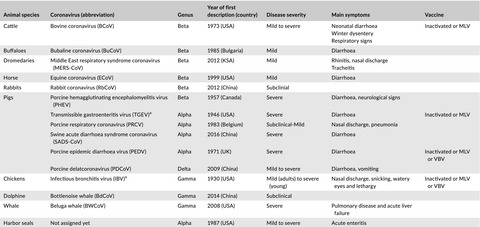
Animals coronaviruses cause mild to severe infections among farm animals, with high economic and public health impacts for some of them. Increasing demand in animal meat, animal trade and mixing different animal species together foster coronaviruses cross-species transmission and expose human to new coronaviruses.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
A retrospective study (2007–2015) on brucellosis seropositivity in livestock in South Africa
- Pages: 348-356
- First Published: 22 October 2020
A rapid and simple single-step method for the purification of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites and bradyzoites
- Pages: 357-361
- First Published: 26 September 2020
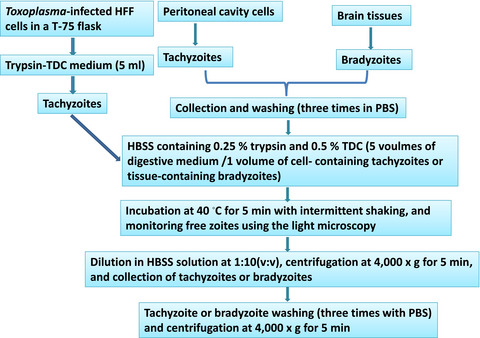
We developed a rapid and simple method for purifying tachyzoites and bradyzoites with optimal yield and purity. The new proposed method has the following advantages: (1) zoites can be obtained quickly and easily; (2) the technique can be performed in low resource settings and capable of handling larger numbers of cells and tissues; (3) zoites obtained in this way are free of cellular debris; and (4) the viability and infectivity of tachyzoites, and bradyzoites are maintained. A more detailed study is required to explore the effect of trypsin on surface antigens of parasites.
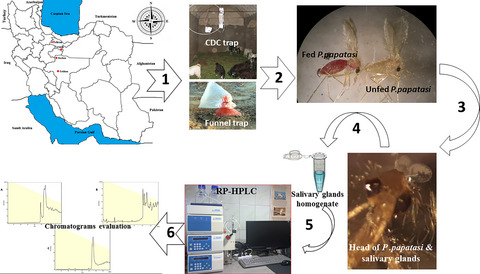
Comparative evaluation of salivary glands proteomes from wild Phlebotomus papatasi–proven vector of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran
- Pages: 362-369
- First Published: 24 September 2020
Enhanced omega-3 index after long- versus short-chain omega-3 fatty acid supplementation in dogs
- Pages: 370-377
- First Published: 06 October 2020
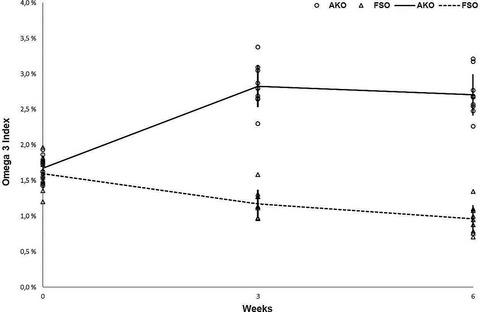
This study investigated supplementation of two different omega-3 fatty acid sources i.e. plant (flaxseed oil, FSO) versus marine (astaxanthin krill oil, AKO) to compare the effects of short- versus long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) on the Omega-3 Index in dogs. The results suggest that preformed marine EPA and DHA sources are needed in dog feeds, as the dietary requirements are not met with conversion from equal dosage of the short-chain omega-3 PUFA precursor, ALA from flaxseed oil.
CASE REPORT
Cutaneous myiasis in cats and dogs: Cases, predisposing conditions and risk factors
- Pages: 378-384
- First Published: 18 December 2020
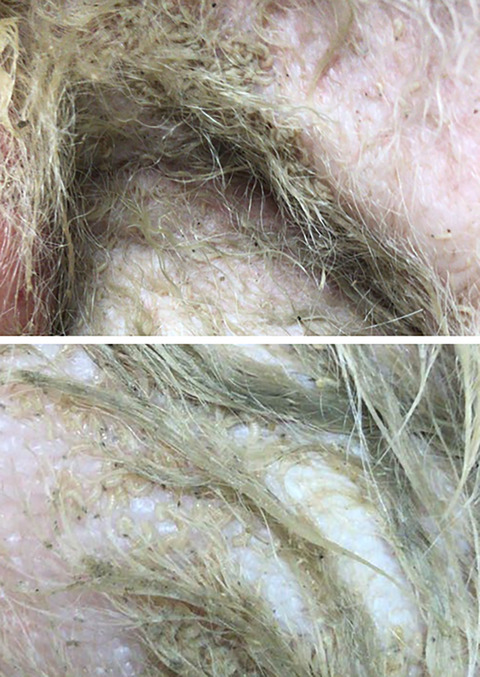
The first case of cutaneous myiasis by Calliphora vicina (Diptera: Calliphoridae) in a domestic cat Felis silvestris catus (Carnivora: Felidae) in Italy was reported. An unusual case of cutaneous myiasis in a domestic dog Canis lupus familiaris (Carnivora: Canidae) caused by Lucilia sericata (Diptera: Calliphoridae) was also reported. The predisposing conditions and risk factors of the cutaneous myiasis in cats and dogs were also discussed.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Plasma Cytokeratin 18 and fecal Alpha-1 Antitrypsin concentrations in dogs with osteosarcoma receiving carboplatin chemotherapy
- Pages: 385-392
- First Published: 22 November 2020
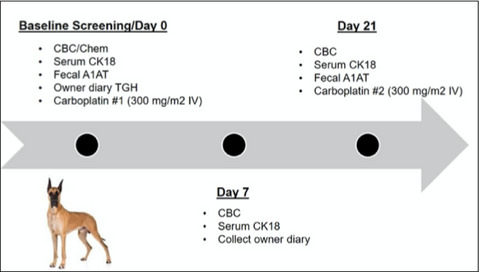
Gastrointestinal (GI) toxicosis is a common side effect of cytotoxic chemotherapy treatment in humans and dogs. This study investigated the clinical utility of plasma cytokeratin 18 and fecal alpha-1 antitrypsin as non-invasive biomarkers of GI epithelial cell damage. In this study population, plasma CK18 and fecal A1-AT concentration were not clinically useful biomarkers for the detection of GI toxicosis secondary to carboplatin administration.
Sequential haematological and serum biochemical changes in Black Bengal goats infected with a local isolate of peste des petits ruminants virus from Bangladesh
- Pages: 393-401
- First Published: 03 October 2020
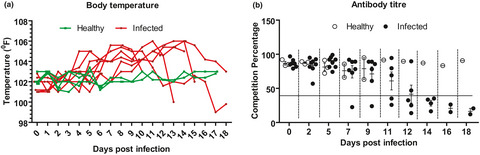
The sequential haematobiochemical changes in a Bangladeshi PPR virus strain was studied in Black Bengal goats upon experimental infection. The PPRV RNA was detected in different tissues of the infected goats. Infected goats showed high fever, nasal discharges, stomatitis and diarrhoea at 9–13 dpi. Leukopenia, hypoproteinemia, elevated serum enzymes and metabolites and electrolyte imbalance were found in the infected goats. The findings would guide in preparing appropriate supportive therapy against PPRV infection.
Evaluation of tree lucerne (Chamaecytisus palmensis) dried leaves as a substitution for concentrate mixture on biological performance and socioeconomic of Washera sheep fed on desho grass hay
- Pages: 402-416
- First Published: 10 October 2020
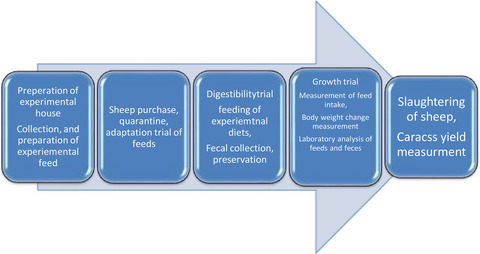
The experiment was conducted to evaluate the effect of tree lucerne dried leaves and to determine the optimum level of substituting for concentrate mixtures (CM) on feed intake, nutrient digestibility, body weight change, carcass characteristics and economic benefits of using Washera sheep fed on desho grass hay as a basal diet.
Echocardiographic evaluation in Dorper ovine fetuses: Applications and limitations
- Pages: 417-423
- First Published: 29 October 2020
Effect of gaseous hydrogen sulphide on growth performance and cecal microbial diversity of weaning pigs
- Pages: 424-431
- First Published: 30 July 2020
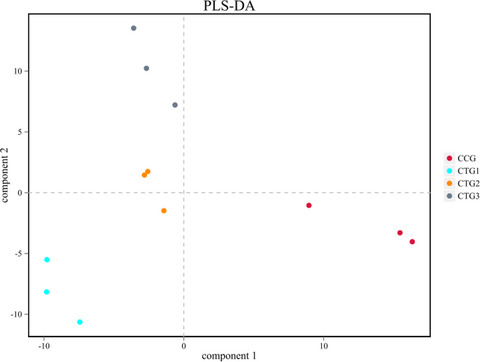
24 weaning pigs were exposed to hydrogen sulfide (0, 5, 10 and 15 mg/m3) in 4 controlled environmental chambers for 28 days.The results showed that exposure to gaseous hydrogen sulfide damaged the growth performance and resulted the microbial bacteria imbalance.The concentration of hydrogen sulfide should fall below 5 mg/m3.
An efficient cephalosporin stewardship programme in French swine production
- Pages: 432-439
- First Published: 08 February 2021
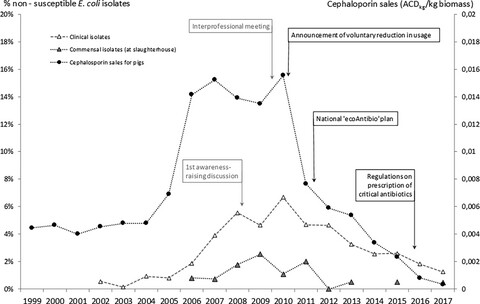
This study details success conditions of an antimicrobial stewardship program in animal agriculture. Based on data provided by complementary and independent monitoring tools, success could be assessed on both usage and resistance. Results highlight the strong relationship between cephalosporins usage and resistance in pig production, supporting a containment perspective through usage restriction.
Antibiotic use in pig farming and its associated factors in L County in Yunnan, China
- Pages: 440-454
- First Published: 07 November 2020
This survey conducted in a county in Yunnan Province of China finds out that 83.7% of the farmers reported ‘self-purchasing’ antibiotics for their pigs and 40.3% of the farmers expressed that they ‘often’ use antibiotics in pig farming with the major purposes being prevention and treatment of pig diseases.
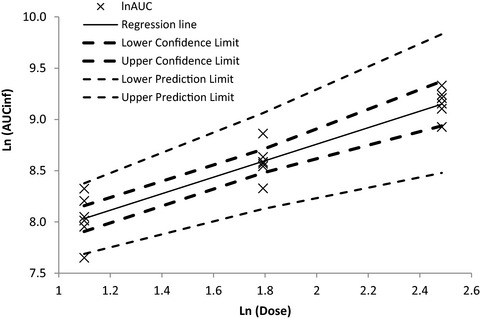
Gamithromycin in swine: Pharmacokinetics and clinical evaluation against swine respiratory disease
- Pages: 455-464
- First Published: 15 October 2020
Identification of optimal assisted aspiration conditions of oocytes for use in porcine in vitro maturation: A re-evaluation of the relationship between the cumulus oocyte complex and oocyte quality
- Pages: 465-473
- First Published: 21 November 2020
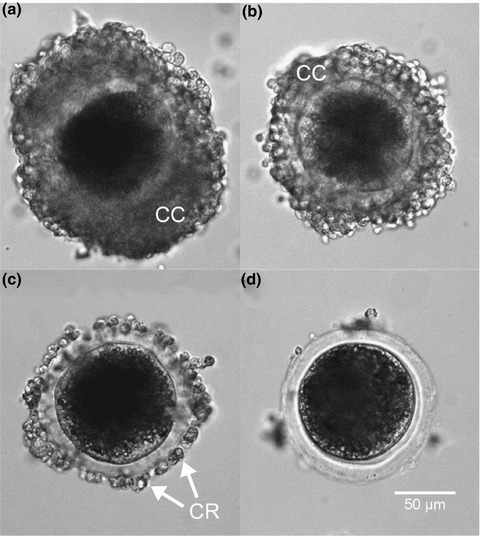
The global population is expected to rise dramatically over the next few decades. This means that the demand for meat, including pig derived products will also increase, and that a more sustainable way to produce such products is necessary. The establishment of production scale pig embryo in vitro production (IVP) could be one answer to this problem, however some challenges still exist, one of which is that pig IVP requires the consistent isolation of large numbers of high-quality oocytes. Here, ways of maximising both the yield and the developmental potential of oocytes from abattoir derived ovaries has been investigated.
Genotyping of PCV3 based on reassembled viral gene sequences
- Pages: 474-482
- First Published: 10 October 2020
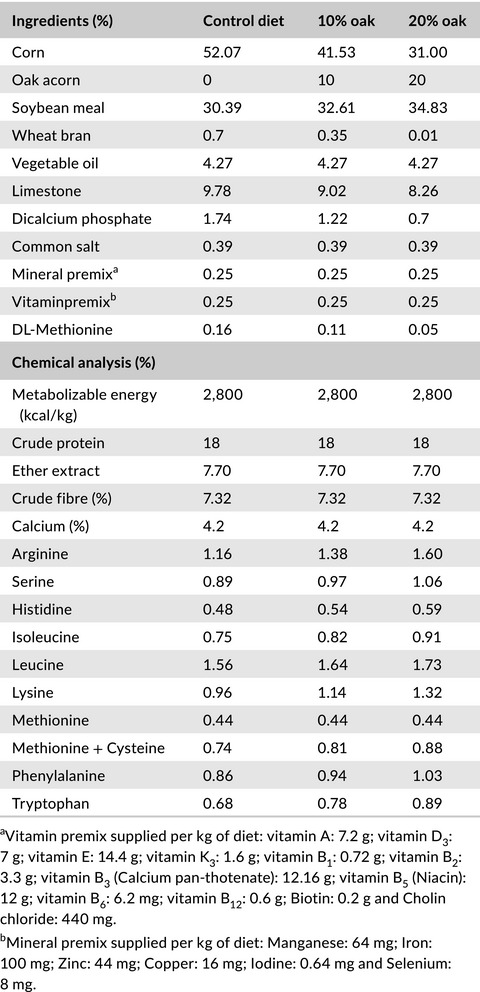
Egg quality traits, blood biochemical parameters and performance of laying hens fed diet included processed oak fruit
- Pages: 483-490
- First Published: 22 October 2020
Evaluation of various levels of sweet almond meal as a source of protein on the production variables and immune response of broiler chickens
- Pages: 491-499
- First Published: 07 November 2020
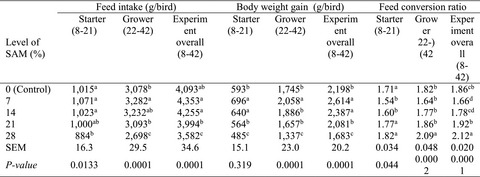
This experiment was conducted to evaluate effects of various levels of sweet almond meal (SAM) as source of protein in broiler nutrition with different levels of SAM (0, 7%, 14%, 21% and 28% of diet). The results of this study show that a diet supplemented with SAM at the level of 14%, due to the improved FCR and decreased blood cholesterol and LDL concentration, can be a good replacement for soybean meal in broiler chicken's nutrition.
Musa paradisiaca L. leaf and fruit peel hydroethanolic extracts improved the lipid profile, glycemic index and oxidative stress in nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Pages: 500-511
- First Published: 05 December 2020
Nutmeg extract potentially alters characteristics of white adipose tissue in rats
- Pages: 512-520
- First Published: 03 January 2021
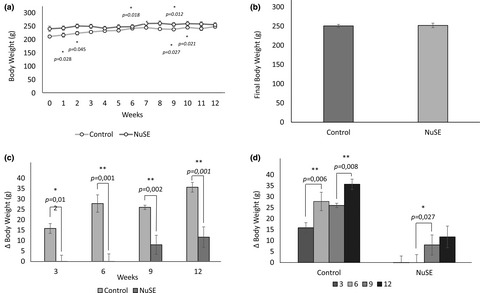
White adipose tissue (WAT) browning has been considered as one of the promising approaches in obesity treatment. In WAT browning process, the characteristics of WAT are transformed into brown-like adipose tissue (known as beige adipose tissue) via stimulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors γ (PPARγ) pathway. Interestingly, Indonesian society has been using nutmeg which may mimic browning effect via inducing macroscopic and microscopic morphological changes of iWAT, marked by significant increase of adipocyte number and decrease of adipocyte size. in addition, The increases in UCP1 and PGC-1α along with histological changes reveal that NuSE may potentially alter the characteristic of iWAT that lead to browning process and contribute to obesity treatment.
Effect of flaxseed oil on biochemical parameters, hormonal indexes and stereological changes in ovariectomized rats
- Pages: 521-533
- First Published: 25 October 2020
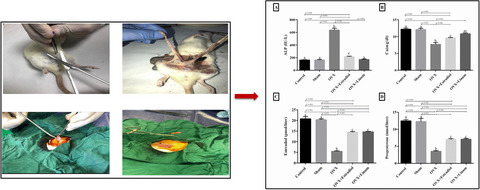
- The potential use of flaxseed oil as the natural source for hormone replacement therapy on the ovariectomized rat model was investigated.
- The antioxidant properties and biochemical parameters including alkaline phosphatase, calcium, estrogen, and progesterone levels were determined in ovariectomy rats.
Influence of Salmonella specific bacteriophages (O1; S16) on the shedding of naturally occurring Salmonella and an orally applied Salmonella Eastbourne strain in bearded dragons (Pogona vitticeps)
- Pages: 534-547
- First Published: 07 November 2020
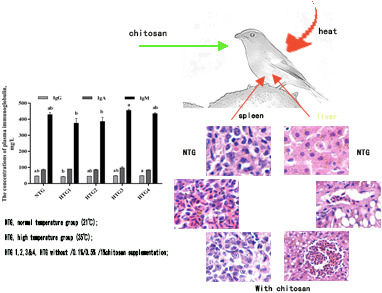
Chitosan supplementation reduces oxidative stress in Leiothrix lutea in acute heat stress
- Pages: 548-553
- First Published: 29 October 2020
Vitamin A deficiency and its treatment in captive Sunda pangolins
- Pages: 554-558
- First Published: 15 October 2020
Evolutionary study of COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as an emerging coronavirus: Phylogenetic analysis and literature review
- Pages: 559-571
- First Published: 18 November 2020
CASE REPORT
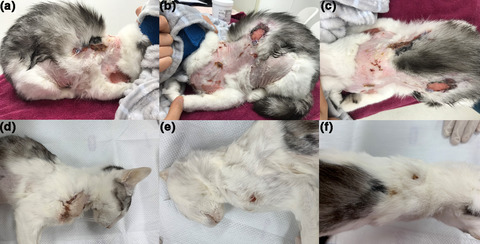
Idiopathic ulcerative dermatitis in a cat with feline infectious peritonitis
- Pages: 572-576
- First Published: 31 December 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Functional analysis of CD44 variants and xCT in canine tumours
- Pages: 577-585
- First Published: 18 November 2020
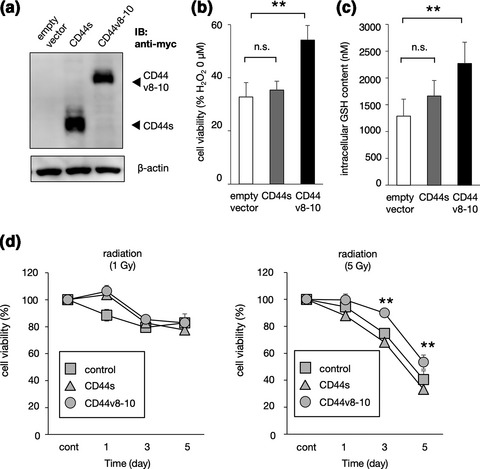
CD44v8-10 contributes H2O2- and radio-resistance of canine breast tumour cells by promoting the production of GSH. A. The expression of CD44s or CD44v8-10 molecules of these transfectants. B. The H2O2-resistance of these transfectants. C. The cellular GSH content of CD44 transfectants. D. The radio-resistance of CD44 transfectants.
The effects of doxapram on haematology, serum biochemical parameters and erythrocyte oxidant/ antioxidant status in dogs anaesthetized with propofol
- Pages: 586-592
- First Published: 18 November 2020

The present prospective randomized experimental study was designed to determine the effects of doxapram on hematological, serum biochemical and antioxidant status in dogs after propofol anesthesia. Twenty four healthy male mixed breed dogs were studied. Doxapram (2 mg kg-1) IV did not induce any major negative effects on hematological, serum biochemical variables and oxidant/antioxidant status in dogs after propofol anaesthesia.
CASE REPORT
Extensive hepatic portal venous gas and gastric pneumatosis in a cat
- Pages: 593-599
- First Published: 22 November 2020
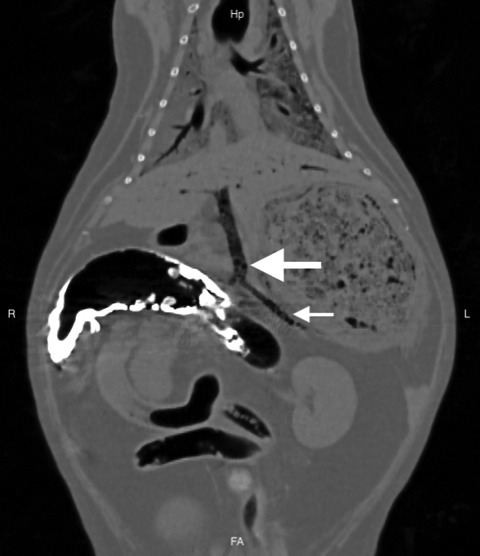
This report describes a case of hepatic portal venous gas (HPVG) in a feline visualized initially on ultrasound and ultimately confirmed with CT, which is considered the gold-standard for identification in humans. HPVG is associated with a variety of underlying disease processes, some of which require emergent aggressive intervention and may result in significant mortality. Reports of HPVG in veterinary medicine are sparse.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A retrospective survey of the seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in wild animals in Japan
- Pages: 600-605
- First Published: 29 November 2020
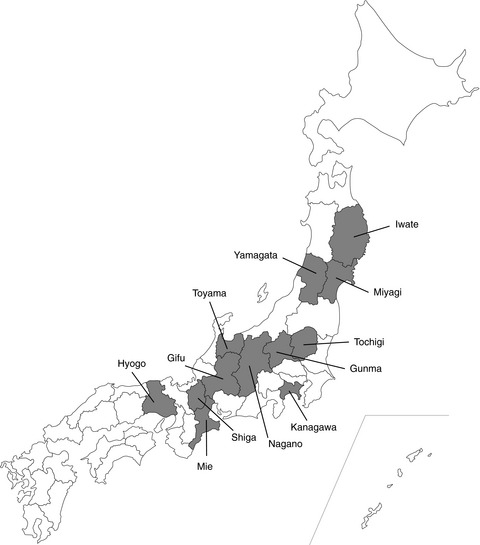
In this study, we investigated the presence of anti-SFTSV antibodies in a total of 521 serum samples from nine wild animal species collected from 11 prefectures in central and eastern Japan between 1980 and 2000. All samples yielded negative results for antibodies to SFTSV, suggesting that there had been few or no SFTSV infections before 2000 in the sampled areas.