Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ENDOSCOPY
AI in colonoscopy and beyond: On the cusp of clinical implementation?
- Pages: 525-526
- First Published: 07 May 2021
Current status and limitations of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy
- Pages: 527-533
- First Published: 07 June 2021
PANCREAS
Serum phosphate is associated with mortality among patients admitted to ICU for acute pancreatitis
- Pages: 534-542
- First Published: 05 May 2021
-
This is the first study that evaluates the role of serum phosphate at baseline for predicting the mortality of acute pancreatitis (AP) in intensive care unit (ICU).
-
This study found that serum phosphate is a useful laboratory marker for predicting the mortality of AP independently of other known factors.
-
This study found that serum phosphate value greater than 3.78 mg/dl within the first 24 h after admission in the ICU could predict mortality (area under curve = 0.7, p < 0.001, sensitivity 58%; specificity 77%).
LUMINAL
Divergent trends of hospitalizations for upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding based on population prescriptions of aspirin, proton pump inhibitors and Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: Trends of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding
- Pages: 543-551
- First Published: 06 May 2021
Summarize the established knowledge on this subject
-
With increasing use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy, the incidences of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) are declining.
-
The increasing use of antiplatelets and anticoagulants, however, increases the risk of both UGIB and lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB).
-
The dynamic contribution of these factors on the incidences of UGIB and LGIB at population level remains uncertain.
What are the significant and/or new findings of this study?
-
The incidences of UGIB showed a clear declining trend while LGIB decreased slightly over the past decade in Hong Kong.
-
LGIB had actually surpassed UGIB as the leading source of GIB, especially among older population.
-
The increasing PPIs prescription was associated with the falling incidences of UGIB, whereas the rising use of aspirin was associated with both an increase in UGIB and LGIB.
-
With the increasing use of aspirin and the lack of effective prevention preventive strategies, LGIB would become a major health challenge.
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
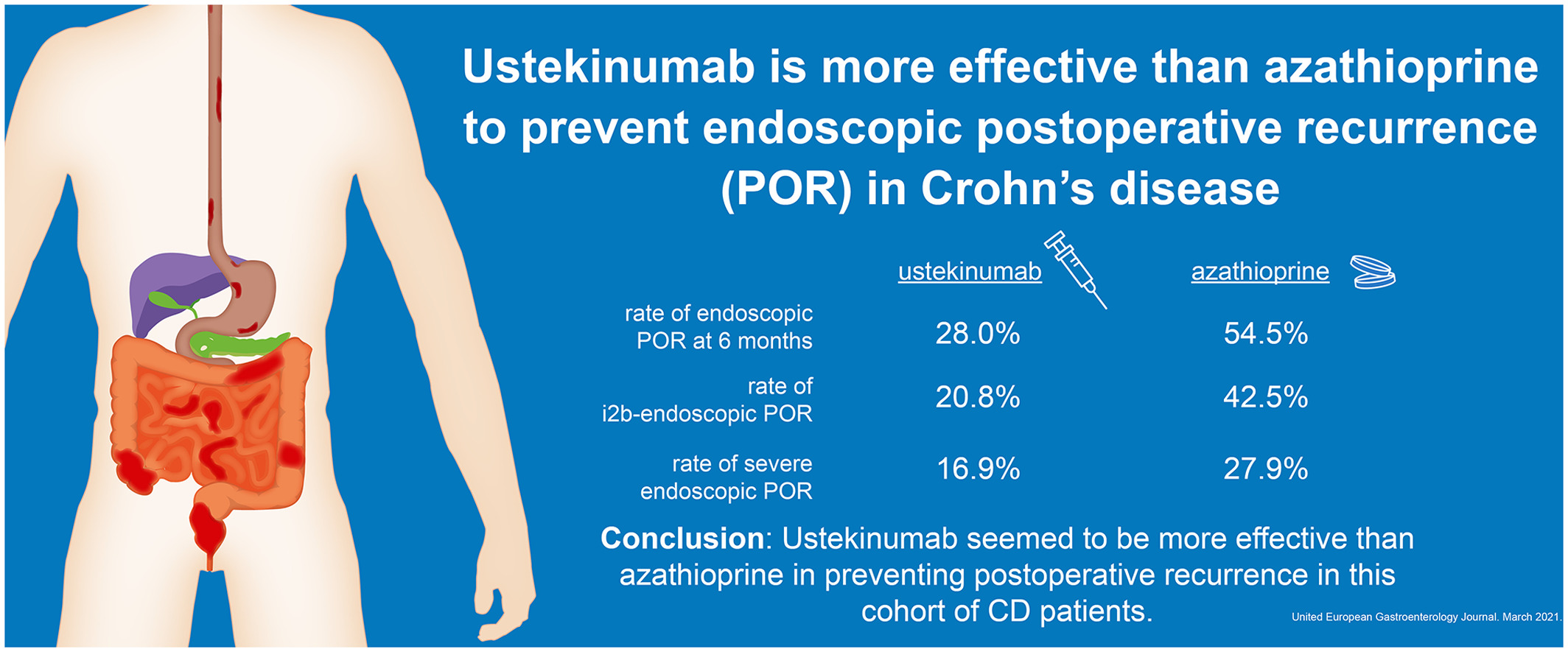
Ustekinumab is more effective than azathioprine to prevent endoscopic postoperative recurrence in Crohn's disease
- Pages: 552-560
- First Published: 05 May 2021
ENDOSCOPY
Morbid obesity but not obesity is associated with increased mortality in patients undergoing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A national cohort study
- Pages: 561-570
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Established knowledge on this subject
-
1. Obesity is a prevalent phenomenon.
-
2. The impact of obesity and morbid obesity on mortality in patients undergoing ERCP remains unclear.
Significant and/or new findings of this study?
-
1. Morbid obesity but not obesity was associated with increased mortality in patients undergoing ERCP.
HEPATOBILIARY
Plasma procalcitonin may be an early predictor of liver injury in acetaminophen poisoning: A prospective cohort study
- Pages: 571-580
- First Published: 28 June 2021
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
The impact of ustekinumab on extraintestinal manifestations of Crohn's disease: A post hoc analysis of the UNITI studies
- Pages: 581-589
- First Published: 02 June 2021
Summarise the established knowledge on this subject
-
Summarise the established knowledge on this subject
-
In a systematic review, ustekinumab was found to be effective in treating
-
dermatologic manifestations such as psoriasis, pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum, and rheumatologic manifestations such as arthralgias and psoriatic arthritis in IBD
-
However, existing evidence is limited due to retrospective evaluations, small sample sizes and lack of comparator groups
-
Overall, there is a paucity of data regarding the effectiveness of ustekinumab for treatment of extraintestinal manifestations in Crohn's disease
What are the significant and/or new findings of this study?
-
Patients with Crohn's disease treated with ustekinumab had overall no significant resolution of EIMs as compared to those treated with placebo at week 6 and week 52
-
Among individual EIMs, only erythema nodosum was significantly reduced in patients treated with ustekinumab at week 52 compared to placebo-treated patients
HEPATOBILIARY
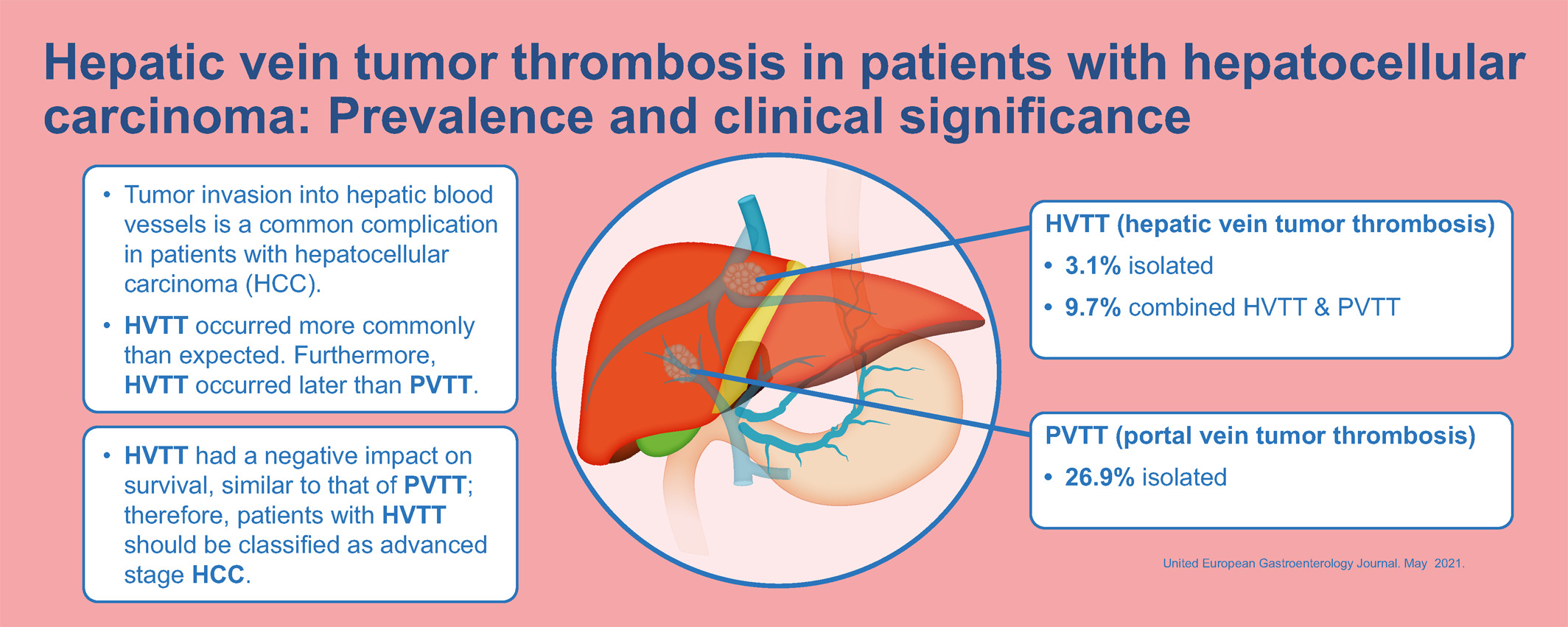
Hepatic vein tumor thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: Prevalence and clinical significance
- Pages: 590-597
- First Published: 02 June 2021
NEUROGASTROENTEROLOGY
European guideline on indications, performance and clinical impact of 13C-breath tests in adult and pediatric patients: An EAGEN, ESNM, and ESPGHAN consensus, supported by EPC
- Pages: 598-625
- First Published: 14 June 2021
LUMINAL
Early risk stratification of patients with suspected chronic mesenteric ischaemia using a symptom and mesenteric artery calcium score based score chart
- Pages: 626-634
- First Published: 02 June 2021
Summarise the established knowledge on this subject
-
Mesenteric artery stenoses are prevalent (6%–29%), but as a result of the compensatory capacity of the mesenteric circulation, the incidence of chronic mesenteric ischaemia (CMI) is 9.2 per 100,000
-
Early risk stratification could facilitate the diagnostic trajectory of chronic mesenteric ischaemia in order to triage patients that do or do not need a further diagnostic workup
-
The mesenteric artery calcium score (MACS) identifies CMI patients with a sensitivity of 88% and can be obtained from both non-contrast enhanced and contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT)
-
The score chart by van Dijk et al. might guide subsequent treatment decisions in patients with a clear suspicion of chronic mesenteric ischaemia, but requires an arterial contrast enhanced computed tomography angiography (CTA)
What are the significant and/or new findings of this study?
-
A CT-based score chart composed of the variables weight loss, postprandial abdominal pain, cardiovascular disease, and MACS, showed excellent discrimination between patients with and without CMI
-
The actual CMI risk was 2.1% in the predicted low-risk group (0–4 points) of the MACS score chart and 39.1% in the increased risk group (5–10 points) of the MACS score chart
-
The near-perfect negative predictive value (97.9%) and sensitivity (97.8%) of the MACS score chart suggests that a score of ≤4 points virtually rules out CMI, while no patients are misclassified
-
In this independent cohort the CTA-based score chart by van Dijk et al. was confirmed to have an excellent discriminative ability to guide treatment decisions in patients with suspected CMI
NEWS
Young gastrointestinal angle: E-learning in gastroenterology: Future is now
- Pages: 635-637
- First Published: 26 May 2021