Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
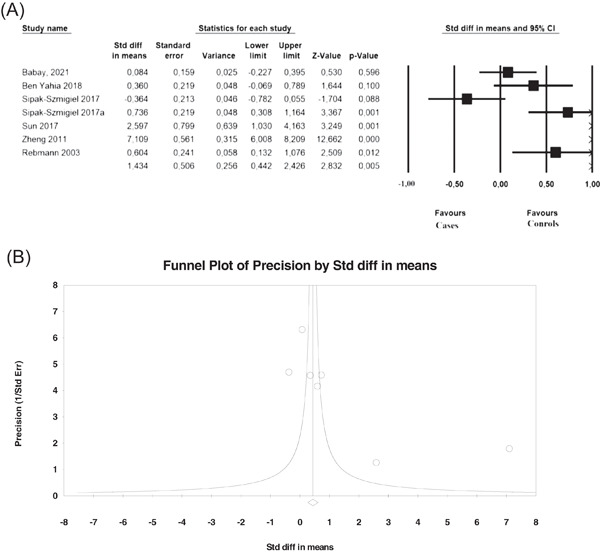
The relationship of 3′UTR HLA-G14-bp insertion/deletion and +3142 C/G polymorphisms and soluble HLA-G expression with gynecological cancers: An updated meta-analysis
- First Published: 06 June 2022
REVIEW ARTICLES
CHD4 orchestrates the symphony of T and B lymphocytes development and a good mediator in preventing from autoimmune disease
- First Published: 06 June 2022
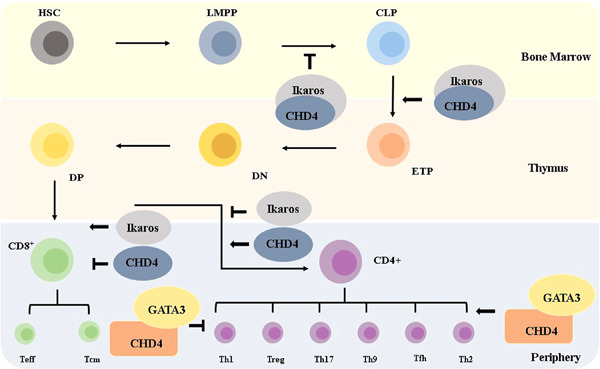
Chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 4 (CHD4) is an ATPase subunit of the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylation complex. It has been implicated in gene transcription, DNA damage repair, maintenance of genome stability, and chromatin assembly. Recently, some researchers have explored the CHD4 functions on the development and differentiation of adaptive immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes. In this review, we will discuss the details of CHD4 in lymphocyte differentiation and development, as well as the critical role of CHD4 in the pathogenesis of the autoimmune disease.
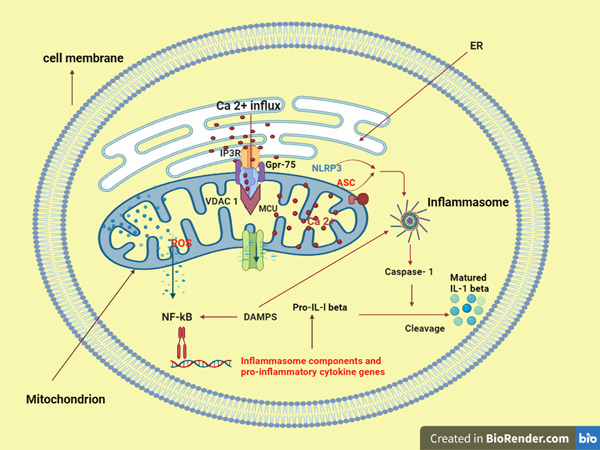
The mitochondrial associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes: A platform for the pathogenesis of inflammation-mediated metabolic diseases
- First Published: 06 June 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
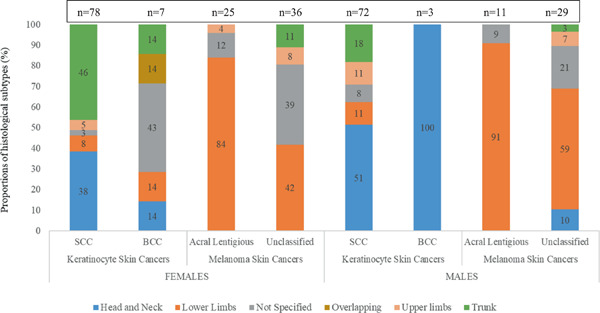
Skin cancer risk factors among Black South Africans—The Johannesburg Cancer Study, 1995–2016
- First Published: 06 June 2022
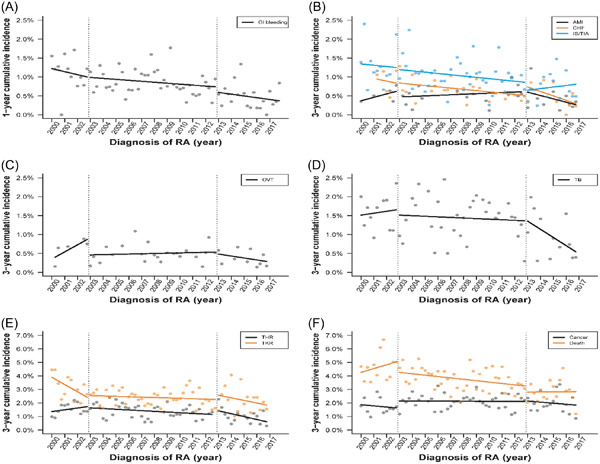
Trends of adverse events and mortality after DMARDs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Interrupted time-series analysis
- First Published: 20 June 2022
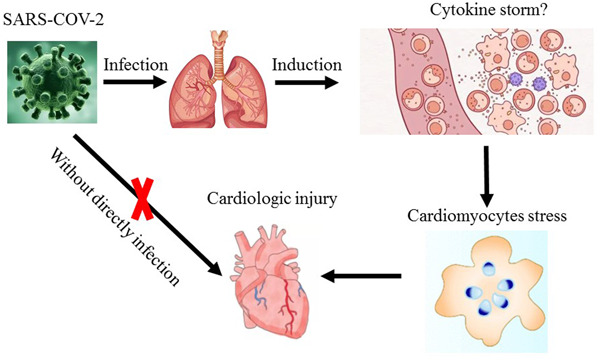
An alternative way of SARS-COV-2 to induce cell stress and elevated DNA damage risk in cardiomyocytes without direct infection
- First Published: 10 June 2022
Insights from a computational analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Host–pathogen interaction, pathogenicity, and possible drug therapeutics
- First Published: 21 June 2022
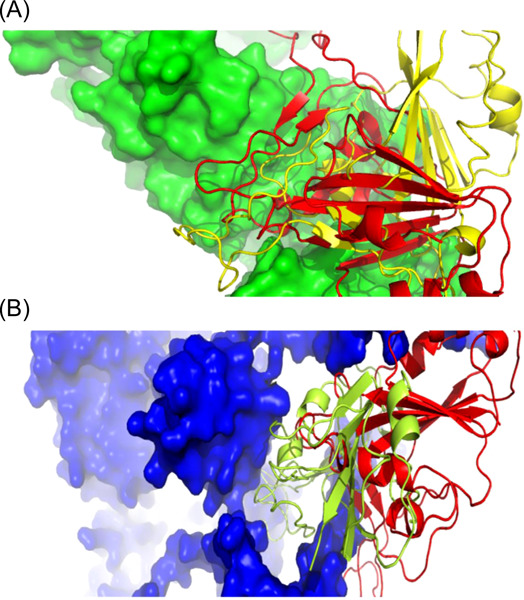
Parvez et al. investigate genomic sequences and drug efficacy via a bioinformatic approach with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. At first, they perform a comparative analysis of Omicron variant with other variants, and then they evaluate the binding affinity with human receptors, ACE2, NRP1, BSG and DPP4. Finally, they analyze the drug effectiveness against the Omicron targeting Main Protease, and found that Nirmatrelvir (Paxlovid), 13b, and Lopinavir displayed increased effectiveness and efficiency
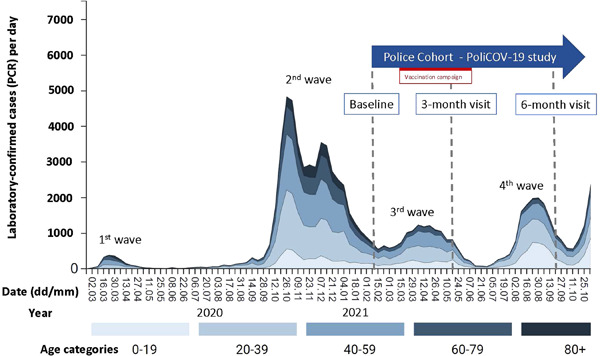
Serosurveillance after a COVID-19 vaccine campaign in a Swiss police cohort
- First Published: 06 June 2022
TRPM7 promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory dysfunction in renal tubular epithelial cells
- First Published: 20 June 2022
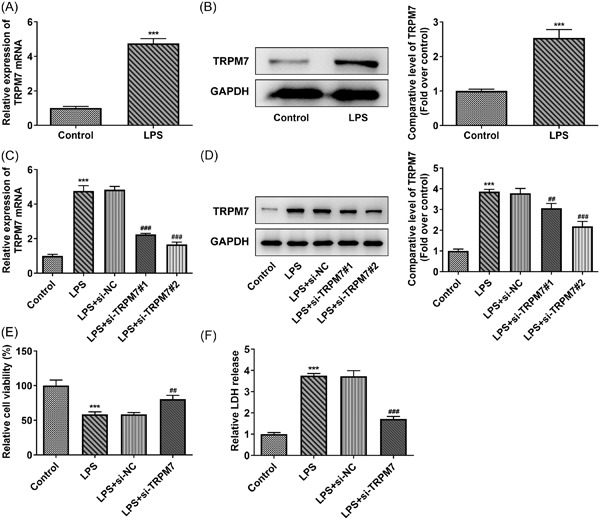
TRPM7 is negatively regulated by KLF2 transcription and promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory dysfunction via activating the MAPK pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. This article lays the necessary theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.
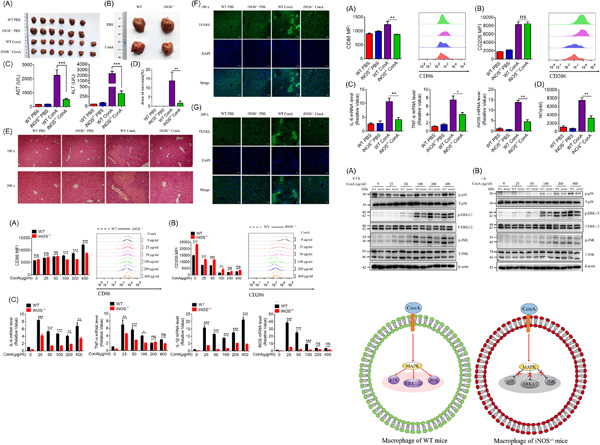
Inducible nitric oxide synthase regulates macrophage polarization via the MAPK signals in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis
- First Published: 06 June 2022
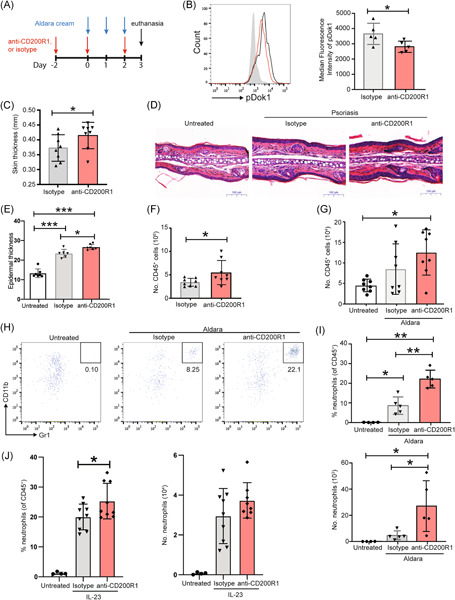
Reduced cutaneous CD200:CD200R1 signaling in psoriasis enhances neutrophil recruitment to skin
- First Published: 06 June 2022
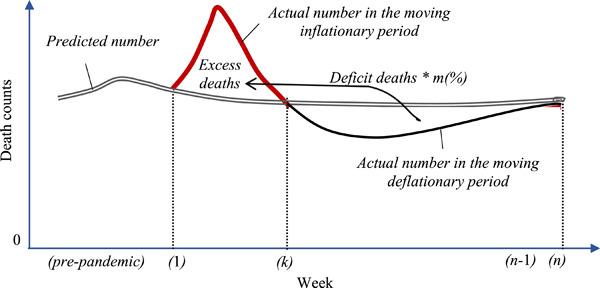
Weeks of life lost to COVID-19, the case of the United States
- First Published: 20 June 2022
PGE2 inhibits neutrophil phagocytosis through the EP2R–cAMP–PTEN pathway
- First Published: 10 June 2022
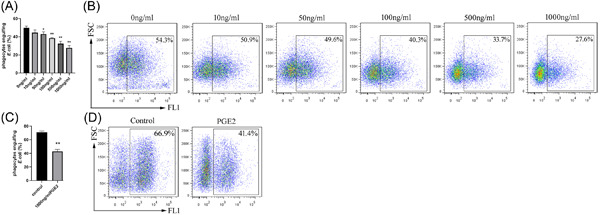
In this study, we assessed the effect of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) on the phagocytosis of bacteria by neutrophils, which are key players during infection and inflammation. Specific inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) enzyme attenuated the inhibition of neutrophil phagocytosis by PGE2, and both PGE2 and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) increased neutrophil PTEN activity, which was associated with decreased PTEN phosphorylation. The results support negative regulation of the antimicrobial activity of neutrophils (i.e., phagocytosis), which has important implications for the future management of bacterial infections.
Overexpression of long noncoding RNA LINC00638 inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
- First Published: 20 June 2022
EBV protection- and susceptibility-related HLA alleles and EBV status in the Chinese population: A single-center study
- First Published: 21 June 2022
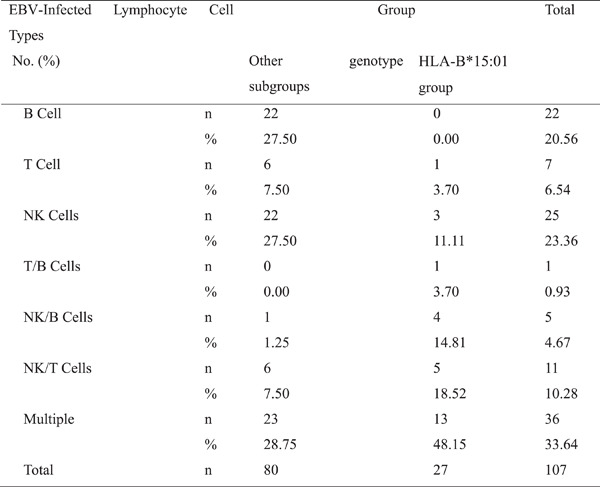
The HLA-B*15:01 group has a higher rate of EBV infection than other genotype subgroups, B*15:01 is more likely to have non-B-cell infections, and the predominant type of EBV-infected lymphocytes in patients with the B*15:01 genotype should be examined. These findings highlight the importance of HLA genotype for EBV infectivity and that HLA genotype may be used as a marker for some important risk classification
Antiviral activity of triptolide on herpes simplex virus in vitro
- First Published: 20 June 2022
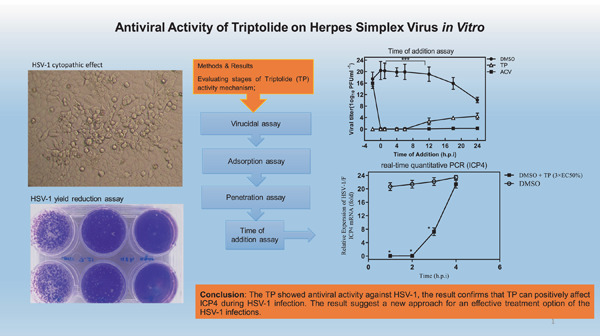
Herpes simplex virus-type 1 (HSV-1) causes significant human diseases, especially in neonates and immunocompromised hosts. Thus, developing novel anti-HSV-1 drugs with low toxicity is necessary for public health. Triptolide (TP) is a diterpenoid triepoxide that, as a natural product, exhibits a broad range of bioactivities. TP also showed antiviral activity against HSV-1. This dose-dependent activity might indicate that a particular cellular component, rather than cytotoxicity, mediated its function. In conclusion, this report proposed new outlooks in investigating the effective treatment options for HSV-1 infections
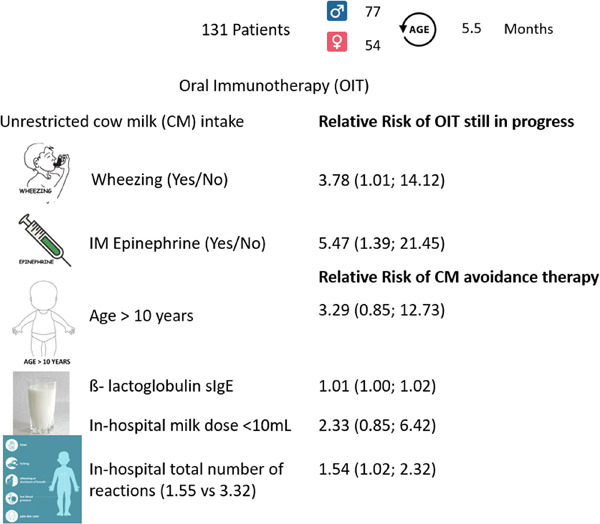
Risk factors for discontinuing oral immunotherapy in children with persistent cow milk allergy
- First Published: 20 June 2022
Association of the MACROD2 rs6110695 A>G polymorphism with an increasing WBC count in a Korean population
- First Published: 25 June 2022

We revealed the MACROD2 rs6110695 AG genotype has an association with increasing white blood cell (WBC) count, which is one of the risk factors for chronic disease in a Korean population. WBC count measurement in individuals with the rs6110695 AG genotype may help manage the future risk of developing chronic disease.
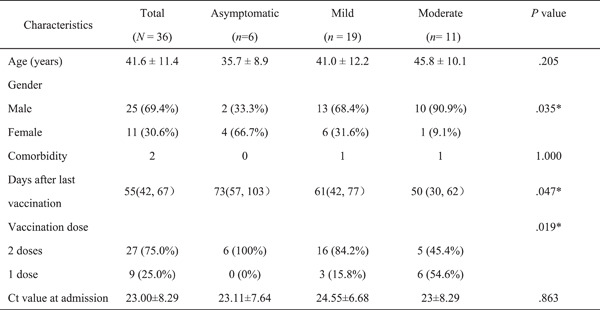
Immunologic features of asymptomatic postvaccination infections with the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 in adults
- First Published: 21 June 2022
SHORT REPORTS
Reduced number of IFN-γ producing cells in peripheral blood is a biomarker for patients with renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 06 June 2022
The latent period of coronavirus disease 2019 with SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant of concern in the postvaccination era
- First Published: 10 June 2022
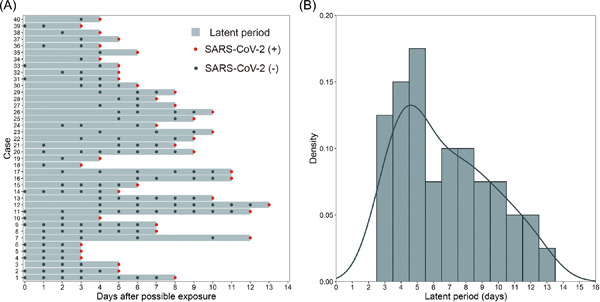
The median latent period of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant of concern (VOC) infection was 6.0 days. No significant difference of the latent period between vaccinated and non-vaccinated patients was found. Our study support that the 14-day quarantine program is sufficient to prevent the transmission of COVID-19 by Delta VOC in the postvaccination era.