Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
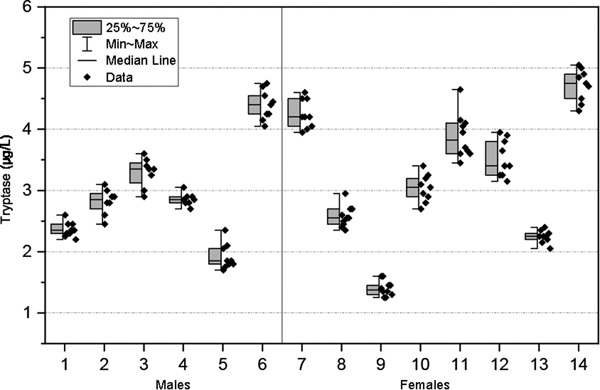
Estimating the within-subject (CVI) and between-subject (CVG) biological variation of serum tryptase
- First Published: 13 December 2021
Oral and intranasal vaccines against SARS-CoV-2: Current progress, prospects, advantages, and challenges
- First Published: 10 March 2022
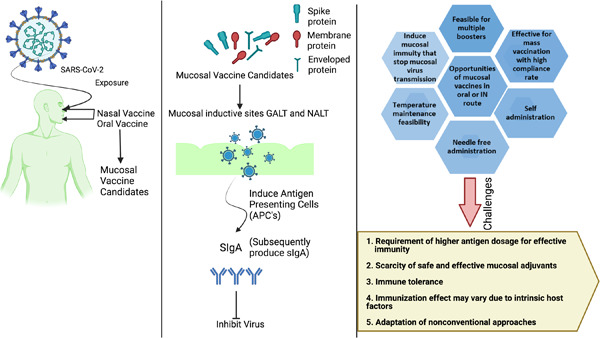
Mucosal vaccines are typically administered either orally or nasally, and several studies have shown promising results for developing these vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that might serve as a viable alternative to current vaccines. SARS-CoV-2 invades the human body via oral and nasal mucosal surfaces; thus, an oral or nasal vaccine can trigger the immune system to inhibit the virus at the mucosal level, preventing further transmission via a strong mucosal and systematic immune response.
Turning point: A new global COVID-19 wave or a signal of the beginning of the end of the global COVID-19 pandemic?
- First Published: 29 March 2022
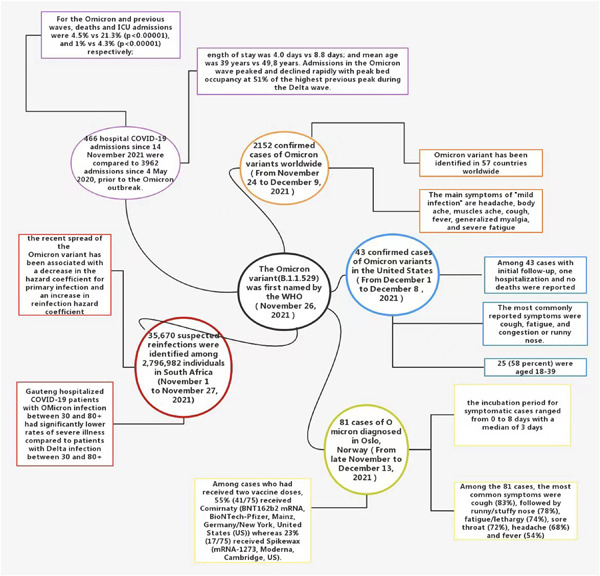
The Omicron variant is highly infectious and highly pathogenic, and some specific mutation sites mean that this variant may be resistant to the vaccine. Some epidemiological evidence has emerged showing that the Omicron variant may lead to milder symptoms in patients. Current vaccines may provide high protection against severe diseases caused by Omicron; therefore, to try to avoid all variants, vaccination and booster shots continue to be recommended.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Kinetics of immune responses to the AZD1222/Covishield vaccine with varying dose intervals in Sri Lankan individuals
- First Published: 22 March 2022
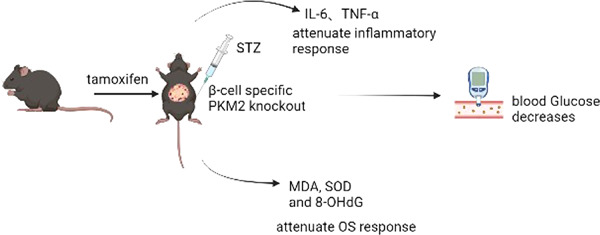
Potential of PKM2 as a drug target in mouse models with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 14 March 2022
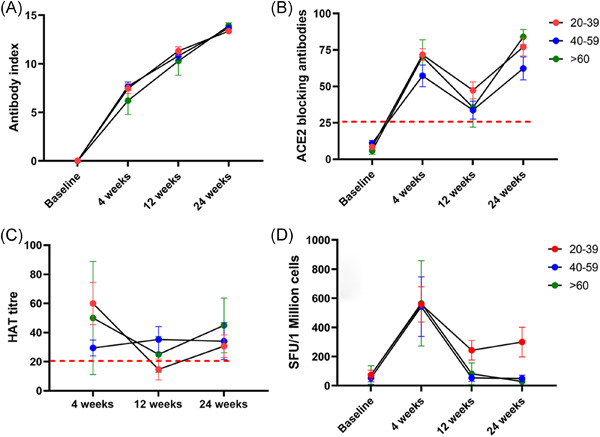
Long-term SARS-CoV-2-specific and cross-reactive cellular immune responses correlate with humoral responses, disease severity, and symptomatology
- First Published: 14 March 2022
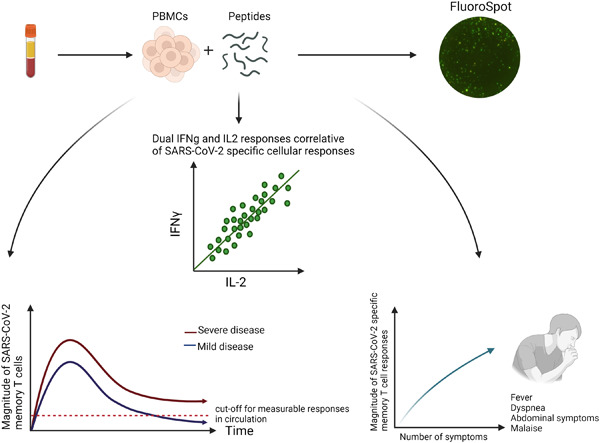
A strong correlation between interferon-gamma (IFNγ) and interleukin-2) (IL-2) producing SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cell responses four months post mild to severe COVID-19. Less cross-reactive responses with a novel designed peptide pool (4%). Cross-reactive T cell secretion in repeatedly seronegative individuals was IFNγ-dominant. Four specific COVID symptoms correlated with the magnitude of the cellular response.
COVID-19 associated EBV reactivation and effects of ganciclovir treatment
- First Published: 10 March 2022
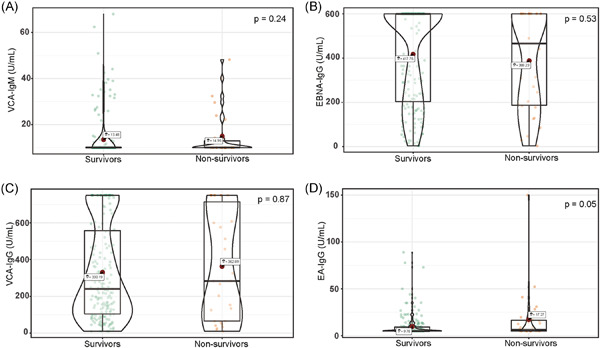
A high proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients had Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) reactivation that may be associated with an increased risk of death. Whether treatment with ganciclovir may decrease the mortality of COVID-19 patients complicated with EBV reactivation warrants to be addressed in a placebo-controlled randomized trial in the future.
Association of increased basic salivary proline-rich protein 1 levels in induced sputum with type 2-high asthma
- First Published: 10 March 2022
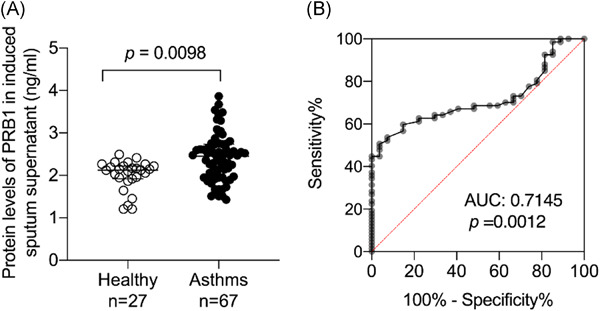
Our study suggests that proline-rich protein BstNI subfamily 1 (PRB1) expression in induced sputum is increased in asthmatic subjects, which demonstrates its association with type 2-high asthma. Thus, PRB1 may be a biological marker for type 2-high asthma. The findings of this study could provide new insights into the diagnosis and treatment of asthma.
Hapten sensitization to vaginal mucosa induces less recruitment of dendritic cells accompanying TGF-β-expressing CD206+ cells compared with skin
- First Published: 10 March 2022
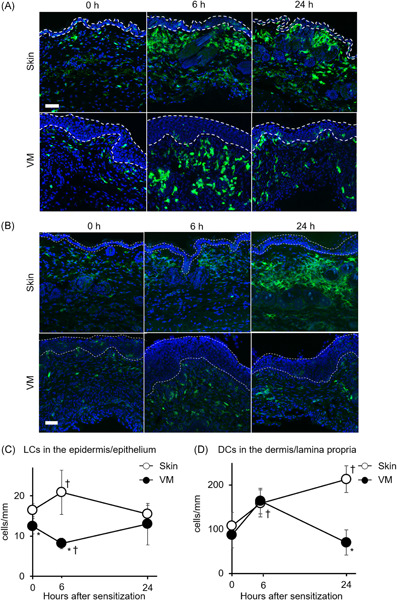
To investigate mechanisms of vaginal mucosa (VM) sensitization in contact hypersensitivity (CHS), we examined migration of hapten-captured dendritic cells (DCs) in the draining lymph nodes (dLNs) and recruitment of DCs at the sensitized local sites in VM sensitization as compared with skin sensitization. We observed that DC migration to dLNs and localization of DCs at the sensitized sites were limited in the VM sensitization with high TGF-β expression levels, increment of CD206+ cells, and TGF-β expression in CD206+ cells in the VM. These results suggested that existence of TGF-β-expressing CD206+ cells may contribute less sensitization ability and CHS responses in the VM.
Life-threatening anaphylaxis in children with cow's milk allergy during oral immunotherapy and after treatment failure
- First Published: 29 March 2022
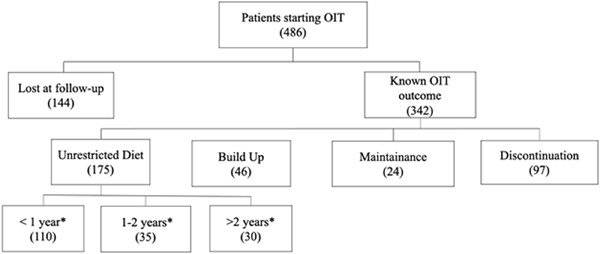
Oral immunotherapy (OIT) is a promising therapeutic approach for children with persistent IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy (CMA). The prevalence of life-threatening anaphylaxis in children with persistent CMA undergoing OIT is nearly two times lower (3.5% vs. 6.3%) than in those who stop the protocol. Patients who stop OIT present more frequently severe reactions, requiring intensive care unit admission, or fatal.
Blood myxovirus resistance protein-1 measurement in the diagnostic work-up of suspected COVID-19 infection in the emergency department
- First Published: 29 March 2022
Elevated myxovirus resistance protein-1 (MxA) levels accurately distinguish COVID-19 infections from bacterial infections and noninfectious diagnoses in patients with suspected COVID-19 infection in the emergency department. MxA measurements may be of added value in the diagnostic workup and patient flow in the emergency department.
SHORT REPORTS
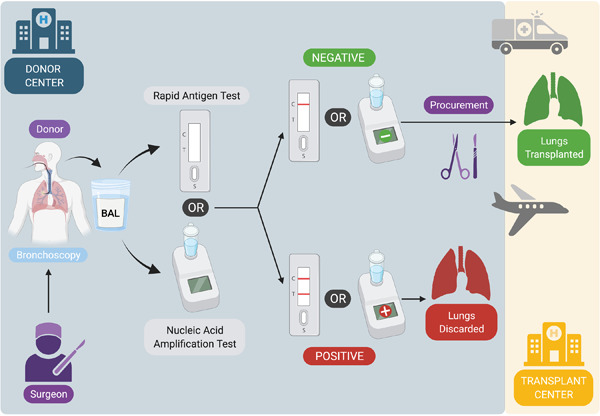
Lung donation and SARS-CoV-2 transmission: Missed detection versus missed opportunity?
- First Published: 10 March 2022