Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Reviews
Disparities in rate, triggers, and management in pediatric and adult cases of suspected drug-induced anaphylaxis in Canada
- Pages: 3-12
- First Published: 01 November 2017
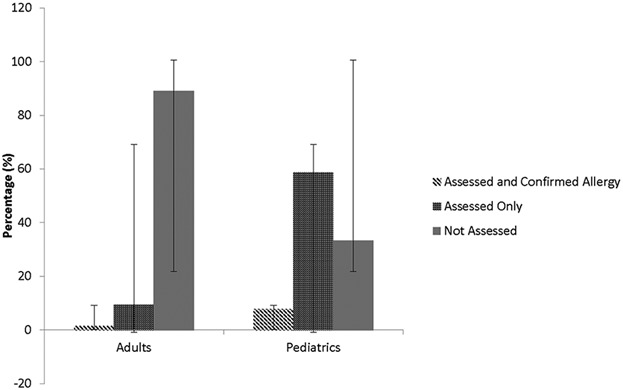
Data is sparse on drug-induced anaphylaxis and there have not been studies assessing the differences in clinical characteristics and management of drug-induced anaphylaxis between adults and children. The percentage of drug-induced anaphylaxis among all cases of anaphylaxis was similar in all three pediatric centers but higher in the adult center in Montreal. The majority of adults and a third of children did not see an allergist after the initial reaction, revealing that most cases of suspected drug allergy are not appropriately diagnosed.
Immunoglobulin G; structure and functional implications of different subclass modifications in initiation and resolution of allergy
- Pages: 13-33
- First Published: 21 November 2017
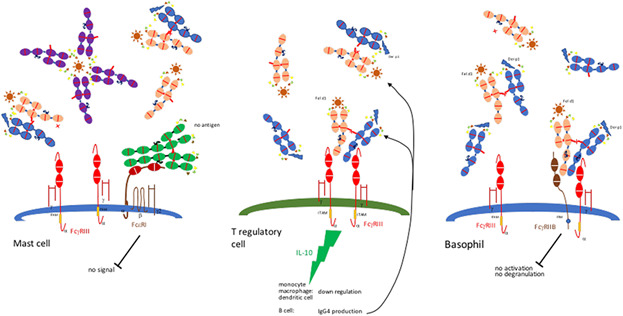
The induction, the pathology, and the resolution of allergy involve antibodies other than specific IgE to allergens. Allergy depends on the pattern of IgG producing plasma cells in atopic children and the tendency for direct or further class switching from IgG to IgE, resulting in the sensitising of mast cells in allergic children.
Original Research
IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells
- Pages: 34-46
- First Published: 27 September 2017
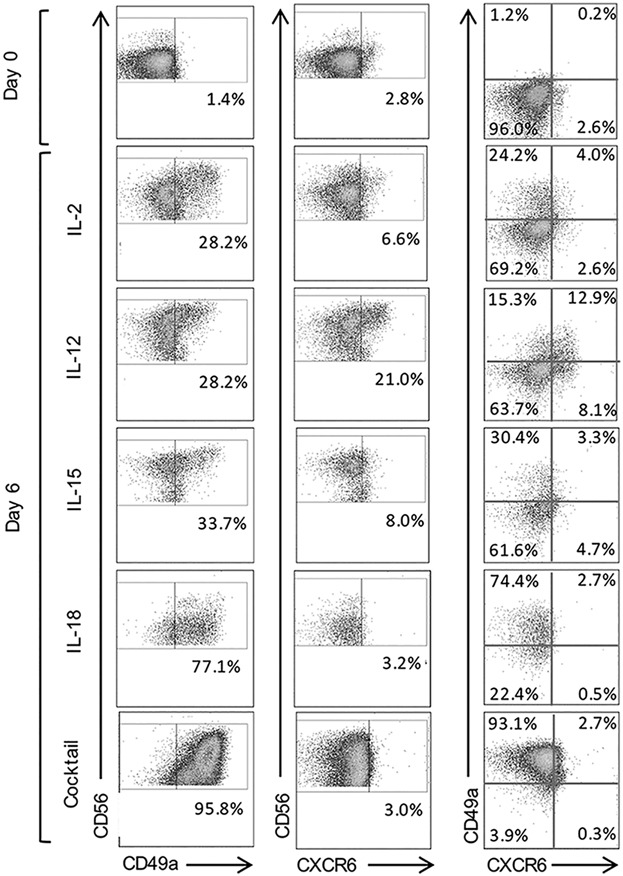
Using flow cytometry, functional assays and RNA sequencing techniques we identify liver-resident CXCR6+ NK cells to have reduced functionality in comparison to CD49a NK cells. Dual positive CXCR6+CD49a+ NK cells more closely resemble the single positive CD49a+ population. We demonstrate that CXCR6+ and CD49a+ NK cells can be induced within the peripheral blood in vitro using cytokines and identify that IL-12 and IL-15 can readily induce a double positive “CD49a+CXCR6+” phenotype. CD49a+CXCR6+ NK cells induced in the periphery are phenotypically similar to liver resident CD49a+ NK cells and express high levels of IFNγ, thus they have an “adaptive” liver-homing phenotype.
T cells responding to Trypanosoma cruzi detected by membrane TNF-α and CD154 in chagasic patients
- Pages: 47-57
- First Published: 01 October 2017
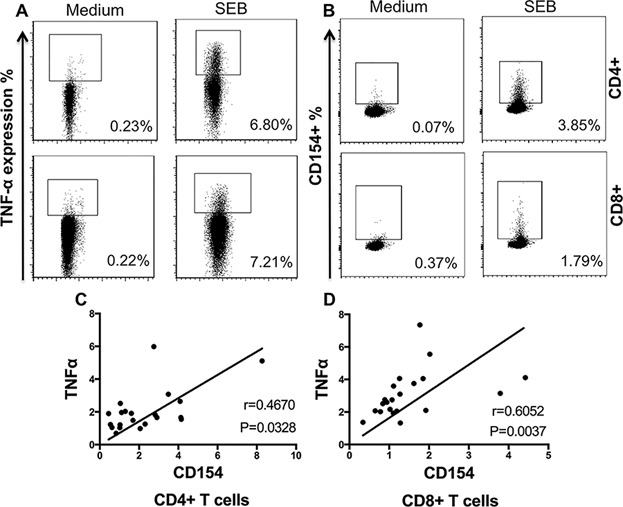
The goal of this study was to determine the fraction of T cells responding to T. cruzi antigen measured by the expression of membrane TNF-α and CD154. The main findings of our study are (1) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in chagasic patients displayed higher percentages of membrane-bound TNF-α+ and CD154+ compared with controls after T. cruzi-antigen stimulation; (2) both markers displayed a positive correlation in the T cell subpopulations analyzed; (3) symptomatic chagasic patients were differentiated from asymptomatic patients based on the expression of CD154 and membrane TNF-α in TCD4+ and TCD8+ compartments, respectively. These results show that both markers could be useful for assessing the pool of antigen-specific T cells in chronic chagasic patients.
A SNP uncoupling Mina expression from the TGFβ signaling pathway
- Pages: 58-71
- First Published: 02 October 2017
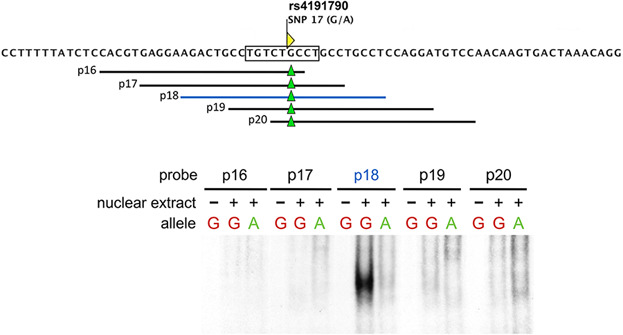
Mina is a ubiquitously expressed JmjC family 2-oxoglutarate oxygenase with pleiotropic roles in cell proliferation, cancer, T cell differentiation, pulmonary inflammation, and intestinal parasite expulsion. Although Mina expression varies according to cell-type, developmental stage and activation state, its transcriptional regulation is poorly understood. Our report demonstrates that the TGFβ signaling pathway plays a critical role in regulating Mina gene expression and that SNP rs4191790 controls heritable variation in Mina expression level.
Adenosine A2A receptor agonist ameliorates EAE and correlates with Th1 cytokine-induced blood brain barrier dysfunction via suppression of MLCK signaling pathway
- Pages: 72-80
- First Published: 12 October 2017
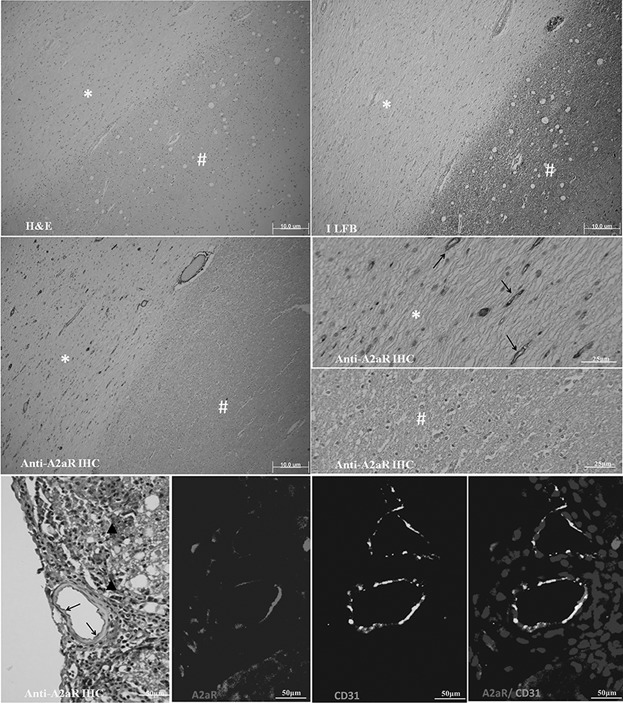
We report on the effects of manipulating the A2A adenosine receptors on BBB permeability which could attenuated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis which is typical experimental model of MS. This is significant because increased permeability of the BBB associated with inflammation is significantly diminished by activation of the A2A receptors. The paper should be of interest to readers in the areas of multiple sclerosis.
A comparison of nanoparticulate CpG immunotherapy with and without allergens in spontaneously equine asthma-affected horses, an animal model
- Pages: 81-96
- First Published: 01 November 2017

The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of a nebulized gelatin nanoparticle-CpG formulation (CpG-GNP) with and without specific allergens for the treatment of spontaneous allergic equine Asthma as a model for human asthma. Immunomodulating agents stimulating T-regulatory cells offer new treatment options beyond conventional symptomatic treatment for human and equine allergic airway diseases, with the goal of a homoeostatic T-helper cell balance. Nonspecific CpG-GNP-based immunotherapy shows potential as a treatment for equine and possibly also human allergic asthma.
Mechanisms of the action of adenine on anti-allergic effects in mast cells
- Pages: 97-105
- First Published: 01 November 2017
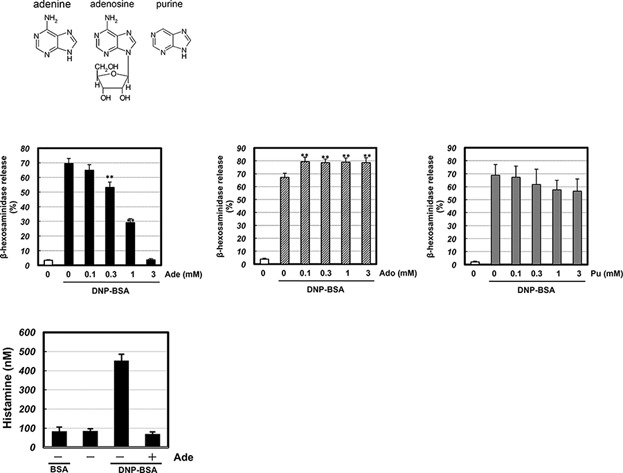
We demonstrated the amino group of adenine may play a key role in IgE/antigen-induced degranulation in mast cells. The inhibitory effects of adenine on degranulation may be mediated before as well as after the Ca2+ raise under the antigen stimulus. We also provided key role of adenine in the attenuation of allergic responses through the inhibition of Syk-mediated signal transduction and IKK-mediated degranulation.
Transcriptional and translational-uncoupling in regulation of the CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4, 7 in THP-1 monocytes and macrophages
- Pages: 106-116
- First Published: 03 November 2017
Mast cells partially contribute to mucosal adjuvanticity of surfactin in mice
- Pages: 117-127
- First Published: 03 November 2017
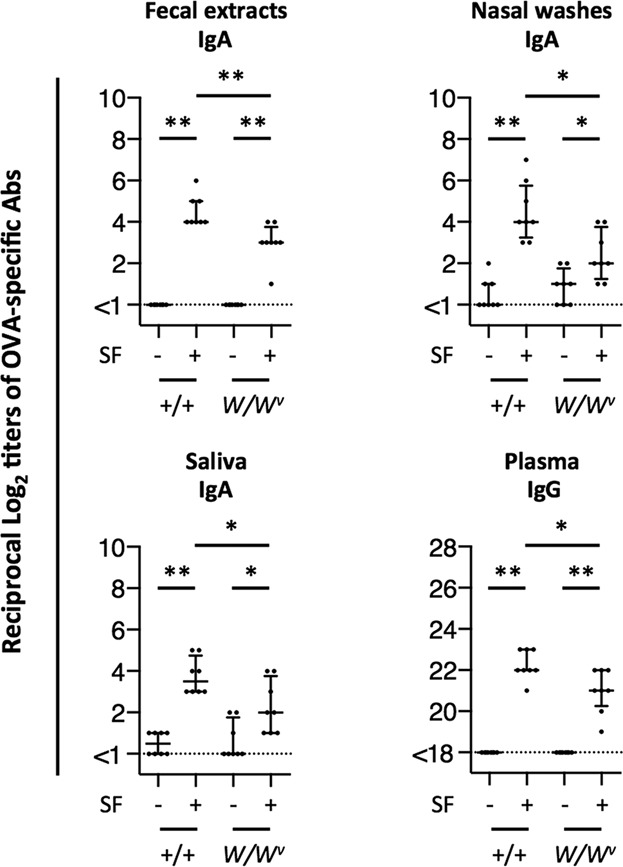
Surfactin is a cyclic lipopeptide that has potent mucosal adjuvant properties. In experiments in vivo, using mast cell deficient W/Wv mice, as well as in tests using cultured MC/9 mast cells, we observed that exposure to surfactin directly activated mast cells and augmented immune responses in vivo and increased expression levels of several important cytokines in vitro.
Impaired expression of CXCL5 and matrix metalloproteinases in the lungs of mice with high susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae infection
- Pages: 128-142
- First Published: 09 November 2017
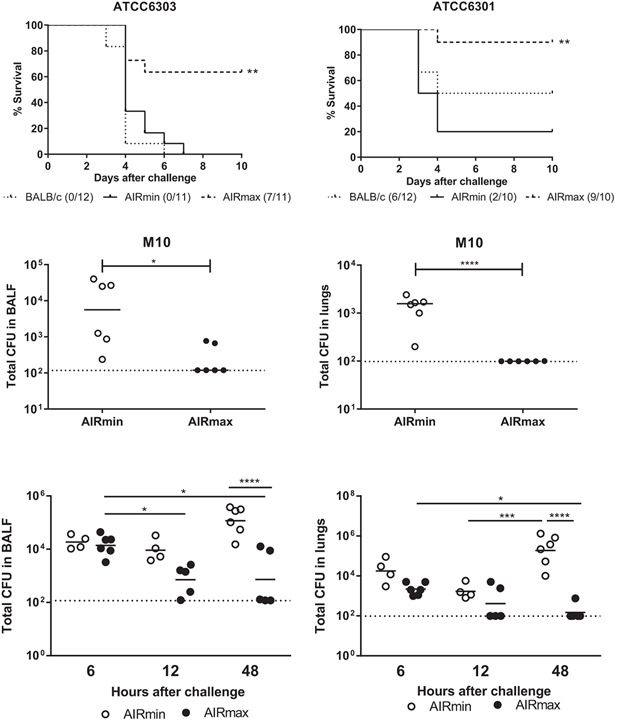
In this work we have compared the susceptibility to pneumococcal respiratory infection of two outbred mouse lines, AIRmin and AIRmax, selected for low or high acute inflammatory responses, respectively. Our results indicate that CXCL5 and MMPs contribute to the resistance to pneumococcal infection in mice.
T-cell responses against rhinovirus species A and C in asthmatic and healthy children
- Pages: 143-153
- First Published: 10 November 2017
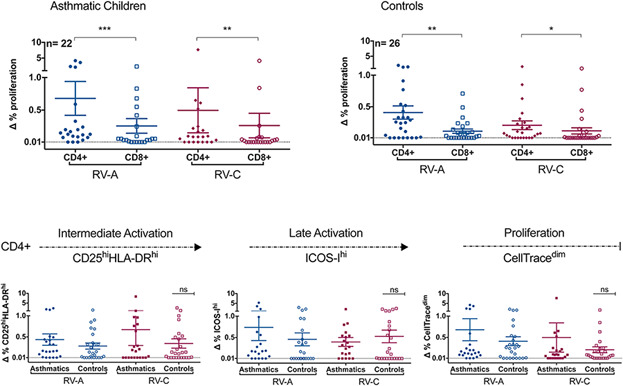
The two most clinically relevant rhinovirus species, RV-A and RV-C, stimulate similar recall CD4+ T cell responses in asthmatic and healthy children. However, the lower number of circulating regulatory T cells found for asthmatic children could contribute to their inability to control the immune response to rhinovirus infections, leading to pathological outcomes such as airway hyper-responsiveness commonly seen in exacerbations of asthma.
Environmental levels of avian antigen are relevant to the progression of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis during antigen avoidance
- Pages: 154-162
- First Published: 22 November 2017
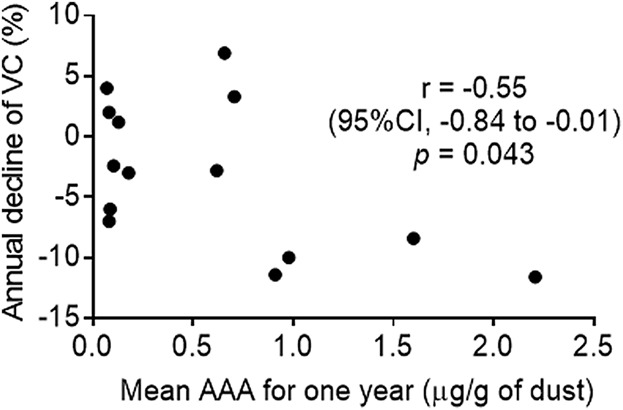
There was a correlation between the mean amount of avian antigen (AAA) and the decline of vital capacity for 1 year (r = −0.55; 95%CI −0.84 to −0.01; P = 0.043). The annual decline in VC from baseline in the high-level exposure group was higher than in the low-level exposure group (≥0.74 µg/g of dust) (332 ± 89 ml vs. 53 ± 116 ml, P = 0.004). Measurements of AAA after diagnosis predict the progression of chronic bird-related HP.
Dendritic cell targeted HIV-1 gag protein vaccine provides help to a recombinant Newcastle disease virus vectored vaccine including mobilization of protective CD8+ T cells
- Pages: 163-175
- First Published: 04 December 2017
Interferon α2 and interferon γ induce the degranulation independent production of VEGF-A and IL-1 receptor antagonist and other mediators from human mast cells
- Pages: 176-189
- First Published: 13 December 2017