Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Articles
IgM and IgA augmented autoantibody signatures improve early-stage detection of colorectal cancer prior to nodal and distant spread
- First Published: 26 September 2021
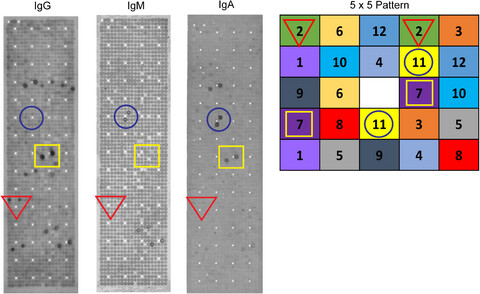
Early-stage detection of colorectal cancer is critical for patient survival. We have conducted a multi-isotype autoantibody (AAbs) screen using a 492-feature CRC protein array. Our study shows that IgM AAbs are associated with early-stage disease and IgA AAbs, although stage-independent, encompass humoral responses associated with mucosal surfaces. Combining IgG, IgM and IgA AAbs is a novel strategy for early disease detection and improvement of patient outcomes.
Expression of CD49f defines subsets of human regulatory T cells with divergent transcriptional landscape and function that correlate with ulcerative colitis disease activity
- First Published: 06 September 2021
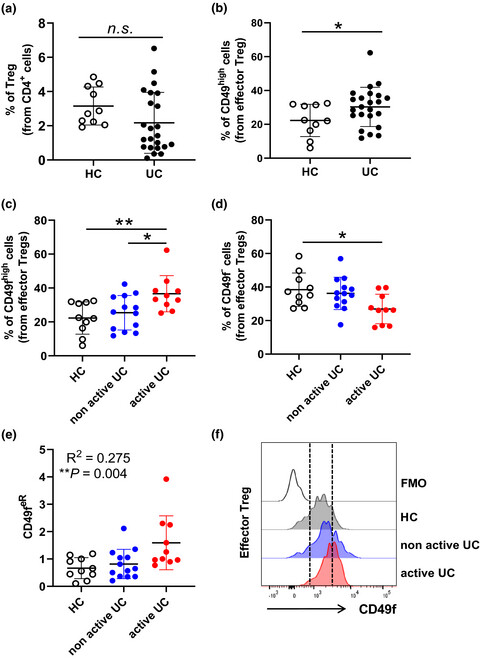
This study defines two distinct subsets of effector regulatory T cells (Treg) circulating in the human blood based on the presence or absence of CD49f with divergent transcriptional landscape and functional activities. CD49f– Treg are enriched for functional Treg markers and present significantly increased suppressive capacity whilst CD49fhigh Treg display a pro-inflammatory Th17-like phenotype and accumulate in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). Dysregulation of CD49f Treg subsets in patients with UC correlates with disease activity and may be assessed as a way to improve UC immune monitoring.
Combinatorial liposomal peptide vaccine induces IgA and confers protection against influenza virus and bacterial super-infection
- First Published: 10 September 2021
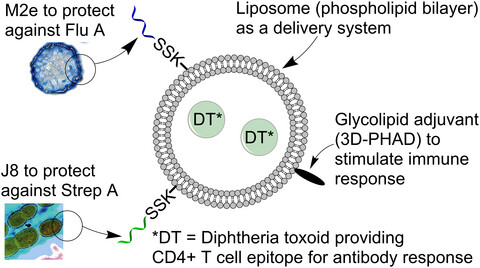
In this study, we report on the potential of a modular multi-pathogen mucosal vaccine. We found that this vaccine construct induces an Immunoglobulin A (IgA) response in both mice and ferrets. Vaccination reduces viral load in ferrets from influenza challenge and protects mice from influenza virus:S. pyogenes super-infection.
Supranutritional selenium suppresses ROS-induced generation of RANKL-expressing osteoclastogenic CD4+ T cells and ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis
- First Published: 20 September 2021
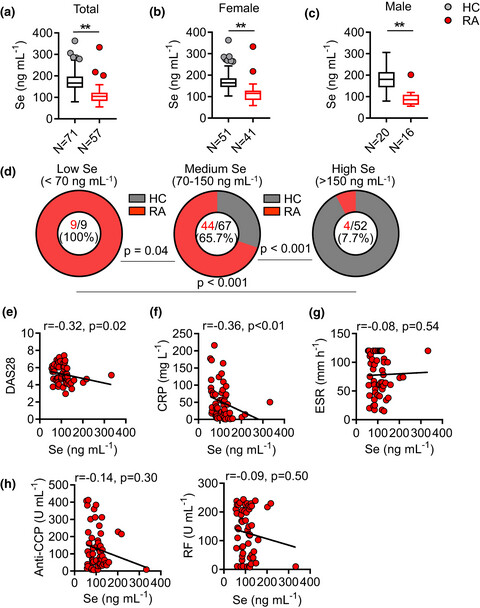
In this study, we found that supranutritional selenium (Se) was associated with improved disease activities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and also ameliorated collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Se attenuated the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and thus suppressed ROS-mediated induction of RANKL expression in activated CD4+ T cells.
SARS-CoV-2 sculpts the immune system to induce sustained virus-specific naïve-like and memory B-cell responses
- First Published: 05 September 2021

We longitudinally studied moderate-to-severe COVID-19 patients to dissect SARS-CoV-2-specific B cell responses overtime. We found a broad virus-specific antibody response during acute infection, which evolved into an IgG1-dominated response. Moreover, we identified a persistent expansion of virus-targeting naïve-like and memory B cells in COVID-19 patients, as well as unique immune signatures that associated with disease severity and inflammation.
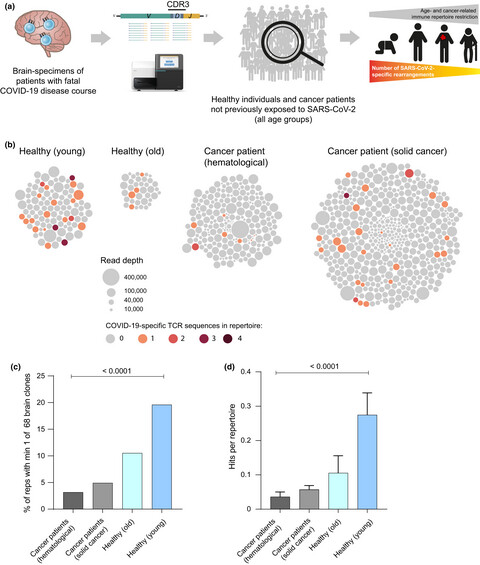
Landscape of T-cell repertoires with public COVID-19-associated T-cell receptors in pre-pandemic risk cohorts
- First Published: 28 August 2021
Original Article
miR-21 sustains CD28 signalling and low-affinity T-cell responses at the expense of self-tolerance
- First Published: 21 September 2021
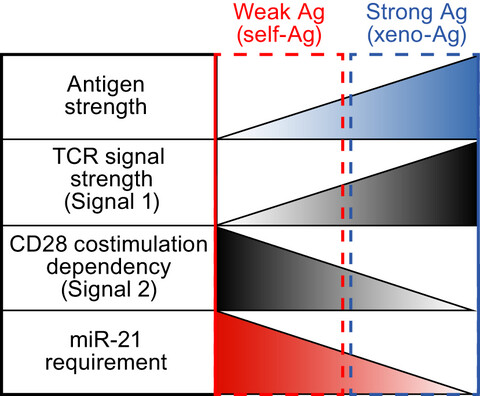
Low-affinity antigens triggering weak TCR signalling (Signal 1) require CD28 costimulation (signal 2) to elicit T-cell responses. In this study, we found that miR-21 sustains the CD28 costimulation pathway, via inhibition of its repressors in a positive feedback circuit, decreasing the T-cell activation threshold. This broadens the range of detected antigens, at the cost of unleashing autoimmunity resulting from the recognition of weak self-antigens by autoreactive T cells. Thus, miR-21 fine-tunes T-cell response and self/non-self-discrimination.
Improvement of Treg immune response after treatment with tocilizumab in giant cell arteritis
- First Published: 12 September 2021
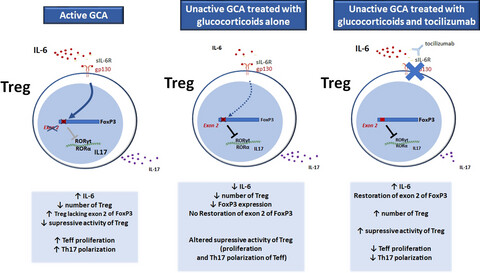
In this study, we demonstrated quantitative and functional disruptions in the regulatory immune response of patients with giant cell arteritis, resulting in increased proliferation and Th17 polarization of effector T cells. In addition, our results suggest that, through a specific blockade of the IL-6 pathway, tocilizumab associated with glucocorticoids restores a better quantitative and qualitative Treg immune response than glucocorticoids alone. GCA, giant cell arteritis. Teff, effector T-cells; Th17, T helper-17 cells; Treg, regulatory T-cells.
High expression of CD38 and MHC class II on CD8+ T cells during severe influenza disease reflects bystander activation and trogocytosis
- First Published: 08 September 2021
Short Communication
T-cell response after first dose of BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine among healthcare workers with previous infection or cross-reactive immunity
- First Published: 08 September 2021
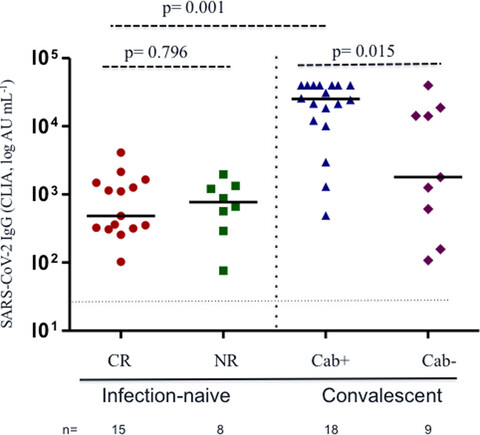
In this study, we found that a single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine generates a strong humoral (100%) and cellular response in convalescent COVID-19 individuals (94%), and also in infection-naïve healthcare workers with cross-reactive immunity because of other coronaviruses (93%). However, this response was not observed in convalescent individuals with previous loss of specific antibodies after the disease, who had a T-cell response similar to that of other infection-naïve individuals. Thus, different factors could influence the rate of humoral and cellular responses to the vaccine.