Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Articles
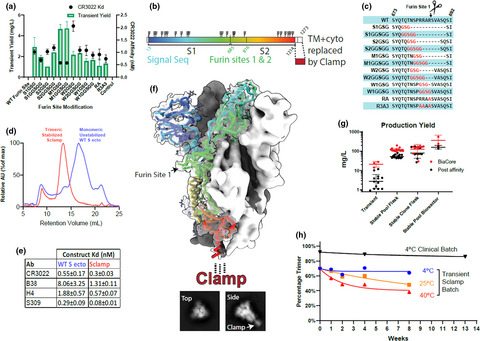
Preclinical development of a molecular clamp-stabilised subunit vaccine for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
- First Published: 05 April 2021
Reviews
TGF-β-secreting regulatory B cells: unsung players in immune regulation
- First Published: 02 April 2021
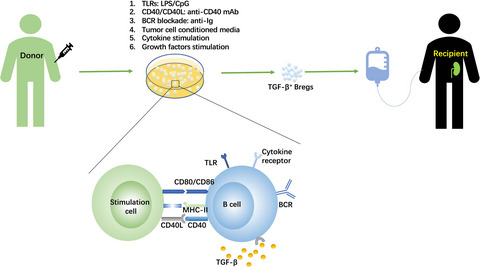
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-producing B cells can regulate T-cell immunity and induce Tregs independently of interleukin-10. Most research on TGF-β+ regulatory B cells has been conducted in various inflammatory diseases but less in the transplant setting. Herein, we review recent investigations seeking to understand how TGF-β-producing B cells direct the immune response in various inflammatory diseases and whether these cells may have a role in fostering tolerance in transplantation.
Original Articles
Complement factor D haplodeficiency is associated with a reduced complement activation speed and diminished bacterial killing
- First Published: 03 April 2021
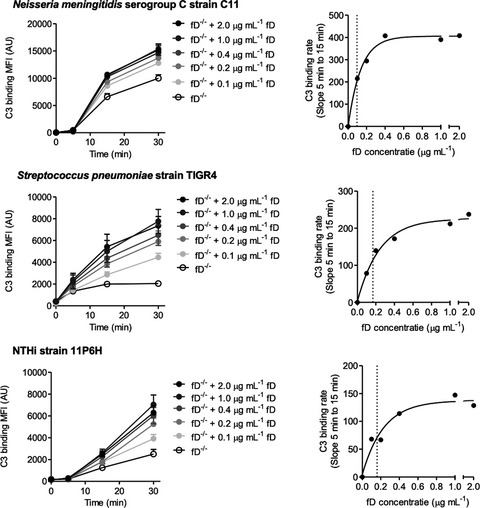
In this study, we show that low complement factor D levels (< 0.5 µg mL−1) result in slower complement activation and increased susceptibility for infections by fast proliferating bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis, Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Vaccination was able to overcome the slower complement pathway activity through robust initiation of the classical pathway.
Short Communications
Localised release of matrix metallopeptidase 8 in fatal cerebral malaria
- First Published: 29 April 2021
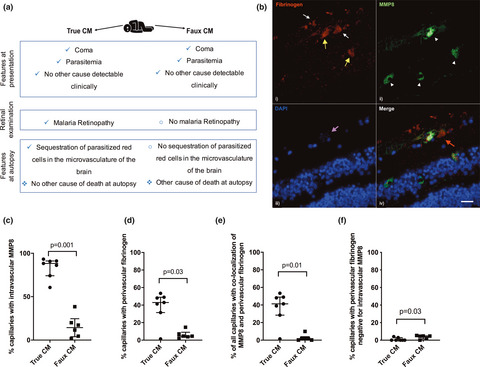
To test the hypothesis that localised release of matrix metallopeptidase 8 (MMP8) within the retina is implicated in microvascular leak in cerebral malaria (CM), we examined its expression and association with extravascular fibrinogen leak in a case-control study of post-mortem retinal samples from 13 Malawian children. MMP8 was extensively expressed in retinal capillaries of children with CM retinopathy and strongly associated with vascular leak. Our findings implicate MMP8 in the vascular endothelial barrier disruption in CM, which may precipitate fatal brain swelling.
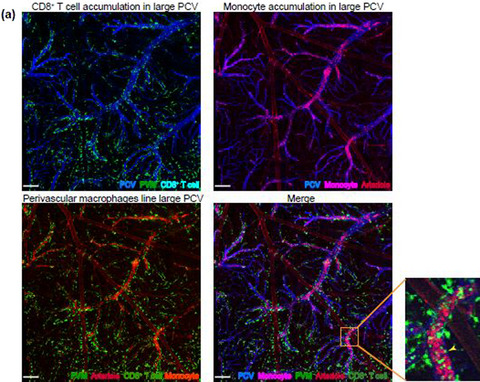
Original Article
Perivascular macrophages create an intravascular niche for CD8+ T cell localisation prior to the onset of fatal experimental cerebral malaria
- First Published: 07 April 2021
Kinetics of peripheral blood neutrophils in severe coronavirus disease 2019
- First Published: 29 April 2021
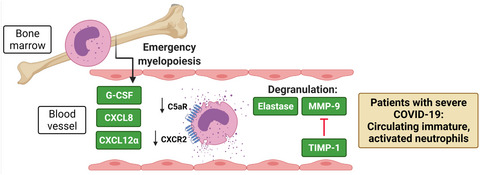
In this study, we found that patients suffering from severe COVID-19 presented with immature, activated blood neutrophils and were characterized by elevated plasma levels of G-CSF and CXCL8 that disappeared towards ICU discharge. Elevated neutrophil-derived proteases in plasma of ICU patients were associated with increased non-metalloproteinase-derived gelatinolytic activity but decreased total MMP proteolytic activity. SARS-CoV-2 failed to replicate inside human neutrophils, suggesting that changes observed in neutrophils from patients with COVID-19 are indirect consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vivo.
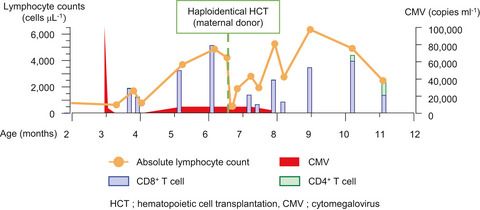
Case Report
Impact of maternal engrafted cytomegalovirus-specific CD8+ T cells in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency
- First Published: 13 April 2021
Original Article
Categorisation of patients based on immune profiles: a new approach to identifying candidates for response to checkpoint inhibitors
- First Published: 29 April 2021
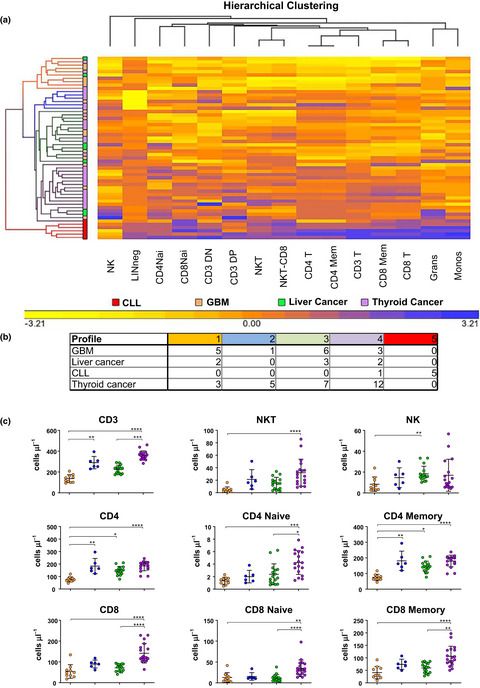
Here, we have developed a multiparameter flow cytometry assay that allowed us to measure checkpoint proteins CTLA-4 and PD-1 on 19 leucocyte populations in the peripheral blood. By looking at the data independent of disease, we used unsupervised hierarchical clustering of PD-1 expression on patients with different types of cancers and identified five patient profiles. These profiles, or groups of immunologically similar patients, can be used for predicting responders vs non-responders and applied towards decisions in choosing appropriate inhibitors.
Original Articles
IL-17 drives salivary gland dysfunction via inhibiting TRPC1-mediated calcium movement in Sjögren’s syndrome
- First Published: 29 April 2021
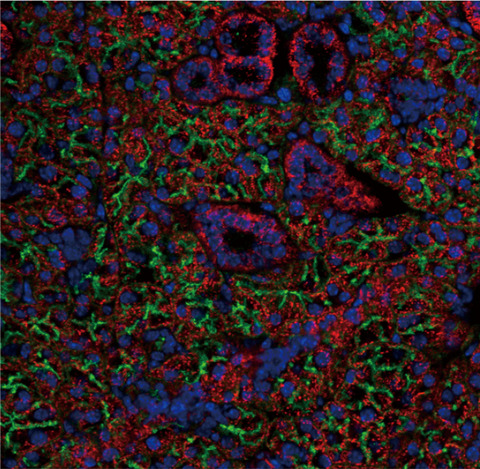
In this study, we found that increased salivary IL-17 levels were negatively correlated with saliva flow rates in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS). We further identified a novel function of IL-17 in driving salivary dysfunction by impairing transient receptor potential canonical 1-mediated calcium movement during pSS pathogenesis. This pre-clinical study demonstrated that neutralization of IL-17 in salivary glands attenuated hyposalivation and ameliorated tissue inflammation in mice with experimental SS, suggesting a therapeutic potential of local targeting IL-17 for treating xerostomia and autoimmune sialadenitis in pSS patients.
SPECIAL FEATURE EDITORIAL
New horizons for natural killer cell research in cancer, infection and inflammation
- First Published: 28 April 2021
Original Articles
No interplay between gut microbiota composition and the lipopolysaccharide-induced innate immune response in humans in vivo
- First Published: 29 April 2021
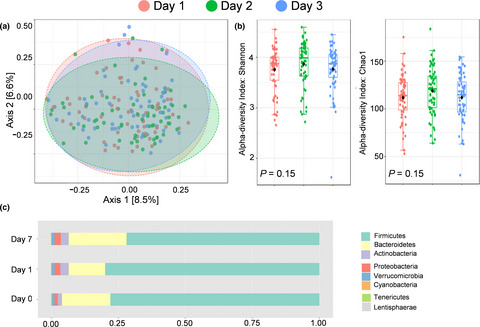
In this study, we found no relation between existing gut microbiota composition and the cytokine response induced by an lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge in healthy volunteers. Furthermore, the LPS-induced systemic innate immune response did not alter the gut microbiota composition in the following week.
Memory stem T cells modified with a redesigned CD30-chimeric antigen receptor show an enhanced antitumor effect in Hodgkin lymphoma
- First Published: 29 April 2021
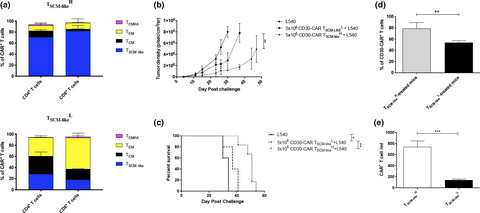
We have studied the efficacy of a redesigned CD30-chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting a proximal epitope to enhance the antitumor efficacy. CD30-CAR T cells show potent in vivo antitumor effect in different Hodgkin lymphoma models, and overcome inhibition by soluble CD30. CD30-CAR memory stem T-cell products show long-term persistence, improved tumor homing and long-lasting immunity.
The myeloid cell type I IFN system promotes antitumor immunity over pro-tumoral inflammation in cancer T-cell therapy
- First Published: 29 April 2021
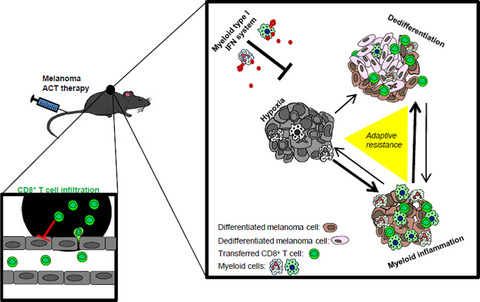
Here, we found that the therapeutic efficacy of an adoptive CD8+ T-cell transfer therapy targeting a melanocytic differentiation antigen required a functional type I IFN system in myeloid immune cells. Importantly, the notion of myeloid type I IFN system as the key regulator in the balance between pro-tumoral inflammation and antitumoral immunity may be exploitable in the development of novel combinatorial immunotherapies targeting this cellular compartment.
Reviews
Autoantibodies against complement component C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus
- First Published: 29 April 2021
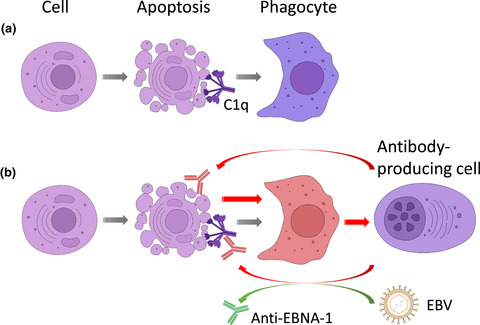
Autoantibodies against complement C1q (anti-C1q) are an exciting biomarker of disease activity and for the occurrence of active proliferative nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The exploration of binding characteristics of anti-C1q and its functional consequences provides important insights into pathogenic mechanisms of the disease involving complement deposition and activation, the clearance mechanisms of apoptotic cell debris, phagocyte function and the role of genetic as well as environmental factors.
Special Feature Reviews
CAR-NK cells: the next wave of cellular therapy for cancer
- First Published: 28 April 2021
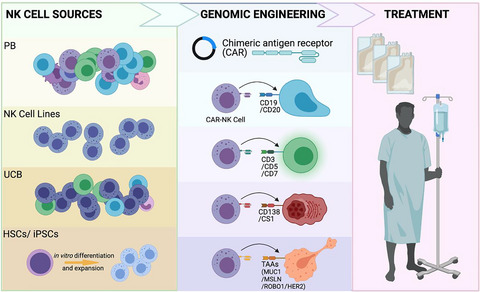
NK cells can be derived from various sources (PB, UCB, HSC, iPSC, NK cell lines) and can be engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to target various surface antigens on cancer cells. These CAR-NK cells can be used as off-the-shelf adoptive cellular therapy to treat patients with various malignancies.