Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
RESEARCH ARTICLES
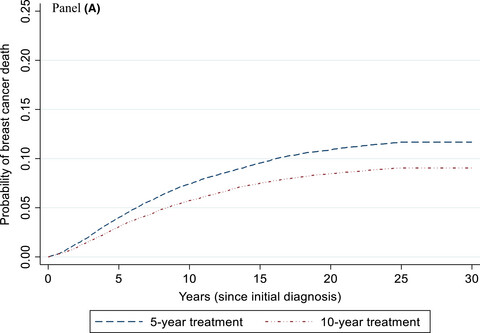
Simulation modeling of breast cancer endocrine therapy duration by patient and tumor characteristics
- Pages: 297-307
- First Published: 16 December 2021
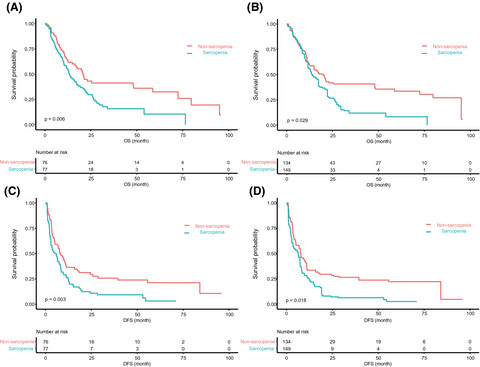
Muscle weakness as an additional criterion for grading sarcopenia-related prognosis in patients with cancer
- Pages: 308-316
- First Published: 10 December 2021
Low muscle strength has been pointed out as a key characteristic of sarcopenia, but the prognostic significance of muscle function next to reduced skeletal muscle mass (SMM) in patients with cancer has been scantily investigated. Muscle weakness was found to be a more powerful predictor of survival than SMM and should be considered as additional key feature of sarcopenia in patients with cancer.
Sarcopenia predicts an adverse prognosis in patients with combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma after surgery
- Pages: 317-331
- First Published: 05 December 2021
What if the future of HER2-positive breast cancer patients was written in miRNAs? An exploratory analysis from NeoALTTO study
- Pages: 332-339
- First Published: 17 December 2021
Despite the improved pathological complete response rate in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with neoadjuvant dual HER2 blockade, it would be desirable to identify patients exquisitely responsive to single agent trastuzumab to minimize or avoid overtreatment. Herein, by analyzing baseline tissue microRNA (miRNA) profile in the trastuzumab arm of NeoALTTO study, we identified a two-miRNA predictive signature and a prognostic signature associated to event-free survival. Analyses of primary tumor tissue miRNAs hold the potential of a parsimonious tool to identify patients with differential clinical outcomes after trastuzumab based neoadjuvant therapy.
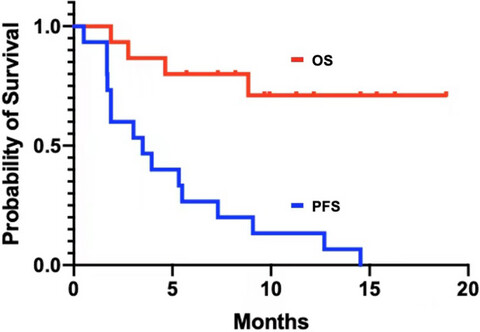
Phase 1 trial of ADI-PEG 20 and liposomal doxorubicin in patients with metastatic solid tumors
- Pages: 340-347
- First Published: 28 November 2021
Better effect of intrapleural perfusion with hyperthermic chemotherapy by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for malignant pleural effusion treatment compared to normothermic chemoperfusion of the pleural cavity
- Pages: 348-357
- First Published: 01 December 2021

There have been some reports on the efficacy of intrapleural perfusion with hyperthermic chemotherapy (IPHC) in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion (MPE), but few studies put emphasis on IPHC under video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and the efficacy of different treatment regimens. This study aims to explore the curative effect of IPHC under VATS and normothermic chemoperfusion of the pleural cavity (NCPC) in the treatment of MPE, and to provide clinical experience for MPE.
Filanesib plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory t(11;14) and 1q21 gain multiple myeloma
- Pages: 358-370
- First Published: 17 December 2021
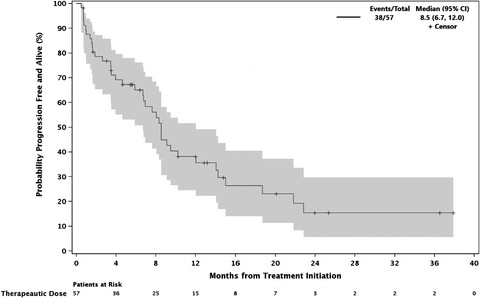
We report on the final analysis of the phase 1 trial of filanesib, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Among patients receiving therapeutic doses of the study drugs, overall response rate was 39% with median duration of response of 14.1 months and median progression-free survival of 8.0 months. The combination continues to show safety and encouraging activity in this population, particularly in those patients with 1q21 gain and t(11;14).
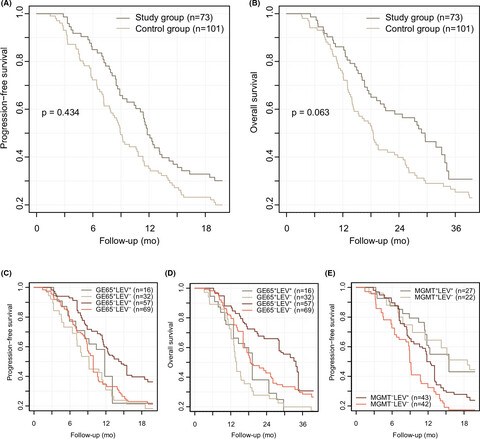
Levetiracetam as a sensitizer of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: An open-label phase 2 study
- Pages: 371-379
- First Published: 30 November 2021
Examining the association between oncology drug clinical benefit and the time to public reimbursement
- Pages: 380-391
- First Published: 01 December 2021

This article examined if oncology drug indications with high clinical benefit, as measured by the American Society of Clinical Oncology Value Framework (ASCO-VF) and European Society for Medical Oncology Magnitude of Clinical Benefit Scale (ESMO-MCBS), received public reimbursement status faster than those with lower clinical benefit from the time of pan-Canadian Oncology Drug Review (pCODR) recommendation. It was found that oncology drug indications with high clinical benefit were not significantly associated with shorter time to public reimbursement. These findings suggest the need to implement a transparent system of prioritization to ensure quicker access to oncology drugs with the greatest benefits.
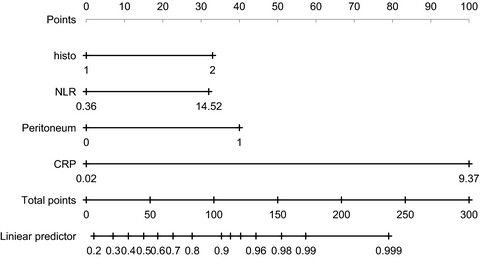
Construction and validation of a prognostic nomogram for anal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 392-405
- First Published: 01 December 2021
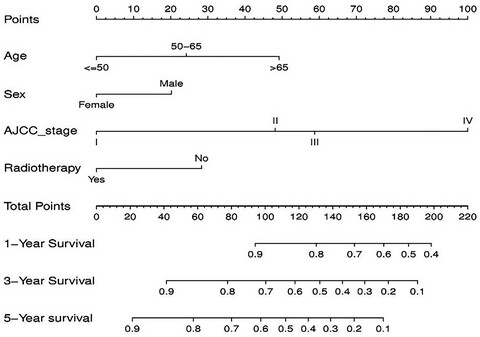
First, from the SEER database, we identified the prognostic factors for anal squamous cell carcinoma (ASCC) patients and develop a nomogram to better predict the prognosis of ASCC patients. Secondly, through comparison, our predictive model is a further improvement of traditional AJCC staging system based on patient’s demographic and clinicopathological features not only in survival prediction, but also in clinical utility.
Prognostic factors to predict the survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer who receive later-line nivolumab monotherapy—The Asahikawa Gastric Cancer Cohort Study (AGCC)
- Pages: 406-416
- First Published: 29 November 2021
PD-L1 expression is associated with the spontaneous regression of patients with methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorders
- Pages: 417-432
- First Published: 29 November 2021
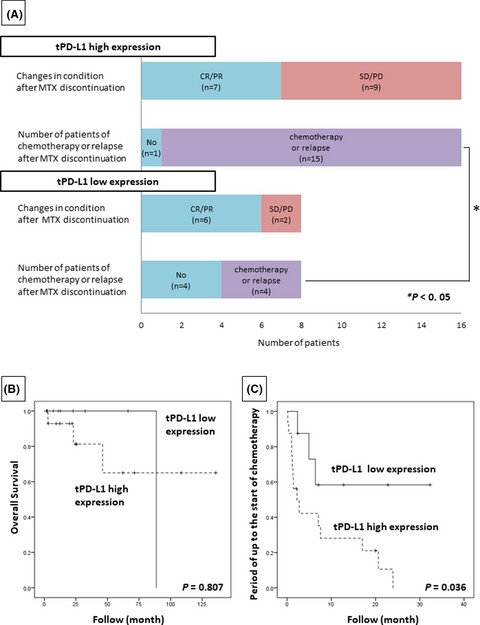
Patients with classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)-type methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorder (MTX-LPD) with high programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression tended to have exacerbations and relapses after MTX discontinuation. Our study suggests that the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway may be involved in refractoriness to MTX discontinuation in CHL-type MTX-LPD.
The prognostic value of TPM1–4 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 433-446
- First Published: 30 November 2021
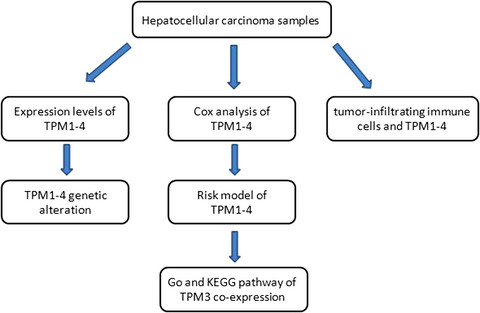
Our study detected the expression of TPM1–4 was all significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting TPM1–4 may serve as an important role in HCC development. High TPM3 expression was found to be associated with poor overall survival, and TPM3 may be independent prognostic factor for HCC.
CANCER BIOLOGY
REVIEW
Barrett's esophagus: The pathomorphological and molecular genetic keystones of neoplastic progression
- Pages: 447-478
- First Published: 06 December 2021
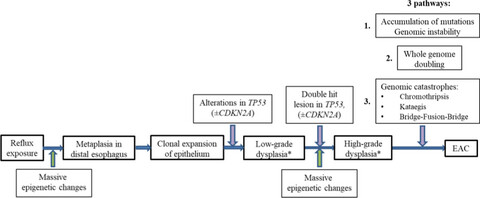
Several important keystone genetic events occur during carcinogenesis in the distal esophagus. These processes should be diagnosed during routine evaluation of patients with Barrett's esophagus to prevent disease progression and malignization. The aforementioned genetic aberrations are detected as early as 2 years before diagnosis of esophageal carcinoma.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
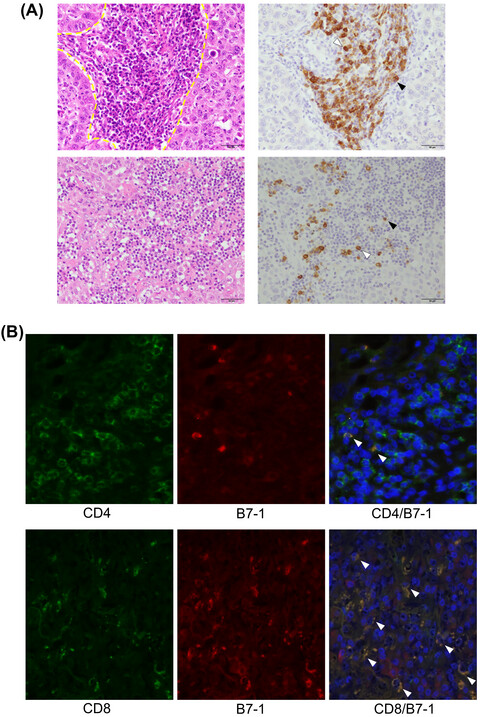
B7-1 and programmed cell death-ligand 1 in primary and lymph node metastasis lesions of non-small cell lung carcinoma
- Pages: 479-491
- First Published: 14 December 2021
Cancer-associated stroma reveals prognostic biomarkers and novel insights into the tumour microenvironment of colorectal cancer and colorectal liver metastases
- Pages: 492-506
- First Published: 07 December 2021
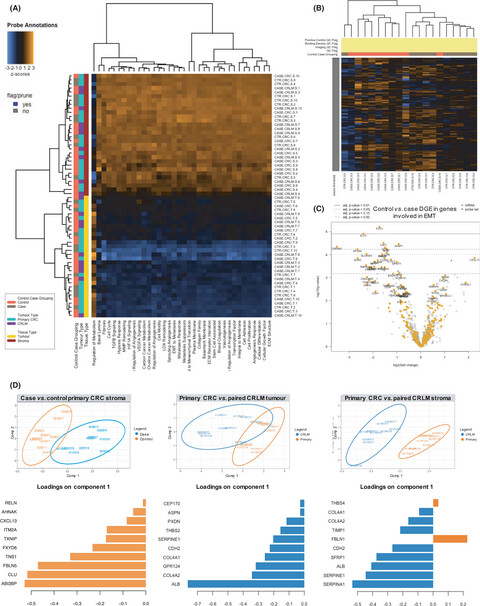
Cancer-associated stroma (CAS) is emerging as a key determinant of metastasis in colorectal cancer (CRC), however, little is known about CAS in colorectal liver metastases (CRLM). This study used a large cohort of paired primary CRC and CRLM in a case–control design to examine the transcriptome of the CAS. The key finding was that the only significant difference between patients who developed liver metastases versus those that had long-term disease-free survival was found in their CAS transcriptome. These data also identified a number of novel targetable stromal genes and pathways that defined poor prognosis CRC and the CAS of CRLM.
CANCER PREVENTION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Incidence and relative risk of metachronous second primary cancers for 16 cancer sites, Osaka, Japan, 2000–2015: Population-based analysis
- Pages: 507-519
- First Published: 29 November 2021
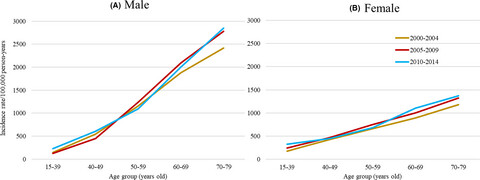
During 2000–2015, 5.8% of cancer survivors in Osaka, Japan, developed metachronous second primary cancers (SPCs) within 10 years of first diagnosis. Cancer survivors were at 1.38 times (male) and 1.44 times (female) higher risks of developing SPCs compared to the general population. Coordinated efforts of survivorship care through risk-based care planning, surveillance, and lifestyle-changing interventions are warranted.
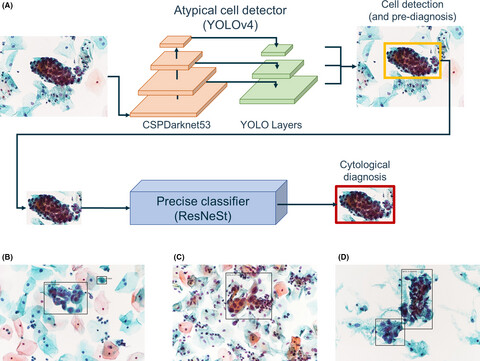
A screening assistance system for cervical cytology of squamous cell atypia based on a two-step combined CNN algorithm with label smoothing
- Pages: 520-529
- First Published: 28 November 2021
Defining comprehensive biomarker-related testing and treatment practices for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a survey of U.S. oncologists
- Pages: 530-538
- First Published: 17 December 2021
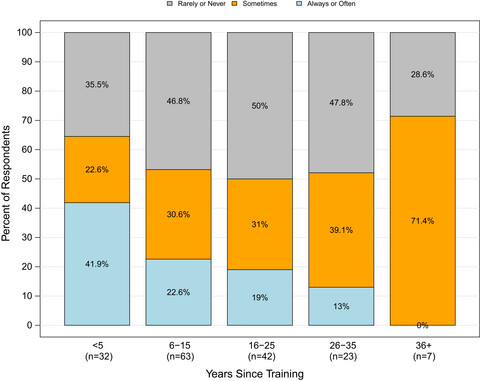
U.S. oncologists who typically waited ≥3 weeks for biomarker test results were more likely to defer initiating treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer until results were reviewed. Treatment decision-making based on biomarker test results was associated with practice setting and physician specialization and years of experience. Frequency that oncologist’s concern about delaying treatment is a reason for not testing, by years since oncology training completed.
BIOINFORMATICS
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Long noncoding RNAs to predict postoperative recurrence in bladder cancer and to develop a new molecular classification system
- Pages: 539-552
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Reliable molecular markers are much needed for early prediction of recurrence in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). It's the first time to build an lncRNA signature to improve recurrence prediction and for lncRNA-based molecular classification of MIBC, which can be used to guide clinical treatment and provide precision therapy.