Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Tolvaptan use in cancer patients with hyponatremia due to the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone: a post hoc analysis of the SALT-1 and SALT-2 trials
- Pages: 723-729
- First Published: 02 March 2017
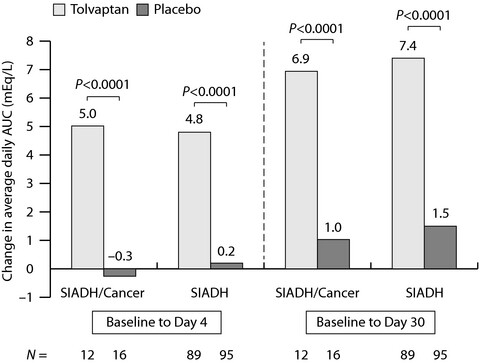
Hyponatremia resulting from para-neoplastic Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone is common in many types of cancer and correlates with poor outcomes. In this subanalysis of the Study of Ascending Levels of Tolvaptan in Hyponatremia (SALT) clinical trials, once-daily oral tolvaptan safely restored serum sodium levels in cancer patients with SIADH, thereby reducing the need for fluid restriction and electrolyte infusions.
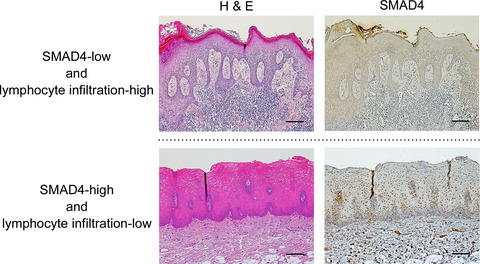
Predictive value of the combination of SMAD4 expression and lymphocyte infiltration in malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia
- Pages: 730-738
- First Published: 03 March 2017
Clinical implications of serum N-glycan profiling as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in germ-cell tumors
- Pages: 739-748
- First Published: 20 March 2017
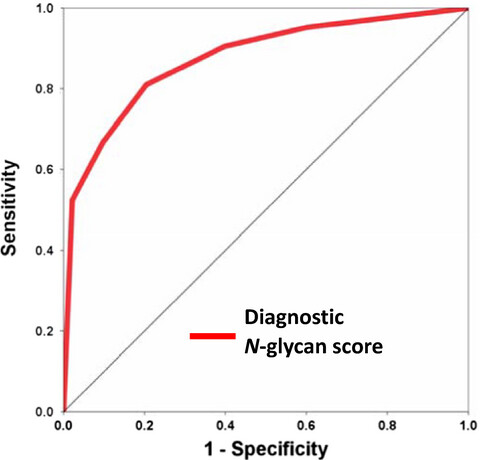
We identified serum N-glycans to be potential biomarkers as a germ-cell tumor (GCT). Our newly developed diagnostic N-glycan score was significantly associated with GCT detection, 10 of 12 (83%) patients with negative conventional tumor markers were detected by N-glycan score. Our results suggest that the serum N-glycan profiles acquired by glycoblotting and mass spectrometry have potential utility as a biomarker for the presence of GCT.
The mitochondrial hinge protein, UQCRH, is a novel prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 749-760
- First Published: 23 March 2017
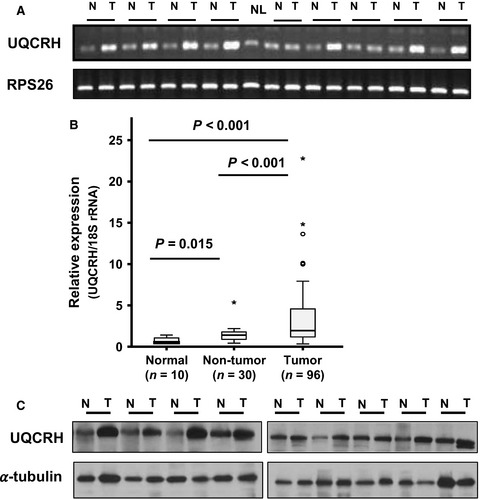
Ubiquinol–cytochrome c reductase hinge protein (UQCRH), a mitochondrial hinge protein, is frequently overexpressed in HCC tissues (46.8%) and an independent poor prognostic factor for HCC patients. In patients with elevated AFP levels considered the “high–risk” group, lack of UQCRH overexpression may be a useful indicator for clinical treatment.
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI perfusion for differentiating between melanoma and lung cancer brain metastases
- Pages: 761-767
- First Published: 17 March 2017
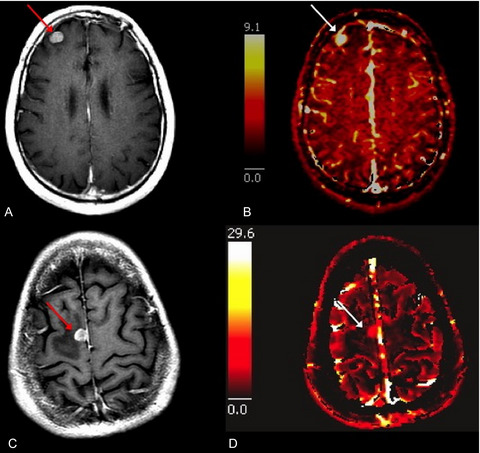
Patients with a personal history of multiple cancers and new brain metastases can be very challenging from a management standpoint because the histology of their brain lesions may not be clear without biopsy. Our study demonstrates that MRI perfusion can help differentiate between hypervascular and hypovascular brain metastases and potentially facilitate more optimal treatment planning.
Antitumor activity of chLpMab-2, a human–mouse chimeric cancer-specific antihuman podoplanin antibody, via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
- Pages: 768-777
- First Published: 23 March 2017
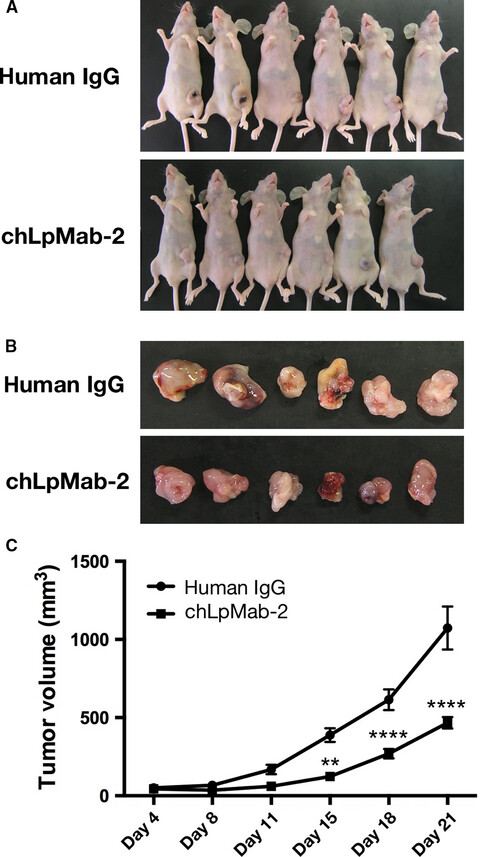
Human podoplanin, a platelet aggregation-inducing transmembrane glycoprotein, is expressed in different types of tumors. In this study, we developed chLpMab-2, a human–mouse chimeric anti-hPDPN cancer-specific antibody. chLpMab-2 could be useful as a novel antibody-based therapy against hPDPN-expressing tumors with no unexpected side effects.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
The regulation of tumor-suppressive microRNA, miR-126, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Pages: 778-787
- First Published: 15 March 2017
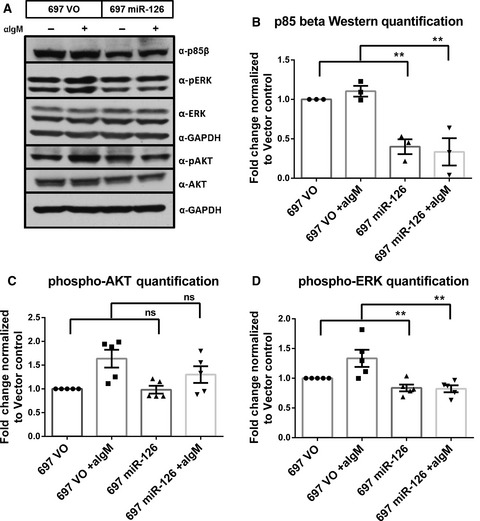
In our studies, we show that miR-126 is downregulated with CLL disease progression. miR-126 expression is negatively correlated with levels of p85β, a regulatory subunit of PI3K complex, in CLL patients. In leukemia cell-line models, miR-126 overexpression can decrease p85β level and prosurvival MAPK signaling.
Acidified bile acids enhance tumor progression and telomerase activity of gastric cancer in mice dependent on c-Myc expression
- Pages: 788-797
- First Published: 01 March 2017

In my manuscript, we have demonstrated acidified bile acids enhanced tumor progression and telomerase activity in gastric cancer, and that these effects are dependent on c-Myc activity. These findings suggest that acidified bile acids play an important role in the malignant progression of reflux gastric cancer.
Novel anticarcinoembryonic antigen antibody–drug conjugate has antitumor activity in the existence of soluble antigen
- Pages: 798-808
- First Published: 17 February 2017
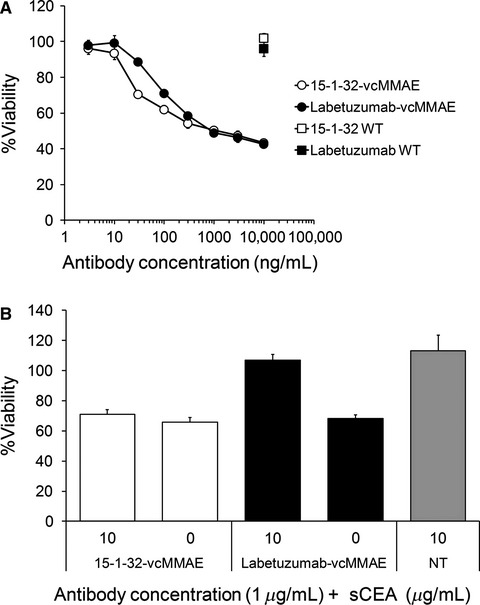
In this study, we succeeded in creating 15-1-32, a fully human antibody that recognizes membrane-bound carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). 15-1-32 shows a higher binding affinity for membrane-bound CEA than other CEA antibodies, and is only slightly influenced by soluble-form CEA. 15-1-32-drug conjugate (15-1-32-vcMMAE) showed enhanced antitumor activity against gastric cancer cell lines in the presence of high concentrations of soluble CEA.
Dasatinib inhibits actin fiber reorganization and promotes endothelial cell permeability through RhoA-ROCK pathway
- Pages: 809-818
- First Published: 18 March 2017
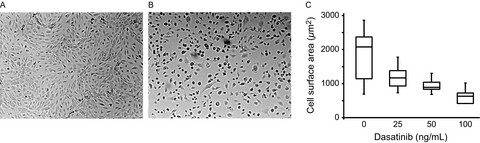
Treatment with dasatinib is often associated with peripheral edema, pleural effusion, and pulmonary hypertension. We investigated the effect of dasatinib on endothelial cells and show that at therapeutic concentrations, dasatinib inhibits endothelial cell spreading and the phosphorylation of p130CAS, paxillin and vinculin, cytoskeletal molecules localized to focal adhesions, forming a basis for increased vascular permeability seen in patients.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
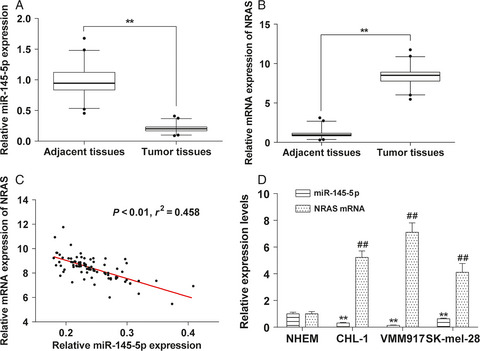
Retracted: Effects of miR-145-5p through NRAS on the cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion in melanoma by inhibiting MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways
- Pages: 819-833
- First Published: 23 March 2017
Cancer Biology
Original Research
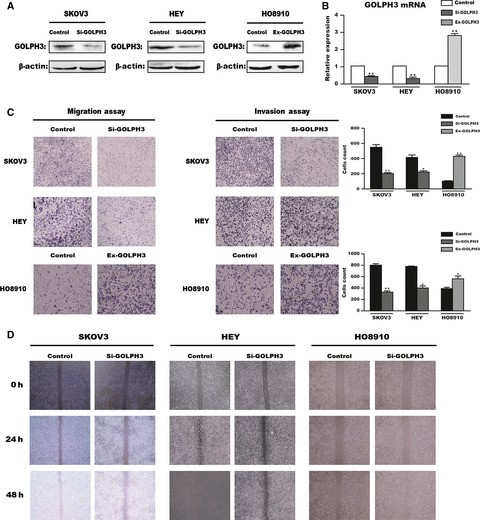
GOLPH3 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in epithelial ovarian cancer
- Pages: 834-844
- First Published: 23 March 2017
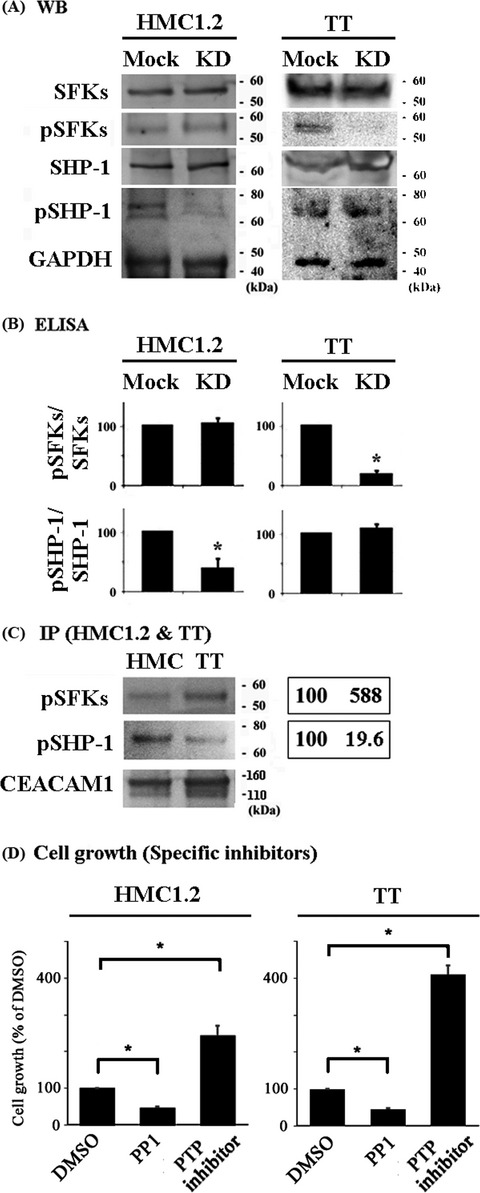
CEACAM1 long isoform has opposite effects on the growth of human mastocytosis and medullary thyroid carcinoma cells
- Pages: 845-856
- First Published: 23 March 2017
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Tobacco use and outcome in radical prostatectomy patients
- Pages: 857-864
- First Published: 20 March 2017
Cardiorespiratory fitness and risk of site-specific cancers: a long-term prospective cohort study
- Pages: 865-873
- First Published: 20 March 2017
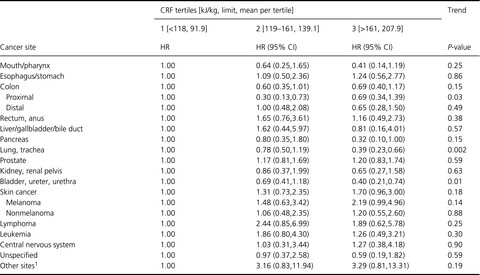
The study is based on measured mid-life cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF), which reflects aerobic activity performed over time and may be well suited to capture health consequences of an active versus sedentary lifestyle. The analyses indicate a benefit of having high CRF, for several cancers. Compared to men with low CRF, men with higher CRF have reduced risk of cancer at proximal colon, lung, pancreas, and bladder.
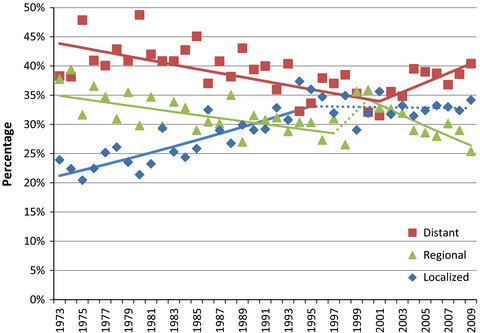
Trend analysis and survival of primary gallbladder cancer in the United States: a 1973–2009 population-based study
- Pages: 874-880
- First Published: 20 March 2017