Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Vitamin D enhances the efficacy of photodynamic therapy in a murine model of breast cancer
- Pages: 633-642
- First Published: 25 February 2015
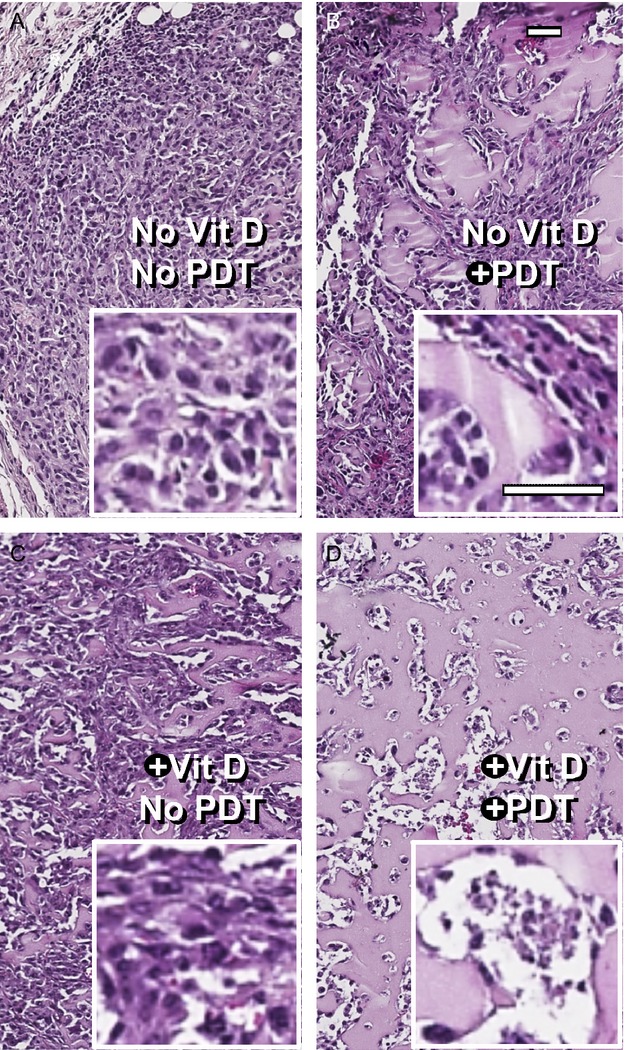
Preconditioning of breast cancer cutaneous tumors with Vitamin D3 (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3; Vit D) increases the cytotoxic, tumor-specific effects of aminolevulinate-based photodynamic therapy (PDT). This novel combination approach offers a potential new way to treat breast cancer metastasis and achieve better efficacy with fewer complications than standard treatment modalities.
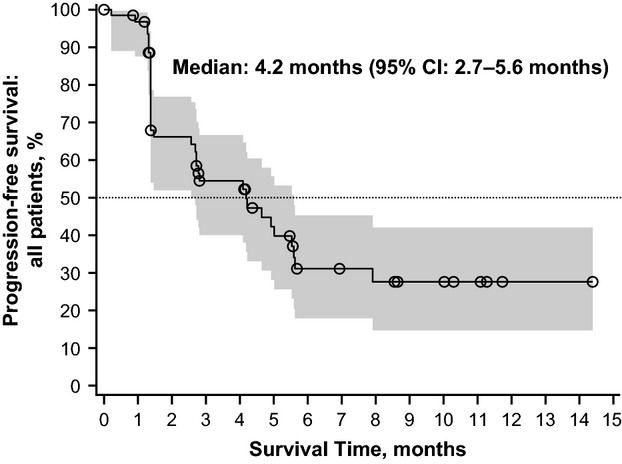
A phase 2, multicenter, open-label study of sepantronium bromide (YM155) plus docetaxel in patients with stage III (unresectable) or stage IV melanoma
- Pages: 643-650
- First Published: 23 December 2014
Clinical outcomes associated with evolving treatment modalities and radiation techniques for base-of-tongue carcinoma: thirty years of institutional experience
- Pages: 651-660
- First Published: 26 January 2015
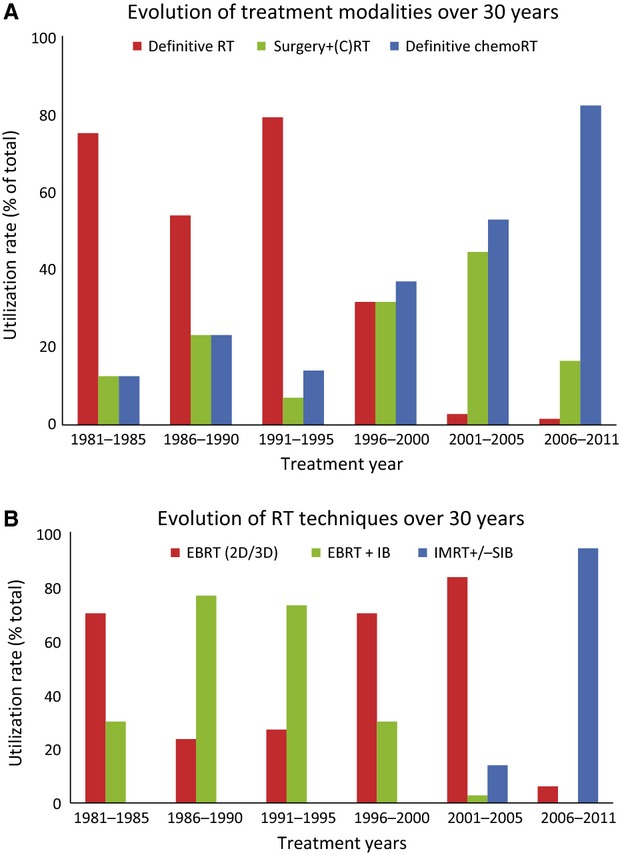
Over the past 30 years, curative treatment modalities for locally advanced base-of-tongue carcinomas at our institution have evolved from surgery to definitive radiotherapy to definitive chemoradiotherapy. Radiation techniques have evolved from external beam radiation therapy plus interstitial brachytherapy to intensity modulated radiation therapy with simultaneous integrated boost. Clinical outcomes associated with evolving treatment modalities and radiation techniques demonstrate excellent locoregional control and survival with modern techniques.
Review
CTLA-4 blockade with ipilimumab: biology, safety, efficacy, and future considerations
- Pages: 661-672
- First Published: 25 January 2015
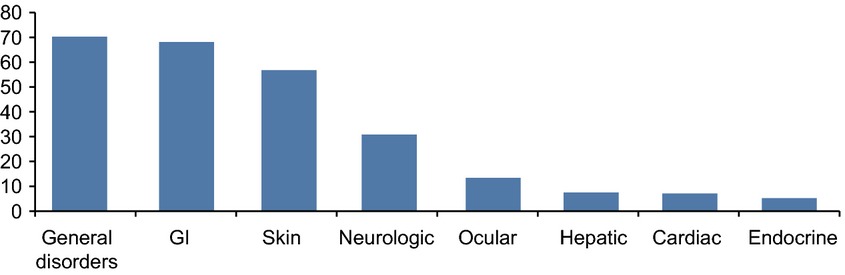
Ipilimumab indirectly targets the tumor by stimulating the patient's immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells and has demonstrated a survival benefit for patients treated in different clinical trials, now exceeding 4 years in some cases. Most patients (84.8%) experience a drug-related adverse event (AE) of any grade, most of these are of low toxicity grade, and a majority these events can be managed following established guidelines.
Original Research
Paclitaxel/carboplatin with or without sorafenib in the first-line treatment of patients with stage III/IV epithelial ovarian cancer: a randomized phase II study of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute
- Pages: 673-681
- First Published: 31 December 2014
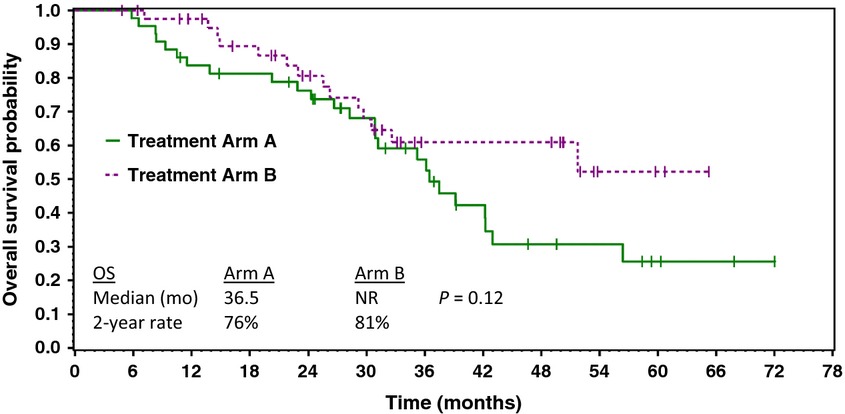
The purpose of this study was to compare the efficacy and toxicity of standard first-line treatment with paclitaxel/carboplatin versus paclitaxel/carboplatin plus sorafenib in patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma. The addition of sorafenib to standard paclitaxel/carboplatin did not improve efficacy and substantially increased toxicity in the first-line treatment of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer.
Imatinib use immediately before stem cell transplantation in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results from Japanese Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group (JPLSG) Study Ph+ALL04
- Pages: 682-689
- First Published: 31 January 2015
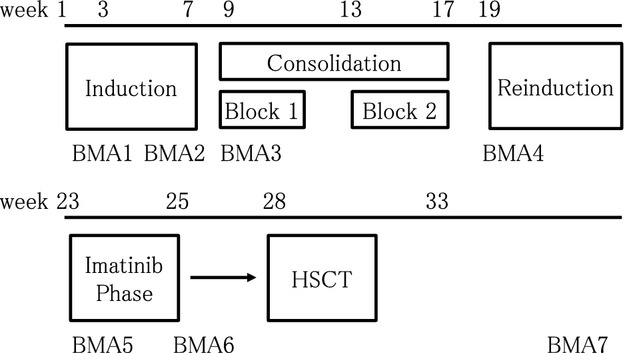
Imatinib, which was produced as a prototype molecular targeting drug, was expected to become a major component in the treatment of children with Ph+ALL, however, the optimal timing and duration of its use was not established 10 years ago. In response, we conducted a nationwide clinical trial to investigate the use of imatinib as a single agent “bridge” between intensive chemotherapy and transplantation, utilizing serial molecular measurements of minimal residual disease (MRD). Forty-two patients were enrolled and a decrease in the amount of MRD or the ability to maintain negative MRD was observed in most patients. In addition, 4-year-overall survival was favorable at 78%, although all the patients were treated with transplantation.
Development and validation of the functional assessment of cancer therapy–antiangiogenesis subscale
- Pages: 690-698
- First Published: 26 January 2015
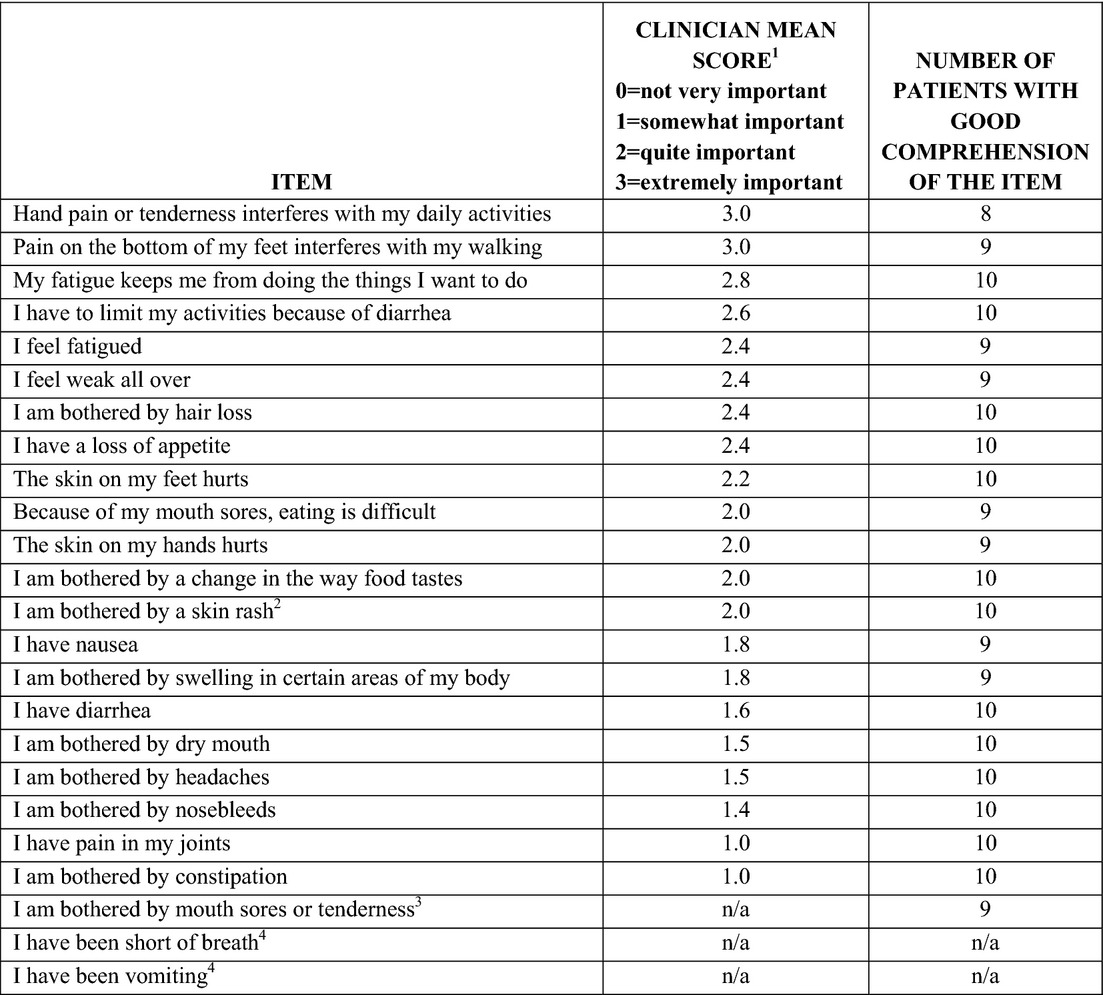
Side effects from anti-angiogenesis therapies may impact health-related quality of life and can result in dose reductions, delays or discontinuation of therapy. The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT) -Anti-Angiogenesis Subscale was developed and validated to enhance treatment decision-making and side effect management for patients receiving anti-angiogenesis therapies.
Xenograft assessment of predictive biomarkers for standard head and neck cancer therapies
- Pages: 699-712
- First Published: 26 January 2015
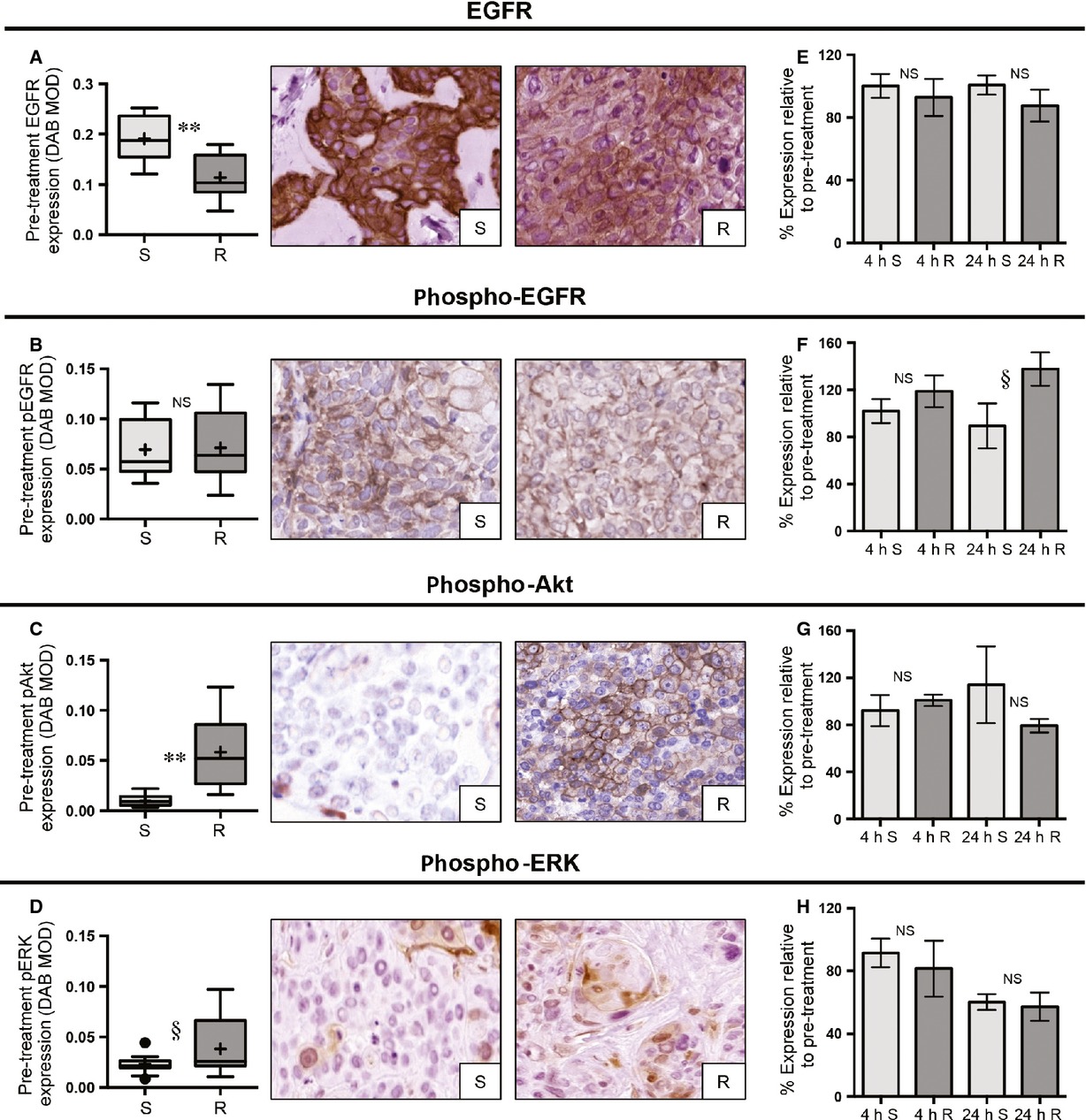
No clinically validated predictive biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) exist. Utilizing a mouse xenograft model generated from HNSCC cell lines, we demonstrate both unique and established relationships including low excision repair cross-complementation group 1 (ERCC1), low phospho-Akt/low phospho-ERK, and high total epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) being associated with cisplatin sensitivity, cetuximab sensitivity, and radiation resistance, respectively. This protocol can be applied to other model systems and provide guidance for the proper validation of putative predictive biomarkers for clinical usage.
Prevalence of renal impairment and use of nephrotoxic agents among patients with bone metastases from solid tumors in the United States
- Pages: 713-720
- First Published: 08 February 2015
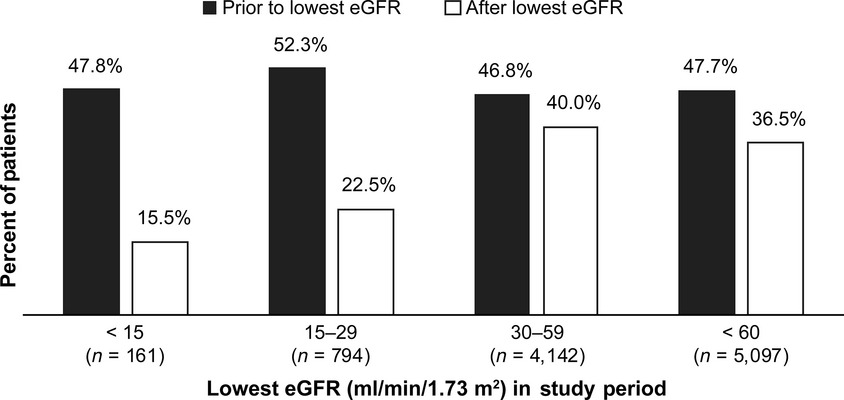
In patients with bone metastases secondary to solid tumors, the 5-year prevalence was 43% for renal impairment (RI) and 71% for chronic kidney disease among evaluable RI patients. Whenever possible, treatments that are potentially less damaging for the kidney should be considered for patients with or predisposed to RI.
Induction therapy with cetuximab plus docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (ETPF) in patients with resectable nonmetastatic stage III or IV squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx. A GERCOR phase II ECHO-07 study
- Pages: 721-731
- First Published: 14 February 2015

This phase II study reports a clinical and radiological complete response of 22% and a primary tumor overall response rate of 58% for ETPF in patients with moderately advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx. The schedule of ETPF evaluated in this study cannot be recommended at this dosage.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
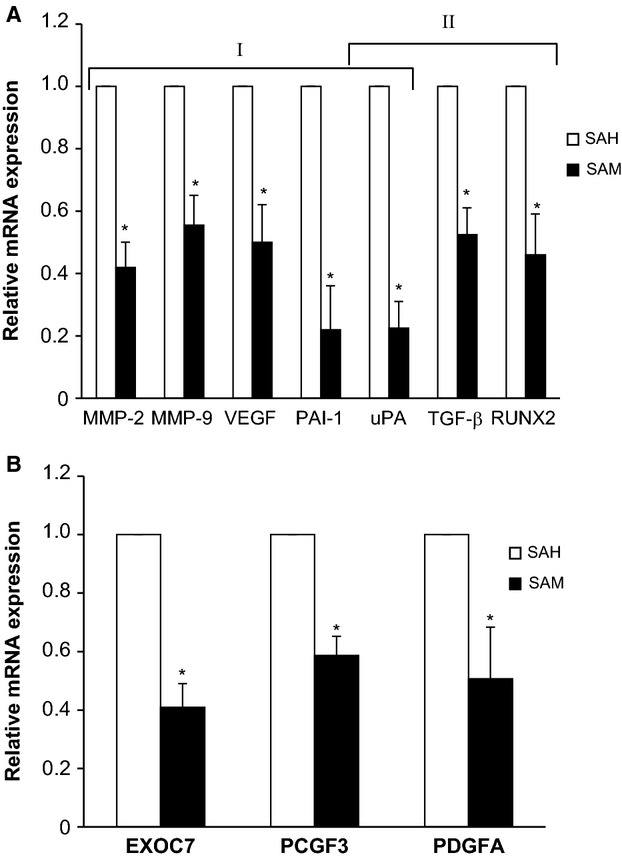
S-adenosylmethionine blocks osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion in vitro and tumor metastasis in vivo: therapeutic and diagnostic clinical applications
- Pages: 732-744
- First Published: 26 January 2015
Overexpression of the microRNA miR-433 promotes resistance to paclitaxel through the induction of cellular senescence in ovarian cancer cells
- Pages: 745-758
- First Published: 15 February 2015
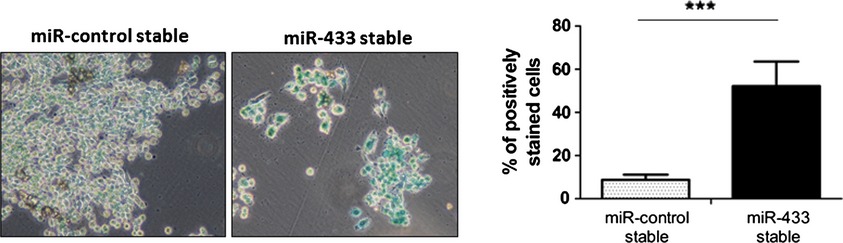
In this manuscript, we describe the role of the microRNA miR-433 in the induction of cellular senescence, by the downregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 6. Interestingly, we show that high miR-433 expressing cells can induce a senescence bystander effect in neighboring cells in nonautonomous manner. Crucially, our bioinformatic analysis demonstrates that miR-433 has a pivotal role in the regulation of the cell cycle, and therefore contributing to mediate chemoresistance to paclitaxel in ovarian cancer cells.
ANGPTL3 is a novel biomarker as it activates ERK/MAPK pathway in oral cancer
- Pages: 759-769
- First Published: 30 January 2015
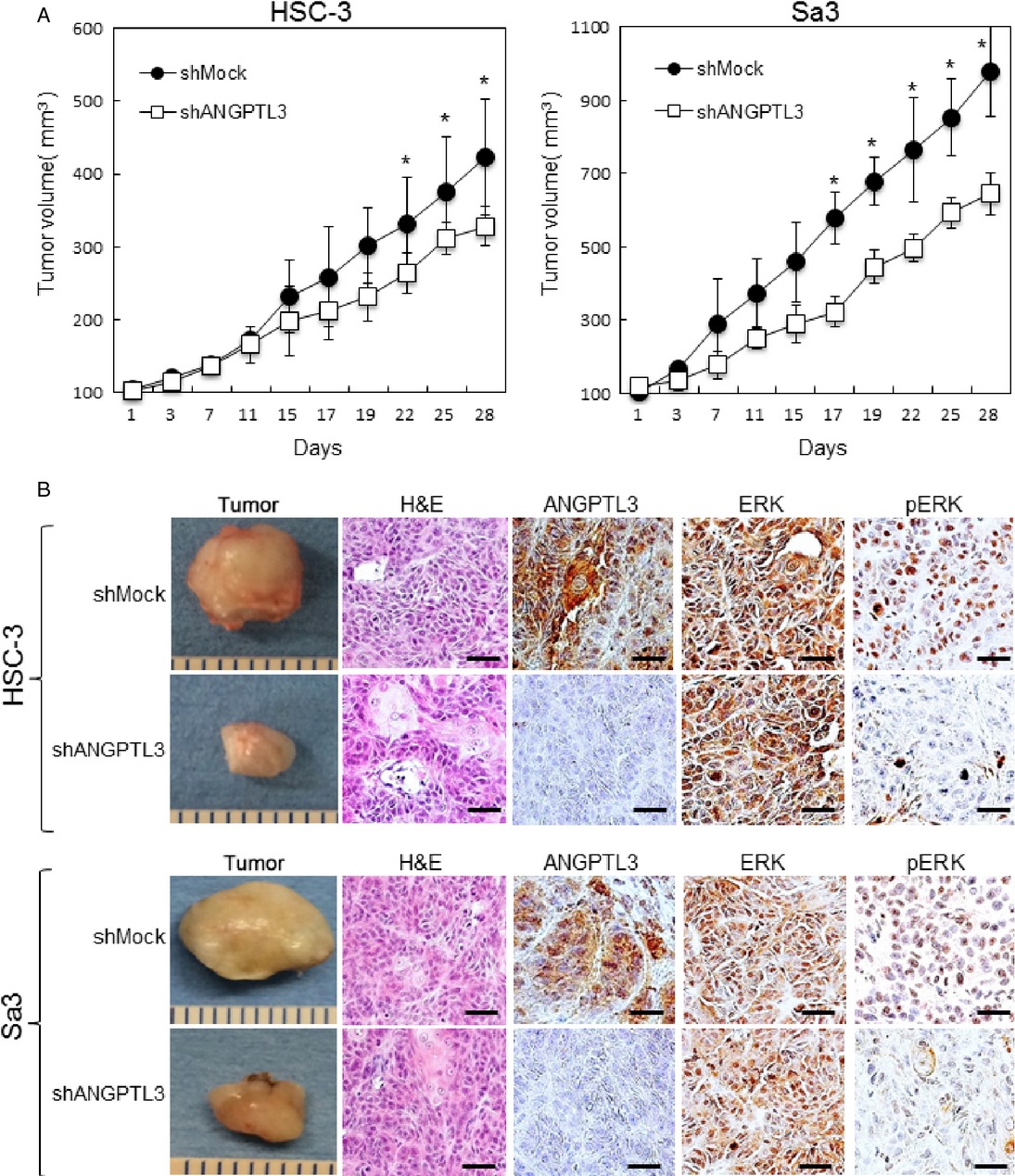
Despite comprehensive treatments, patient with advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) usually reveals poor prognosis. The authors have shown a predictive relevance of ANGPTL3 expression status in future patients with OSCC. Thus, it would be interesting to design clinical studies to elucidate the predictive relevance of ANGPTL3 expression status in future patients with OSCC because advanced OSCC cases have been divided into two groups, those with favorable and unfavorable prognoses.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Statins use and the risk of all and subtype hematological malignancies: a meta-analysis of observational studies
- Pages: 770-780
- First Published: 21 March 2015
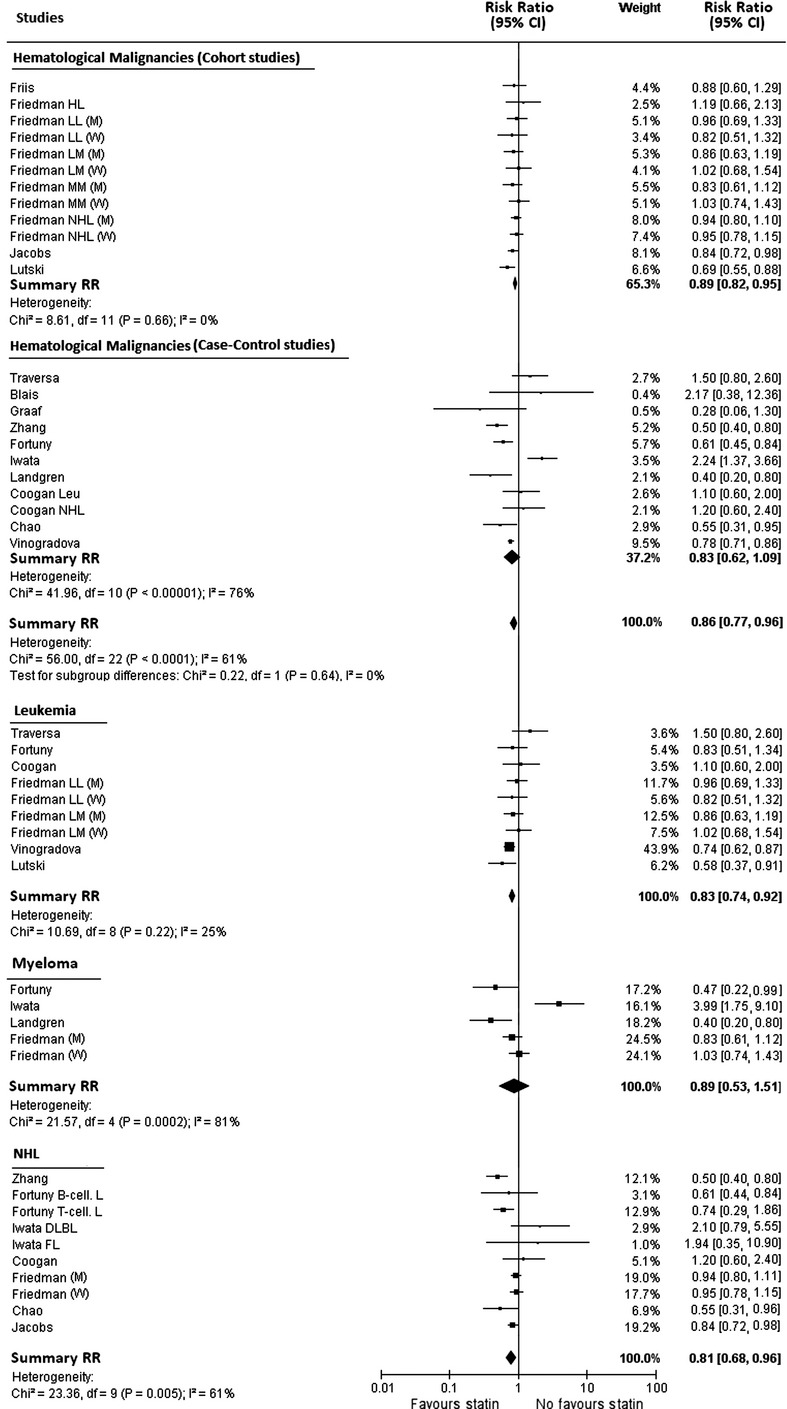
In order to quantify the association between use of statins and the risk of all hematological malignancies and of subtypes, we performed a meta-analysis of observational studies. Our study provides evidence that statins seem to reduce the risk of hematological malignancy. We also found that statins users had a significant reduced risk of leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma than nonusers.
Family history of cancer and childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group and the Utah Population Database
- Pages: 781-790
- First Published: 23 March 2015
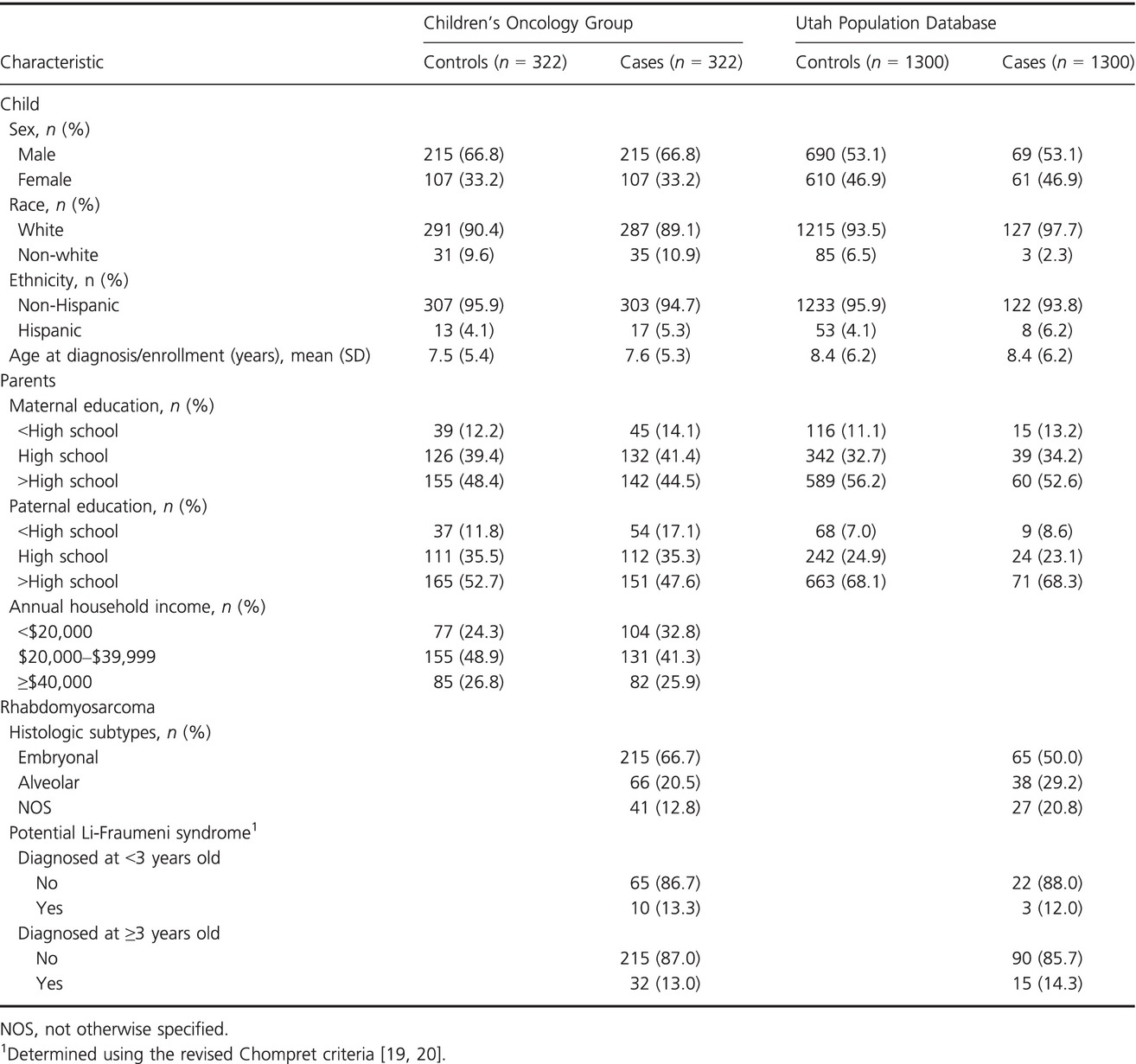
Using data obtained from the Children's Oncology Group and the Utah Population Database, we found an increased risk of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) in children who have a first-degree relative with cancer. This risk was stronger among those whose relatives were diagnosed with cancer at <30 years of age. As little is known about the epidemiology of RMS, this study is an important step in characterizing the role of inherited susceptibility to this important childhood malignancy.