Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Cancer stem cells and cisplatin-resistant cells isolated from non-small-lung cancer cell lines constitute related cell populations
- Pages: 1099-1111
- First Published: 25 June 2014
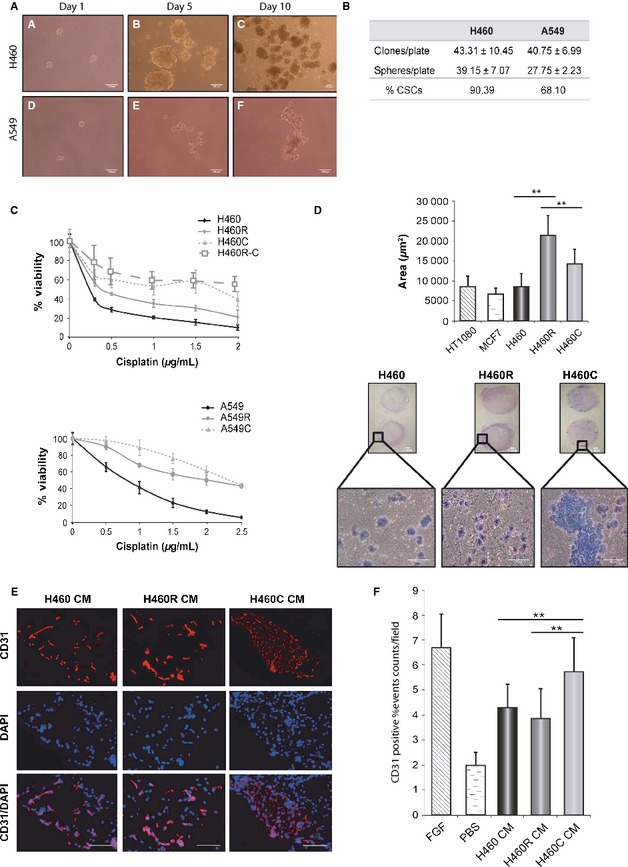
Cisplatin-resistant cells were isolated from H460 and A549 non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines after a single treatment with the drug, simulating patient-treatment protocols. Cancer stem cells were also isolated from these cell lines for comparison. Both cisplatin resistant and stem cells showed increased cisplatin resistance, tumorigenicity, angiogenic, and metastatic capacity. Their gene expression profiles were highly related. Furthermore, the presence of cells with Stem characteristics in patient's surgical samples was related to their sensitivity to cisplatin.
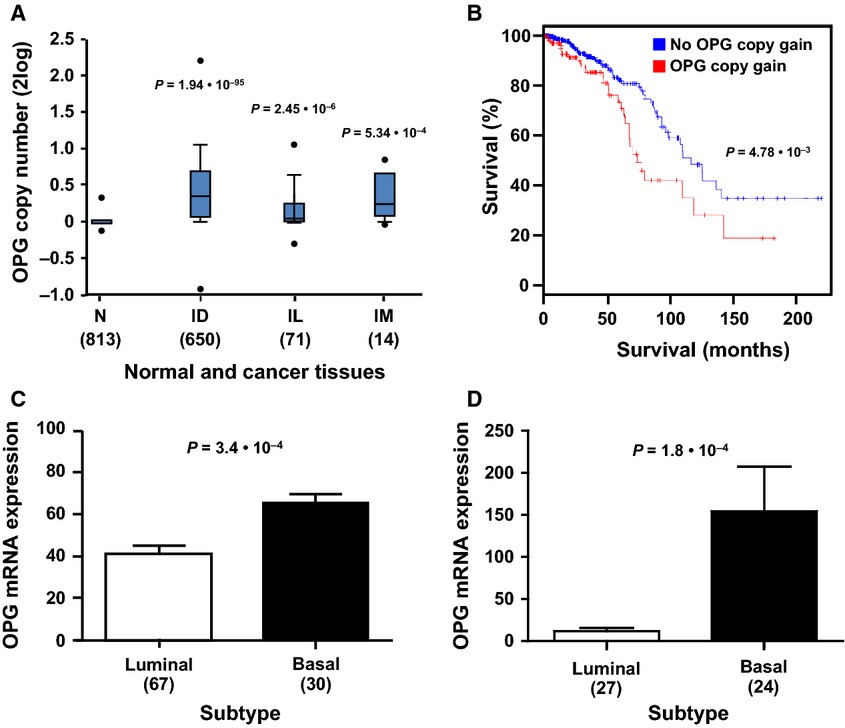
Osteoprotegerin expression in triple-negative breast cancer cells promotes metastasis
- Pages: 1112-1125
- First Published: 28 June 2014
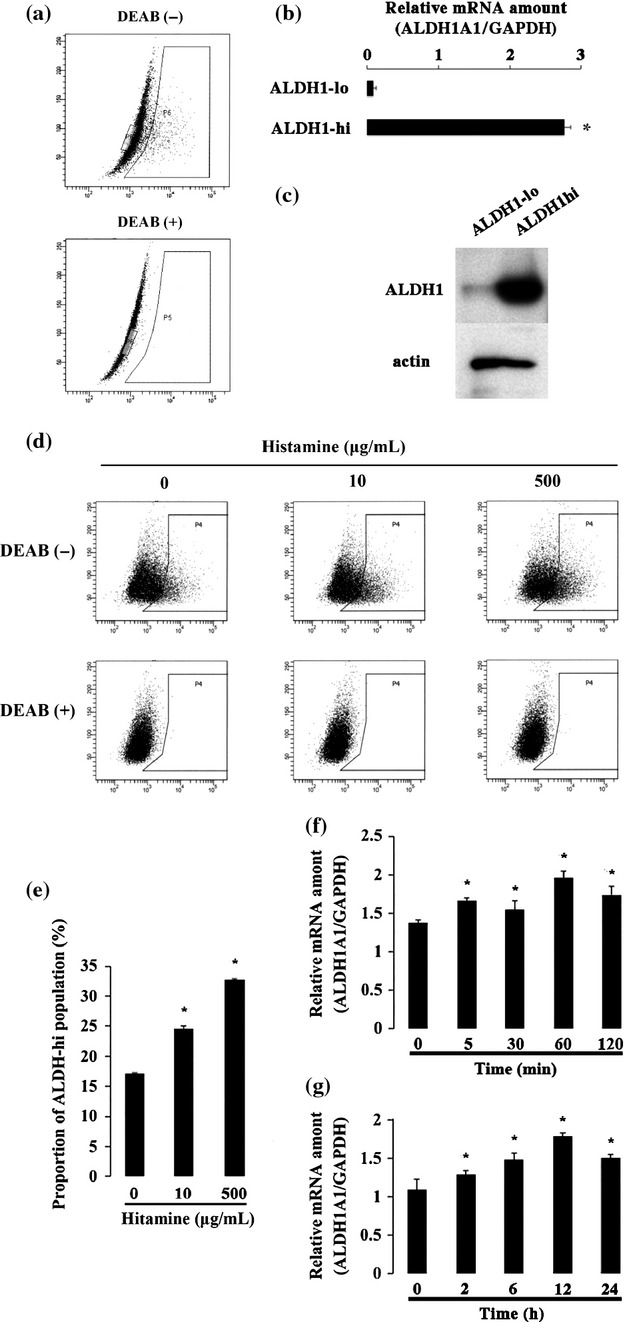
Roles of histamine on the expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in endometrioid adenocarcinoma cell line
- Pages: 1126-1135
- First Published: 10 July 2014
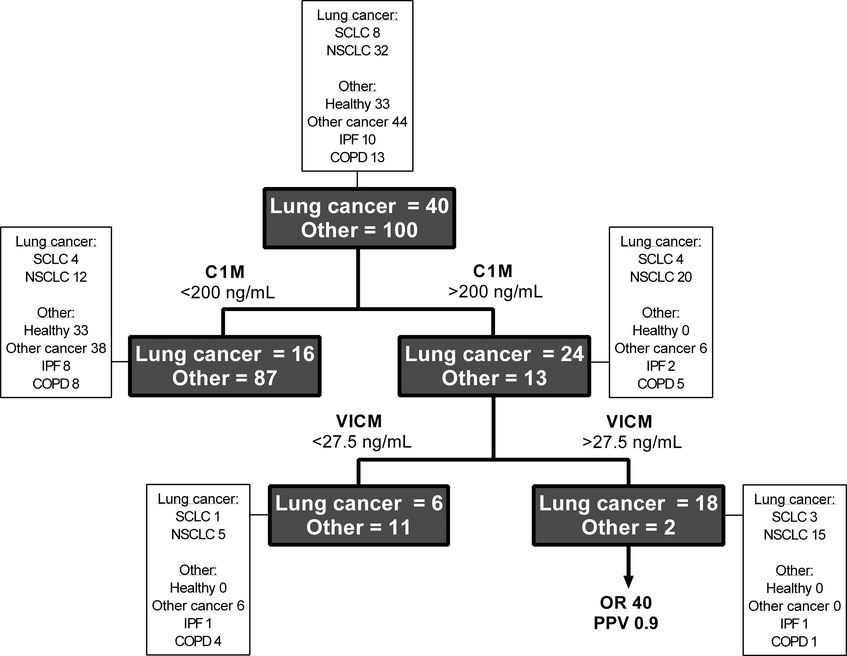
Serum biomarkers reflecting specific tumor tissue remodeling processes are valuable diagnostic tools for lung cancer
- Pages: 1136-1145
- First Published: 18 July 2014
Inhibition of epidermal growth factor signaling by the cardiac glycoside ouabain in medulloblastoma
- Pages: 1146-1158
- First Published: 23 July 2014
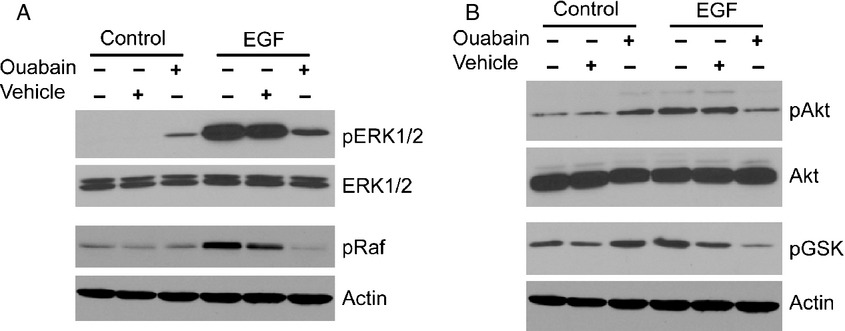
Aberrant activation of EGFR signaling has been observed in a high percentage of cancers and often is associated with poor outcome but targeted therapy for EGFR/ErbB signaling has remained a challenge due to its complex nature. We now show that the cardiac glycoside ouabain, an inhibitor of Na,K-ATPase, inhibits EGF signaling in medulloblastoma cells and prevents EGF-induced cell migration, a prerequisite for an invasive phenotype in these tumors. Thus, Na,K-ATPase is an attractive target to develop novel therapeutic strategies for cancers with aberrant activation of EGFR signaling.
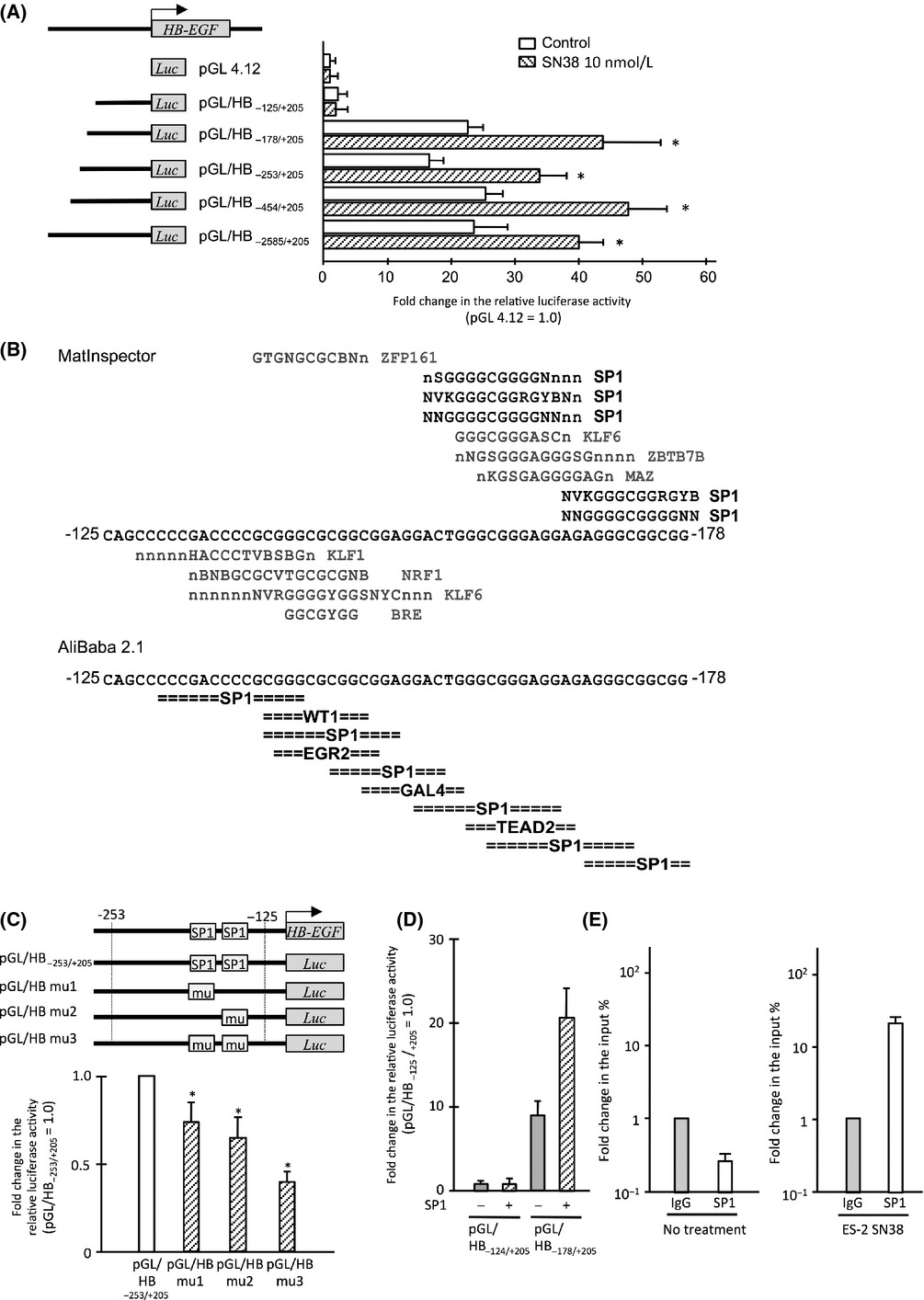
Contribution of transcription factor, SP1, to the promotion of HB-EGF expression in defense mechanism against the treatment of irinotecan in ovarian clear cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1159-1169
- First Published: 24 July 2014
Recurring DNA copy number gain at chromosome 9p13 plays a role in the activation of multiple candidate oncogenes in progressing oral premalignant lesions
- Pages: 1170-1184
- First Published: 24 July 2014
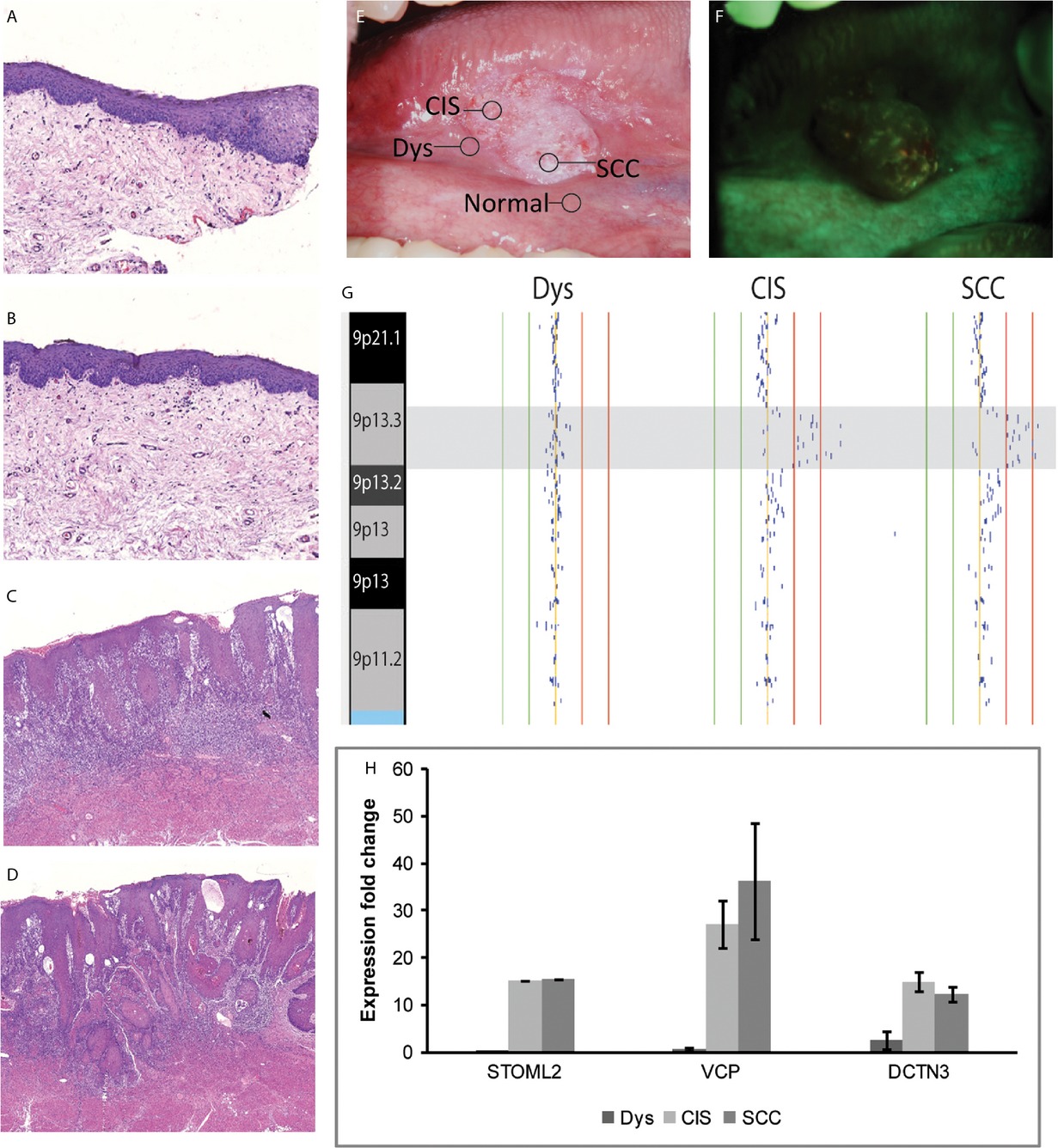
We report a recurrent DNA copy number gain event at chromosome 9p13 that is detectable in the earliest stages of oral premalignancy and is associated with increased progression likelihood for early stage oral lesions (which currently have no clinically viable means of delineating this risk). We find evidence that this alteration event is a product of selection for the activation of multiple oncogenes in parallel, each of which we show to be capable of regulating oral cancer phenotypes.
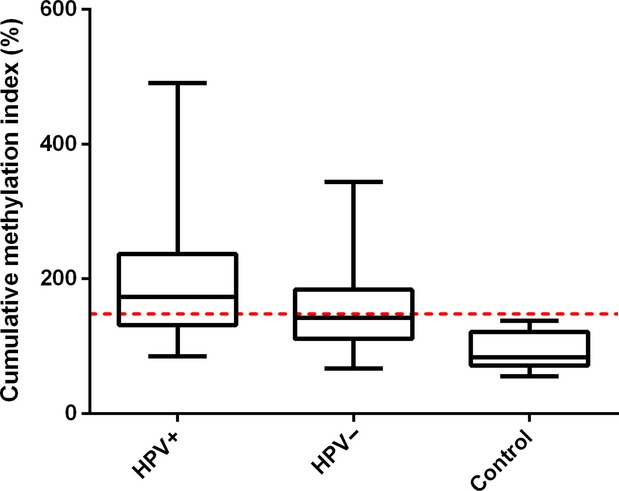
HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with TIMP3 and CADM1 promoter hypermethylation
- Pages: 1185-1196
- First Published: 26 July 2014
Functional relationship between matrix metalloproteinase-11 and matrix metalloproteinase-14
- Pages: 1197-1210
- First Published: 01 August 2014
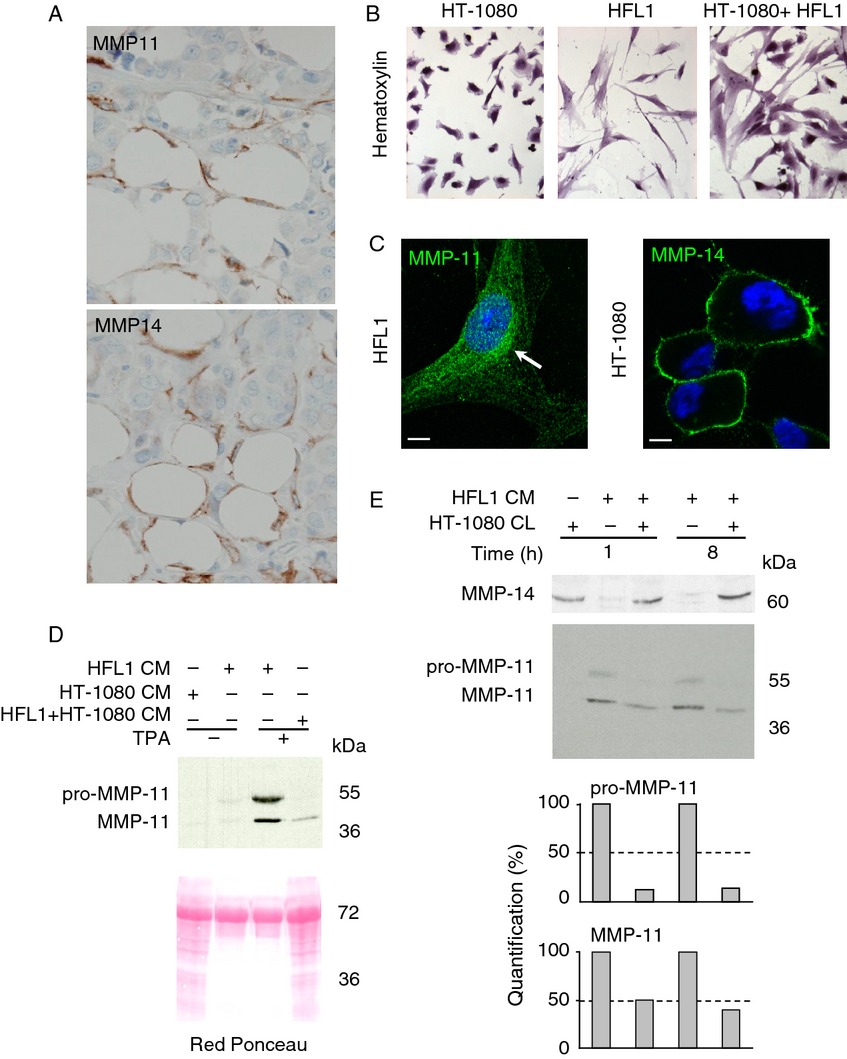
MMP-11 is a novel substrate of MMP-14. This leads to MMP-11 inactivation, representing therefore one new critical regulatory mechanism to control the extent of pericellular MMP-11 bioavailability. Thus, in addition to the canonical reversible TIMP-dependent process, irreversible MMP inactivation might occur by direct cleavage of the catalytic domain in a MMP-dependent manner.
Acetylation-dependent regulation of essential iPS-inducing factors: a regulatory crossroad for pluripotency and tumorigenesis
- Pages: 1211-1224
- First Published: 13 August 2014
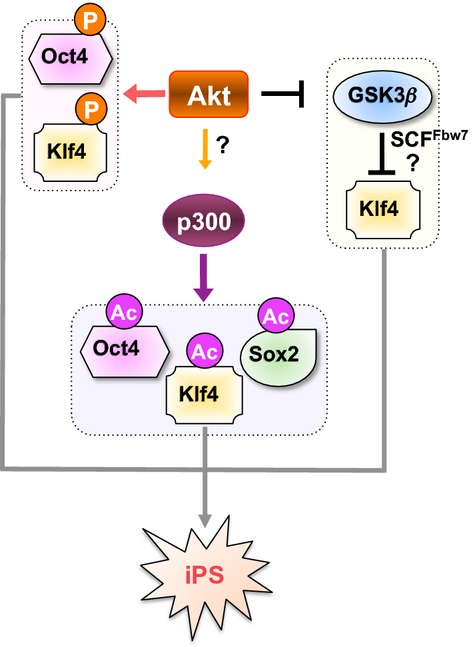
Akt regulates the induced pluripotent stem (iPS) process by modulating posttranslational modifications of iPS factors in both direct and indirect manners. Specifically, Akt directly phosphorylates Oct4 to modulate the Oct4/Sox2 heterodimer formation. Furthermore, Akt either facilitates the p300-mediated acetylation of Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4, or stabilizes Klf4 by inactivating GSK3, to indirectly modulate stemness.
Molecular subtyping of bladder cancer using Kohonen self-organizing maps
- Pages: 1225-1234
- First Published: 20 August 2014
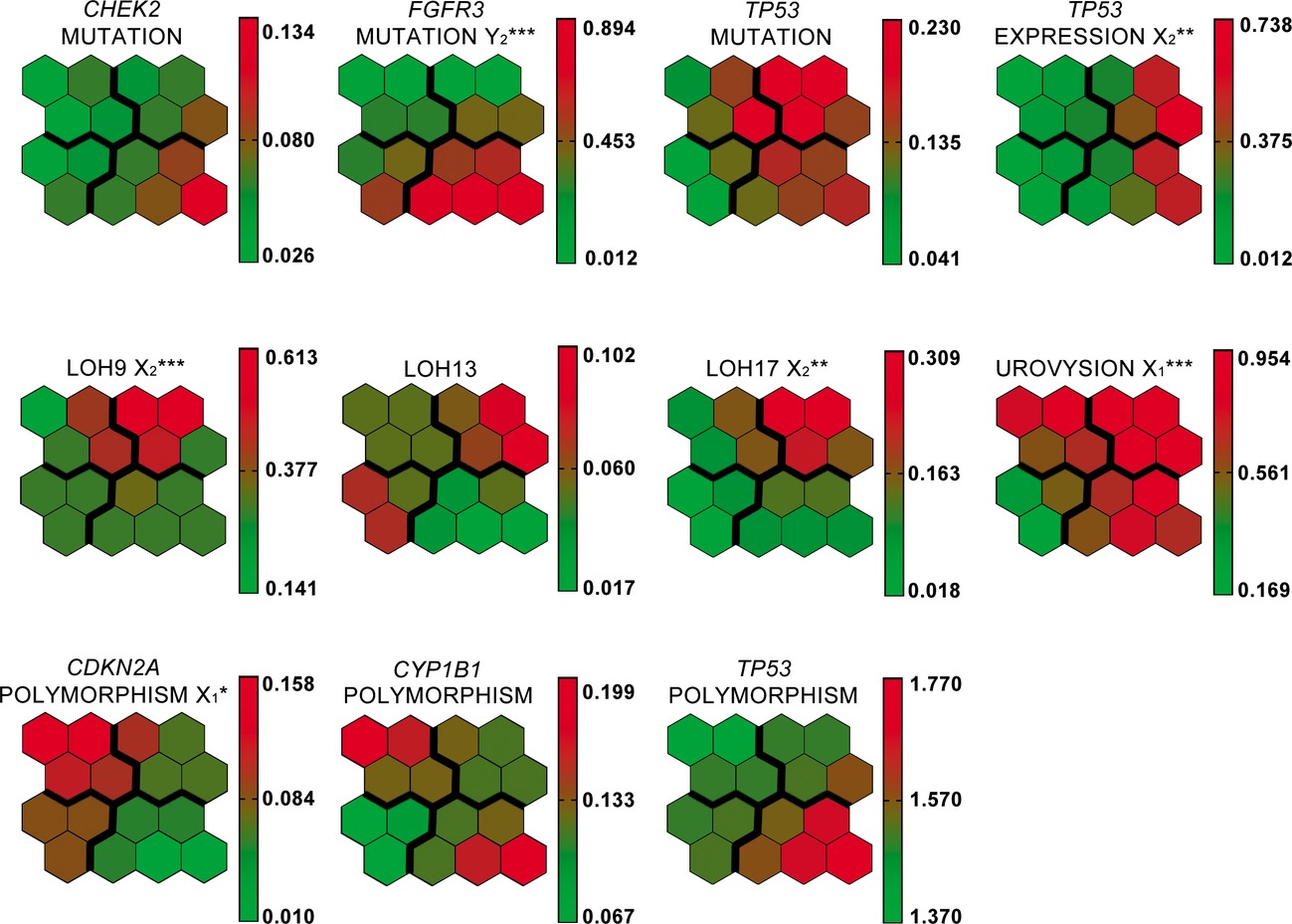
We find that Kohonen self-organizing maps (SOMs) are able to stratify tumors according to biological outcomes rather than clinical phenotypes. In our comparison, SOM outperformed hierarchical clustering (its closest competition), suggesting that SOMs may offer a solution to this problem. This work represents the first of its type, in this field.
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
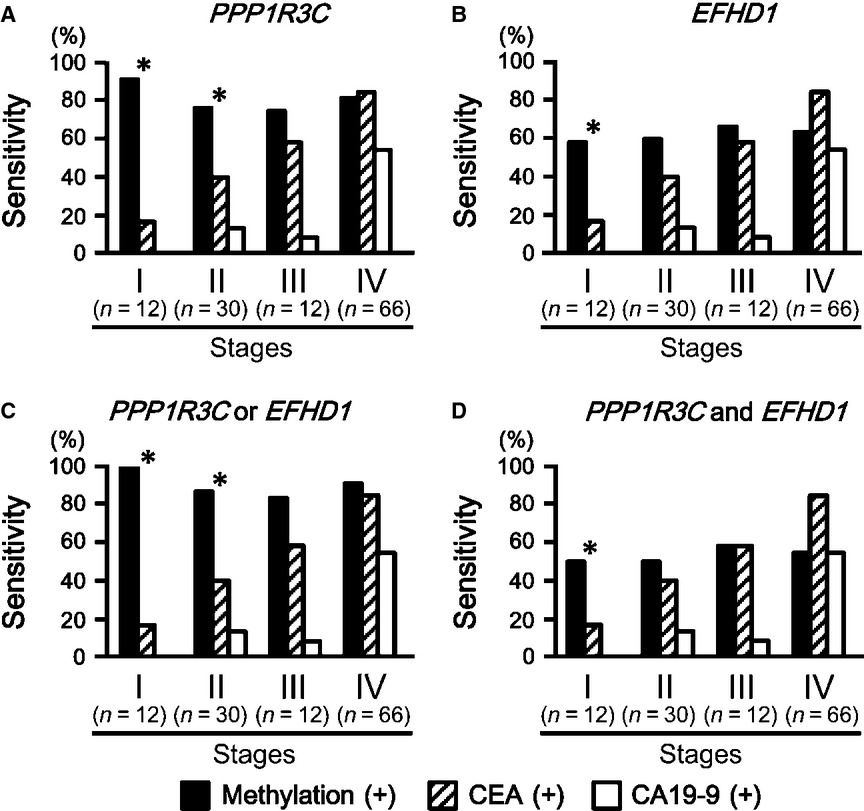
Aberrant promoter methylation of PPP1R3C and EFHD1 in plasma of colorectal cancer patients
- Pages: 1235-1245
- First Published: 24 May 2014
High expression of L-type amino acid transporter 1 as a prognostic marker in bile duct adenocarcinomas
- Pages: 1246-1255
- First Published: 02 June 2014
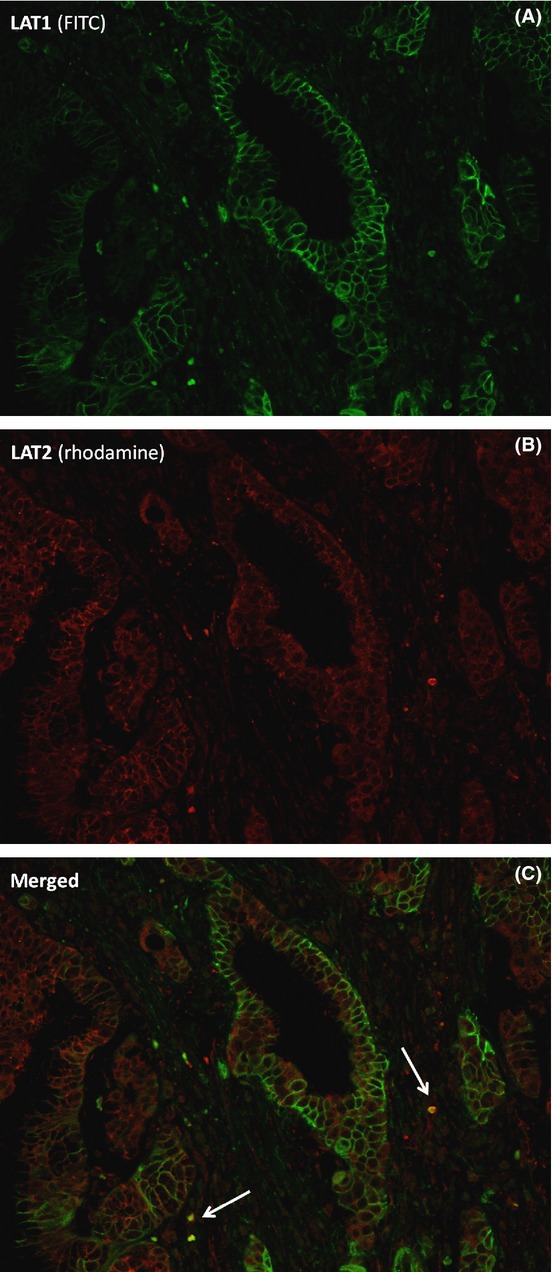
In this study, we analyzed LAT1, LAT2, and CD98 expressions in a total of 134 bile duct adenocarcinomas including distal extrahepatic bile duct adenocarcinomas (EHCs), hilar cholangiocarcinomas (HCs), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas (ICCs), and ampullary adenocarcinomas (ACs). We found that LAT1 is useful as a significant prognostic marker in bile duct cancer as well as EHC. These results strongly suggest a potential target for future anticancer therapy with its inhibitors.
T-DM1, a novel antibody–drug conjugate, is highly effective against primary HER2 overexpressing uterine serous carcinoma in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 1256-1265
- First Published: 02 June 2014
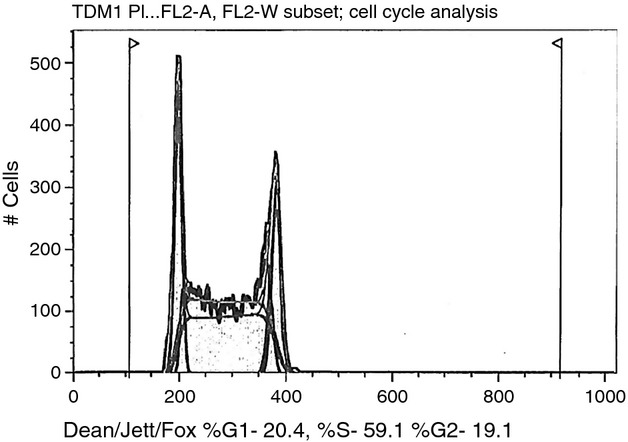
Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) shows significant antitumor effect in epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-positive uterine serous carcinoma (USC) cell lines and USC xenografts. T-DM1 may represent a novel treatment option for HER2-positive USC patients harboring disease refractory to chemotherapy and/or unresponsive to trastuzumab.
A three-protein biomarker panel assessed in diagnostic tissue predicts death from prostate cancer for men with localized disease
- Pages: 1266-1274
- First Published: 07 June 2014
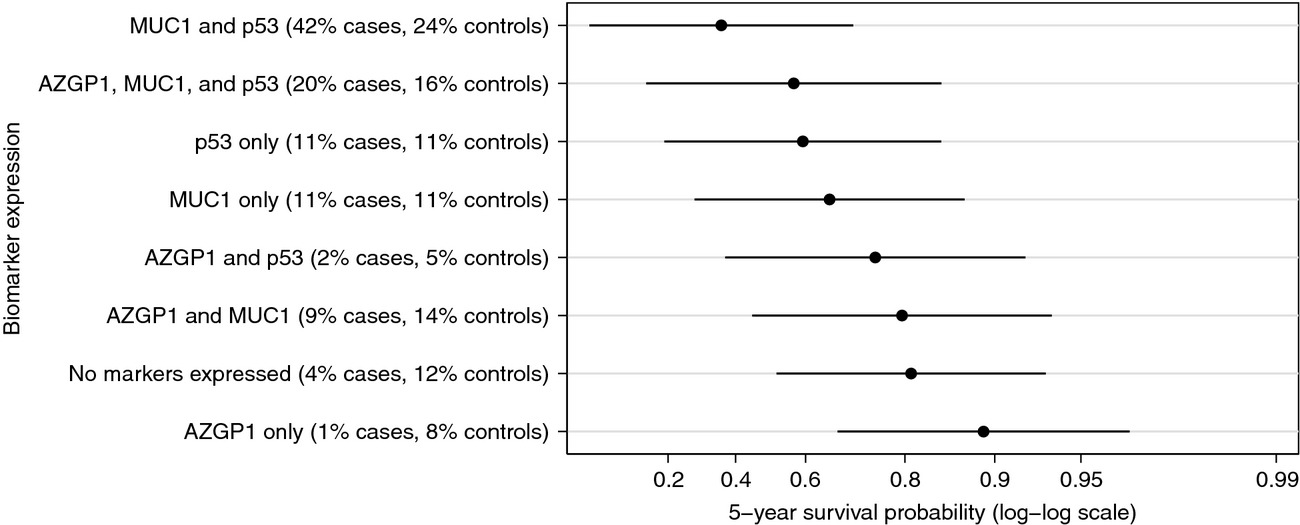
We evaluated whether a panel of biomarkers (AZGP1, MUC1, NKX3.1, p53, and PTEN), assessed by immunohistochemistry on diagnostic tissue, could predict death from prostate cancer in men with localized disease. Expression of MUC1 and p53 was associated with increased mortality (MRR 2.51 and 3.08, P < 0.03), whereas AZGP1 expression was associated with decreased mortality (MRR 0.44, P = 0.04). For men with localized disease at diagnosis, assessing the expression of these three proteins in diagnostic tissue could potentially improve estimates of risk of dying from prostate cancer based only on Gleason score and clinical stage.
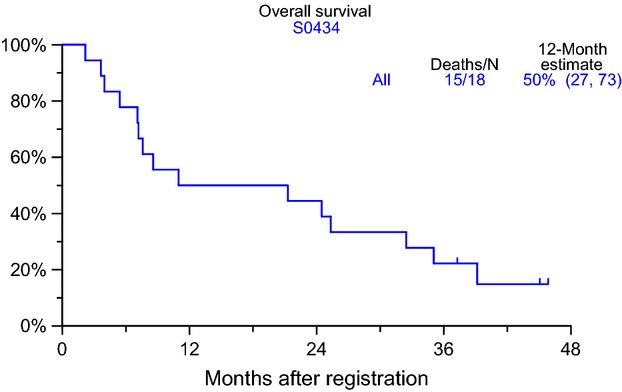
A phase II trial of BAY 43-9006 (sorafenib) (NSC-724772) in patients with relapsing and resistant multiple myeloma: SWOG S0434
- Pages: 1275-1283
- First Published: 10 June 2014
Statin use and its effect on all-cause mortality of melanoma patients: a population-based Dutch cohort study
- Pages: 1284-1293
- First Published: 17 June 2014
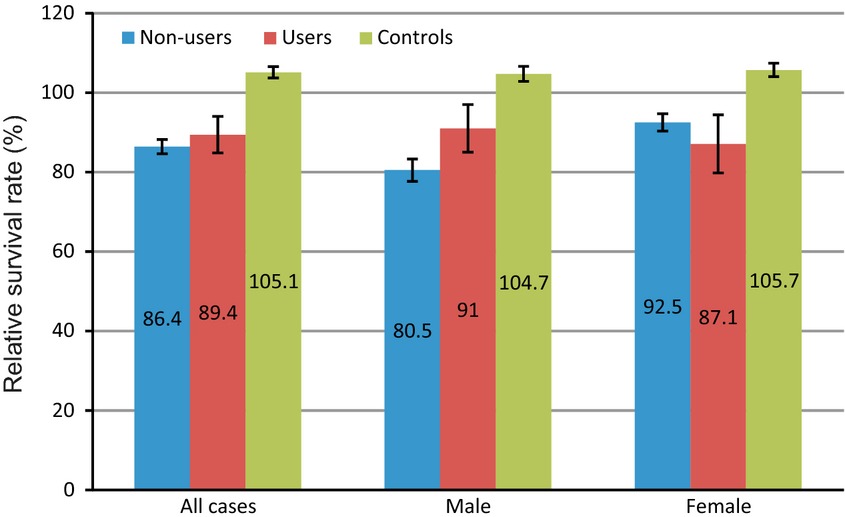
Statins have demonstrated anticancer effects on melanoma cell lines and in mouse models. In this population-based study, statin use either before or after melanoma diagnosis did not have a significant effect on survival of melanoma patients. Stratification on gender, however, showed a favorable outcome in male statin users compared to nonusers but was unchanged in females.
CT versus FDG-PET/CT response evaluation in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with irinotecan and cetuximab
- Pages: 1294-1301
- First Published: 18 June 2014
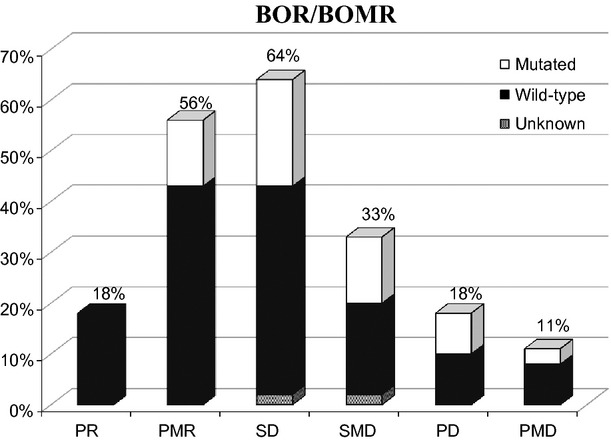
Colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan and cetuximab were evaluated with both computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET/CT). Morphologic and metabolic response agreement was poor. Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors and Positron Emission Tomography Response Criteria in Solid Tumors response distribution correlated differently with survival.
Early inflammatory response in epithelial ovarian tumor cyst fluids
- Pages: 1302-1312
- First Published: 20 June 2014
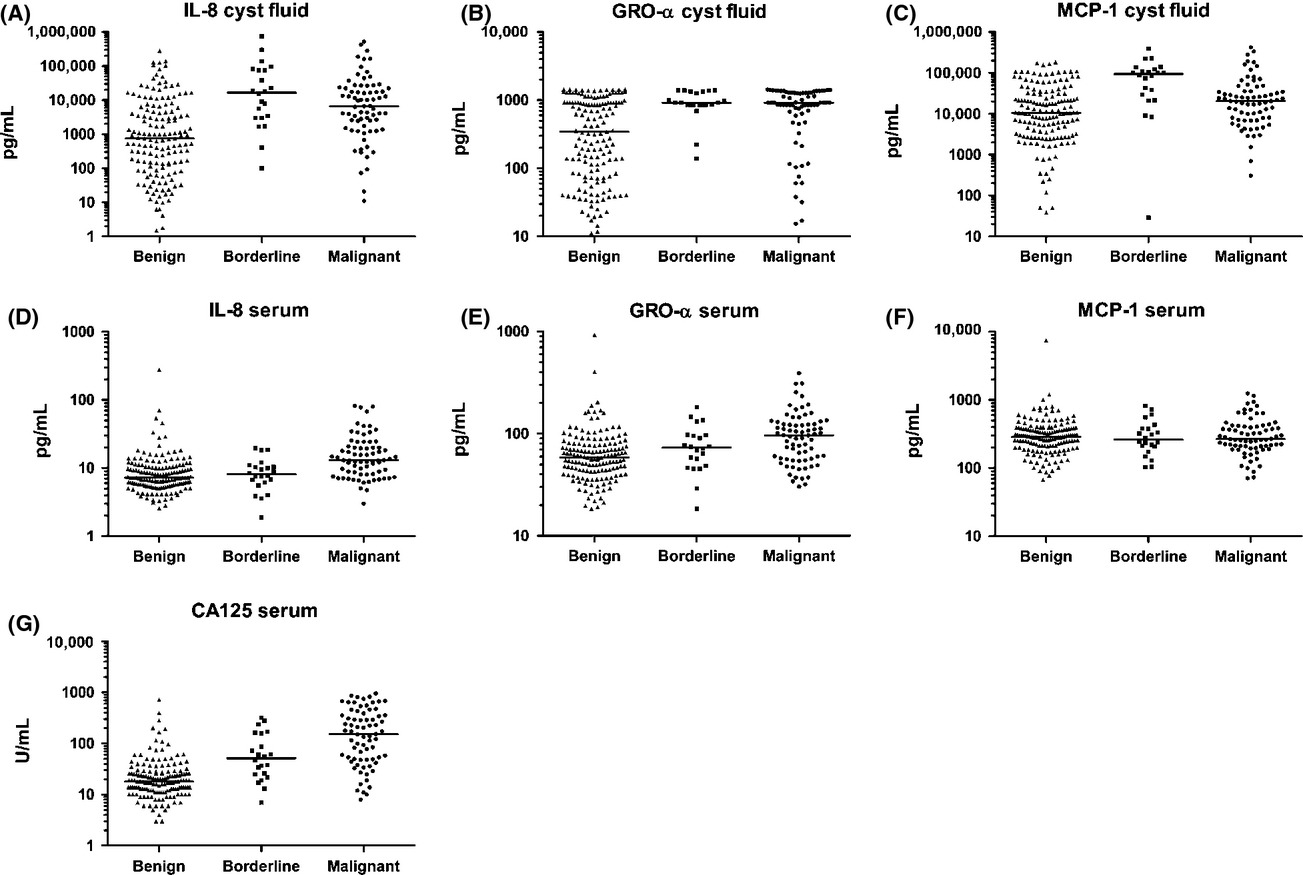
The majority of epithelial ovarian cancer consists of cysts, the cyst fluid is in direct contact or inside the pathology itself. Inflammation has a central role in all steps of cancer, and we hypothesized and confirmed that inflammatory response could be found in the closeness to the pathology before it presents in the peripheral circulation.
Intensity-modulated pelvic radiation therapy and simultaneous integrated boost to the prostate area in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: a preliminary report of disease control
- Pages: 1313-1321
- First Published: 28 June 2014
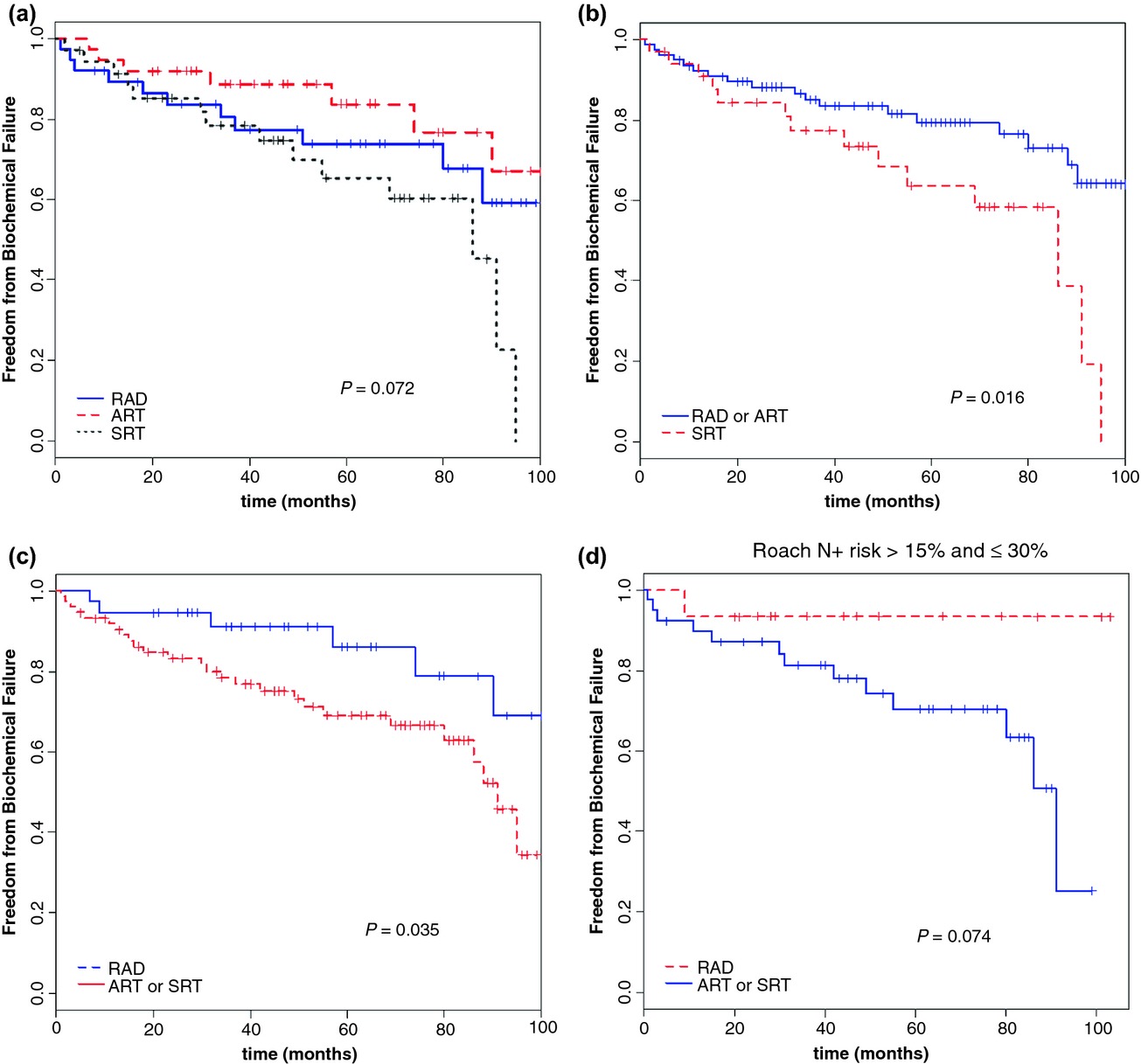
The treatment of pelvic nodes for high-risk prostate cancer is still controversial. The benefit and safety of whole pelvic irradiation using pelvic intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and simultaneous boost to the prostatic area in association with 2-year androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) was evaluated. It was found that simultaneous integrated boost (SIB) technique is a well-tolerated treatment. High disease control in patients with prostate cancer requiring lymph node treatment was achieved.
Combining the pan-aurora kinase inhibitor AMG 900 with histone deacetylase inhibitors enhances antitumor activity in prostate cancer
- Pages: 1322-1335
- First Published: 03 July 2014
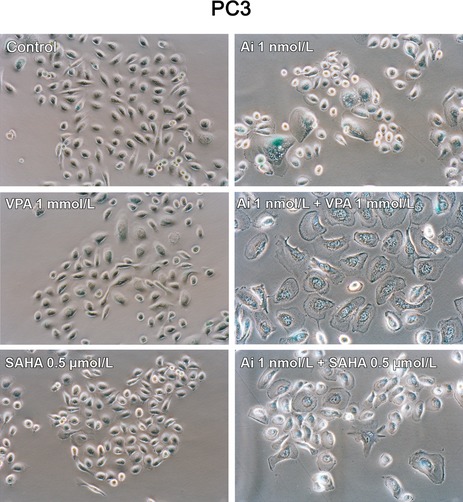
Combination therapy consisting of AMG 900, a pan-aurora kinase inhibitor, with the histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) valproic acid (VPA), and vorinostat (SAHA) was tested in prostate cancer cells. In vitro, the combination had synergistic antitumor activity. In vivo studies indicated decreased tumor growth in mice treated with low-dose AMG 900 and vorinostat compared to either agent alone.
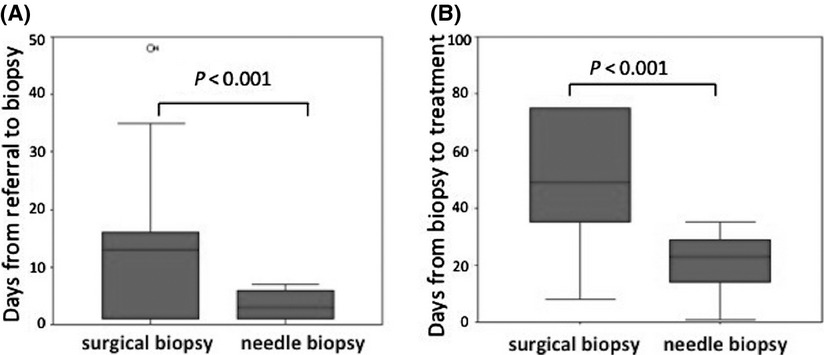
Use of percutaneous image-guided coaxial core-needle biopsy for diagnosis of intraabdominal lymphoma
- Pages: 1336-1341
- First Published: 08 July 2014
Cardiovascular event-free survival after adjuvant radiation therapy in breast cancer patients stratified by cardiovascular risk
- Pages: 1342-1352
- First Published: 10 July 2014
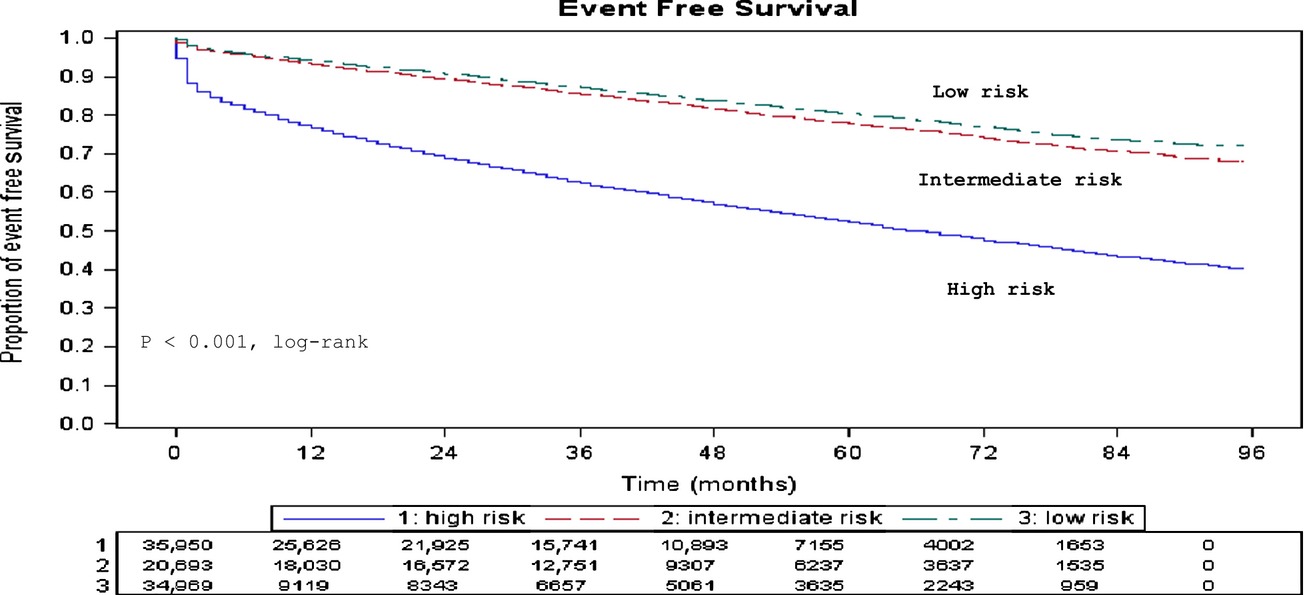
The objective of this study was to estimate the risk of a cardiovascular event or death associated with modern radiation in breast cancer patients with varying baseline cardiovascular risk. This study showed that elderly women with breast cancer who had preexisting cardiovascular disease and receiving radiation treatment are at a greater risk for the combined outcome in the first 6 months.
Fatigue in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib on an intermittent versus continuous dosing schedule in a randomized phase II trial
- Pages: 1353-1358
- First Published: 10 July 2014
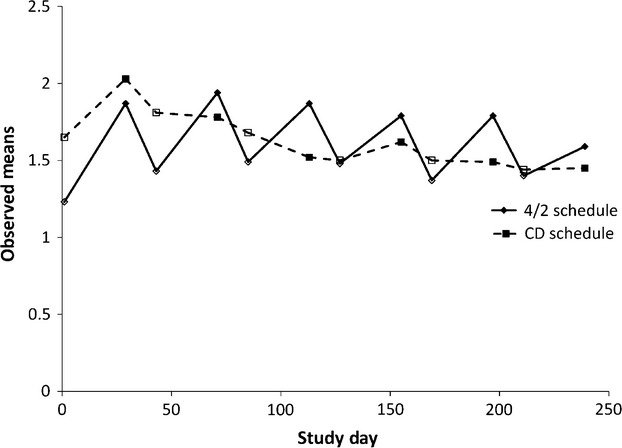
In a randomized trial comparing the sunitinib 4-week on/2-week off schedule to a continuous daily dose schedule, the 4/2 arm was associated with a greater degree of variability in fatigue reflecting a possible “on-off” effect whereby patients receiving the 4/2 schedule reported less fatigue at the beginning of each cycle compared to Day 29. The findings can inform the care for individuals with advanced renal cell carcinoma receiving intermittent dosing of sunitinib.
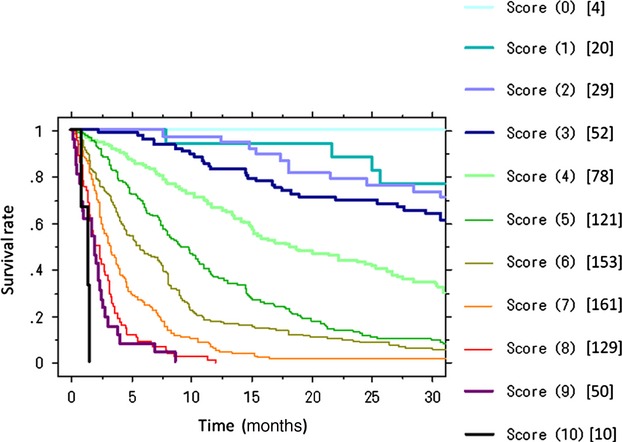
New prognostic factors and scoring system for patients with skeletal metastasis
- Pages: 1359-1367
- First Published: 10 July 2014
Volumetric PET/CT parameters predict local response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to chemoradiotherapy
- Pages: 1368-1376
- First Published: 10 July 2014
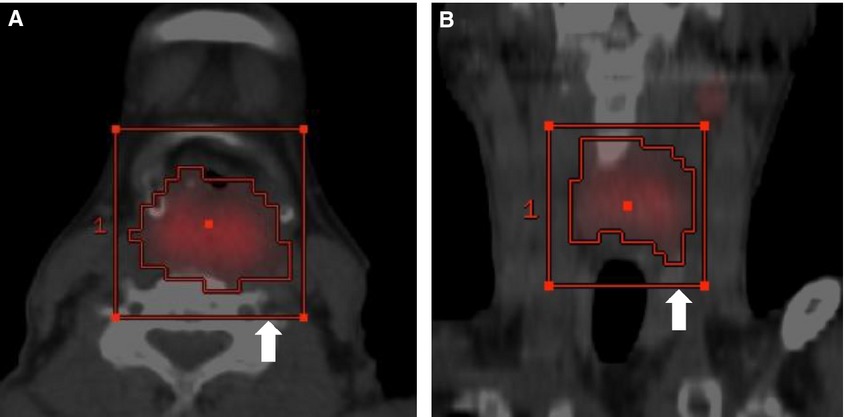
It is not well established whether pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT can predict local response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to chemoradiotherapy. Predictive efficacy of pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT varies with different primary sites and chosen parameters. Local response of laryngohypopharyngeal cancer is highly predictable by volume-based PET/CT parameters.
Newly established ELISA for N-ERC/mesothelin improves diagnostic accuracy in patients with suspected pleural mesothelioma
- Pages: 1377-1384
- First Published: 10 July 2014
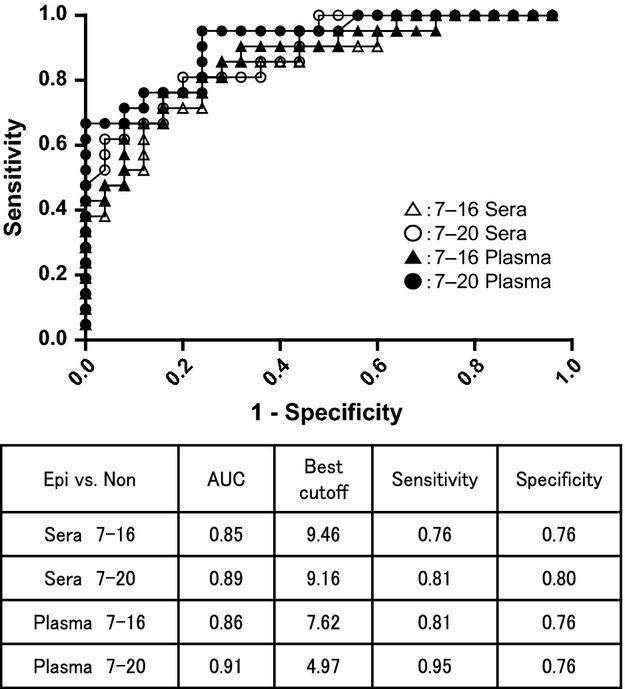
The current study was designed to improve our previous enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) system for measuring N-ERC/mesothelin and to demonstrate the clinical usefulness of the modified ELISA system in patients with suspected pleural mesothelioma. A newly established ELISA system improved the sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma in the current cohort compared with our previous system. A new ELISA showed better reproducibility and displayed the tendency of both higher sensitivity and higher specificity in plasma than in serum.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
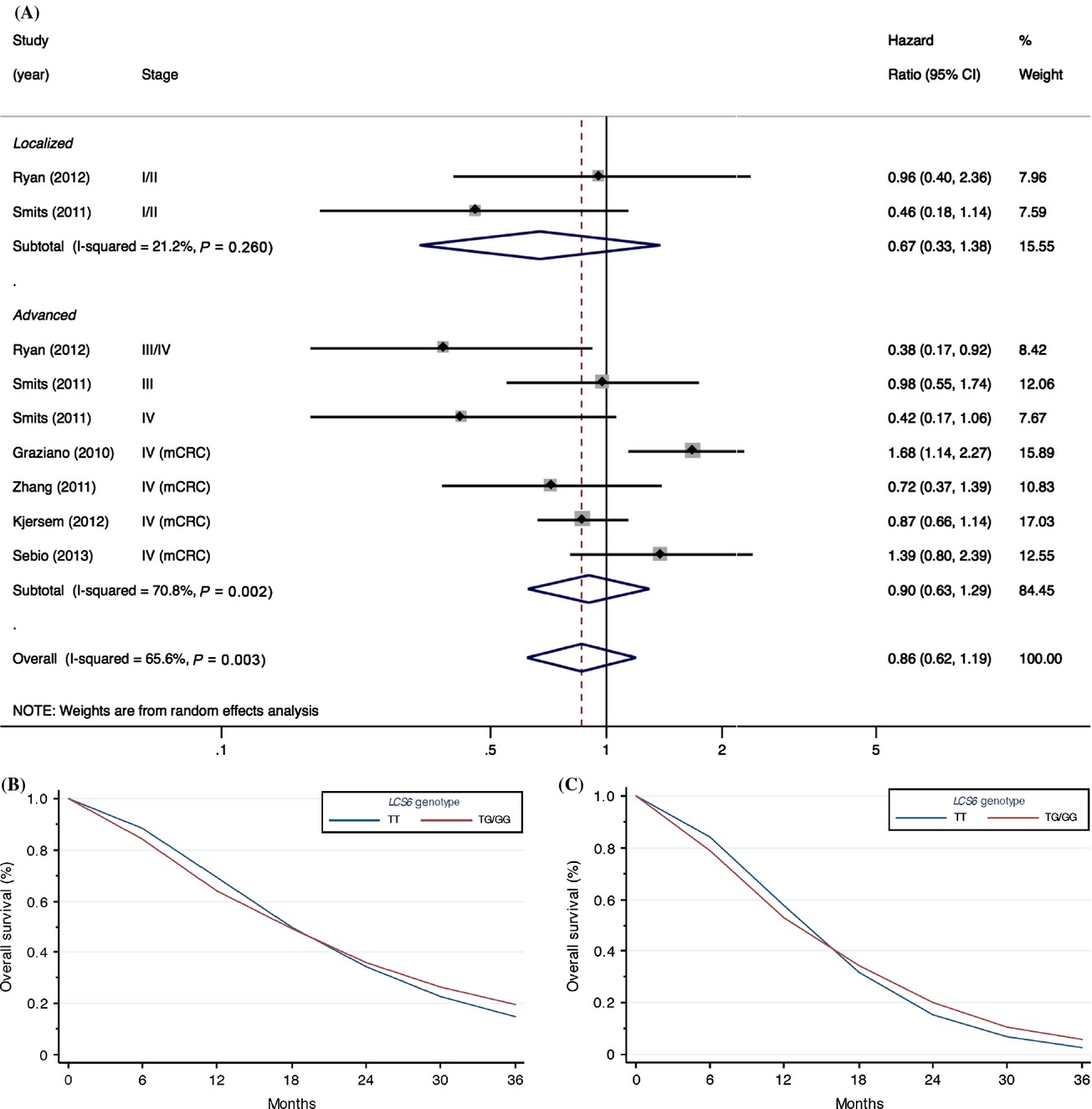
Let-7 microRNA-binding-site polymorphism in the 3′UTR of KRAS and colorectal cancer outcome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1385-1395
- First Published: 02 June 2014
Primary squamous cell carcinomas in the thyroid gland: an individual participant data meta-analysis
- Pages: 1396-1403
- First Published: 04 July 2014
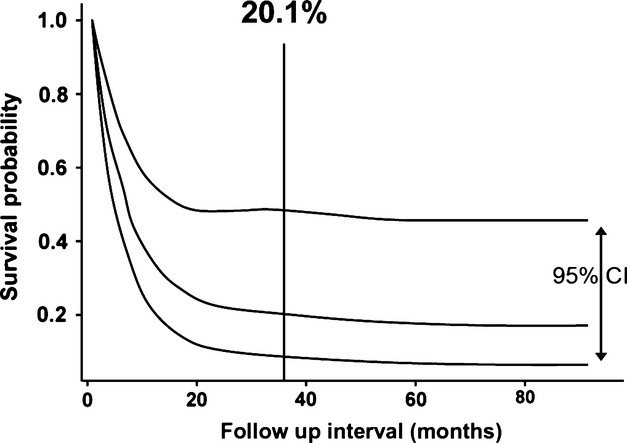
To better understand the clinical characteristics of primary thyroid squamous cell carcinomas and to identify the prognostic factors, we performed a systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. The survival of these patients was ~20% in 3 years, but complete resection of disease correlated with improved survival.
Epidemiology and survivorship of soft tissue sarcomas in adults: a national cancer database report
- Pages: 1404-1415
- First Published: 08 July 2014
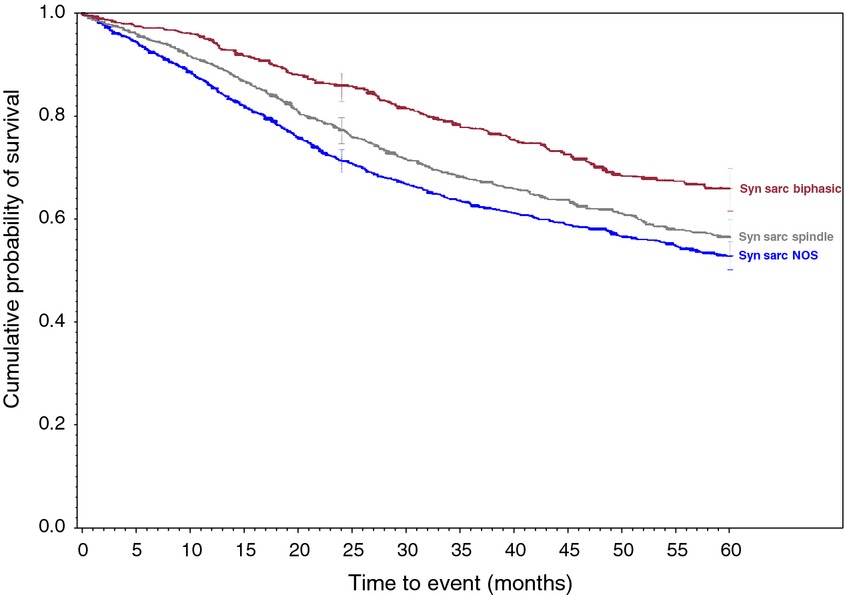
The data reported herein contains demographic and survivorship data on 34 distinct soft tissue sarcomas in 63,714 patients. These data are unprecedented in its scope and size and provides an accurate oversight picture of the number of such cases in the USA and the true overall associated survivorship for these entities over the years reported. These data should form a reference baseline for comparisons of future series.
Pharmacovigilance in practice: erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
- Pages: 1416-1429
- First Published: 03 June 2014
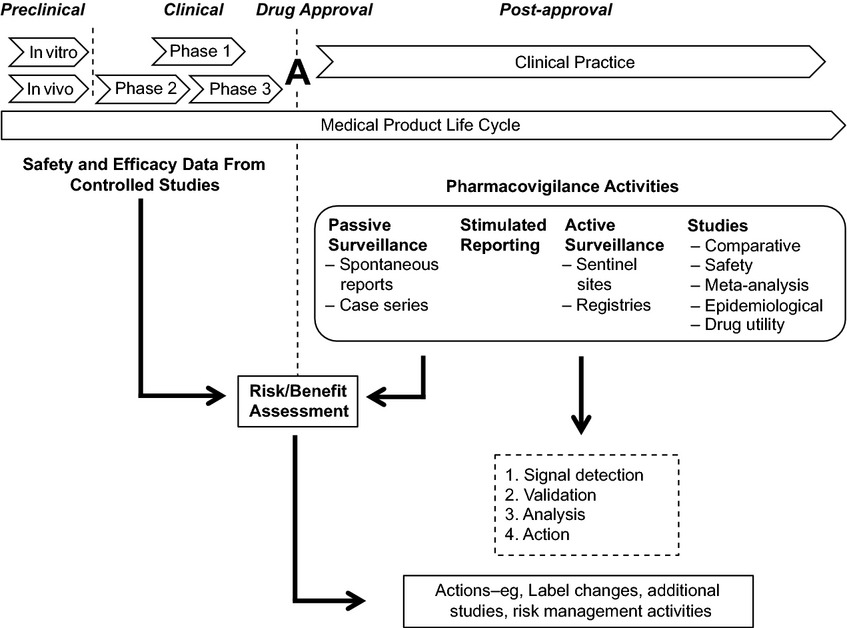
Pharmacovigilance seeks to advance the safe use of marketed medical products by detecting and assessing potential safety issues and taking appropriate action to balance risks and benefits to patients. The pharmacovigilance process was employed to identify and minimize potential risks of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) used to treat anemia in patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy.
African American women's perceptions of cancer clinical trials
- Pages: 1430-1439
- First Published: 06 June 2014
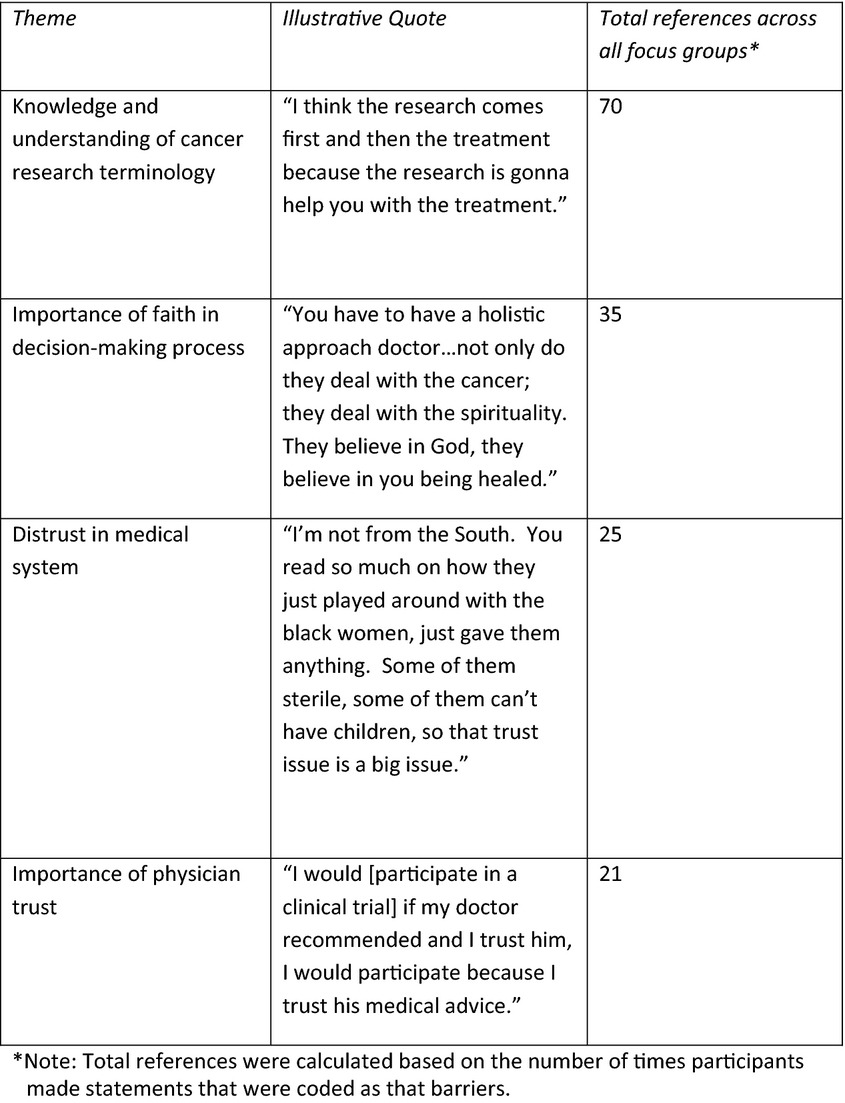
Cancer clinical trials are important for resolving cancer health disparities for several reasons; however, clinical trials participation among African Americans is significantly lower than among Caucasians. This study engaged focus groups with African American cancer survivors or cancer caregivers. Trust in the health system and in one's physician was seen as important factors associated with patient willingness to enroll in clinical trials, and participants suggested that physicians who were compassionate and who engaged and educated their patients would build important trust requisite for patient participation in clinical trials.
Risk of squamous cell skin cancer after organ transplant associated with antibodies to cutaneous papillomaviruses, polyomaviruses, and TMC6/8 (EVER1/2) variants
- Pages: 1440-1447
- First Published: 10 June 2014
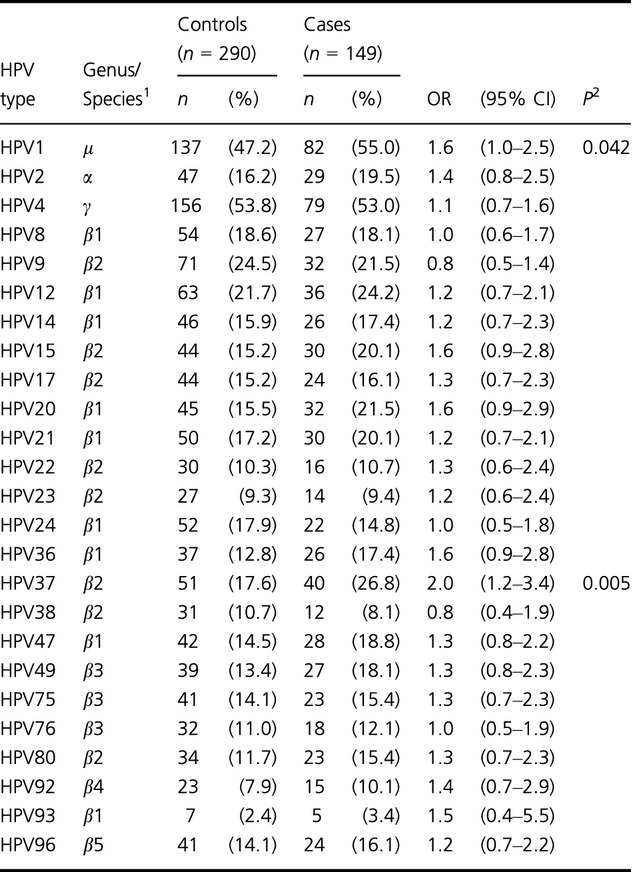
Squamous cell skin cancer (SCSC) disproportionately affects organ transplant recipients, and may be related to increased viral replication in the setting of immune suppression after transplant. This study suggests that HPV37, a betapapillomavirus, may play a role in the excess risk of SCSC among transplant recipients.
The association between lifetime smoking exposure and breast cancer mortality – results from a Norwegian cohort
- Pages: 1448-1457
- First Published: 30 July 2014
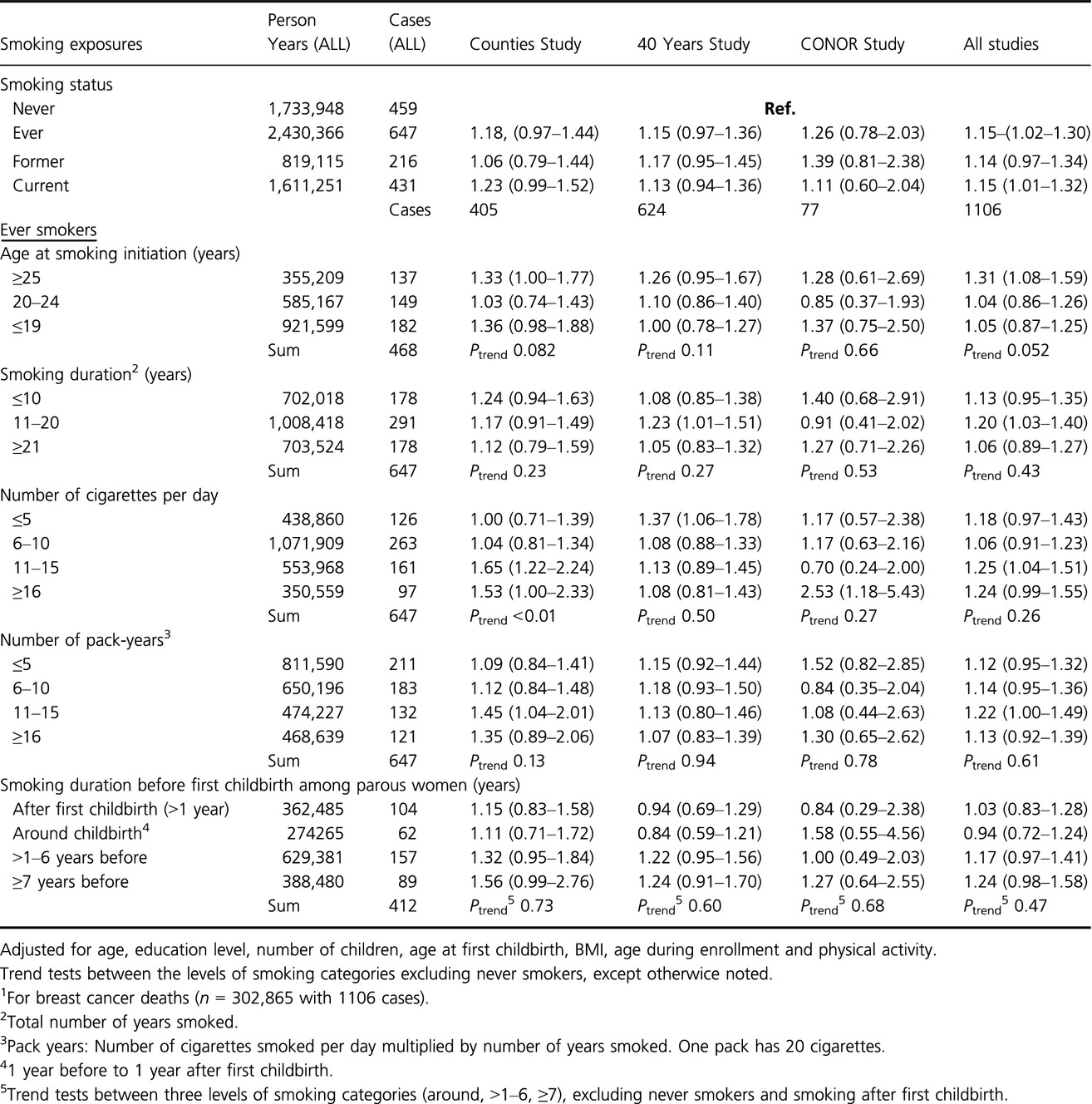
The Association between smoking and breast cancer mortality is not well described in literature, but some recent interesting new papers have been published. We provide interesting new data, especially for the Association between breast cancer mortality and smoking initiation before first childbirth.
Long-term use of metformin and colorectal cancer risk in type II diabetics: a population-based case–control study
- Pages: 1458-1466
- First Published: 05 August 2014
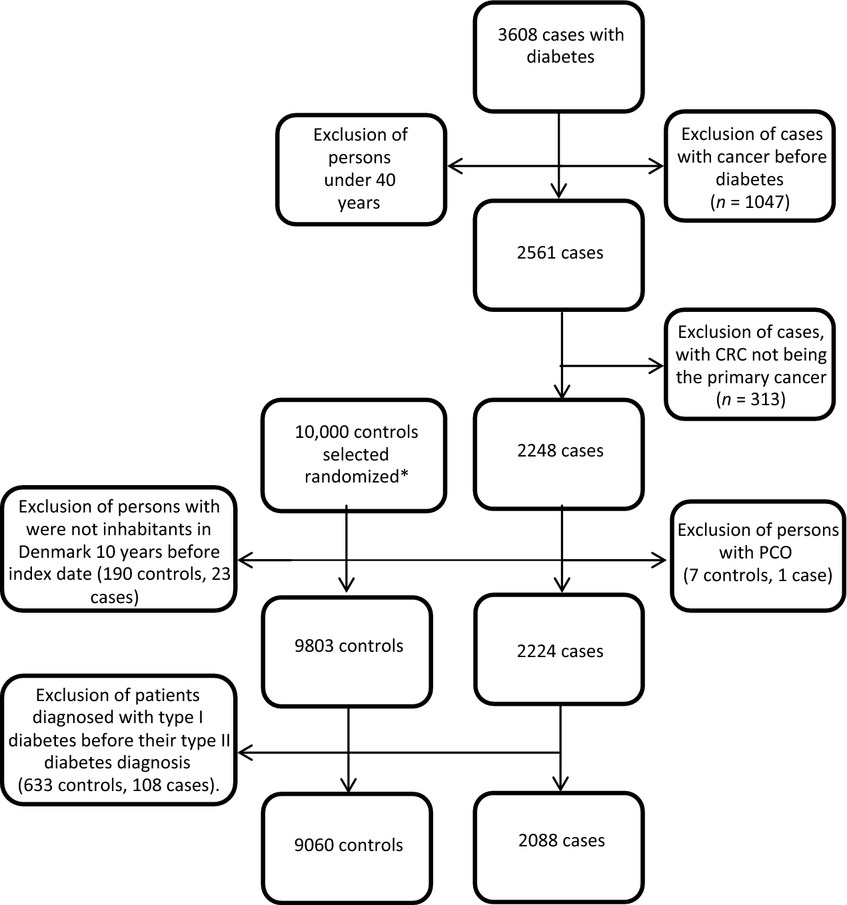
We performed a nested case–control study restricted to Danish citizens with type II diabetes. The association between long-term metformin use and colorectal cancer (CRC) gave an adjusted odds ratios at 0.83 (95 % CI 0.68–1.00). A protective effect on CRC with long-term use of metformin was only evident for women (OR 0.66 vs. 0.99 for men). There was a significant dose–response association of metformin use >250 defined daily dose (DDD) and for the duration of metformin use >1 year.