Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Crosstalk between the mesothelium and lymphomatous cells: insight into the mechanisms involved in the progression of body cavity lymphomas
- Pages: 1-13
- First Published: 19 November 2013
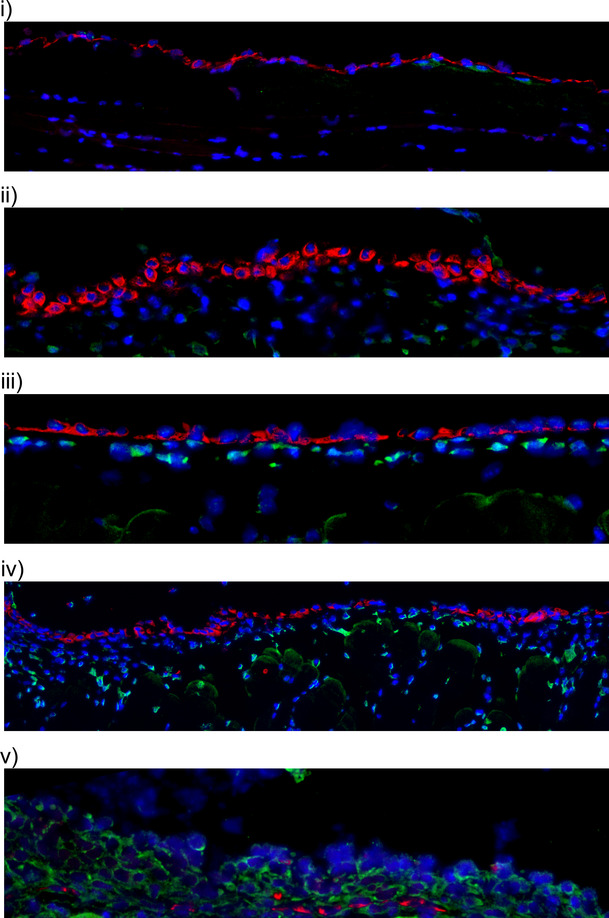
Particular types of lymphoma, such as primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), develop preferentially in body cavities, suggesting a specific contribution of the intracavitary microenvironment to tumor pathogenesis. In this study, we show that epithelial–mesenchymal transition of mesothelium is involved in PEL progression and that mesothelium creates a milieu favorable to lymphoma growth. These findings provide new insights into the mechanisms governing body cavity lymphoma progression and reveal new potential targets for lymphoma treatment.
The significance of dynamin 2 expression for prostate cancer progression, prognostication, and therapeutic targeting
- Pages: 14-24
- First Published: 18 December 2013
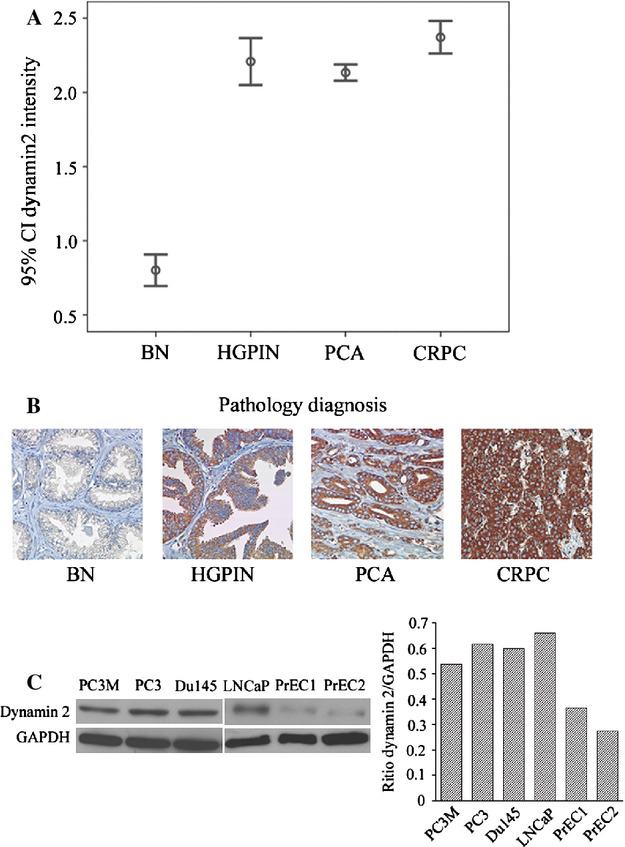
Dynamin 2 (Dyn 2) overexpression is a predictive marker for prostate cancer (PCA) progression and poor prognosis. Dyn2 inhibition prevents cell invasiveness in androgen-responsive and androgen-refractory PCA models, which support the potential of Dyn2 to serve as a therapeutic target for advanced PCA.
Identification of novel candidate compounds targeting TrkB to induce apoptosis in neuroblastoma
- Pages: 25-35
- First Published: 01 January 2014
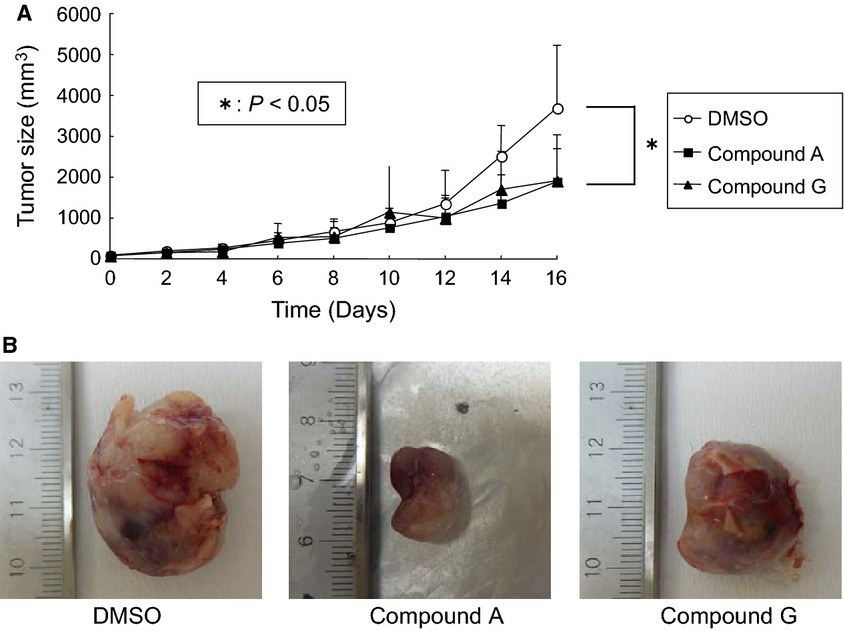
An in silico Docking screening strategy demonstrated that novel small-molecular-weight chemicals were rapidly and effectively identified, followed by in vitro assays. Utilizing this approach, we found the candidate compounds targeting the extracellular domain of TrkB, which may help to develop a novel treatment and cure for childhood cancers including neuroblastoma.
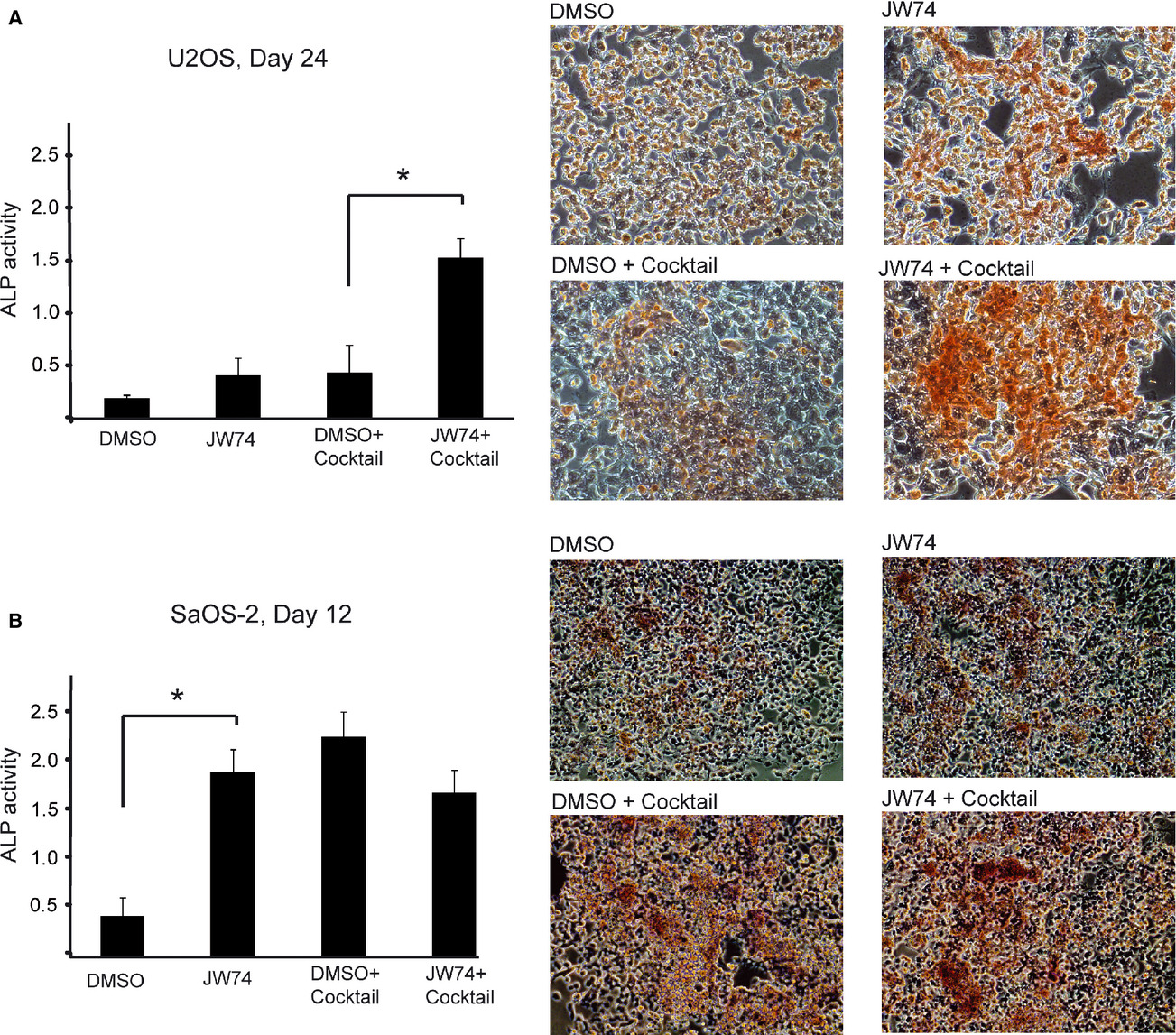
The tankyrase-specific inhibitor JW74 affects cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis and differentiation in osteosarcoma cell lines
- Pages: 36-46
- First Published: 17 December 2013
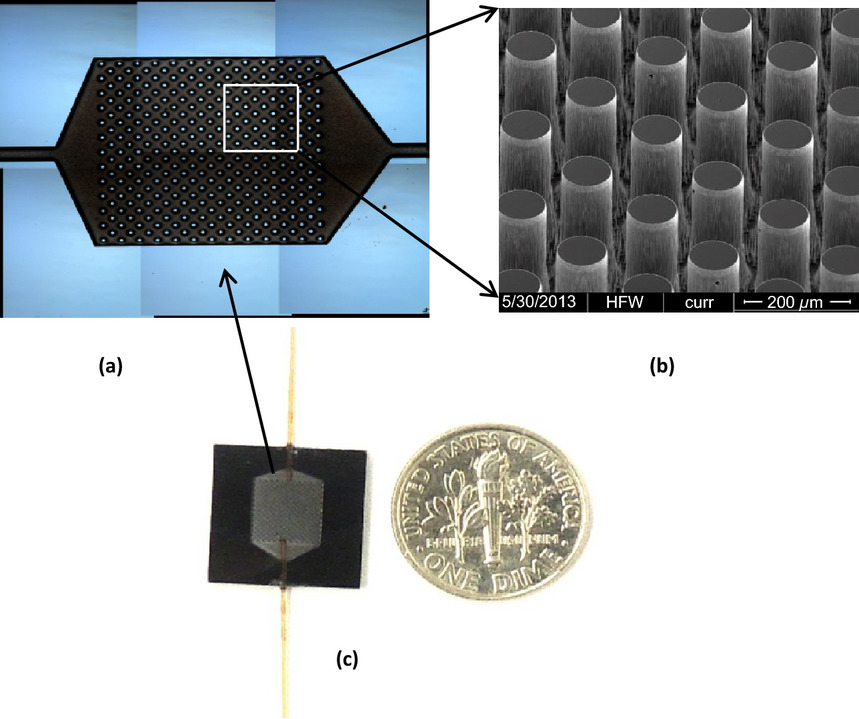
Early detection of antiangiogenic treatment responses in a mouse xenograft tumor model using quantitative perfusion MRI
- Pages: 47-60
- First Published: 06 January 2014
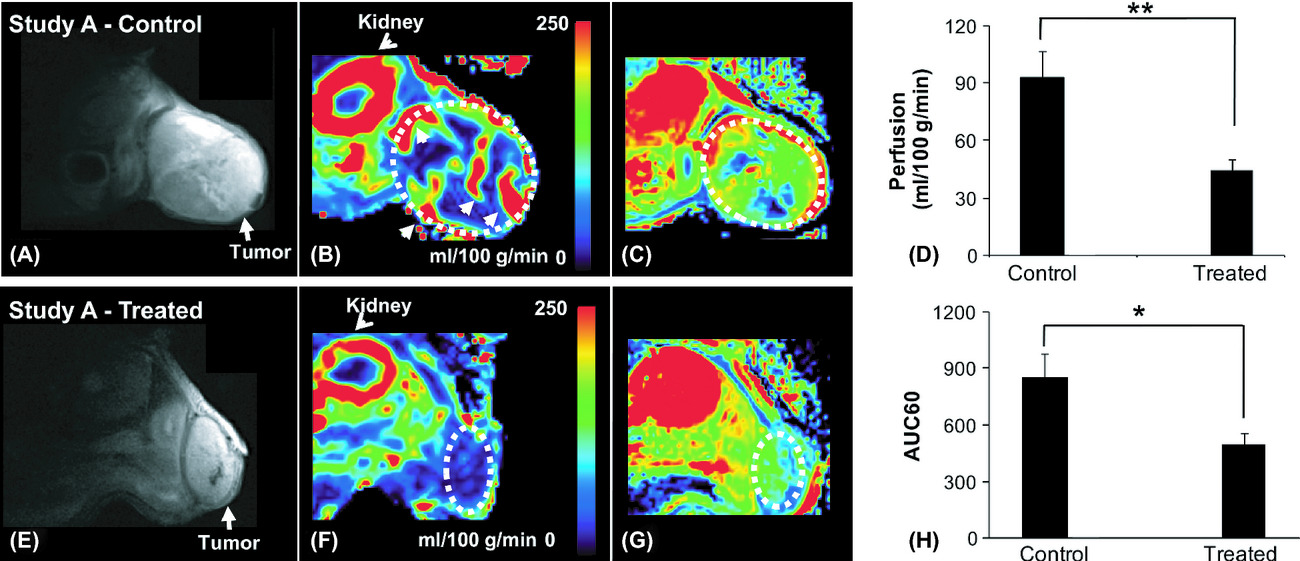
Tumor angiogenesis provides essential functional information for diagnosis and prognosis and tumor perfusion is regarded as a marker for angiogenesis. We investigated a noninvasive technique, arterial spin labeling (ASL) MRI, to measure tumor perfusion quantitatively. Our results indicate that tumor perfusion measured by ASL can detect early vascular responses, confirmed by histology, to treatment.
Factors associated with early progression of non-small-cell lung cancer treated by epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitors
- Pages: 61-69
- First Published: 10 January 2014
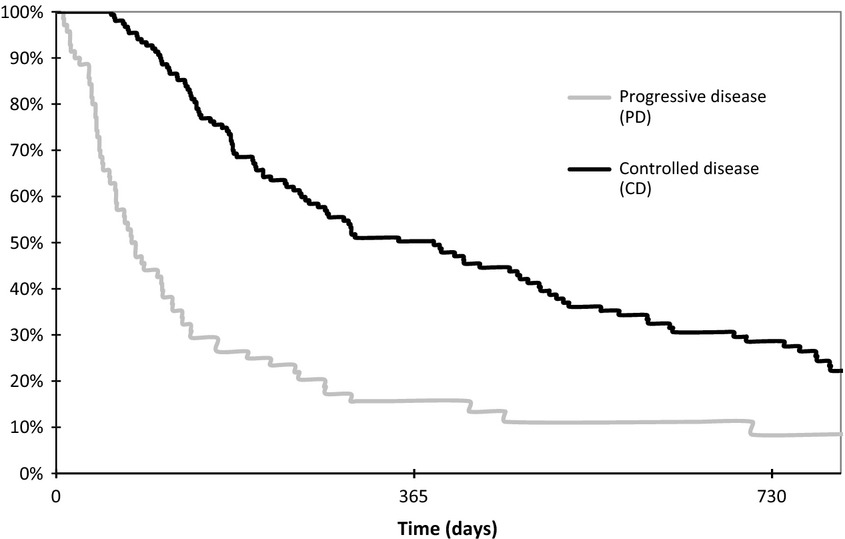
In non-small-cell-lung cancer, the choice between EGFR-TKI and cytotoxic therapy is still debated for second- or third-line therapy. In this setting, there is no restriction according to the EGFR-gene status. Our goal was to identify markers of early progression under treatment by EGFR-TKI in order to help clinicians to choose the best regimen. In a cohort of 268 patients that have been treated by EGFR-TKI, characteristics of patients who experienced early progression were compared to those of patients whose disease was controlled. We showed that presence of abdominal metastasis was independently associated with early progression in this cohort. Studies that address this matter are scarce. Although the clinical, pathological, and molecular markers that can predict a response to EGFR-TKI therapy are now well-known, no studies have searched potential markers associated with early progression versus stabilization under these treatments.
Clinical Cancer Research
Review
Cancer in indigenous people in Latin America and the Caribbean: a review
- Pages: 70-80
- First Published: 03 December 2013
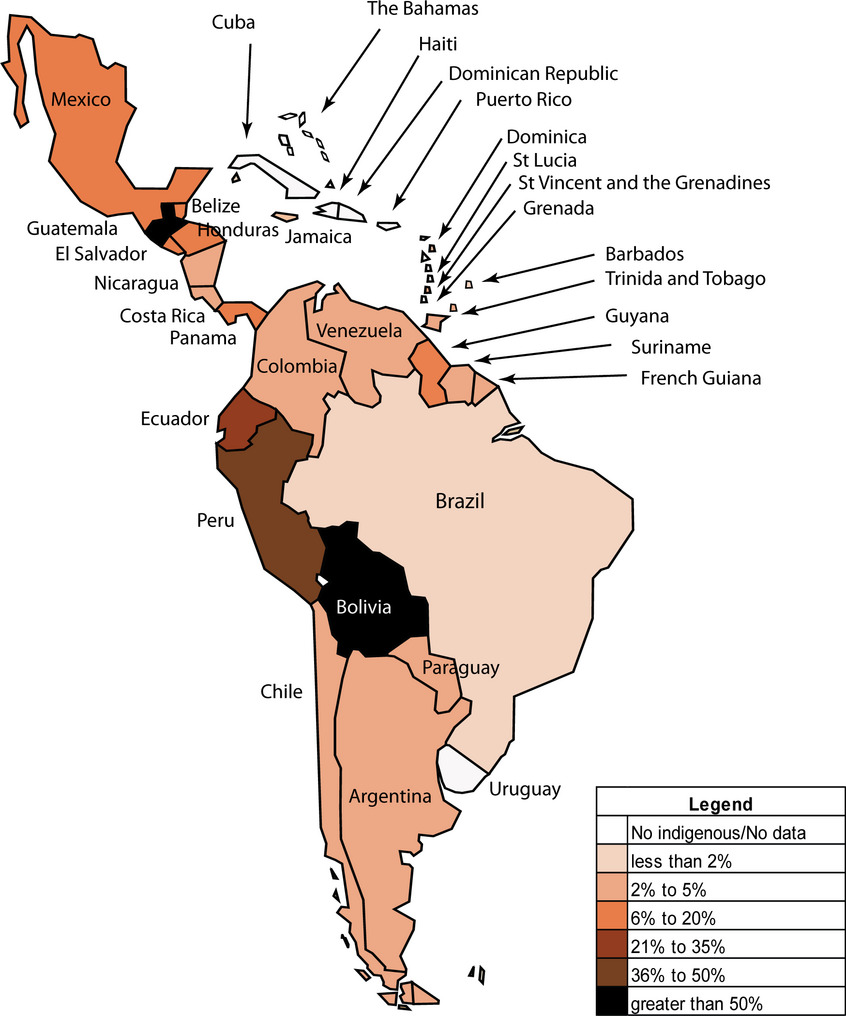
This systematic review, the first global assessment of cancer profiles among indigenous peoples in Latin America and the Caribbean, found a paucity of published data. The results assembled do, however, point to poorer cancer outcomes among indigenous people, although aspects of the scale of the burden and the specific cancer profile of indigenous people in different countries are still to be elucidated, and require further research.
Original Research
Expression of FAP, ADAM12, WISP1, and SOX11 is heterogeneous in aggressive fibromatosis and spatially relates to the histologic features of tumor activity
- Pages: 81-90
- First Published: 26 November 2013
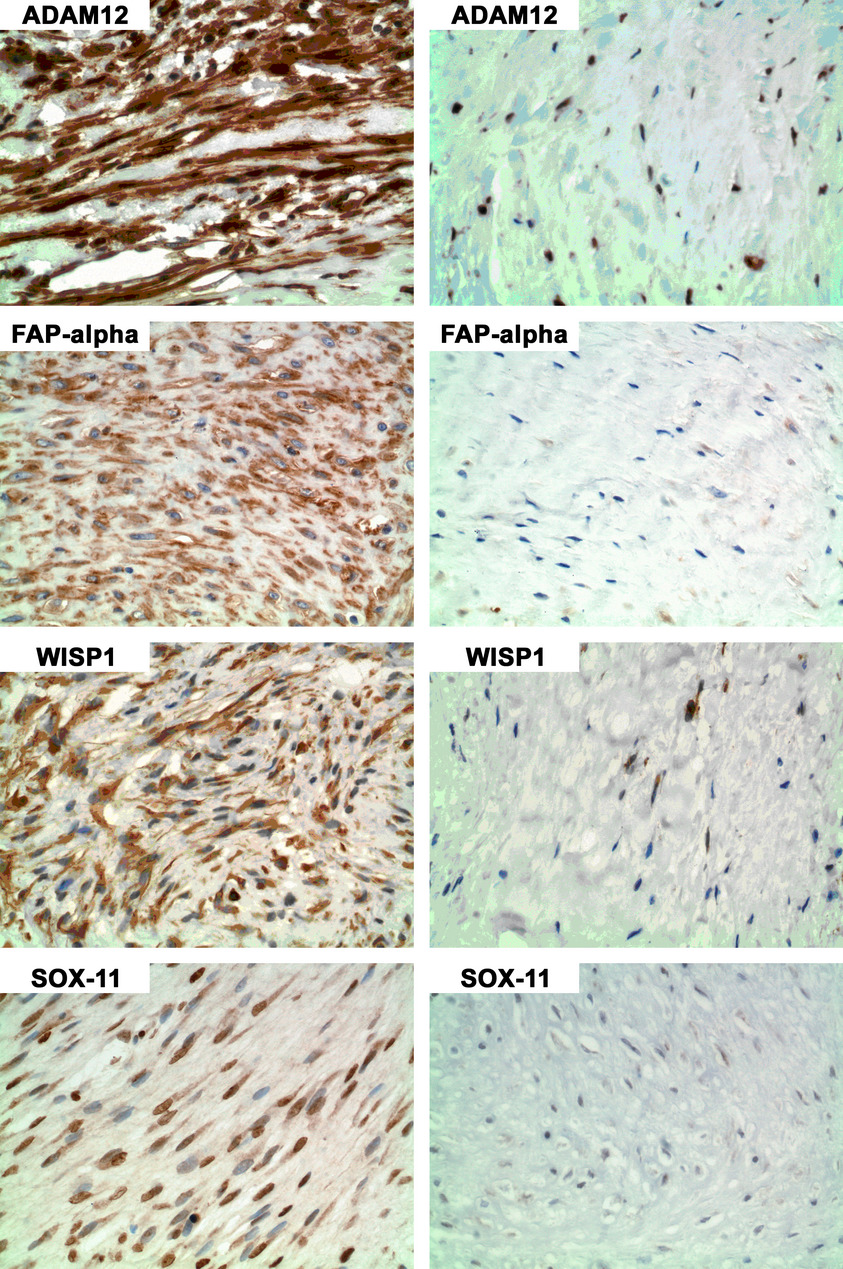
Immunohistochemistry and digital image analysis showed that the expression of ADAM12, FAP, WISP1, and SOX11 were markedly heterogeneous between and within aggressive fibromatosis (AF) cases, with higher expression in tumor areas in which cells had more “active” appearing nuclear features, suggesting that the corresponding pathways could serve as potential targets of therapy. High levels of protein expression of ADAM12, FAP, and WISP1, and low expression of SOX11, were associated with worse clinical outcome, defined by early (≤1 year) recurrence after excision versus nonrecurrence at ≥5 years.
Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor: improved long-term survival with an intensive multimodal therapy and delayed radiotherapy. The Medical University of Vienna Experience 1992–2012
- Pages: 91-100
- First Published: 11 December 2013
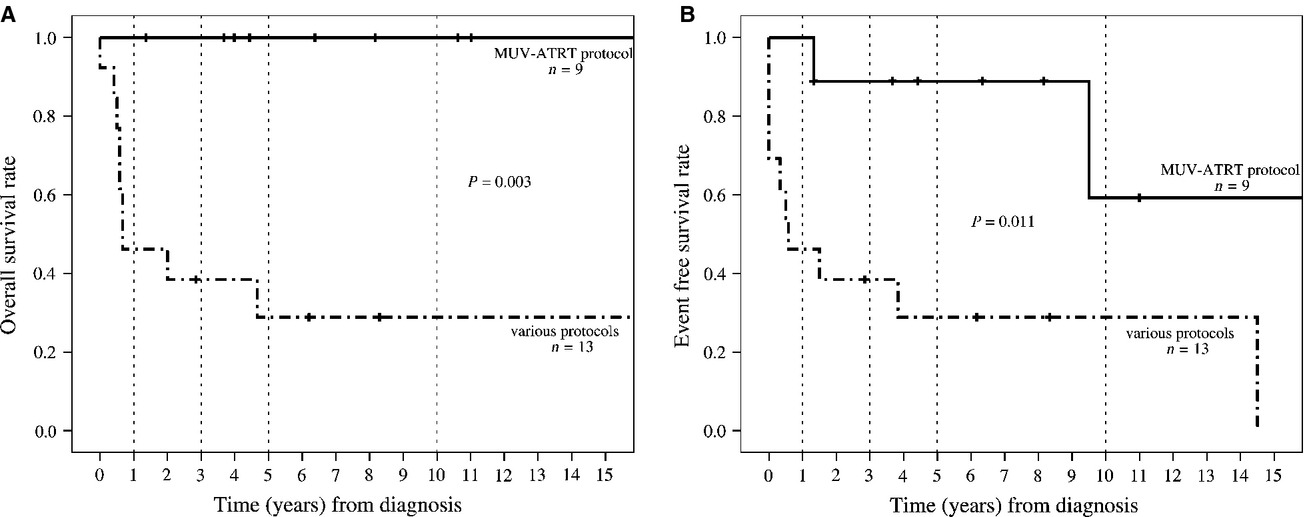
We report on 22 consecutive patients with atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (ATRT) for whom long-term survival could be achieved in a higher number of patients than previously reported and propose a new treatment strategy. The drug combination and sequence used in the proposed regimen appear to be efficacious in preventing early relapses also in young children with M1–M3 stage disease allowing postponement of local radiotherapy to the end of treatment.
Psychological care of caregivers, nurses and physicians: a study of a new approach
- Pages: 101-110
- First Published: 04 January 2014
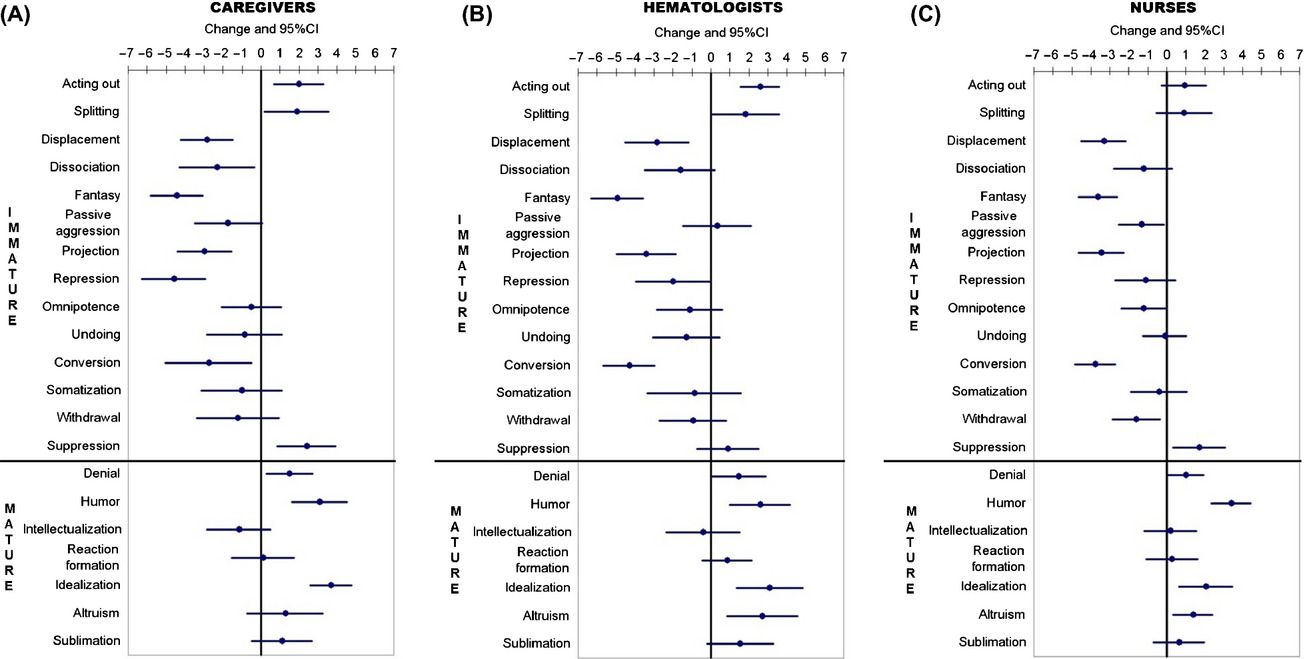
This study suggests that a work group, promoting sharing and collaboration, leads to the induction of mature defenses enabling reality to be faced in a more adaptive and effective way. Results of this study offer a useful starting point for the planning and the development of future studies with the aim to evaluate the efficacy of the “Balint Group” modified method on caregivers' quality of life and on the ability of physicians and nurses to deal with stressful situations.
Chemoradiotherapy response in recurrent rectal cancer
- Pages: 111-117
- First Published: 16 December 2013
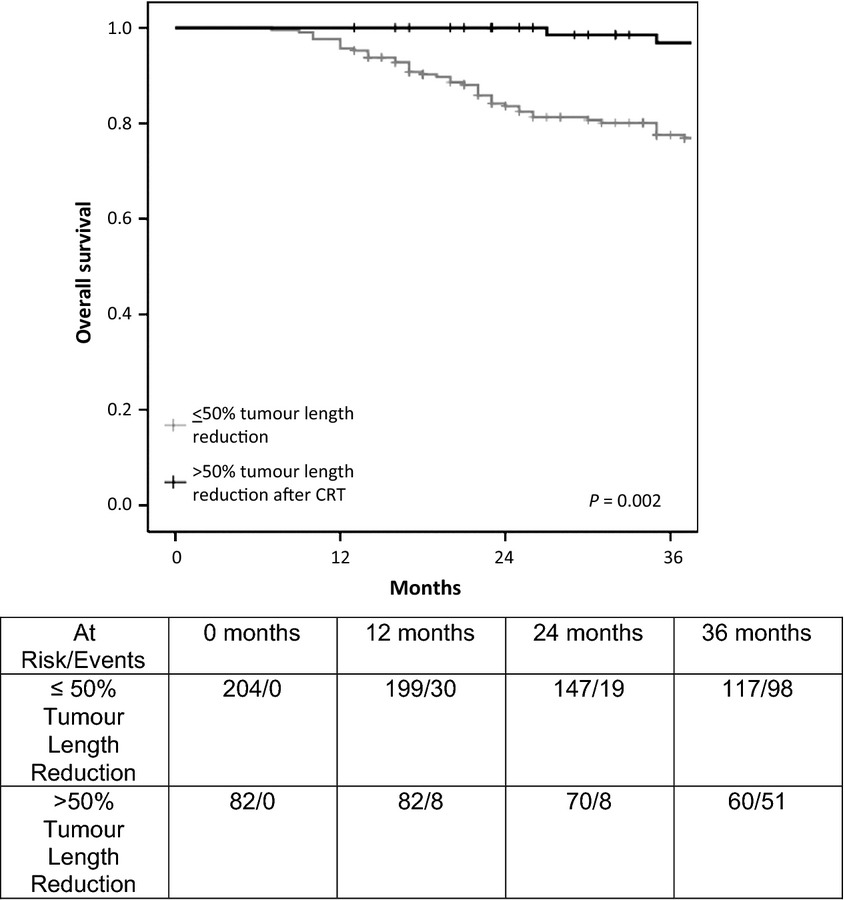
Only patients who demonstrate >50% size reduction show a survival benefit. Recurrent rectal cancer appears radioresistant compared with primary tumors for tumor size after chemoradiotherapy. Further investigation into improving/intensifying chemotherapy and radiotherapy for locally recurrent rectal cancer is justified.
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene rearrangements in patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer: CT characteristics and response to chemotherapy
- Pages: 118-123
- First Published: 27 December 2013
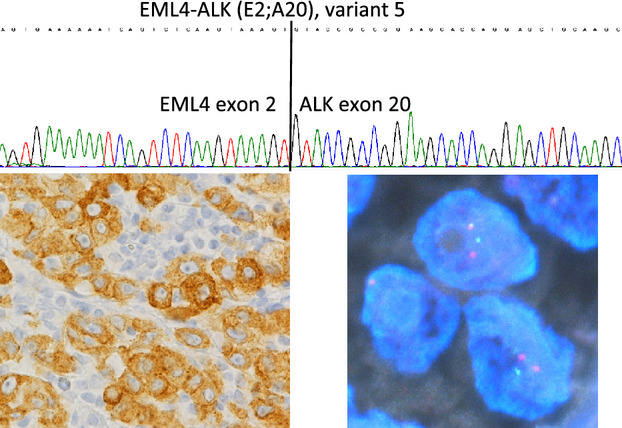
Advanced-stage anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive tumors have a relatively aggressive phenotype, which cannot be inferred from the size of the tumor alone. ALK-positive patients have a good response to first-line cytotoxic drugs and to crizotinib as second-line therapy, but a relatively poor response to cytotoxic drugs as second-line therapy.
Does the type of first-line regimens influence the receipt of second-line chemotherapy treatment? An analysis of 3211 metastatic colon cancer patients
- Pages: 124-133
- First Published: 07 January 2014
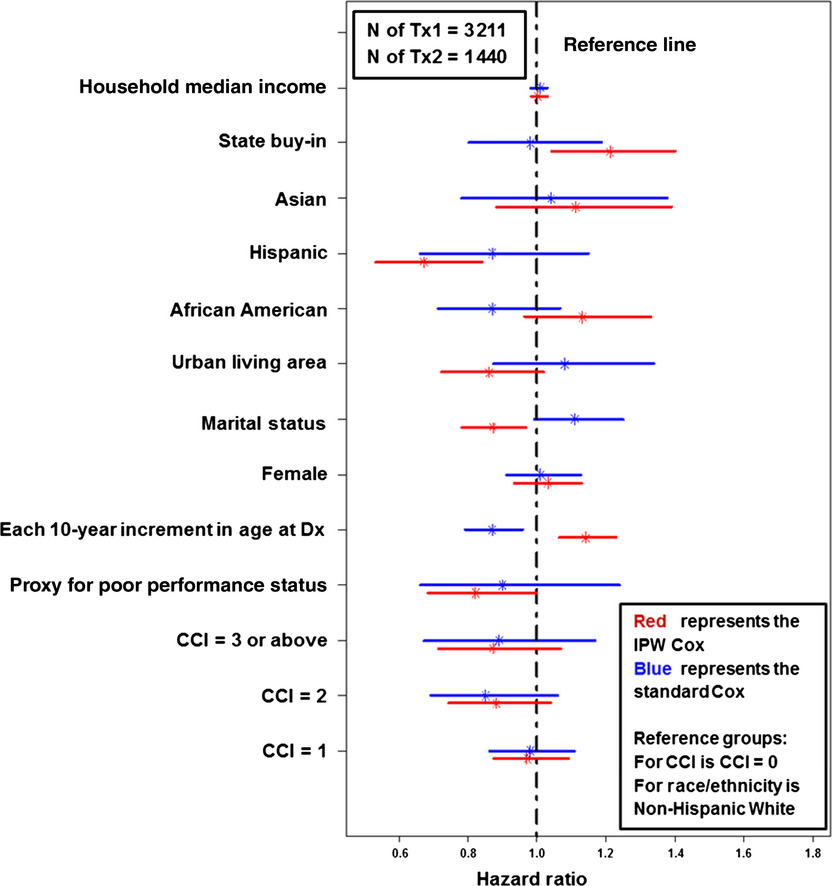
The specific first line regimens influence elderly metastatic colon cancer (mCC) patients' likelihood of receiving second-line treatment. Second-line treatment among elderly mCC patients requires clinicians and policy makers to consider patients' initial treatment as well as patient characteristics.
HER2 overexpression a major risk factor for recurrence in pT1a-bN0M0 breast cancer: results from a French regional cohort
- Pages: 134-142
- First Published: 10 January 2014
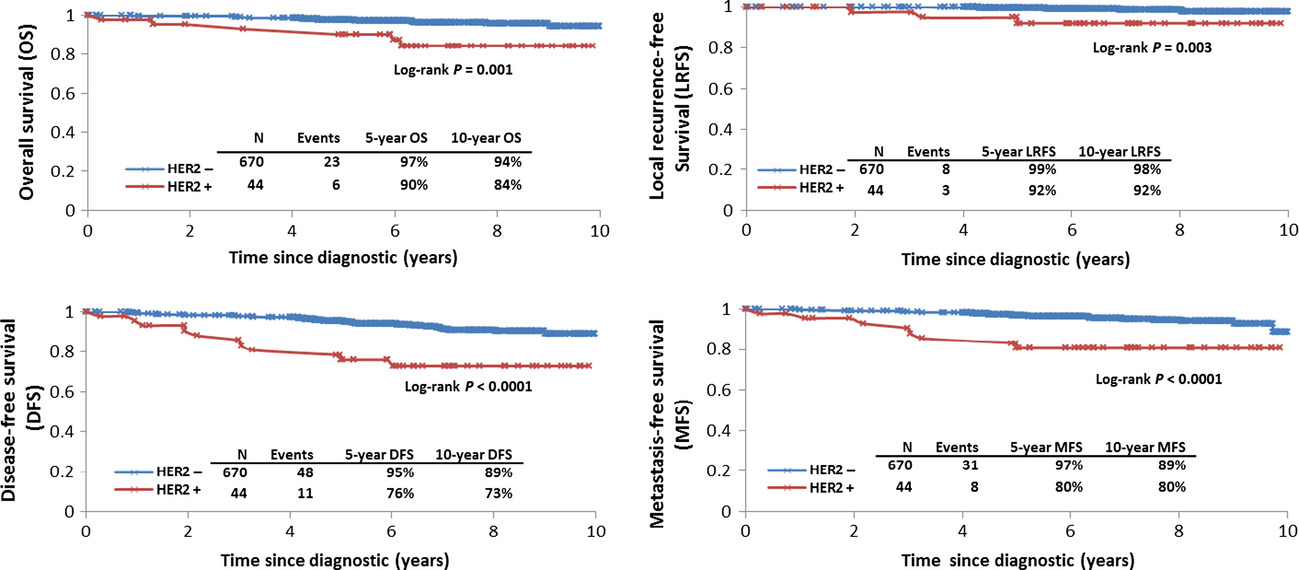
The management of pT1a-bN0M0 breast cancer remains an area of controversy. Ten-year results from 714 small breast carcinoma (SBC) showed 6.1% human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression, a 10-year overall survival of 94%, worse for HER2+ tumors (hormonal receptor [HR]:3.89). Hormonal therapy for HR+ HER2+ SBC is not sufficient, a personalized management may be required.
Classification of AIDS-related lymphoma cases between 1987 and 2012 in Japan based on the WHO classification of lymphomas, fourth edition
- Pages: 143-153
- First Published: 10 January 2014
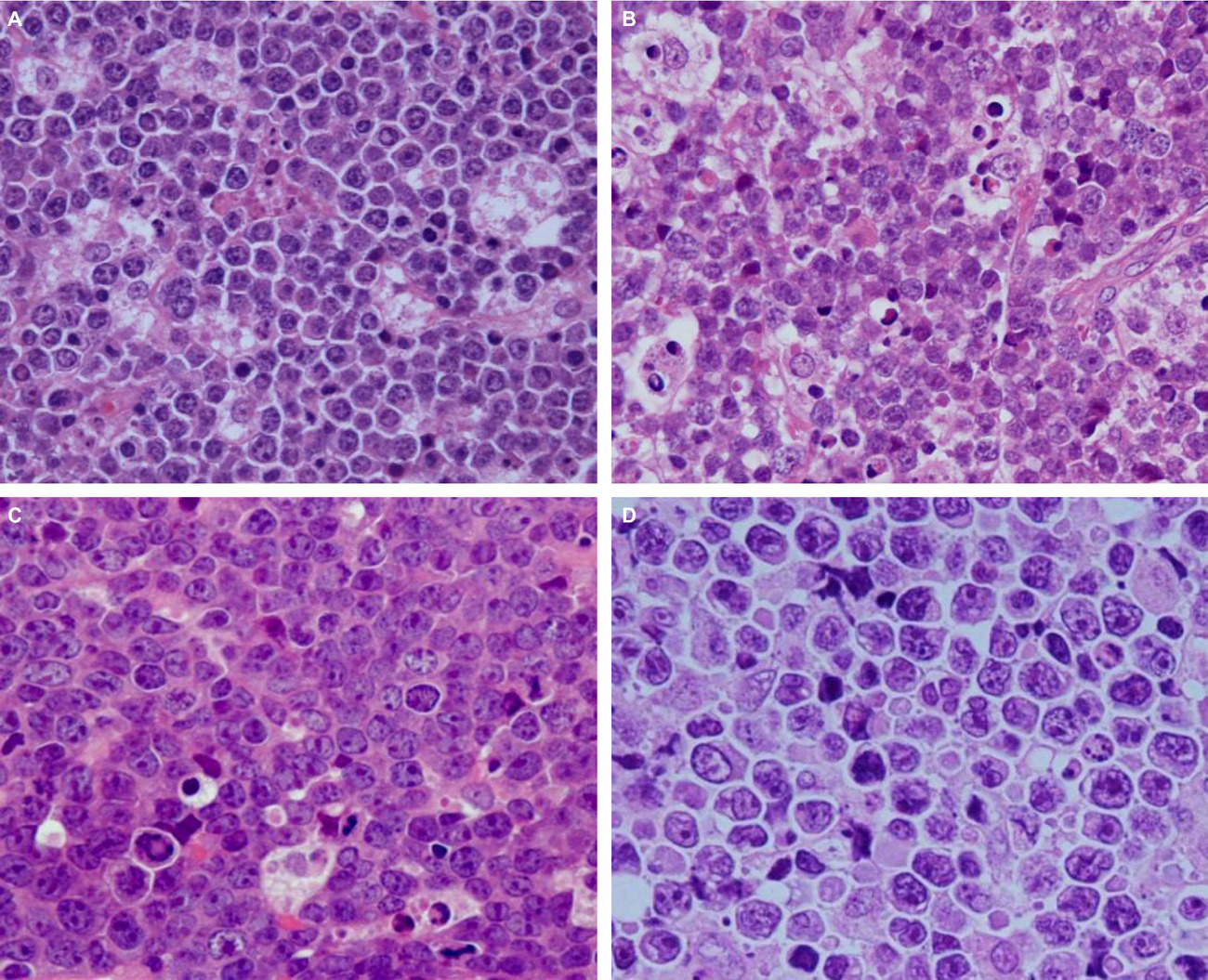
In this study, the authors classified AIDS-related lymphoma cases, diagnosed between 1987 and 2012 in Japan, according to the WHO classification of lymphomas, fourth edition. This study revealed the proportions and clincopathological features of each histological subtype of AIDS-related lymphoma during the study period. The authors also propose a set of biological markers that can be used for the classification of AIDS-related lymphoma.
Access, excess, and overdiagnosis: the case for thyroid cancer
- Pages: 154-161
- First Published: 10 January 2014
The funders of health care are facing progressively increasing costs due to the increasing numbers of women with thyroid cancer. The rates of diagnosis varied up to four times across the health care/geographic regions of Ontario and our findings suggest that differences in access to or use of medical diagnostic tests by more educated, urban and healthier patient populations is driving the increasing incidence of thyroid cancer.
BMVC test, an improved fluorescence assay for detection of malignant pleural effusions
- Pages: 162-173
- First Published: 10 January 2014
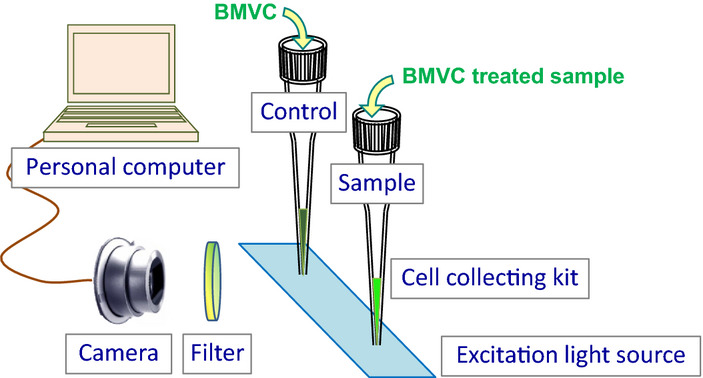
In this study, we developed a system, named BMVC test, to provide simple, fast and accurate detection of malignant pleural effusions without human bias or grey zone in traditional cytologic examination. With a sensitive fluorescence probe, cell collecting kits, and digital process, BMVC test provides results in a short time with a high accuracy of 91.6% (98/107). Also, the digital and objective results could assist cytologic examination to become more clear-cut.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Noninvasive detection of lung cancer using exhaled breath
- Pages: 174-181
- First Published: 20 November 2013
HPV DNA testing improves CIN2+ risk stratification and detection of CIN2+ in delayed triage of ASCUS and LSIL. A population-based follow-up study from Western Norway
- Pages: 182-189
- First Published: 17 December 2013
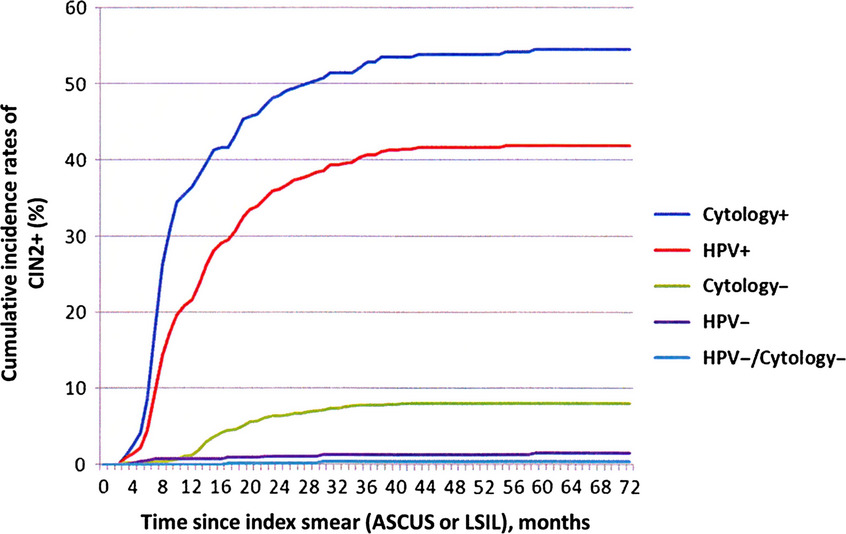
The effect of implementing human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in delayed triage of ASCUS and low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) was studied in a cohort of women from Western Norway. An improved stratification of CIN2+ risk and selection of more clinical relevant lesions was reported on. Also, more CIN2+ was recovered and CIN2+ detected at an earlier time point.
A variant upstream of HLA-DRB1 and multiple variants in MICA influence susceptibility to cervical cancer in a Swedish population
- Pages: 190-198
- First Published: 07 January 2014
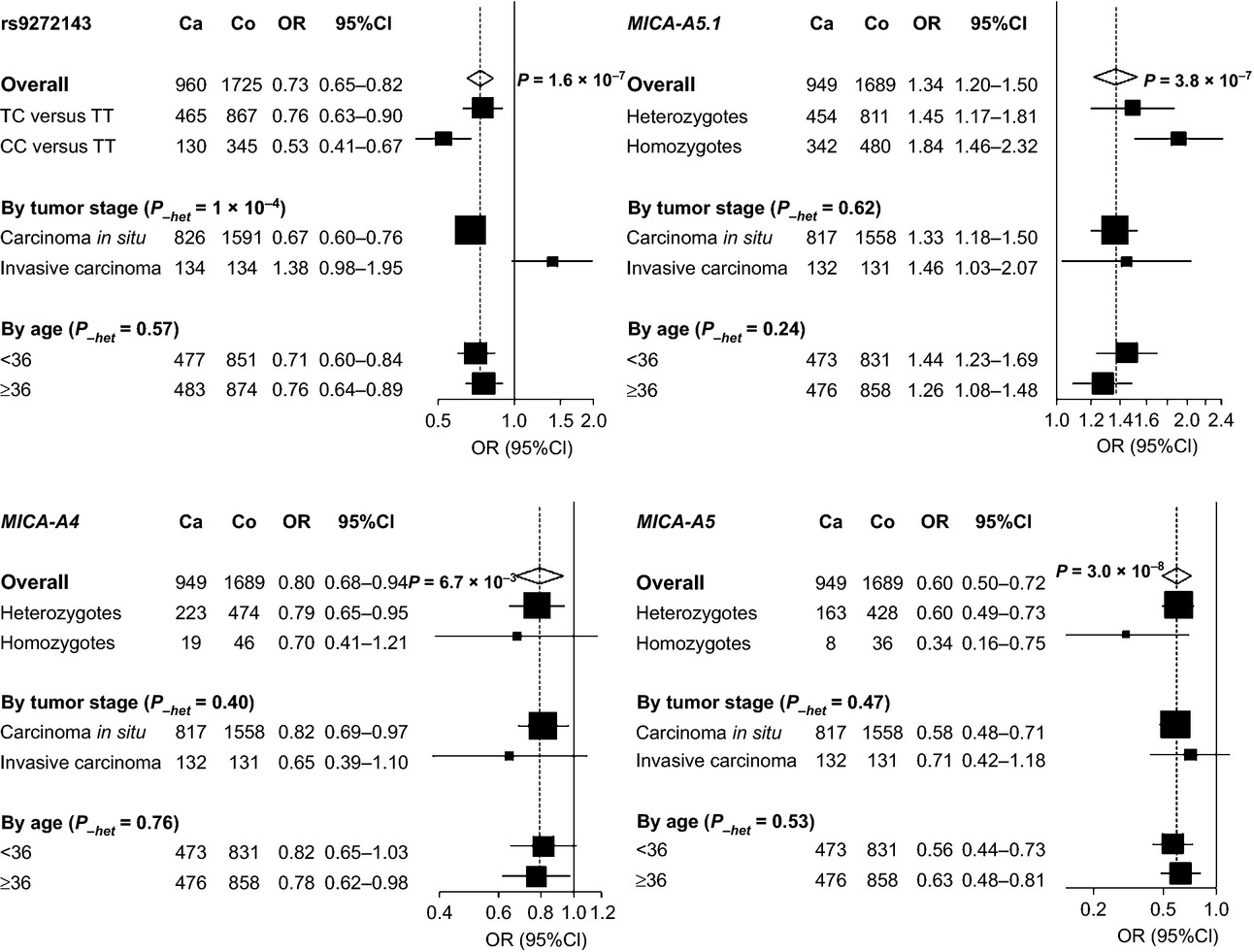
We have performed a large nested case–control cohort to validate findings in the first cervical cancer GWAS. We replicated the associations with rs9272143 located in the MHC class II region as well as with rs2516448 and MICA-A5.1 in the class I region. In addition, we found protective effects of MICA-A4 and MICA-A5 against cervical cancer, attesting to the importance of the allelic variability at MICA for both recognition of infection and evasion of tumor surveillance.