Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
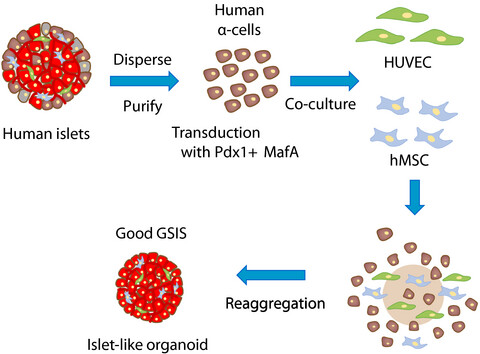
How do you make new β-cells in humans? An attempt to create human β-cells from α-cells of brain-dead donors
- Pages: 513-515
- First Published: 13 December 2019
Review Article
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline is a valuable endogenous antifibrotic peptide for kidney fibrosis in diabetes: An update and translational aspects
- Pages: 516-526
- First Published: 29 January 2020
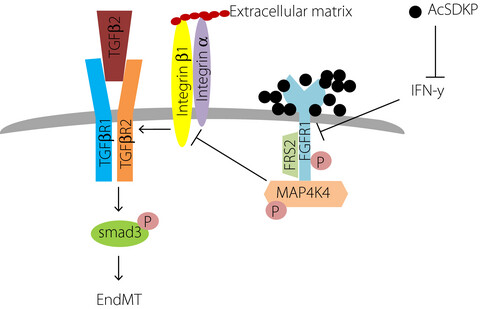
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (AcSDKP) is an endogenous peptide that has been confirmed to show excellent organ-protective effects. The antifibrotic mechanism of AcSDKP is not yet clear, we have established that AcSDKP could target endothelial mesenchymal transition program through the induction of the endothelial fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway. Also, recent reports suggested the clinical significance of AcSDKP.
Commentaries
CREDENCE: A silver lining in the dark cloud of diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 527-529
- First Published: 09 November 2019
Incidence of severe urinary tract infections not increased by initiating sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors
- Pages: 530-531
- First Published: 25 November 2019
JDI Updates
New perspective on type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 532-534
- First Published: 30 March 2020
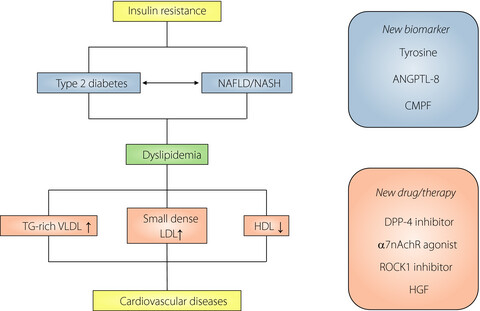
Serum lipid abnormalities (dyslipidemias) are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Recent findings provide new evidence that dyslipidemia characterized by elevated triglycerides and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels with a decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level are risk factors for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. There are multiple therapeutic agents to help patients to achieve target lipid levels, but understanding the molecular mechanisms could provide useful information for new treatment strategies for diabetic dyslipidemia.
Articles
Basic Science and Research
Electronegative low-density lipoprotein of patients with metabolic syndrome induces pathogenesis of aorta through disruption of the stimulated by retinoic acid 6 cascade
- Pages: 535-544
- First Published: 09 October 2019
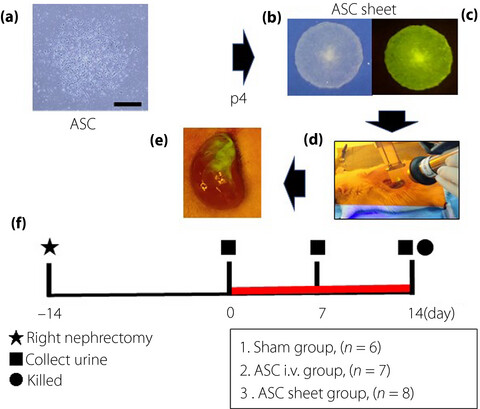
Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell sheets directly into the kidney suppresses the progression of renal injury in a diabetic nephropathy rat model
- Pages: 545-553
- First Published: 17 October 2019
Epidemiology
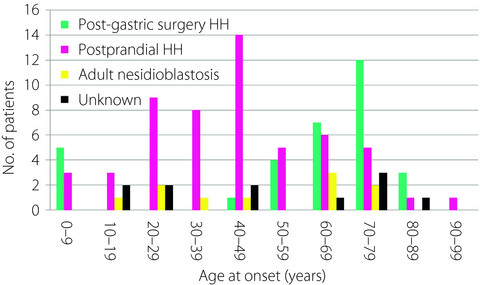
Nationwide survey of endogenous hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in Japan (2017–2018): Congenital hyperinsulinism, insulinoma, non-insulinoma pancreatogenous hypoglycemia syndrome and insulin autoimmune syndrome (Hirata’s disease)
- Pages: 554-563
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Family history of diabetes in both parents is strongly associated with impaired residual β-cell function in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 564-572
- First Published: 09 November 2019
In type 2 diabetes patients patients, the degree of the associations between family history of diabetes and clinical characteristics differs according to the number and the type of family history of diabetes. In particular, family history of diabetes in both parents is most strongly associated with impaired residual β-cell function.
Clinical Science and Care
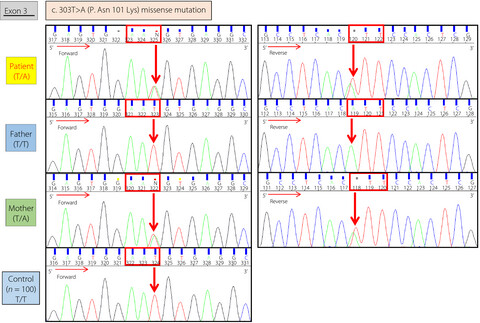
Clinical and genetic analysis in a family with familial renal glucosuria: Identification of an N101K mutation in the sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 encoded by a solute carrier family 5 member 2 gene
- Pages: 573-577
- First Published: 04 October 2019
Identification of insulin gene variants in patients with neonatal diabetes in the Chinese population
- Pages: 578-584
- First Published: 12 October 2019
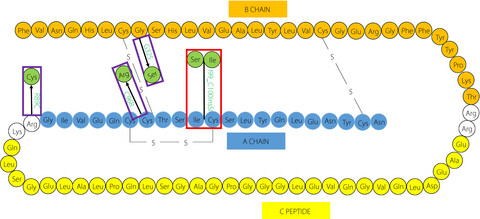
In this study, we discovered four mutations in the insulin gene (INS), one of which was novel and was considered to cause permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. We explored the clinical and genetic characteristics of Chinese permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus caused by INS mutations. This study enriches our awareness of the mutant spectrum in INS, and suggests the important role of INS in the development of permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus.
Association between cancer antigen 19-9 and diabetes risk: A prospective and Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 585-593
- First Published: 29 October 2019
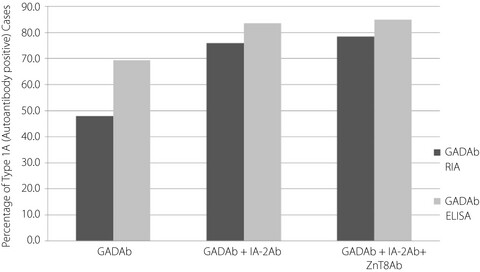
Increased diagnosis of autoimmune childhood-onset Japanese type 1 diabetes using a new glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit, compared with a previously used glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody radioimmunoassay kit
- Pages: 594-602
- First Published: 22 November 2019
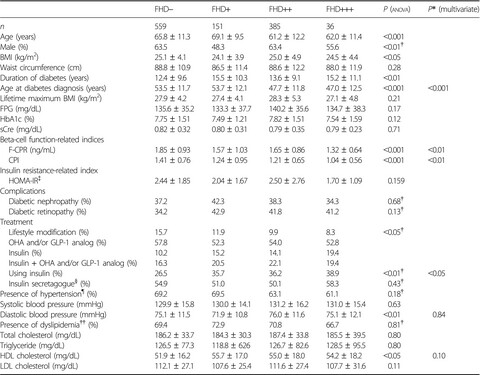
Clinical characteristics of insulin resistance syndromes: A nationwide survey in Japan
- Pages: 603-616
- First Published: 02 November 2019

(a) Rabson–Mendenhall/Donohue syndrome and type B insulin resistance syndrome (IRS) showed the highest and second highest levels of hyperinsulinemia, respectively, and those with type A and type X IRS were similar. Fasting serum insulin levels for 26 of the 27 (96.3%) type A and type X IRS patients for whom such data were available were >30 μU/mL. (b) Type A and type X IRS, as well as Rabson–Mendenhall/Donohue syndrome were associated with low birthweight.
Elevation of the renal threshold for glucose is associated with insulin resistance and higher glycated hemoglobin levels
- Pages: 617-625
- First Published: 26 November 2019
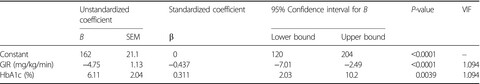
The renal threshold for glucose (RTg) corresponds to a blood glucose level of ~180 mg/dL; however, in hospitals, patients are often encountered who are hyperglycemic, but urine glucose test strip-negative, implying a high RTg value. In this study, we aimed to identify factors determining high RTg in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. We estimated RTg (eRTg) using urinalysis data from 67 type 2 diabetes mellitus patients for whom the glucose infusion rate was determined by hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, and found that a high eRTg is associated with a low glucose infusion rate and high glycated hemoglobin, with the glucose infusion rate making a substantial contribution.
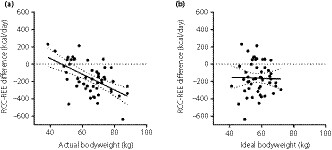
Standard medical nutrition therapy of 25 kcal/kg ideal bodyweight/day often does not reach even resting energy expenditure for patients with type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 626-632
- First Published: 28 October 2019
Impact of physical activity and sedentary time on glycated hemoglobin levels and body composition: Cross-sectional study using outpatient clinical data of Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 633-639
- First Published: 22 November 2019
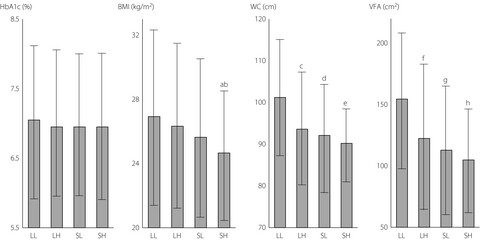
In this study, to manage the quantity and quality of bodyweight in patients with type 2 diabetes, a primary goal should be the promotion of increased physical activity and reduced sedentary time. It is likely that the combination of seeking out physical activity and avoiding sedentary behavior is important for the management of bodyweight in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Factors associated with the glucose-lowering efficacy of sitagliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pooled analysis of Japanese clinical trials
- Pages: 640-646
- First Published: 19 November 2019
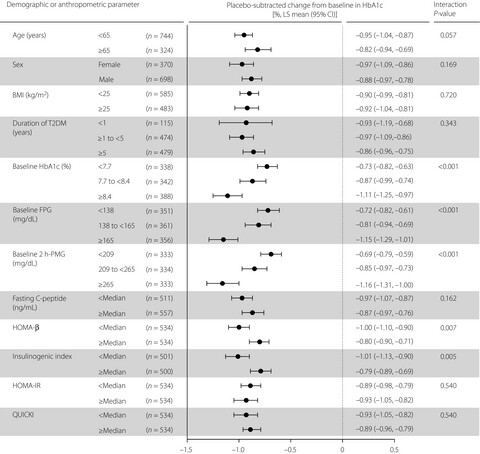
Sitagliptin treatment was associated with clinically meaningful improvement in glycemic control in all subgroups of Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes that were evaluated. Higher baseline glycemic status and lower baseline β-cell function were identified as factors associated with greater hemoglobin A1c reduction after sitagliptin treatment.
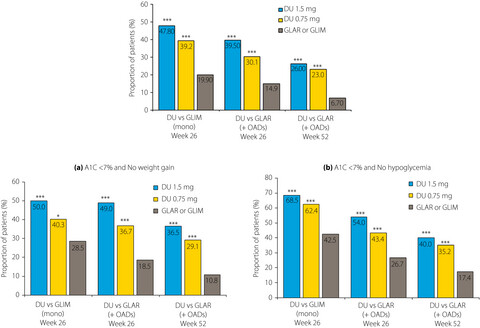
Achieving the composite end-point of glycated hemoglobin <7.0% without weight gain or hypoglycemia with once-weekly dulaglutide in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A post-hoc analysis
- Pages: 647-652
- First Published: 23 November 2019
Effects of dapagliflozin on the serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 and myokines and muscle mass in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled trial
- Pages: 653-661
- First Published: 13 November 2019
Add-on effects of a sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, on type 2 diabetes were examined. Dapagliflozin reduced serum myostatin levels and elevated the SMM-to-bodyweight ratios with improving metabolic parameters. Dapagliflozin would contribute to reducing the risk of muscle loss.
Long-term (52-week) efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin add-on therapy to insulin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: An uncontrolled, open-label extension of a phase III study
- Pages: 662-671
- First Published: 19 November 2019
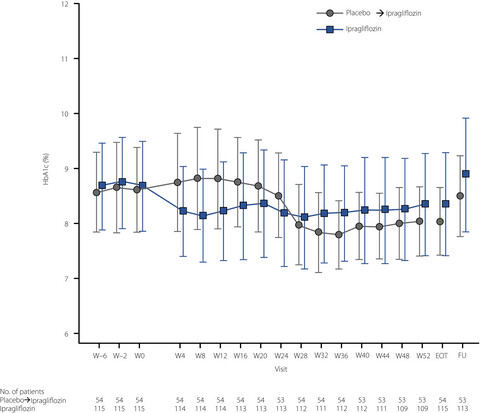
This long-term (52-week), open-label extension of a phase III study investigated the efficacy and safety of add-on ipragliflozin in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus who experienced inadequate glycemic control. Ipragliflozin at a once-daily 50 mg dosage, which was titrated to 100 mg in patients with inadequate control, reduced the mean glycated hemoglobin levels by −0.33% (standard deviation 0.72): reduction was sustained from week 4 onwards in the ipragliflozin group (n = 108); and from week 28 onwards, which corresponds to 4 weeks after switching to ipragliflozin treatment, in the placebo switched to ipragliflozin group (n = 53). No safety concerns related to severe hypoglycemia or diabetic ketoacidosis were reported.
Ultra-Rapid Lispro results in accelerated insulin lispro absorption and faster early insulin action in comparison with Humalog® in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes
- Pages: 672-680
- First Published: 09 December 2019
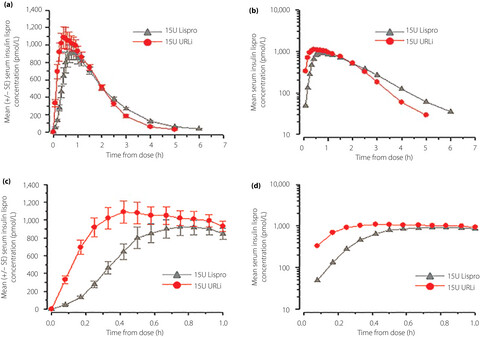
Ultra-rapid lispro is a novel ultra-rapid mealtime insulin. This study compared the pharmacokinetic and glucodynamic profiles, safety, and tolerability of ultra-rapid lispro and lispro (Humalog®) in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Overall, ultra-rapid lispro showed accelerated insulin lispro absorption, reduced late exposure, overall shorter duration and faster early insulin action compared with lispro in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
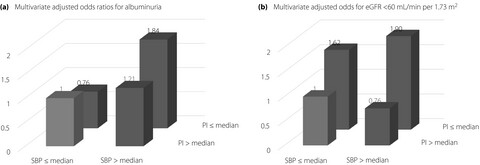
Decreased microcirculatory function measured by perfusion index is a novel indicator of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 681-687
- First Published: 28 November 2019
Vitreous hemorrhage in diabetes patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy undergoing hemodialysis
- Pages: 688-692
- First Published: 16 October 2019
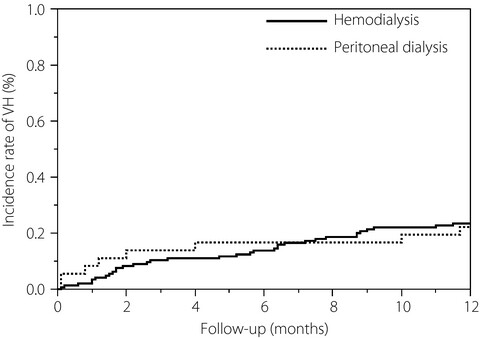
This study aimed to determine whether hemodialysis is associated with vitreous haemorrhage in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. These results suggest that hemodialysis therapy does not seem to be a significant risk for vitreous haemorrhage in proliferative diabetic retinopathy patients.
Long-term safety and efficacy of mirogabalin in Asian patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain
- Pages: 693-698
- First Published: 13 November 2019
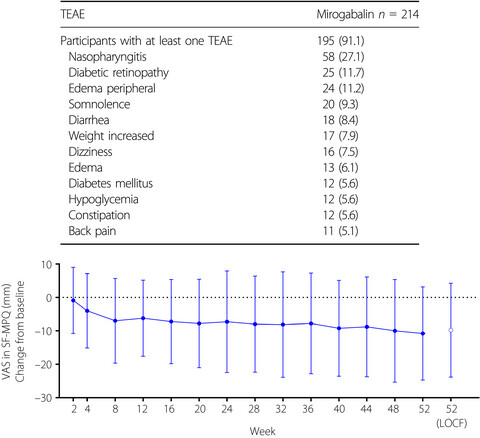
Mirogabalin 30 mg/day effectively reduced pain compared with placebo and was well tolerated in a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Asian patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. This open-label extension study was carried out to evaluate the long-term safety of flexible doses of mirogabalin 20 or 30 mg/day in Asian patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain; long-term efficacy of mirogabalin was also evaluated. This study showed the safety and efficacy of a long-term flexible dosing regimen of mirogabalin 10 or 15 mg twice daily in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain.
Association between gut microbiota composition and glycoalbumin level during pregnancy in Japanese women: Pilot study from Chiba Study of Mother and Child Health
- Pages: 699-706
- First Published: 13 November 2019
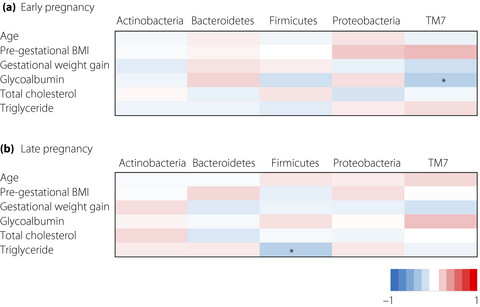
This study attempted to confirm whether gut microbiota change during pregnancy, by comparing the gut microbiota in stool samples from 45 women, both early and late in their pregnancies. The composition of microbiota in early and late pregnancy did not differ, except that the proportion of the phylum, TM7, significantly decreased in late pregnancy. The Shannon index of late pregnancy was negatively associated with pregestational body mass index and positively correlated with glycoalbumin levels.
Association between the ferritin level and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of observational studies
- Pages: 707-718
- First Published: 31 October 2019
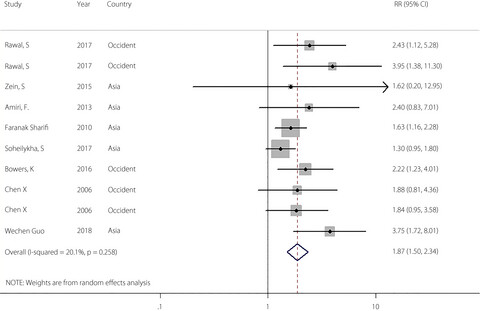
This is the first meta-analysis on this topic. We found that paying attention to the change of ferritin level during pregnancy can effectively prevent gestational diabetes mellitus. The association between ferritin and gestational diabetes mellitus might be mediated by body mass index or reactive protein as an intermediate factor. The causal relationship between ferritin and gestational diabetes mellitus can be obtained by the dose–response relationship to some extent.
Associations of anemia and hemoglobin with hemoglobin A1c among non-diabetic workers in Japan
- Pages: 719-725
- First Published: 12 October 2019
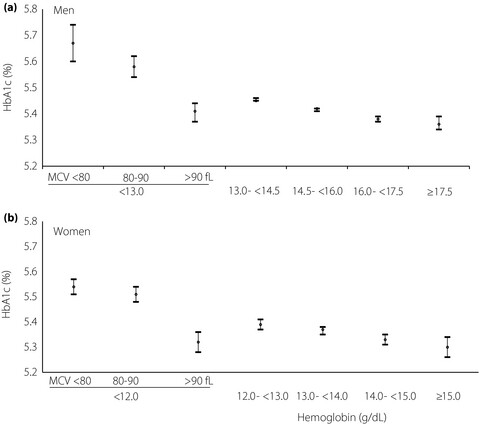
We observed elevated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) among anemic people with MCV <80 fL or MCV 80–90 fL, and decreased HbA1c among anemic people with MCV >90 fL, suggesting that iron deficiency anemia and non-iron deficiency anemia might influence HbA1c differently. In addition, non-anemic people with lower hemoglobin levels had higher HbA1c levels, suggesting that hemoglobin levels are in need of consideration when interpreting HbA1c values among non-anemic people.
Ceritinib-associated hyperglycemia in the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report Database
- Pages: 726-730
- First Published: 29 October 2019
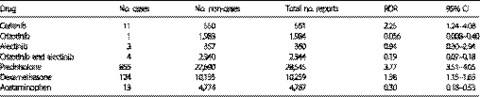
Reporting odds ratio analysis using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database shows that ceritinib might be significantly associated with hyperglycemia in clinical settings. The structural similarities between insulin receptor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase mutation (L1196M) might be related to their susceptibilities to ceritinib. The possibility of hyperglycemia should be carefully monitored in patients receiving ceritinib.
Opportunistic invasive fungal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from Southern China: Clinical features and associated factors
- Pages: 731-744
- First Published: 22 November 2019
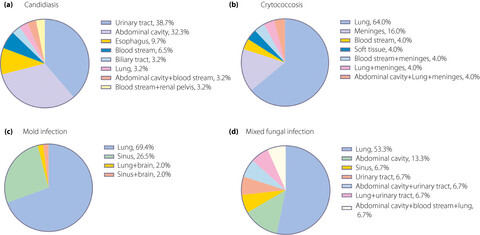
We investigated the characteristics and associated factors of invasive fungal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from Southern China for the first time. We found that Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus fumigatus were the leading agents. Prolonged hyperglycemia results in unfavorable outcomes. Correction of anemia and hypoalbuminemia might improve prognosis.
Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor and sarcopenia in a lean elderly adult with type 2 diabetes: A case report
- Pages: 745-747
- First Published: 03 September 2019
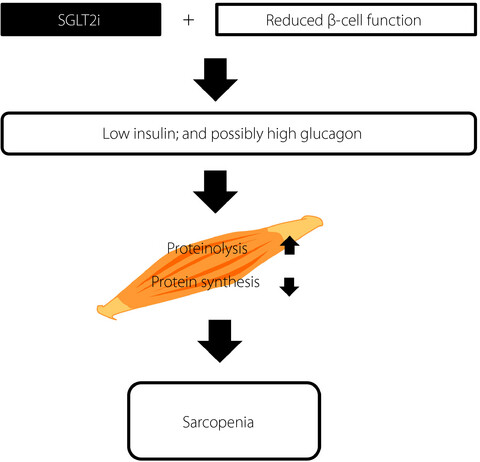
We report a case in which the sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, contributed to the development of ketosis and sarcopenia in a lean elderly woman with type 2 diabetes. Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor use and reduced β-cell function together resulted in insulinopenia and probably hyperglucagonemia, which enhanced proteinolysis and impaired protein synthesis in the muscle, thereby leading to the patient developing sarcopenia.
Letters to the Editor
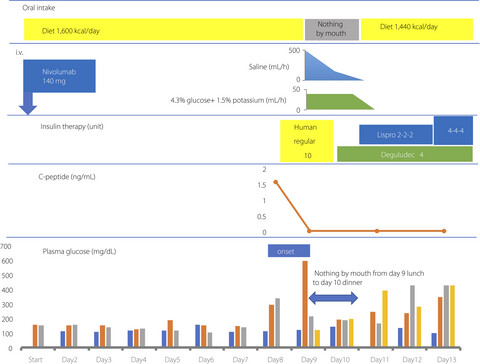
Nivolumab-induced fulminant type 1 diabetes with precipitous fall in C-peptide level
- Pages: 748-749
- First Published: 06 October 2019
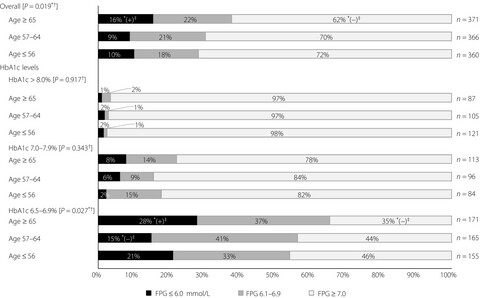
Levels of fasting plasma glucose in non-hospitalized older people with high hemoglobin A1c levels
- Pages: 750-751
- First Published: 29 November 2019