Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Time to treat the climate and nature crisis as one indivisible global health emergency
- Pages: 531-533
- First Published: 07 December 2023
VIEWPOINTS
New opportunity for targeting systemic inflammation in patients with heart failure through leucocyte immunomodulation
- Pages: 534-536
- First Published: 23 February 2024
Iron replacement therapy in heart failure: Contextualizing the results of the HEART-FID trial
- Pages: 537-539
- First Published: 04 March 2024
BIOMARKERS
Research articles
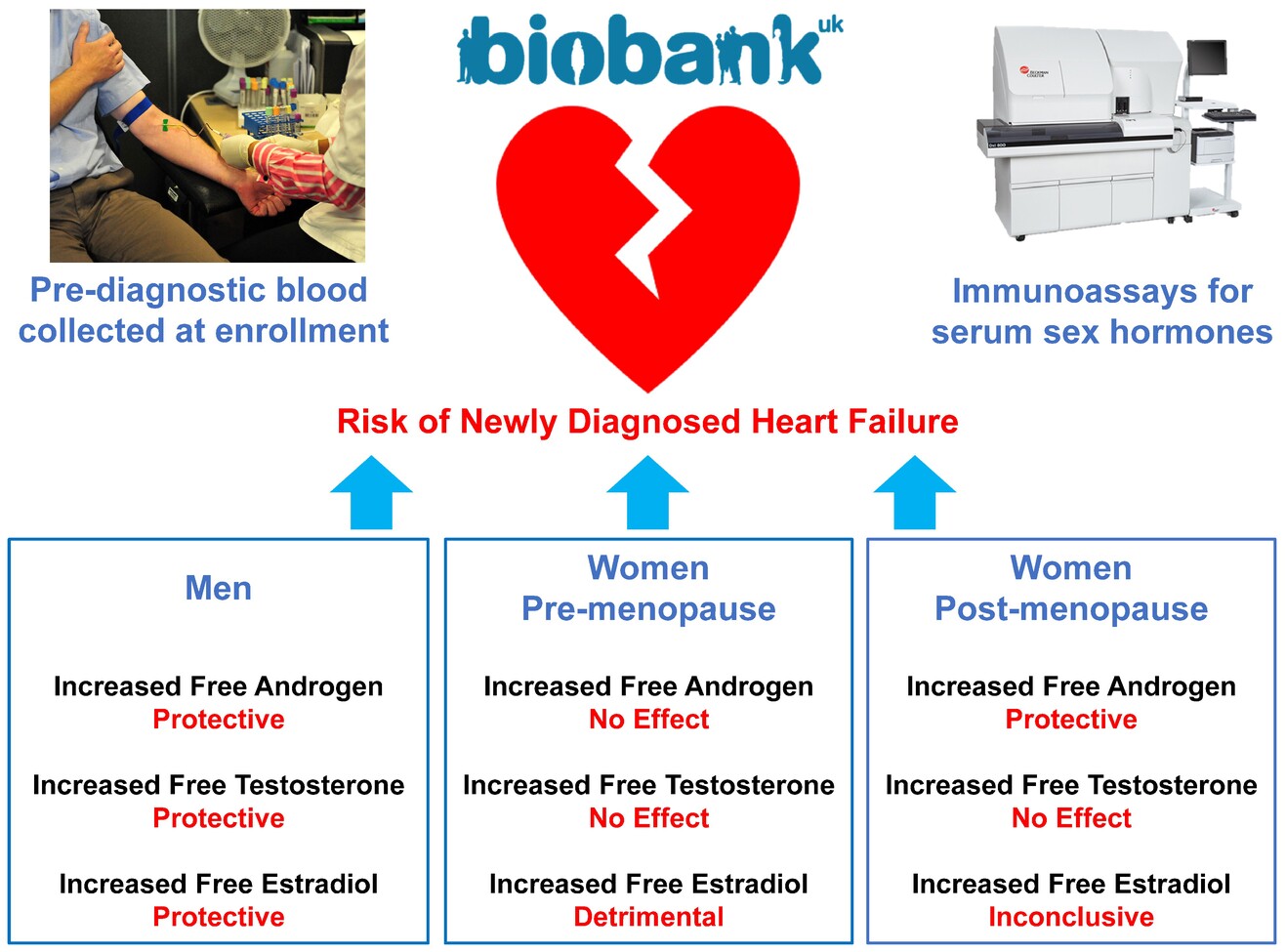
Pre-diagnostic free androgen and estradiol levels influence heart failure risk in both women and men: A prospective cohort study in the UK Biobank
- Pages: 540-550
- First Published: 25 March 2024
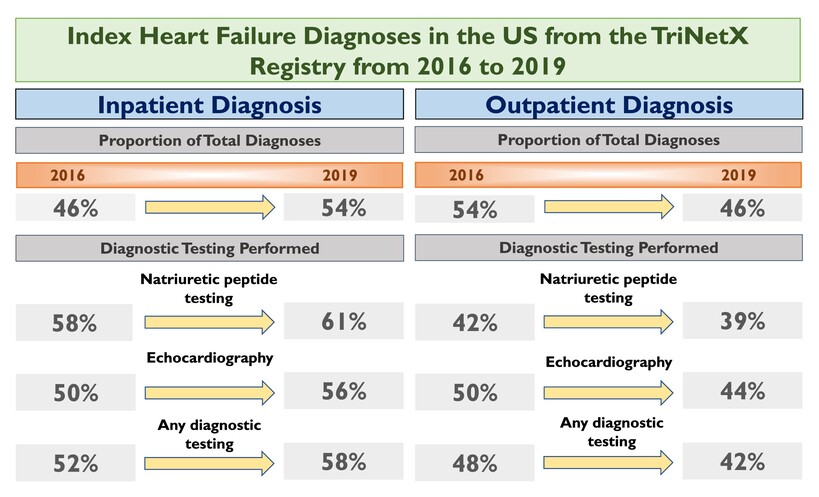
Use of natriuretic peptides and echocardiography for diagnosing heart failure
- Pages: 551-560
- First Published: 20 February 2024
Invited editorial
More than just a clinical syndrome: Biomarkers and echocardiography should be rapidly advised for anyone with suspected heart failure!
- Pages: 561-563
- First Published: 27 March 2024
HFpEF
Research article
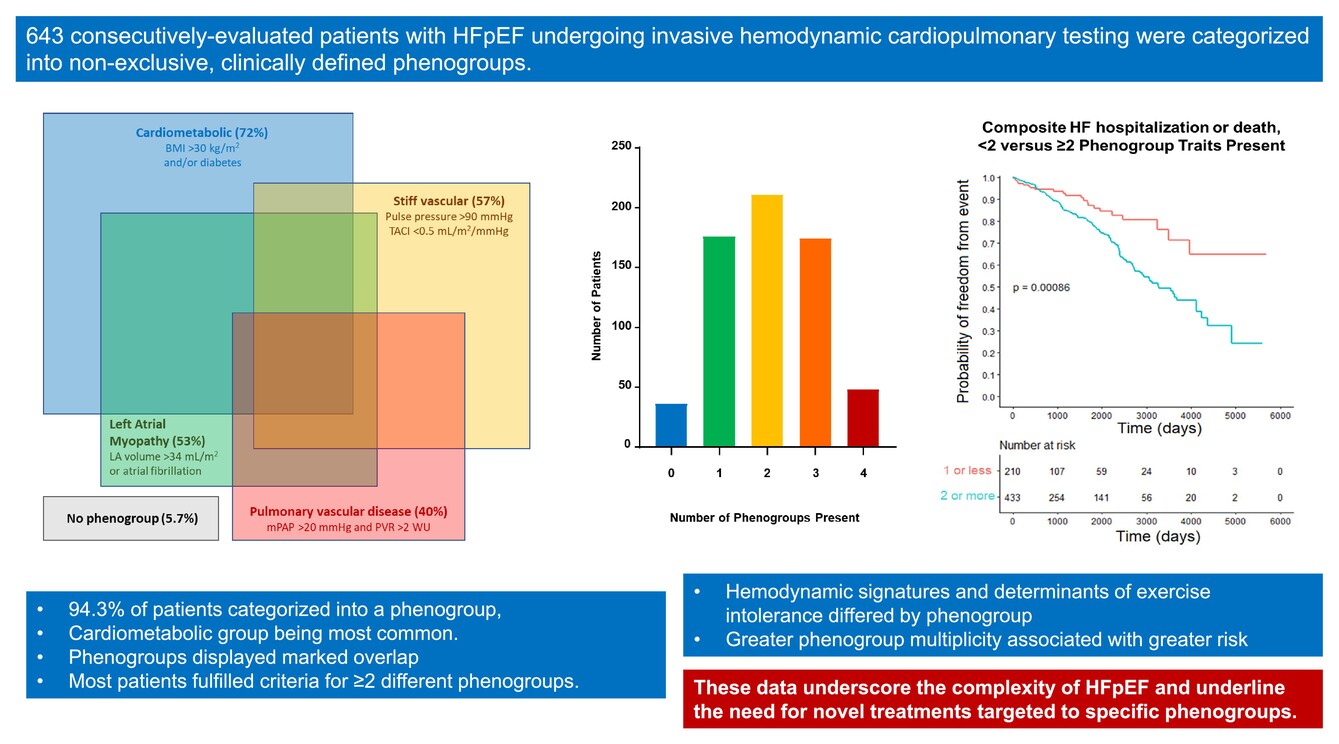
Clinical phenogroup diversity and multiplicity: Impact on mechanisms of exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Pages: 564-577
- First Published: 29 December 2023
Invited editorial
An exercise enigma: Unravelling the complexity of exercise intolerance in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Pages: 578-580
- First Published: 27 February 2024
CARDIOMYOPATHIES
Research articles
Role of arrhythmic phenotype in prognostic stratification and management of dilated cardiomyopathy
- Pages: 581-589
- First Published: 26 February 2024
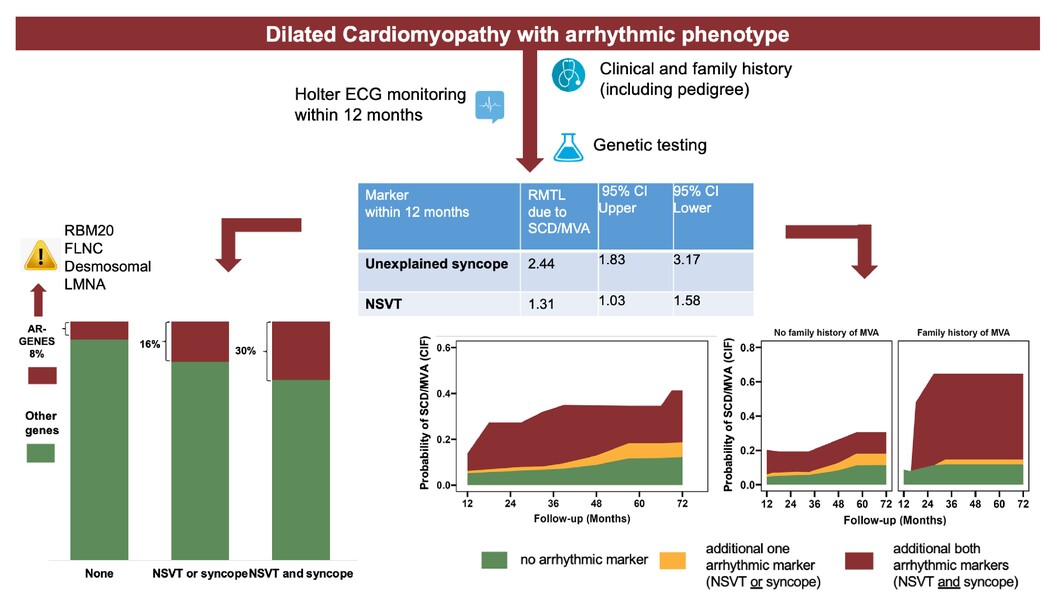
Dilated cardiomyopathy with arrhythmic phenotype. AR, arrhythmogenic; CI, confidence interval; CIF, cumulative incidence function; ECG, electrocardiogram; FLNC, filamin C; LMNA, lamin; MVA, major ventricular arrhythmia; NSVT, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia; RBM20, RNA binding motif 20; RMTL, restricted mean time lost; SCD, sudden cardiac death.
Apoptosis, a useful marker in the management of hot-phase cardiomyopathy?
- Pages: 590-597
- First Published: 27 February 2024
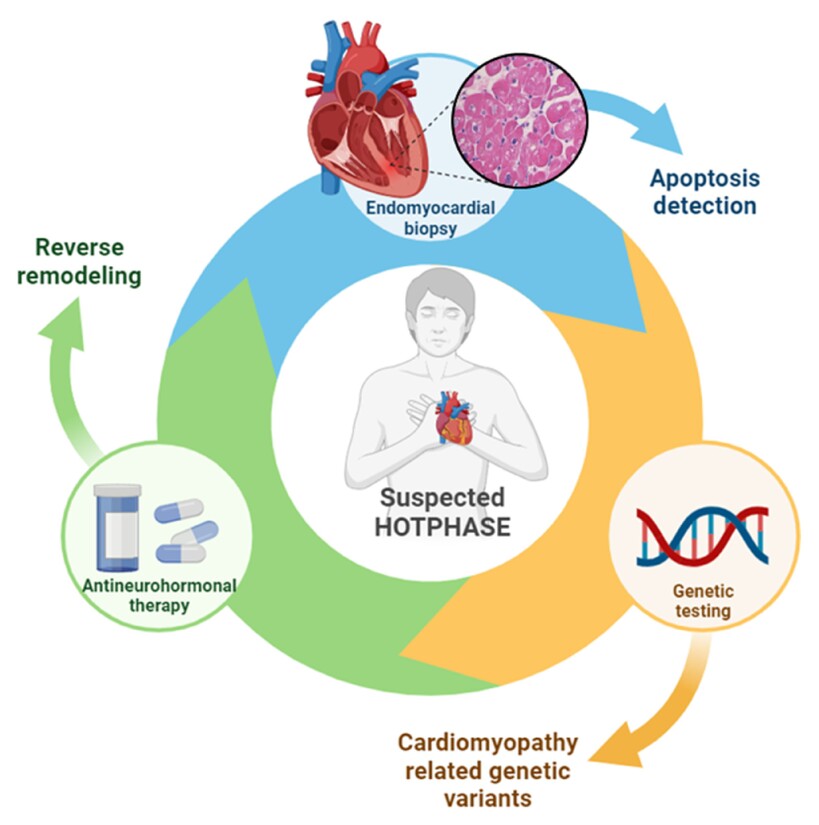
Seventeen patients hospitalized for suspected hot-phase cardiomyopathy underwent both endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) and genetic testing: histological detection of apoptosis at EMB was frequent (77% of cases) and all patients that tested positive for pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants showed apoptosis at EMB. In patients with apoptosis at EMB, left ventricular ejection fraction was lower at first clinical presentation and improved during follow-up with anti-neurohormonal therapy.
Myocardial perfusion in cardiac amyloidosis
- Pages: 598-609
- First Published: 21 January 2024
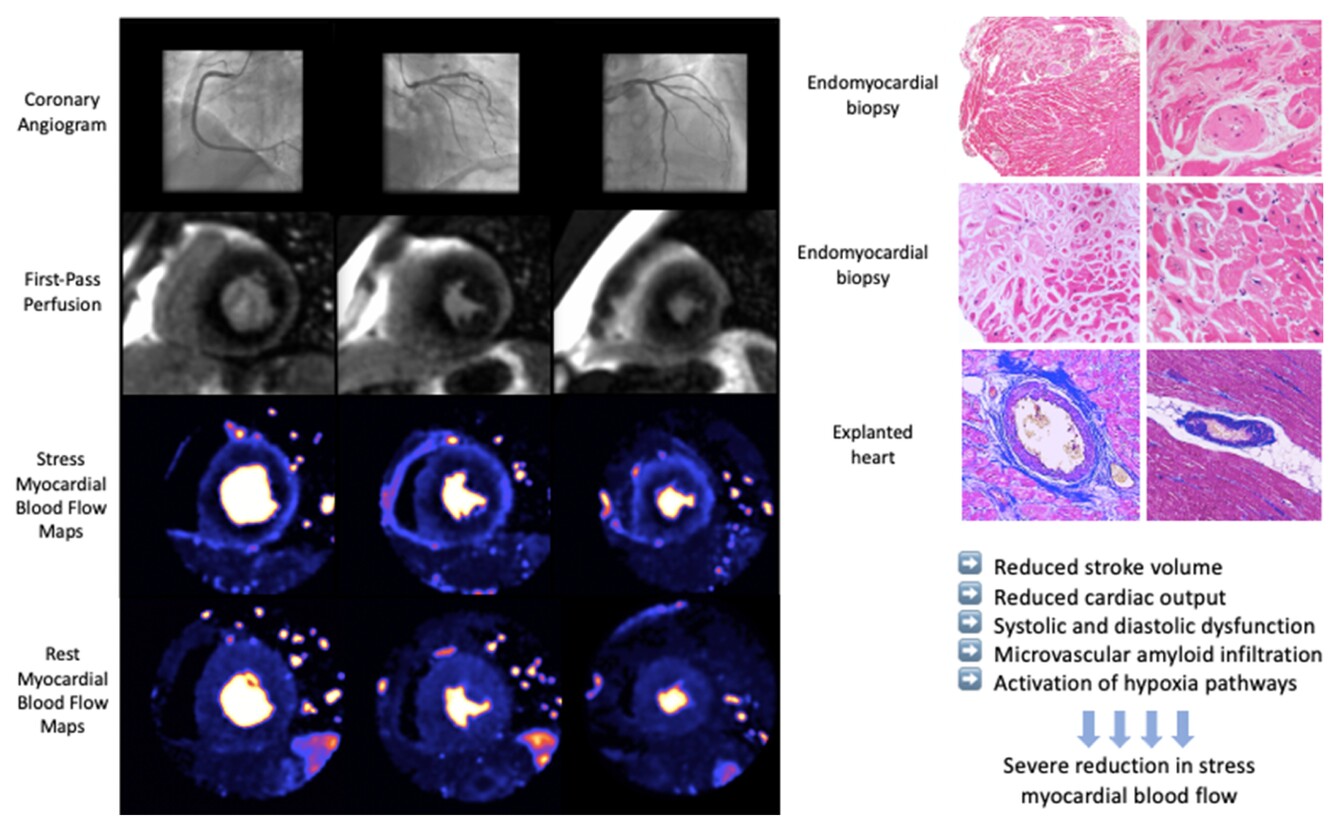
Myocardial perfusion in cardiac amyloidosis. Images on the left panel show an example of coronary angiography, first-pass perfusion maps and stress and rest myocardial perfusion maps of a patient with cardiac amyloidosis. The coronary angiogram is unobstructed and visual analysis of first-pass perfusion shows a global reduction in myocardial blood flow. Stress myocardial perfusion maps show extensive global ischaemia. Images on the top and middle right panel are endomyocardial biopsy samples showing extensive small vessel amyloid deposition (top) and myocyte atrophy and cytoplasmic vacuolization (middle). The bottom right panel shows intramural vessels with amyloid deposits from an explanted whole heart.
Invited editorial
All roads lead to… myocardial ischaemia in cardiac amyloidosis
- Pages: 610-611
- First Published: 18 February 2024
Short report
Effect of long-term tafamidis treatment on health-related quality of life in patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy
- Pages: 612-615
- First Published: 04 March 2024
MEDICAL THERAPY
Research article
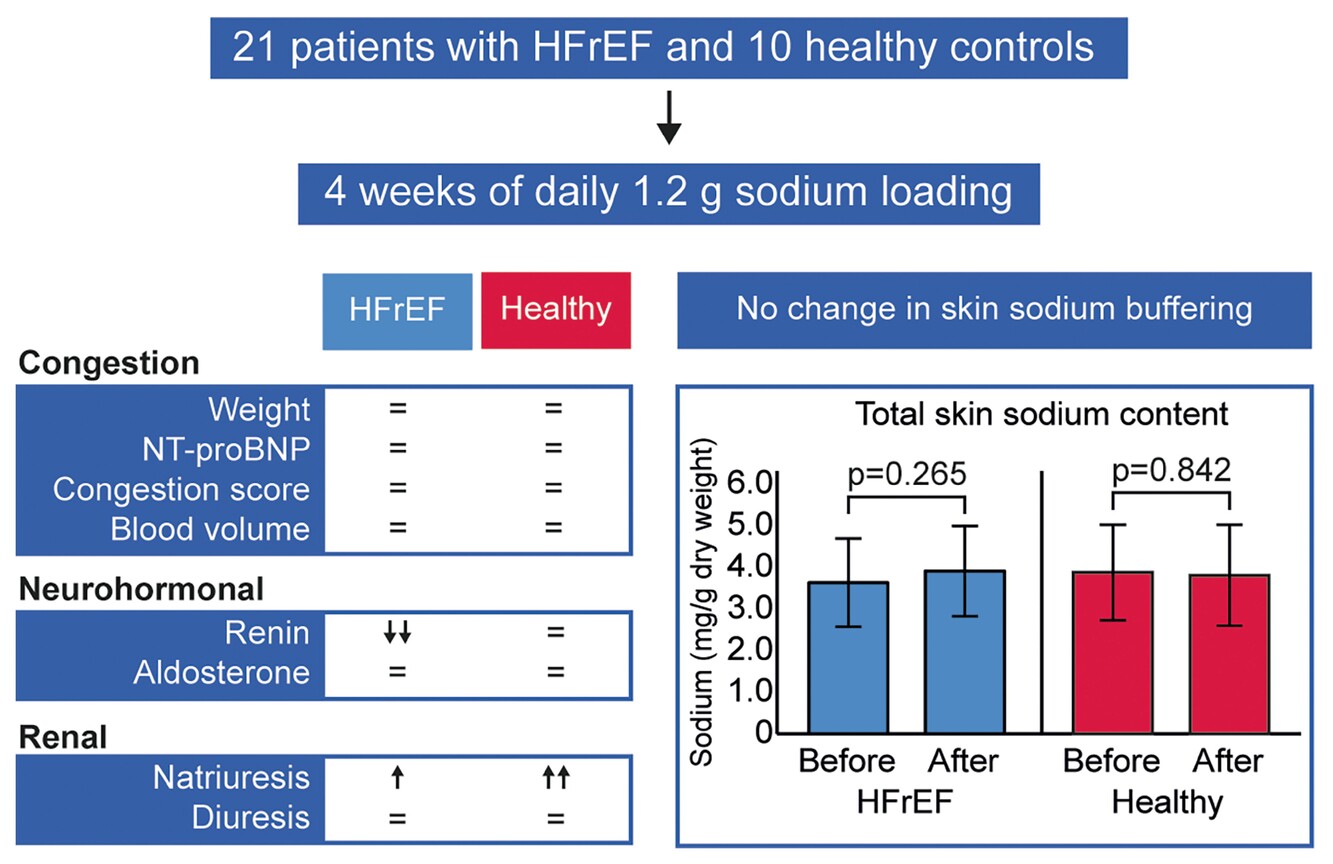
Sodium loading in ambulatory patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Mechanistic insights into sodium handling
- Pages: 616-624
- First Published: 21 January 2024
Invited editorial
Research articles
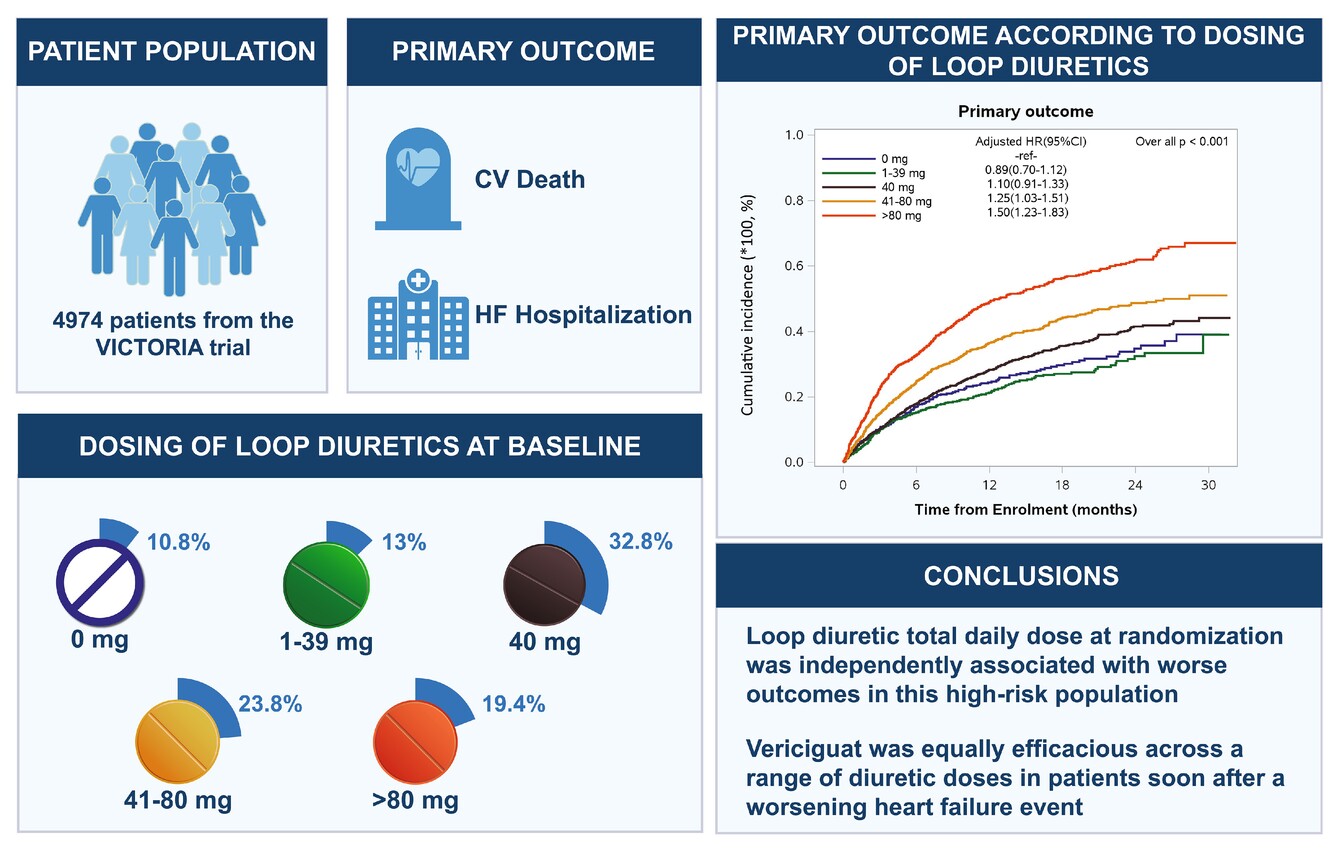
Diuretic use and outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Insights from the VICTORIA trial
- Pages: 628-637
- First Published: 07 March 2024
Blood pressure and intensive treatment up-titration after acute heart failure hospitalization: Insights from the STRONG-HF trial
- Pages: 638-651
- First Published: 05 March 2024
Effect of a transitional care model following hospitalization for heart failure: 3-year outcomes of the Patient-Centered Care Transitions in Heart Failure (PACT-HF) randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 652-660
- First Published: 01 February 2024
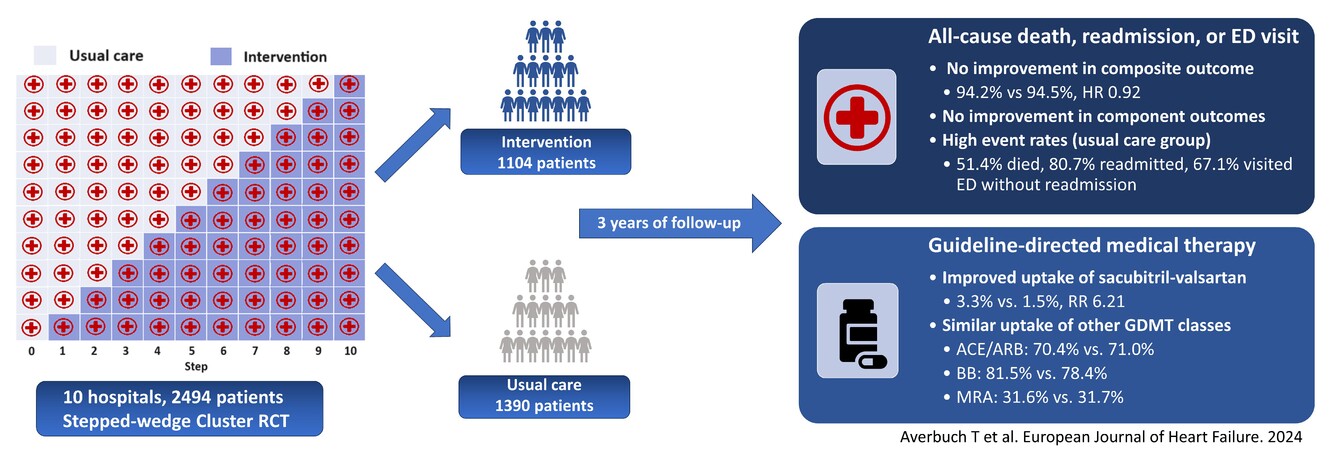
Three-year outcomes of the Patient-Centered Care Transitions in Heart Failure (PACT-HF) stepped wedge cluster RCT in patients hospitalized for HF. Hospitals were randomized to a group of transitional care services versus usual care. Clinical event rates were high and the treatment effect on the primary composite outcome of all-cause death, readmission, or ED visit was neutral at 3 years, likely due to similar uptake of guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) in both groups. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; ARNI, angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitor; BB, beta-blocker; ED, emergency department; HR, hazard ratio; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; RCT, randomized controlled trial; RR, relative risk.
Invited editorial
A PACT for the future: Improving medication adherence in heart failure
- Pages: 661-663
- First Published: 12 February 2024
Research article
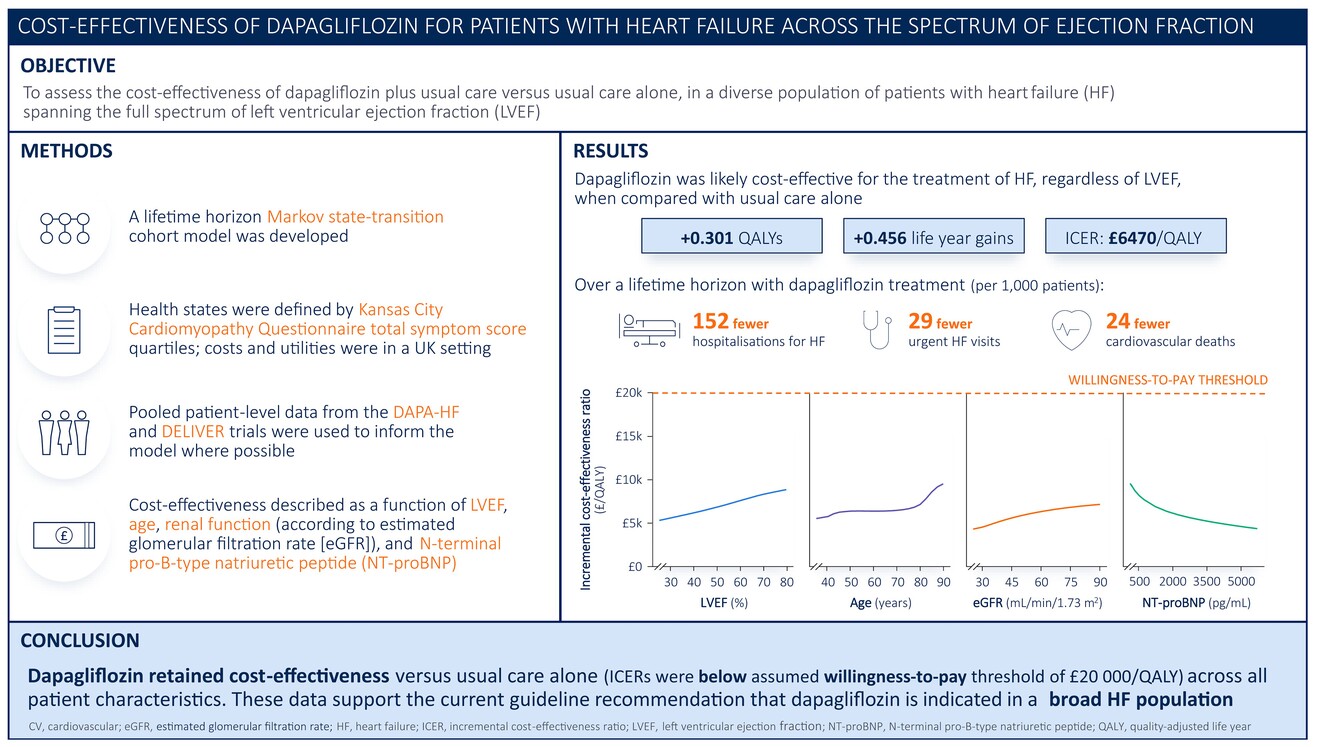
Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin for patients with heart failure across the spectrum of ejection fraction: A pooled analysis of DAPA-HF and DELIVER data
- Pages: 664-673
- First Published: 20 March 2024
Study design
Efficacy and safety of CDR132L in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction after myocardial infarction: Rationale and design of the HF-REVERT trial
- Pages: 674-682
- First Published: 25 January 2024
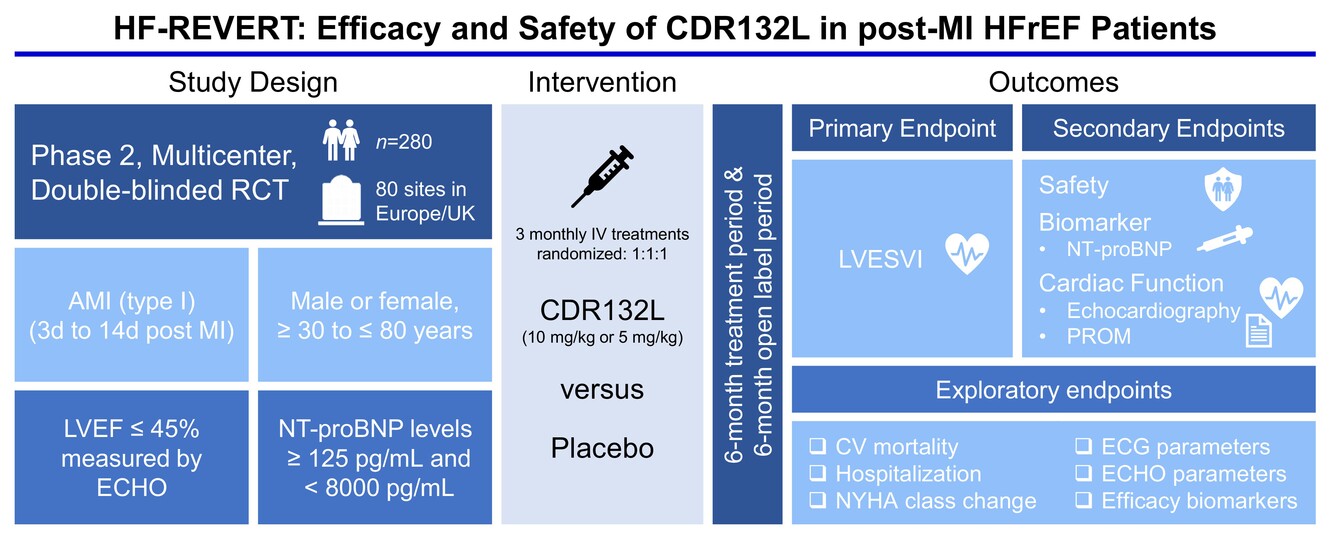
Study design and intended outcomes of the HF-REVERT study with CDR132L, a synthetic antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor selectively targeting microRNA-132, in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) after myocardial infarction (MI). AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CV, cardiovascular; ECG, electrocardiogram; ECHO, echocardiography; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; IV, intravenous; LVESVI, left ventricular end-systolic volume index; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; NYHA, New York Heart Association; PROM, patient-reported outcome measure; RCT, randomized clinical trial.
Invited editorial
‘Micro’-managing heart failure: Restoring that which was lost in translation
- Pages: 683-685
- First Published: 04 March 2024
DEVICES
Research article
Efficacy and safety of the Aria pulmonary endovascular device in pulmonary hypertension
- Pages: 686-694
- First Published: 13 March 2024
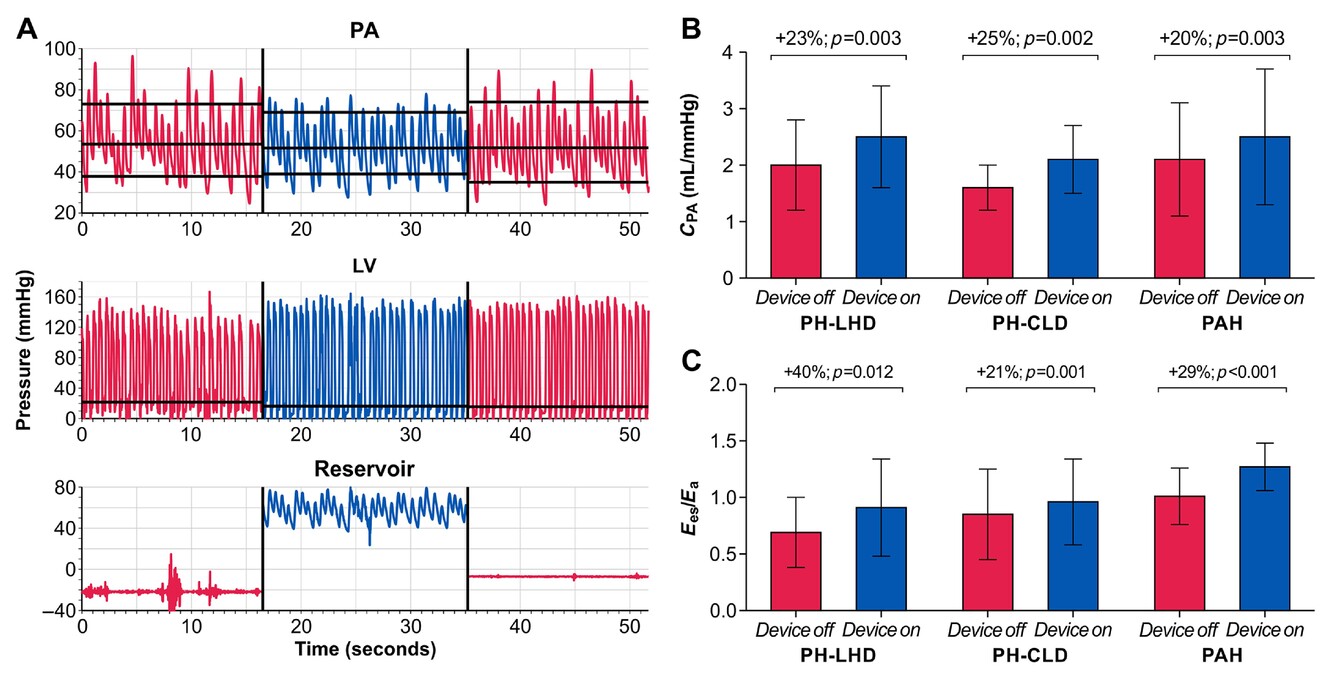
Impact of the Aria pulmonary endovascular device on hemodynamics. Hemodynamics and reservoir pressures are depicted in blue during device activation and in red when the device is deactivated. Panel A demonstrates the effect of temporary device activation on pulmonary arterial (PA) and left ventricular (LV) pressures in a patient with pulmonary hypertension associated with left heart disease (PH-LHD). Panel B shows the effect of the Aria pulmonary endovascular device on pulmonary arterial compliance (CPA) and right ventricular-to-pulmonary vascular coupling assessed by the ratio of right ventricular end-systolic elastance to effective arterial elastance (Ees/Ea) in patients with PH-LHD, PH associated with chronic lung disease (PH-CLD) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, panel C).
RESEARCH LETTERS
Prevalence of wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis in a prospective heart failure cohort with preserved and mildly reduced ejection fraction: Results of the Amylo-VIP-HF study
- Pages: 695-698
- First Published: 04 March 2024
Association of diabetes-specific heart failure risk score with presence of subclinical cardiomyopathy among individuals with diabetes: A prospective study
- Pages: 699-701
- First Published: 04 March 2024
Early left ventricular unloading via active transseptal left atrial venting in case of cardiogenic shock under veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 701-703
- First Published: 19 February 2024
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Artificial intelligence in heart failure improving the efficiency or dependency on it? Letter regarding the article ‘Artificial intelligence and heart failure: A state-of-the-art review’
- Page: 704
- First Published: 27 August 2023
The gap between real-world and guidelines in the use of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction: Is it underestimated or overestimated? Letter regarding the article ‘Real-world use of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction: Data from the Swedish Heart Failure Registry’
- Pages: 704-705
- First Published: 08 February 2024