Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Two-step artificial intelligence algorithm for liver segmentation automates anatomic virtual hepatectomy
- Pages: 1205-1217
- First Published: 25 September 2023
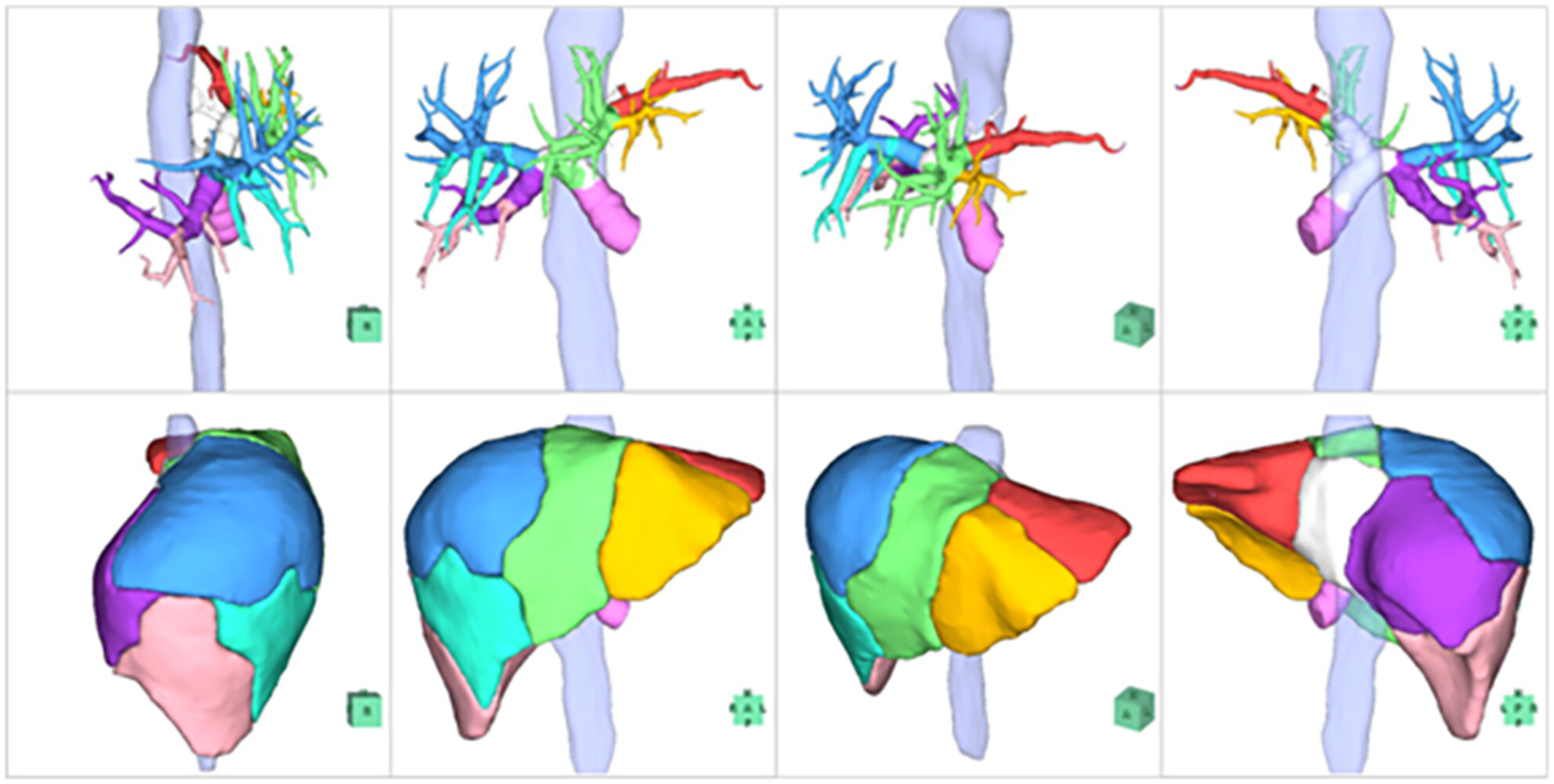
No artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm for liver segmentation has yet been reported. Kazami and colleagues developed a two-step AI algorithm based on 174 donor livers, along with an evaluation method. The AI algorithm without human intervention correctly divided all hemilivers, 92.8% of the sectors, and 91.6% of the 8 segments.
A multicenter validation study for determining the condition of nonanatomical or minor anatomical hepatectomies satisfying technical difficulty of current high-level hepatectomy certificated by the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery
- Pages: 1218-1226
- First Published: 05 October 2023
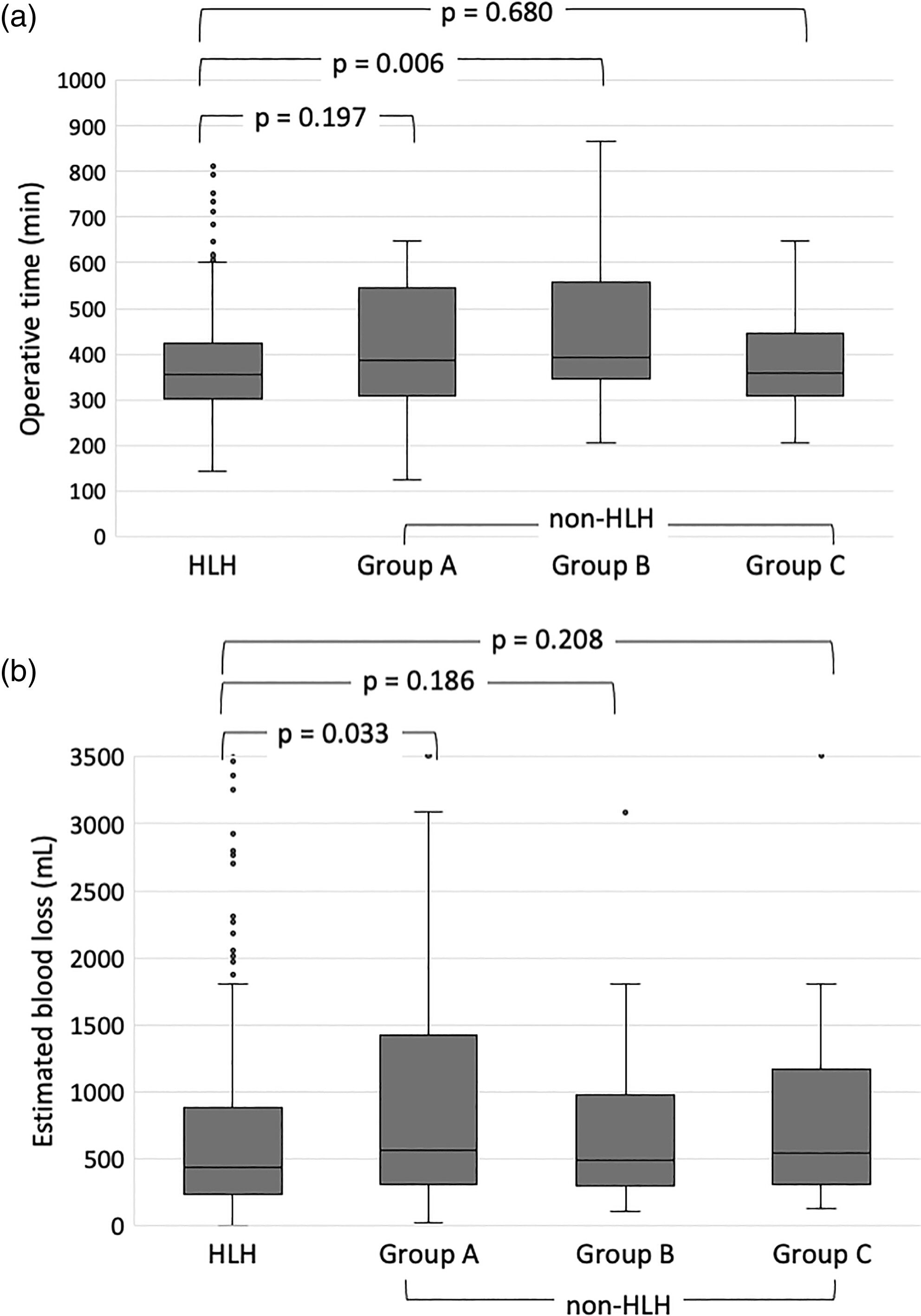
Matsuki and colleagues conducted this multicenter study to develop new criteria for JSHBPS-certified high-level hepatectomy. Hepatectomies satisfying one of three conditions (A: depth of hepatectomy ≥5 cm, B: number of resections ≥3 including at least one with depth ≥3 cm, C: paracaval involvement) posed no lesser technical difficulties than current high-level hepatectomy.
LncRNA–mRNA coexpression analysis reveals distinct pathogenic mechanisms for subtypes of congenital biliary dilatation
- Pages: 1227-1240
- First Published: 26 October 2023
Variations of the hepatic artery and bile duct in patients with pancreaticobiliary maljunction: Impact on postoperative outcomes
- Pages: 1241-1248
- First Published: 25 October 2023
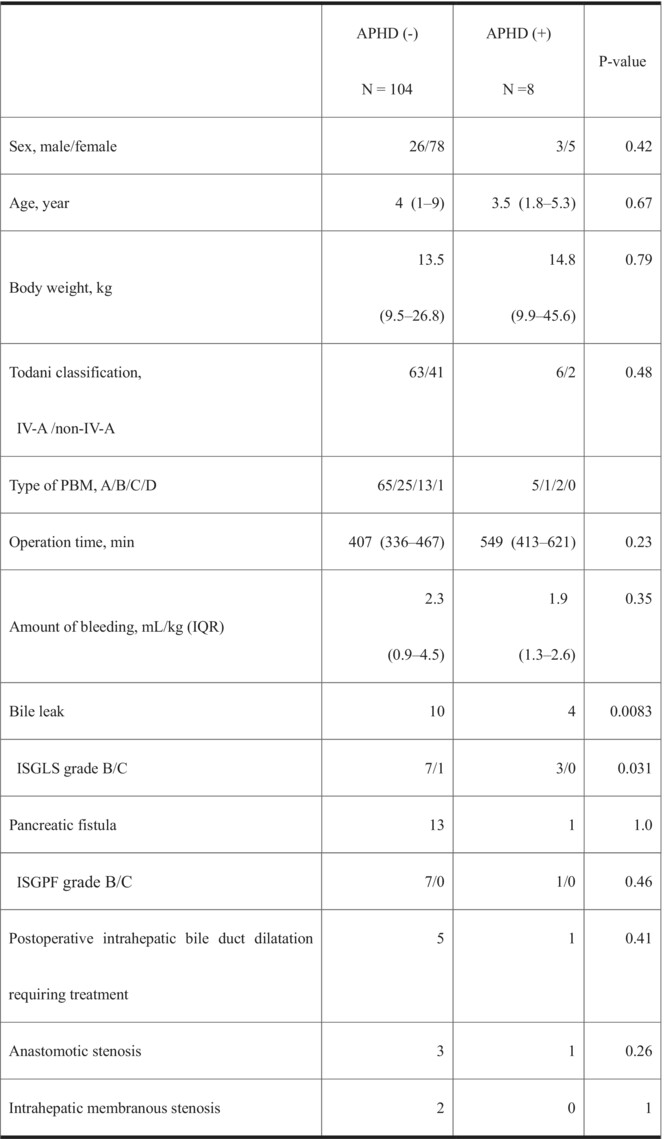
Takada and colleagues analyzed the impact of anatomical variations on postoperative outcomes in patients with congenital biliary dilatation. An aberrant right hepatic artery running ventral to the common hepatic duct, and an aberrant posterior hepatic duct, which is associated with postoperative risk of bile leakage, require careful identification and manipulation.
Randomized phase II trial of chemoradiotherapy with S-1 versus combination chemotherapy with gemcitabine and S-1 as neoadjuvant treatment for resectable pancreatic cancer (JASPAC 04)
- Pages: 1249-1260
- First Published: 25 September 2023
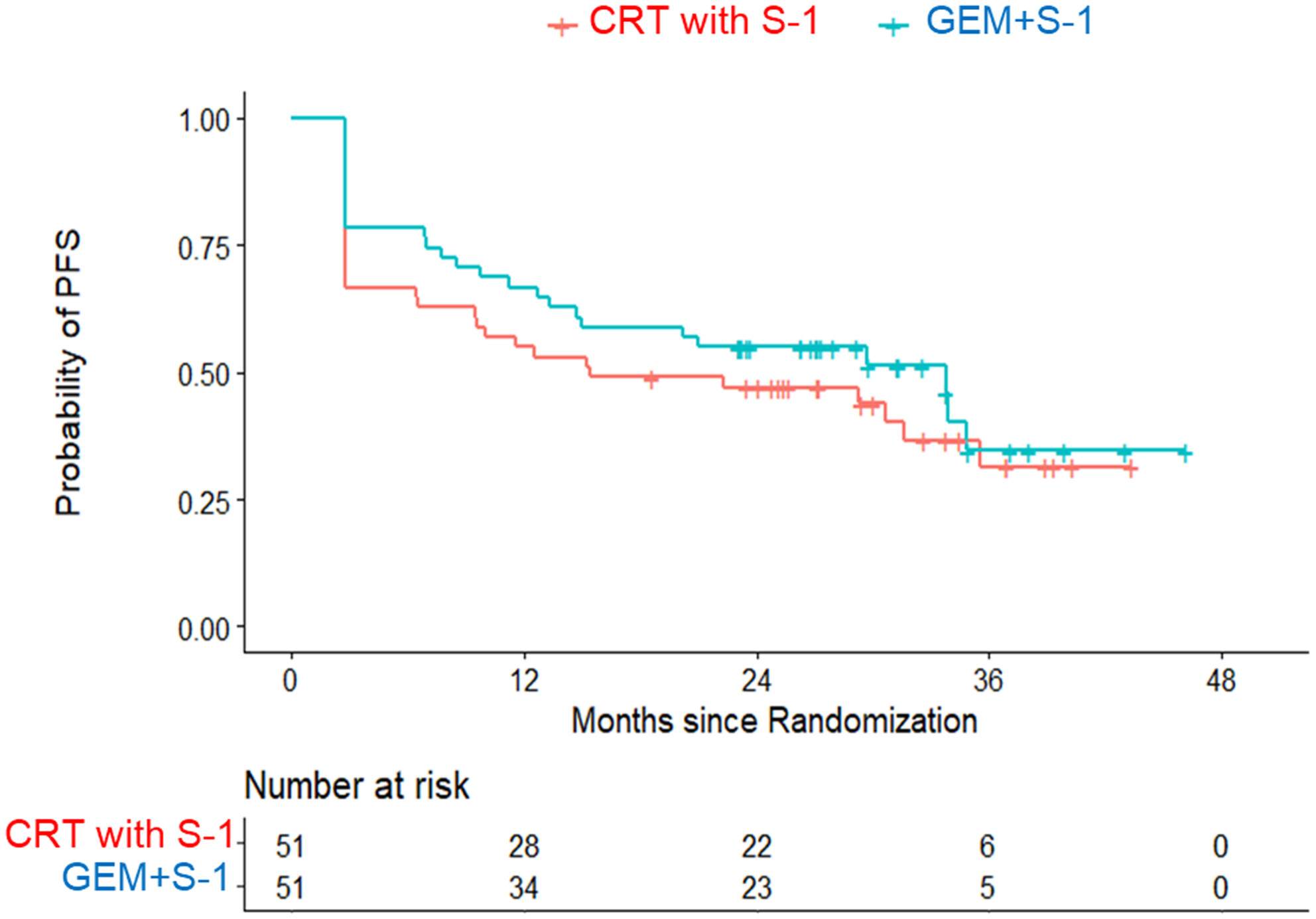
The JASPAC 04 study was conducted to investigate which treatment for resectable pancreatic cancer, neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with S-1 or chemotherapy with gemcitabine and S-1, is more promising in terms of effectiveness and safety. With 2-year progression-free survival rates of 45.0% and 54.9%, respectively, Sugiura and colleagues conclude that both are promising treatments.
Efficacy of staging laparoscopy for resectable pancreatic cancer on imaging and the therapeutic effect of systemic chemotherapy for positive peritoneal cytology
- Pages: 1261-1272
- First Published: 26 September 2023
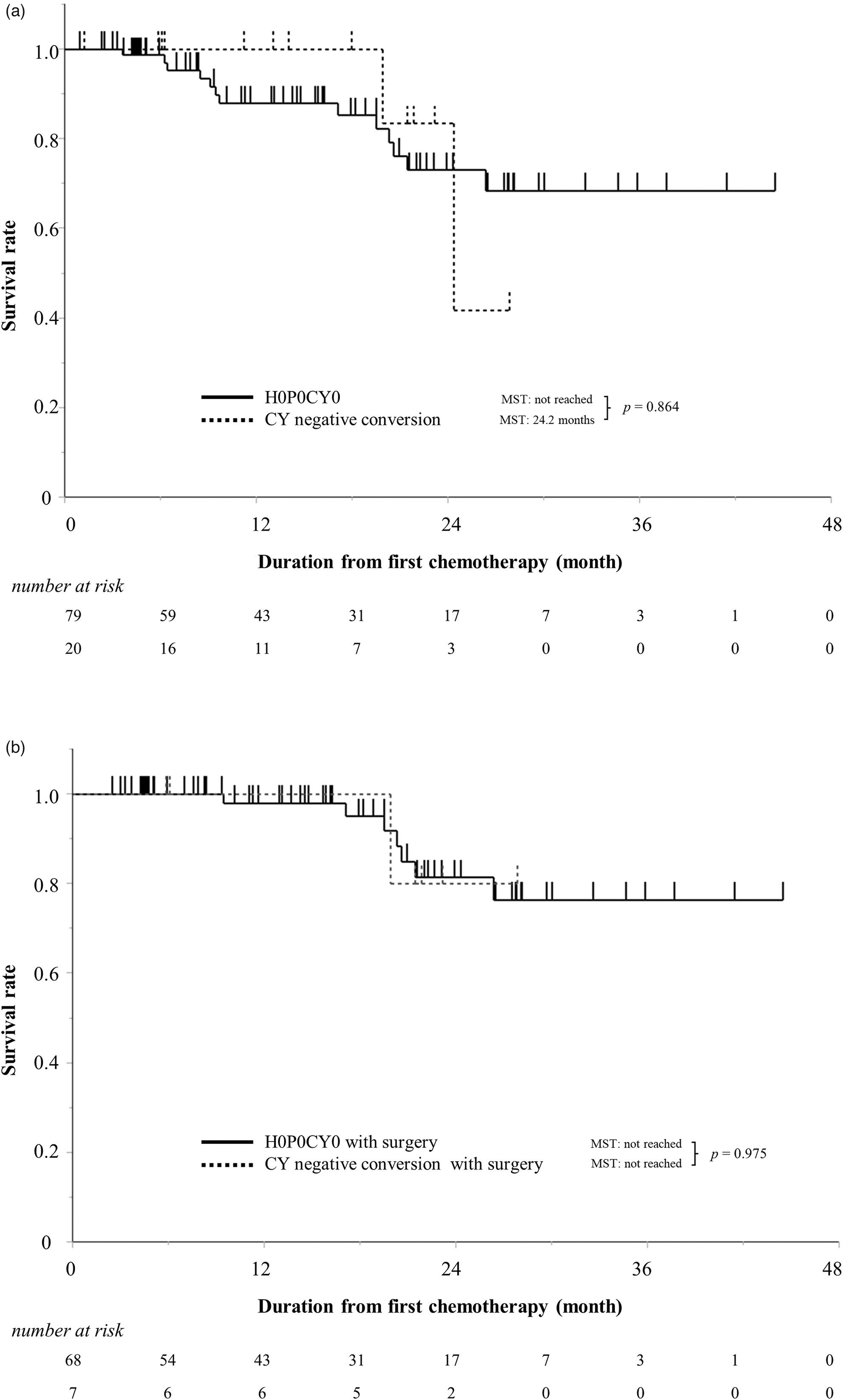
In 115 patients with resectable pancreatic cancer, pre-treatment staging laparoscopy revealed positive peritoneal washing cytology in 22 patients and liver metastases or peritoneal dissemination in 9 patients. Fukasawa and colleagues found comparable overall survival in patients with positive cytology converted to negative following systemic chemotherapy and those with initially negative cytology.
Predictive impacts of peritoneal washing cytology for surgical resection-intended pancreatic cancer cases: Establishment of planned staging laparoscopy criteria
- Pages: 1273-1281
- First Published: 05 October 2023
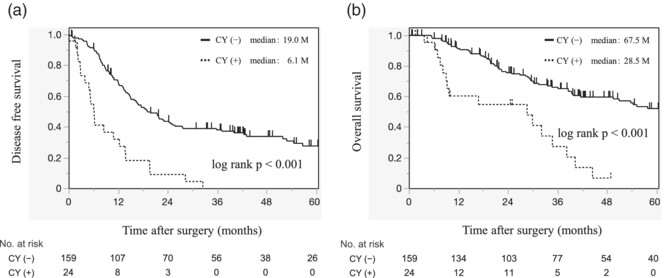
Tanaka and colleagues identified positive peritoneal washing cytology status to be an independent prognostic predictor of resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer without preoperative treatment. High CA19-9 or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer were associated with washing cytology positivity, and staging laparoscopy is recommended in such cases before planning multimodal therapy.
HOW I DO IT
Right lateral approach to the superior mesenteric artery in robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Pages: e73-e74
- First Published: 24 September 2023
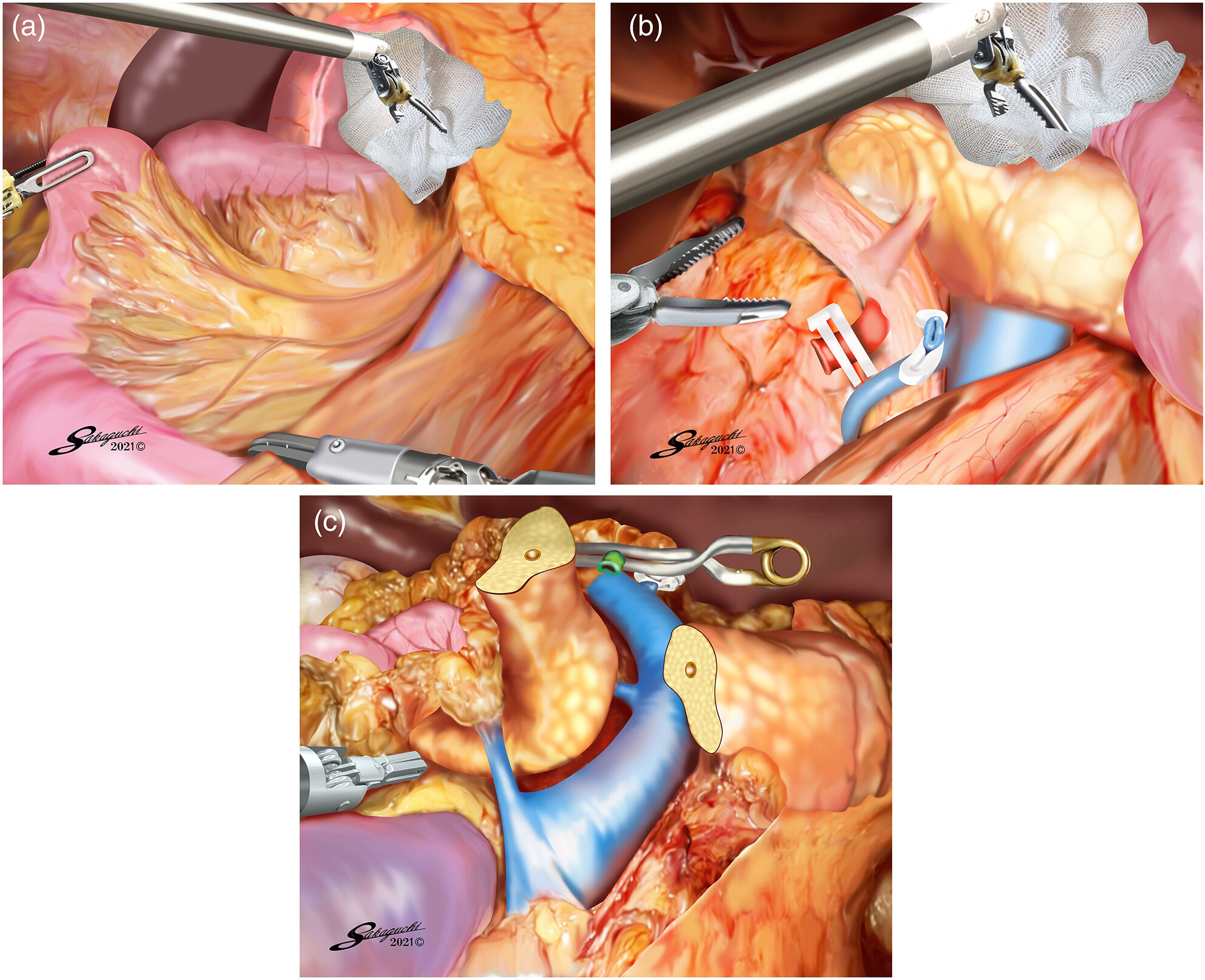
Ninomiya and colleagues introduced a novel approach to the superior mesenteric artery in robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. The right lateral approach allows repositioning of the superior mesenteric artery to the right-most surface, facilitating safer artery division and simplifying detachment around the superior mesenteric vein, potentially reducing operative time and minimizing blood loss.
Tip-in endoscopic papillectomy for ampullary adenoma near diverticulum to minimize complications
- Pages: e75-e77
- First Published: 30 September 2023
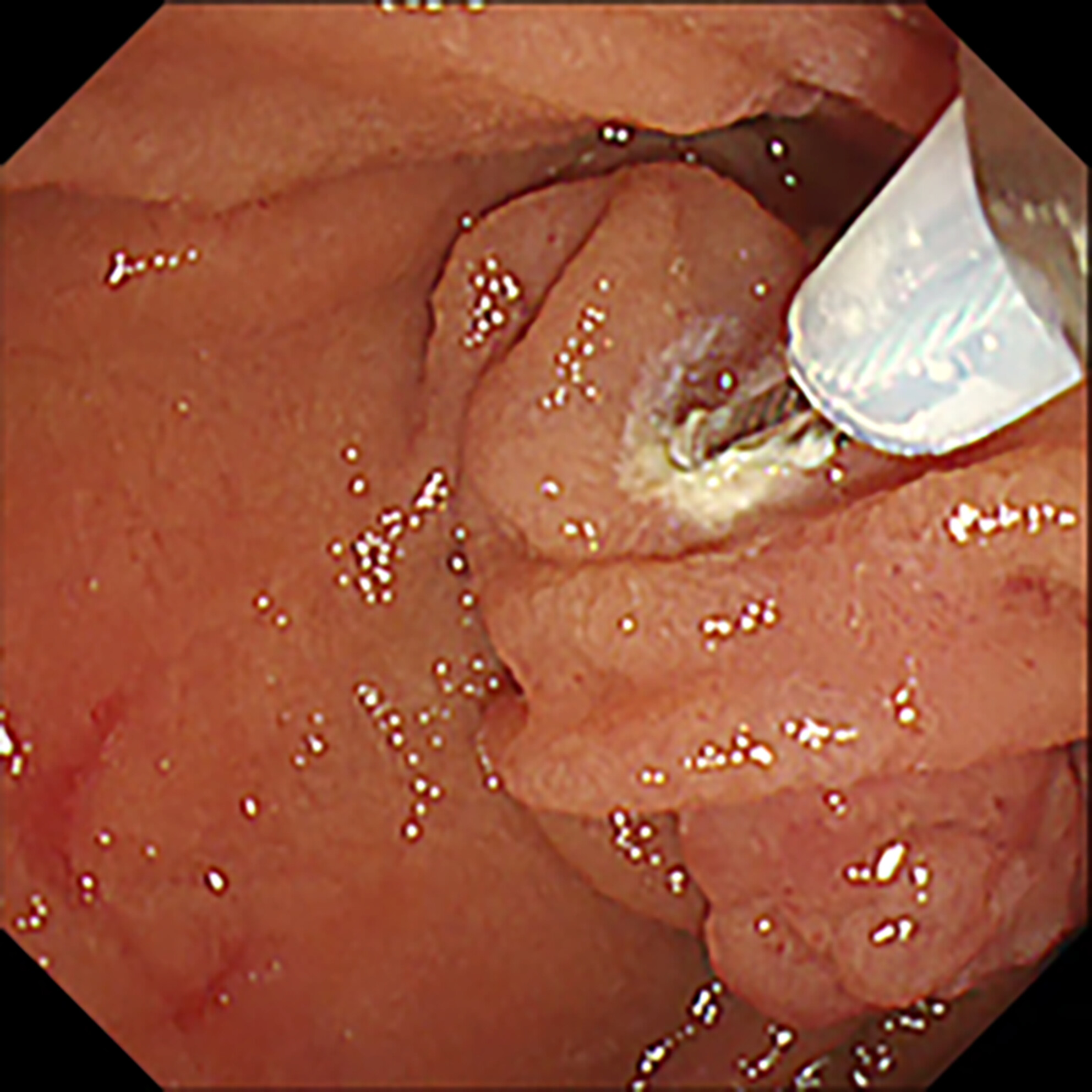
Toyonaga and colleagues present a novel “tip-in endoscopic papillectomy” approach for resecting ampullary tumors, aiming to minimize complications like perforation and residual tumor by adapting the colonic polyp endoscopic mucosal resection tip-in method. The technique is described with accompanying video in a case of ampullary tumor near a diverticulum.





