Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLES
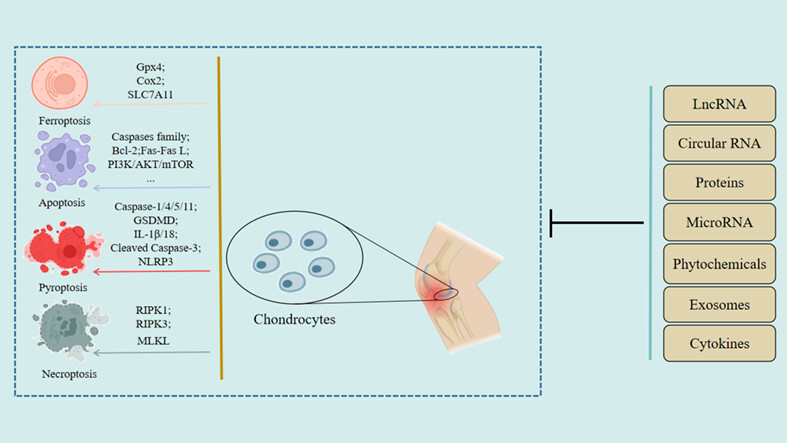
Recent Therapeutic Strategies for Excessive Chondrocyte Death in Osteoarthritis: A Review
- Pages: 1437-1453
- First Published: 18 April 2023
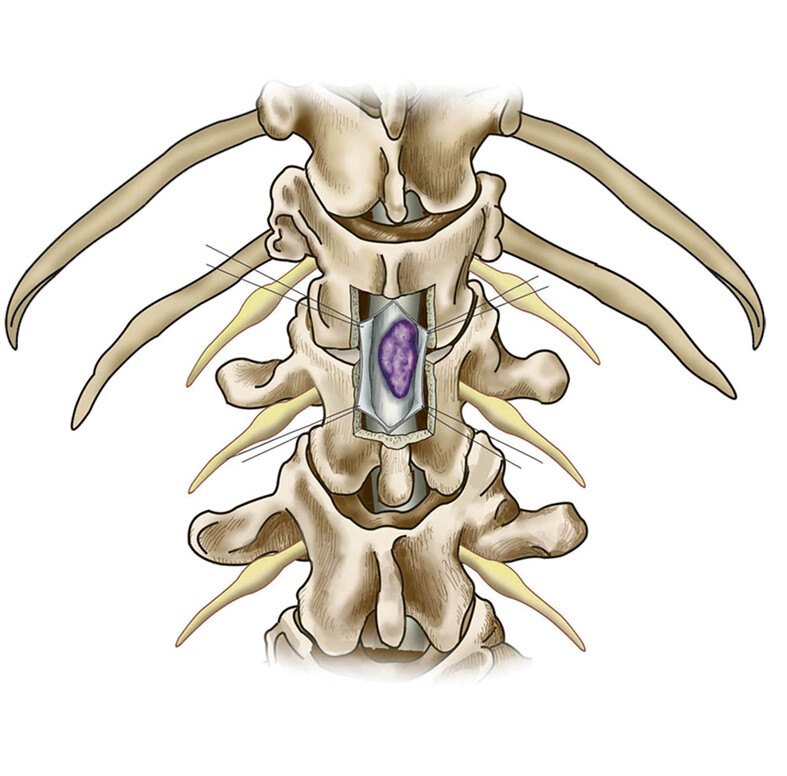
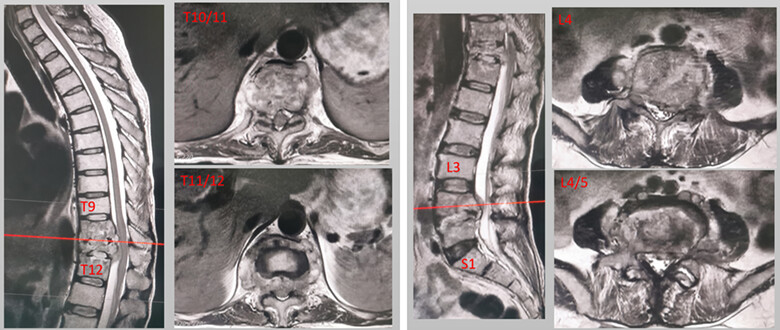
Diagnosis and Treatment of Skipped Multifocal Spinal Tuberculosis Lesions
- Pages: 1454-1467
- First Published: 25 April 2023
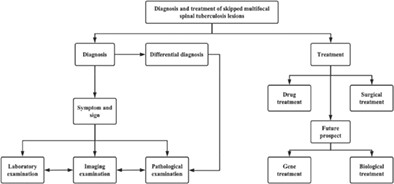
This article starts by collecting all the reported cases on skipped multifocal spinal tuberculosis lesions, thus reviewing the diagnostic methods, differential diagnosis, standard and new therapies, and putting forward the direction and prospect for the future, to provide reference and guidance for clinical treatment and diagnosis direction.
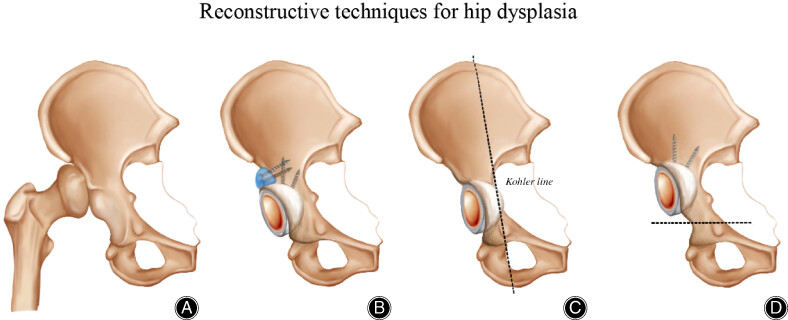
Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients with Crowe III/IV Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: Acetabular Morphology and Reconstruction Techniques
- Pages: 1468-1476
- First Published: 28 April 2023
CLINICAL ARTICLES
Clinical and Radiographic Comparison of Oblique Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Patients with L4/5 grade-1 Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
- Pages: 1477-1487
- First Published: 08 May 2023
Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium Periprosthetic Joint Infections Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Case Series and Review of the Literature
- Pages: 1488-1497
- First Published: 08 May 2023
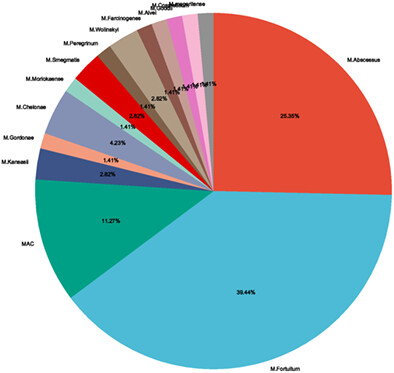
Non-Tuberculosis Mycobacterium (NTM) is a rare but devasting causative pathogen of PJI. And orthopaedic surgeons should consider NTM when negative cultures or antibiotic therapy is ineffective. NTM should be diagnostically differentiated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Additionally, it is crucial to differentiate RGM from SGM accurately, and PCR or NGS is the recommended testing method. The preferred treatment for NTM PJI is a two-staged exchange in combination with multi-antibiotic therapy.
Total Hip Arthroplasty or Arthroscopy for Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Hip: A Retrospective Study with 3-Year Follow-Up at Minimum
- Pages: 1498-1504
- First Published: 24 April 2023
The Interval of Two-Stage Bilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty under Enhanced Recovery Affects Perioperative Complications and Cost of Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study
- Pages: 1505-1513
- First Published: 18 April 2023
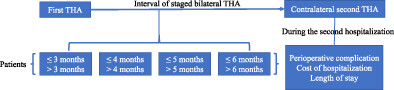
We retrospectively reviewed patients who received staged bilateral THA under enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS). The staged time was divided into two groups using four different cutoff points: (1) ≤3 months versus >3 months, (2) ≤4 months versus >4 months, (3) ≤5 months versus >5 months, and (4) ≤6 months versus >6 months. The outcomes included the rate of perioperative complications, the cost of hospitalization, and the length of hospital stay (LOS). With the application of ERAS, the rate of perioperative complications in the >150-day group was significantly lower than that in the ≤5 months group (13/195 vs. 45/307, p = 0.01). Concerning the cost of hospitalization, the >5 monthly intervals spent significantly less than the ≤5 monthly intervals ($ 8695.91 vs. $ 8919.71, p = 0.02). The mean LOS was significantly shorter in those hips performed more than 5 months apart from the contralateral first THA (4.87 ± 1.25 days vs. 5.14 ± 1.41 days, p = 0.02). ERAS could reduce the interval of staged bilateral THA to 5 months regarding the rate of perioperative complications and the cost of hospitalization.
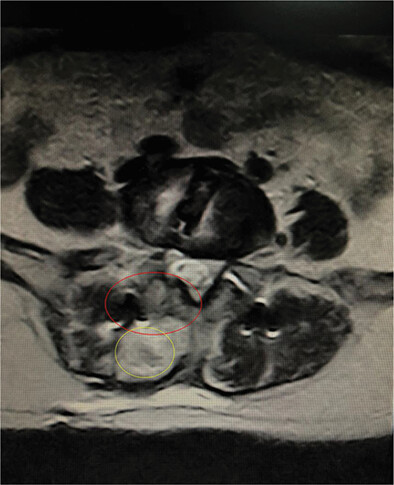
3D MRI PD-SPACE-COR Predicting Safety Margin for Coracoid Transfer
- Pages: 1514-1520
- First Published: 24 April 2023
Primary Cooperative Application of a LARS® Tube and 3D-Printed Prosthesis for Reconstruction of the Distal Radius after en bloc Resection of Giant Cell Tumor of Bone: A Comparative Retrospective Study
- Pages: 1521-1533
- First Published: 20 April 2023
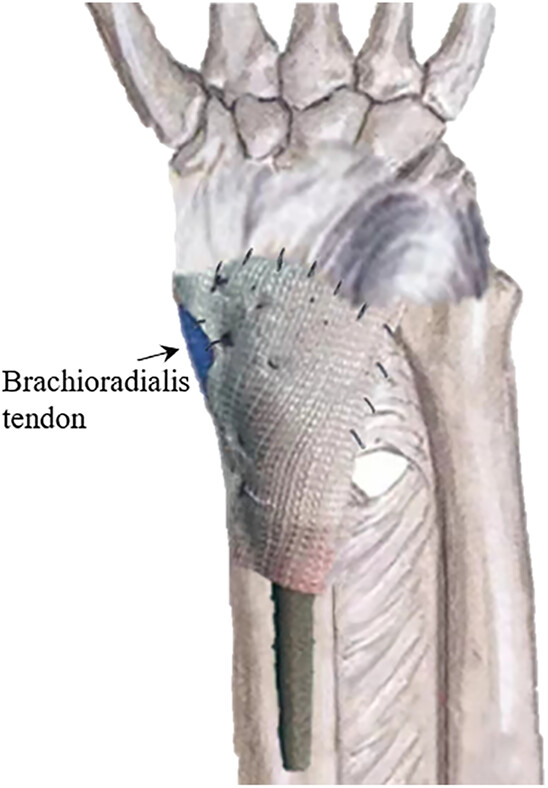
With consideration both to bone and soft tissue reconstitution, the cooperative application of LARS® and 3D-printed prostheses is an optimized modality for reconstructing musculoskeletal defects after en bloc resection of distal radial GCTBs, which can improve functional outcomes, diminish complication rates, and promote wrist stability and motion.
Analysis of the Risk Factors for Free Flap Necrosis in Soft Tissue Reconstruction of the Lower Limbs
- Pages: 1534-1540
- First Published: 24 April 2023
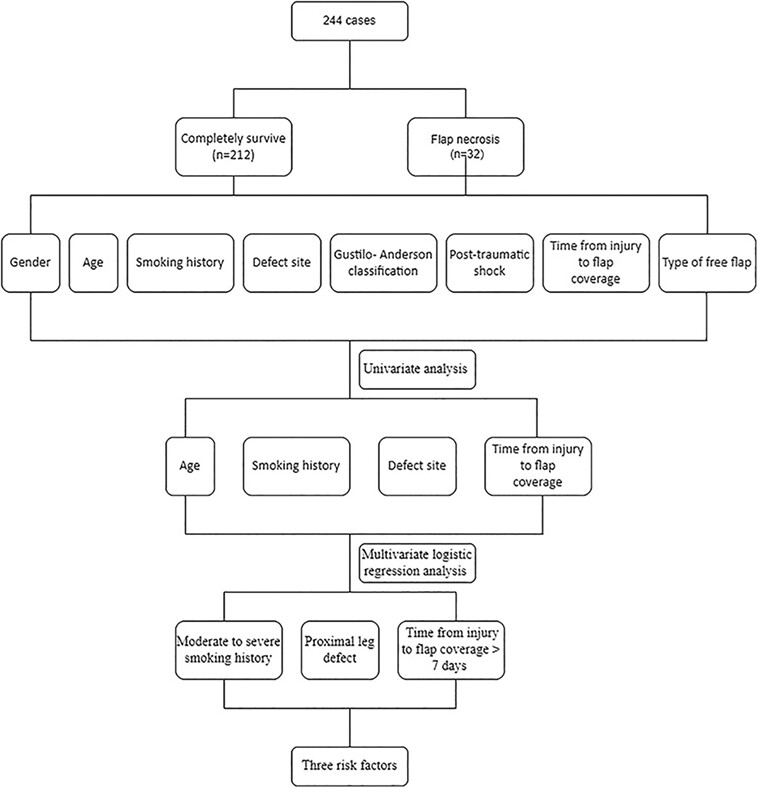
The risk of flap necrosis was significantly increased when the soft tissue defect was located in the proximal leg, the time from injury to flap coverage was >7 days, and the patient had a moderate-to-severe smoking history. These three risk factors have an increased influence on flap necrosis and have guiding significance in predicting flap prognosis.
Detection of Common Anatomical Landmarks and Vertical Trajectories for Freehand Pedicle Screw Placement
- Pages: 1541-1548
- First Published: 14 May 2023
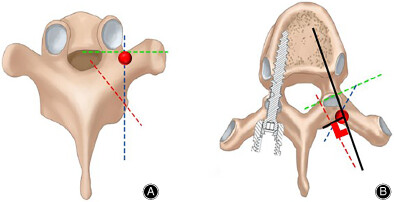
There are tens of thousands of patients with spinal deformities in our hospital. There is no universal standard and method of nail placement. This method of screw placement is a summary of the clinical experience of senior physicians, especially the laminae depression and vertical trajectory are very useful, and it is hoped that it will bring convenience to the growth of the future spinal surgery screw placement. 3D model: A: transversally probe into the injection location and the isthmic lamina or joint plane (inferior, inferior, medial, lateral, inferior, posterior lamina). B: Probe the needle point laterally and maintain a vertical trajectory. C: Maintain a vertical trajectory with the aid of a right Angle instrument (white right Angle).
Bone-to-Bone Ligament Preserving Laminoplasty with Ultrasonic Osteotome Assistance for Intraspinal Tumors: A Technical Note and Clinical Follow-Up
- Pages: 1549-1555
- First Published: 05 May 2023
Beyond Magnification and Illumination: Ergonomics with a 3D Exoscope in Lumbar Spine Microsurgery to Reduce Musculoskeletal Injuries
- Pages: 1556-1563
- First Published: 08 May 2023
Satellite Rod Fixation around Rod-fracture Area in Revision Surgery after Three-column Osteotomy for Severe Kyphoscoliosis
- Pages: 1564-1570
- First Published: 10 May 2023
Satellite rod fixation around rod-fracture area is indicated for patients in the requirement of revision surgeries due to rod fracture after 3CO. Compared with traditional revision strategies, revision surgery with satellite rods, if patients are selected adequately, is a simpler procedure with less intraoperative blood loss and shorter operating time.
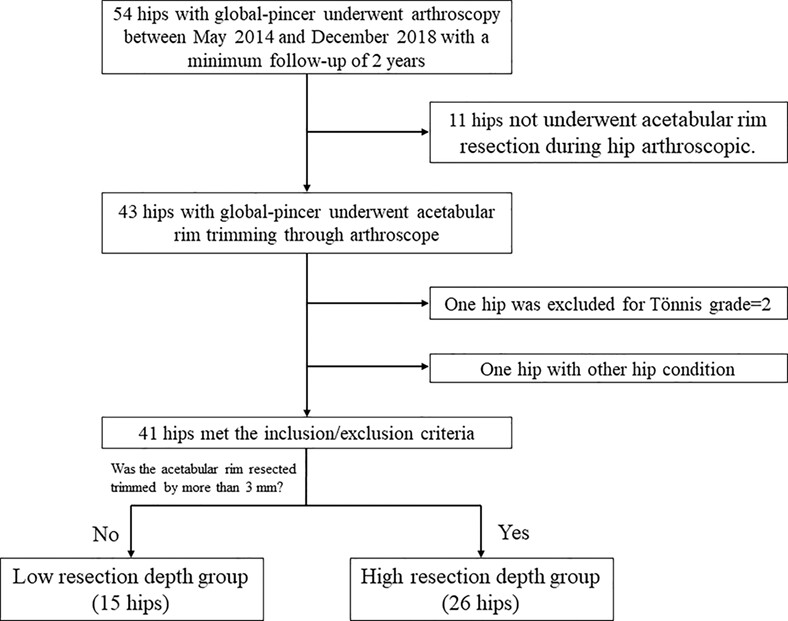
Relationship between the Depth of Acetabuloplasty and Outcomes of Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Global Pincer Femoroacetabular Impingement: Study with a Minimum Follow-Up Period of 2 Years
- Pages: 1571-1578
- First Published: 27 April 2023
Multiple Hemivertebrae: The Natural History and Treatment of 50 Patients
- Pages: 1579-1589
- First Published: 27 April 2023
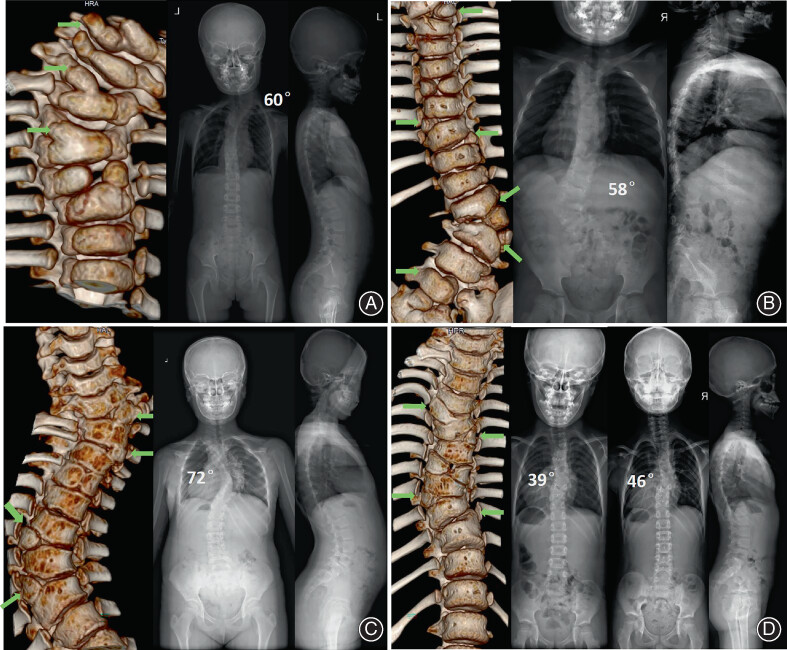
Multiple hemivertebrae (MHV) is defined as three or more hemivertebrae. Patients with MHV were divided into the unbalanced (UB) group (A), partially unbalanced (PUB) group (B, C), and completely balanced (CB) group (D). Patients with unbalanced and partially unbalanced MHV had a larger main curve than those with completely balanced MHV at the initial visit and final follow-up before surgery. All patients in the UB and PUB group met the criteria for surgery. In contrast, only 10 of 23 patients in the CB group had surgical indications. Early surgical intervention should be considered for patients with UB or PUB MHV. For patients with CB MHV, surgical treatment may not be urgently needed at the first visit.
A Novel Classification of Cervical Spine Trauma in Ankylosing Spondylitis and Corresponding Surgical Outcomes
- Pages: 1590-1598
- First Published: 02 May 2023

Based on the combination of surgical experience and follow-up observation, we innovatively proposed a new classification for cervical spine trauma in ankylosing spondylitis. For different types, the corresponding surgical methods and outcomes were also analyzed and shared, in order to offer references for clinical decision-making and academic communication.
Modified Total en Bloc Spondylectomy with Self-Made Intervertebral Hook Blade in Spinal Tumors: A Retrospective Study
- Pages: 1599-1606
- First Published: 08 May 2023
Characteristics of Sagittal Alignment in Patients with Severe and Rigid Scoliosis
- Pages: 1607-1616
- First Published: 08 May 2023
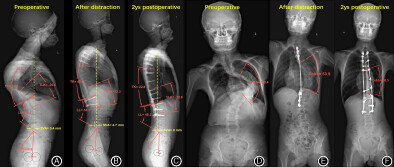
Preoperative sagittal imbalance appears in the majority of severe and rigid scoliosis patients, accounting for approximately 69%. And those patients usually present with thoracic hyperkyphosis, especially in syringomyelia-associated scoliosis. Sagittal imbalance can generally be corrected by surgery, except for patients with a pelvic incidence less than 39°. To achieve good postoperative sagittal alignment, we recommend controlling thoracic kyphosis to within 31°.
Safety and Efficacy of Cortical Bone Trajectory Screw Fixation Combined with Facet Fusion for the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disease
- Pages: 1617-1626
- First Published: 18 May 2023
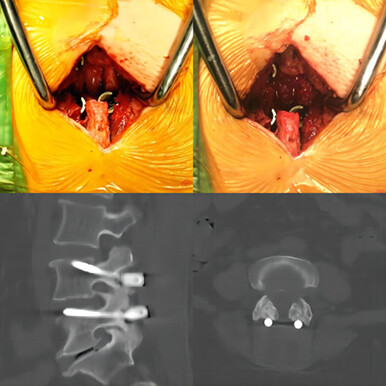
CBT screw fixation combined with FF is safe and efficacious in patients with single-level lumbar stenosis or grade I degenerative spondylolisthesis. This minimally invasive approach to lumbar fusion is simple and easy to perform. Patient recovery is faster after CBT screw fixation combined with FF than after TLIF.
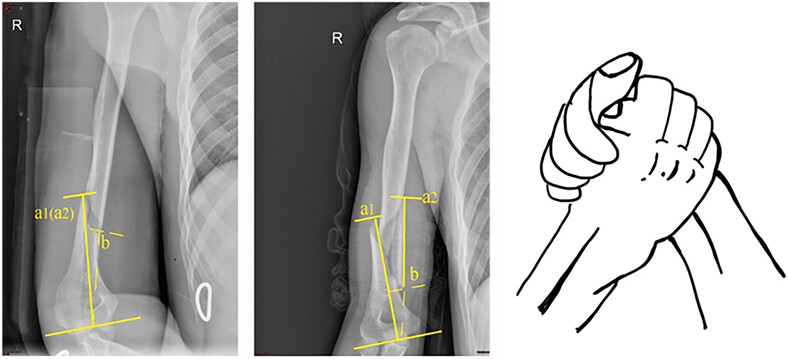
Clinical Characteristics, Mechanism, and Outcome of Humeral Shaft Fractures Sustained during Arm Wrestling in Young Men: A Retrospective Study
- Pages: 1627-1635
- First Published: 25 April 2023
Adductor Canal Block Combined with General Analgesia for Patients with Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Undergoing “3-in-1” Procedure Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
- Pages: 1636-1644
- First Published: 16 May 2023
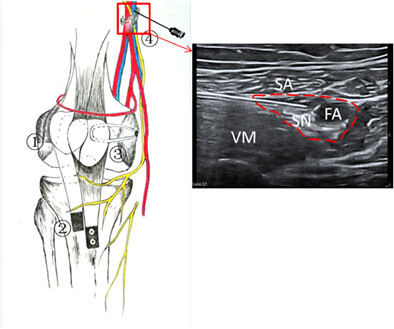
Postoperative pain of the “3-in-1” procedure surgery in RPD is acute. ACB + GA showed excellent analgesia effectiveness. Meanwhile, it was good for early rehabilitation. “3-in-1” procedure surgery with recurrent patellar dislocation and adductor canal block under ultrasound-guidance. ① Lateral patellofemoral ligament release. ② Lower-inner transfer of the tibial tuberosity. ③ Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament. ④ The operational procedure of adductor canal block:SA, sartorius; VM, vastus medialis; SN, saphenous nerve; FA, femoral artery.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Effect of Bone Cement Thickness on the Risk of Scalded Skin in Joint Surgery
- Pages: 1645-1653
- First Published: 24 April 2023
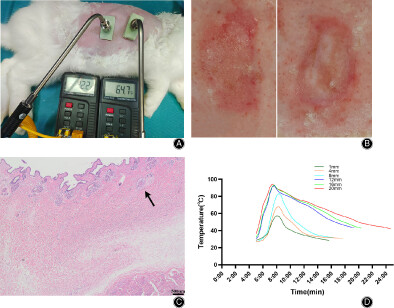
The maximum temperature and the duration of severe burns caused by different thicknesses of bone cement are different, resulting in different degrees of skin burns. For better diagnosis and treatment, surgeons should combine the clinical situation with the pathological observation of scald. Care should be taken to discard excess bone cement promptly to prevent this potential complication. (A) The measured method and instruments; (B) Appearance of skin scalded by different thicknesses of bone cement (12 mm and 16 mm); (C) Pathological features of scalded skin with bone cement, the arrow represents vacuolar degeneration of nerve fibers and hyperemia of blood vessels in the reticular layer, and collagen fiber aggregation, degeneration; (D) The change in temperature with time in different thickness of bone cement
Bilateral Idiopathic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Clinical-Functional Characterization and Efficacy of Two Combined Postoperative Physiotherapeutic Treatments
- Pages: 1654-1663
- First Published: 08 May 2023
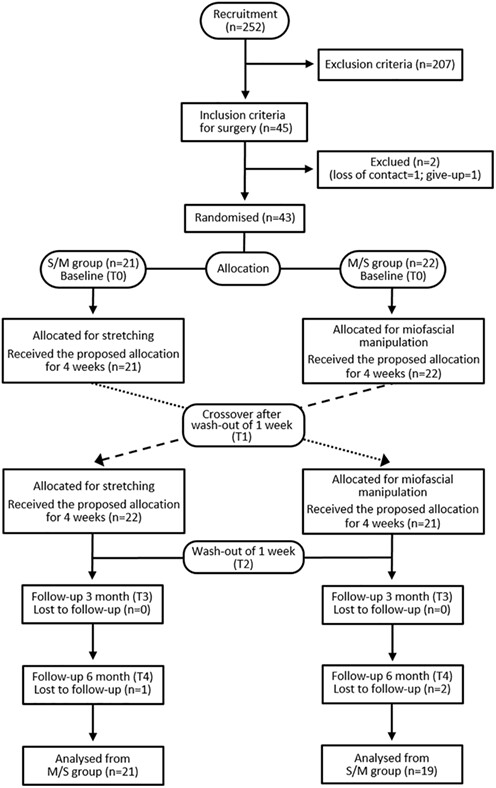
A randomized controlled crossover study with 43 participants using the objective outcome variables and the subjective variables. Patients were randomly assigned to two groups: starting with stretching followed by instrument myofascial mobilization (IASTM) and starting with IASTM followed by stretching.
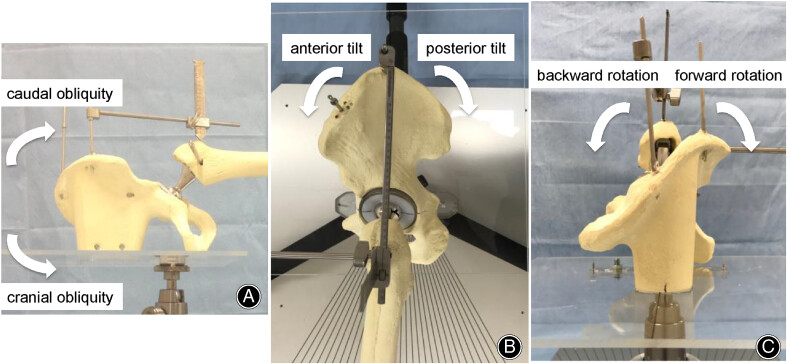
Relationship of Pelvic Positional Change with Leg Length and Offset Measurement in Experimental Total Hip Arthroplasty
- Pages: 1664-1669
- First Published: 24 April 2023
A Retrospective, Long-term Follow-up of the Clinical Outcomes and Cost-effectiveness of Single-anesthetic Multiple Total Joint Procedures in Hemophilic Arthropathy
- Pages: 1670-1676
- First Published: 05 May 2023
Hemophilic patients with simultaneous multiple total joint replacements (TJRs) had no significant increase of major complications compared to that with single TJR. Meanwhile the factors replacement therapy cost, hospital stay, and joint range of motion and function were similar in three groups at the final follow up. In our practice, simultaneous multiple TJRs is a good feasible choice for treating hemophilia patients with multiple joints are affected.
The Relation between the Dynamization of Hexapod Circular External Fixator and Tibial Mechanical Properties
- Pages: 1677-1684
- First Published: 08 May 2023

The experimental platform. A hexapod circular external fixator was fixed on the bone model by six 5 mm half-pins. The hexapod circular external fixator consisted of two rings, 12 hinges and six struts. All the struts were coded from #1 to #6. The tensile testing machine was used to apply axial extral load and the triaxial forces sensor was used to record the force condition of the silicone sample simulated the callus.
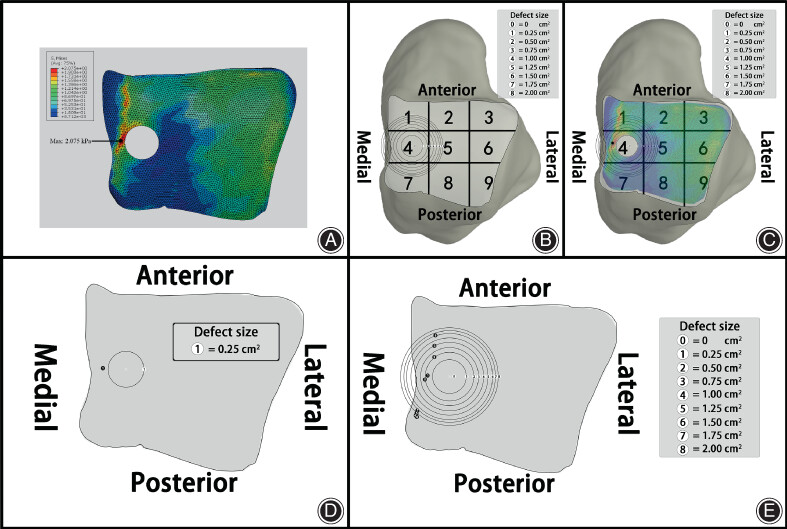
The Biomechanical Influence of Defected Cartilage on the Progression of Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: A Three-dimensional Finite Element Analysis
- Pages: 1685-1693
- First Published: 17 May 2023
CASE REPORTS
Lumbar Intradural Disc Herniation Caused by Injury: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Pages: 1694-1701
- First Published: 18 April 2023
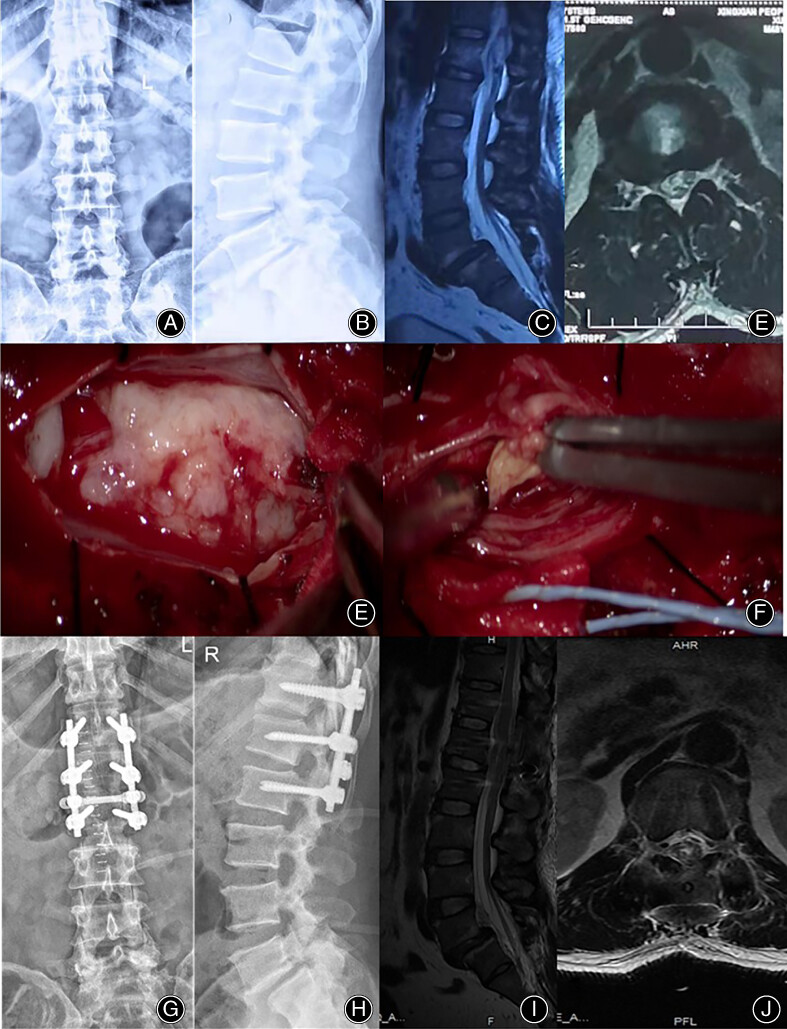
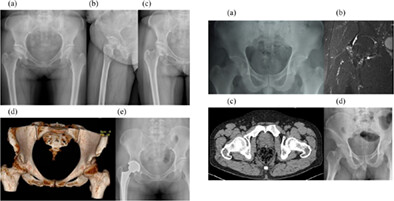
Figures A, B, C and D are preoperative data. We reported a 48-year-old male who fell from a scaffold at a height of 2 m. Later, he developed low back pain, restricted movement, numbness and hyperalgesia of the left lower limb, decreased left muscle strength. He was diagnosed as IDH. Figures E and F are preoperative data. When the dura mater was opened, a large piece of white, soft and nonvascular tissue could be seen on the dorsal side of the cauda equina nerve. White plaque-like tissue with a clear boundary and no vascular infiltration was observed between the cauda equina nerve bundles. Figures H, I, J and K are postoperative data. X-ray showing stable and effective internal fixation, and MRI showing effective decompression. His postoperative course was uneventful and followed up regularly. Good neurologic symptoms improvement was achieved. Disc herniation is a common indication for spinal surgery. When the nucleus pulposus breaks through the annulus fibrosus, posterior longitudinal ligament and dura into the dural sac, this is called intradural disc herniation (IDH), which is a rare type of intervertebral disc herniation. Intradural disc herniation is rare, and thus his treatment options are very challengeable. Accurate diagnosis and early decompression of laminae and intramedullary decompression can achieve good improvement of neurologic impingement.
Hip Pain after Distal Femoral Derotational Osteotomy for a Patient with Patellar Instability: A Case Report
- Pages: 1702-1706
- First Published: 14 April 2023
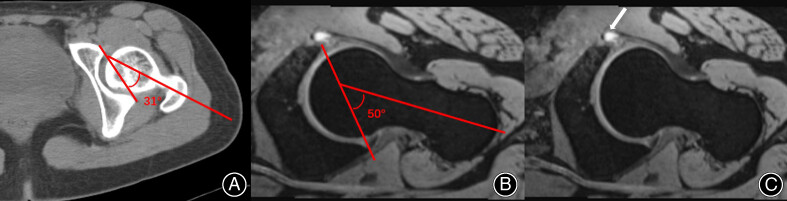
For patients with patellar instability caused by increased femoral internal torsion, we should know that derotational osteotomy may affect the hip joint simultaneously because the patients wants to correct the toe out gait by internal rotation of the hip. This may cause groin pain after derotational osteotomy, especially for active patients.
Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection of the Spine in a Patient Without Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Pages: 1707-1715
- First Published: 24 April 2023