Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front cover
- Page: i
- First Published: 04 July 2022
The Front cover image is based on the Research Article Acute high altitude hypoxia exposure causes neurological deficits via formaldehyde accumulation by Changhong Ren et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13849.
ADDITIONAL COVER
Additional Cover
- Page: ii
- First Published: 04 July 2022
The Additional cover image is based on the Research Article Which one is the superior target? A comparison and pooled analysis between posterior subthalamic area and ventral intermediate nucleus deep brain stimulation for essential tremor by Yutong Bai et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13878.
Additional Cover
- Page: ii
- First Published: 04 July 2022

The Additional cover image is based on the Review Article Perioperative neurocognitive disorders: A narrative review focusing on diagnosis, prevention, and treatment by Hao Kong et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13873.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Perioperative neurocognitive disorders: A narrative review focusing on diagnosis, prevention, and treatment
- Pages: 1147-1167
- First Published: 01 June 2022
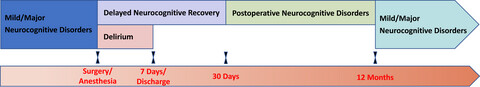
Perioperative neurocognitive disorders constitute a great challenge for older patients scheduled for surgery because their occurrence is associated with increased morbidity and mortality as well as enormous medical costs. Preoperative risk stratification and perioperative risk reduction should be adopted for perioperative NCDs prevention and treatment.
META-ANALYSIS
Pre- and post-conditioning with poly I:C exerts neuroprotective effect against cerebral ischemia injury in animal models: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1168-1182
- First Published: 05 May 2022
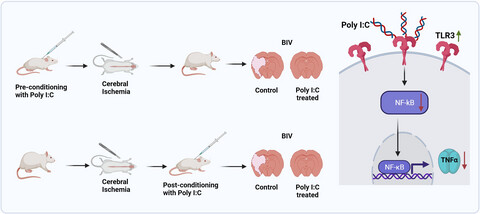
Polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) has shown promise as a neuroprotective agent in rodents with induced ischemic stroke in both adults and neonates. Previous studies have focused on either preconditioning (preC) or post-conditioning (postC) leading to ambiguity in determining the neuroprotective potential of poly I:C. This study showed a combined as well as a separate meta-analysis of preC and postC of poly I:C against cerebral ischemia (CI). Interestingly, we observed that both preC and postC offer neuroprotection against CI and act via the TLR3/NF-κB/TNF-α pathway.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Acute high-altitude hypoxia exposure causes neurological deficits via formaldehyde accumulation
- Pages: 1183-1194
- First Published: 18 May 2022
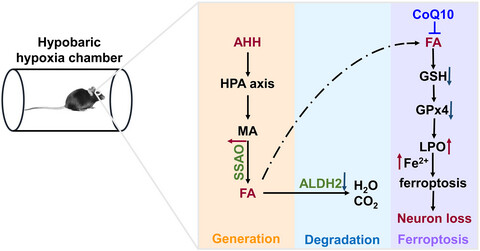
Proposed molecular mechanism of acute hypobaric hypoxia induced neurological deficits via formaldehyde accumulation. AHH, acute hypobaric hypoxia; MA, methylamine; SSAO, semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase; FA, formaldehyde; ALDH2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2; H2O, water; CO2, carbon dioxide; GSH, glutathione; GPx4, glutathione peroxidase 4; LPO, lipid peroxidation; Fe2+, ferrous iron.
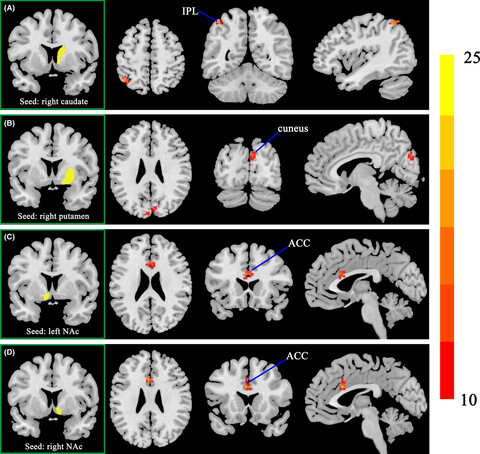
Interactions between cigarette smoking and cognitive status on functional connectivity of the cortico-striatal circuits in individuals without dementia: A resting-state functional MRI study
- Pages: 1195-1204
- First Published: 04 May 2022
Partial restoration of spinal cord neural continuity via vascular pedicle hemisected spinal cord transplantation using spinal cord fusion technique
- Pages: 1205-1217
- First Published: 12 May 2022

In this clinical trial, vascular pedicle hemisected spinal cord transplantation (vSCT), one of the spinal cord fusion clinical translation models, was demonstrated the clinical feasibility and efficacy in re-establishing the continuity of spinal nerve fibers. vSCT could provide the anatomic, morphologic, and histologic foundations to potentially restore the motor, sensory, and autonomic nervous functions in paraplegic patients.
Group-based trajectory modeling of intracranial pressure in patients with acute brain injury: Results from multi-center ICUs, 2008–2019
- Pages: 1218-1228
- First Published: 25 May 2022
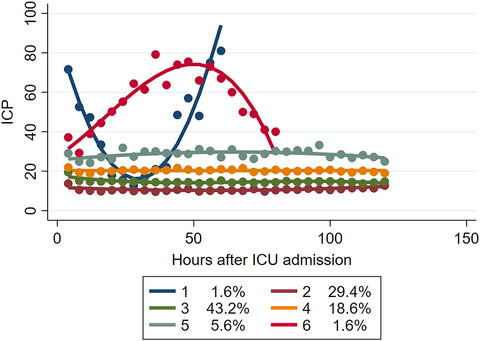
To summarize, a novel ICP trajectory that could enable us to move the treatment of ABI from a fixed threshold approach to a more individualized treatment was proposed. ICP values and variability differed across these six identified trajectory groups with favorable vs. unfavorable outcomes. The epidemiological shift toward a larger proportion of physiologically fragile elderly patients calls for more attention.
Evolution of ischemic stroke drug clinical trials in mainland China from 2005 to 2021
- Pages: 1229-1239
- First Published: 01 June 2022
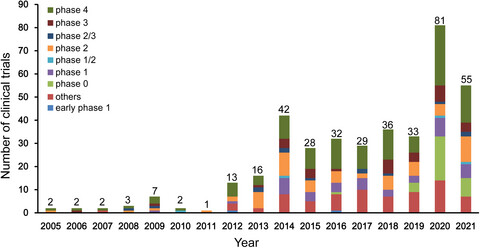
In the past 17 years, great progress has been made in the research and development of drugs and clinical trials for ischemic stroke in mainland China. Phase IV trials showed the greatest growth, with an average annual growth rate of 27.8%. The most extensive progress was observed in TCMs, antithrombotic therapy, and cerebral protection agents. This is the first study to depict the evolution of acute ischemic stroke drug clinical trials in mainland China in 2005–2021.
Prior statin and short-term outcomes of primary intracerebral hemorrhage: From a large-scale nationwide longitudinal registry
- Pages: 1240-1248
- First Published: 23 May 2022
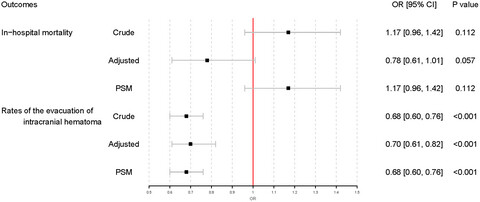
The relationship between statins and intracerebral hemorrhage outcomes is unclear. We aimed to compare the in-hospital mortality and the rates of evacuation of intracranial hematoma in patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage between prior statins users and non-users. A retrospective study was conducted and data were derived from the Chinese Stroke Center Consortium (CSCA). Patients aged 50 years or older with a diagnosis of primary intracerebral hemorrhage were included. Demographic data, medical history, NIHSS, and Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score were collected. Outcome measures included death at discharge and evacuation of intracranial hematoma. Multivariable logistic regression analyses and propensity score matching analyses were used to investigate the relationship between prior statins use and the clinical outcomes. The final study population included 66,263 patients. Multivariable logistics analyses showed that prior statins use was not associated with in-hospital mortality for primary intracerebral hemorrhage (adjusted OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.61–1.01), but reduced the proportion of patients undergoing evacuation of intracranial hematoma (adjusted OR 0.70, 95% CI 0.61–0.82), and propensity score matching analyses yielded similar results. Prior statins use is not associated with in-hospital mortality, but reduced the rates of evacuation of intracranial hematoma.
Long-term functional prognosis and related factors of spinal cord stimulation in patients with disorders of consciousness
- Pages: 1249-1258
- First Published: 20 May 2022
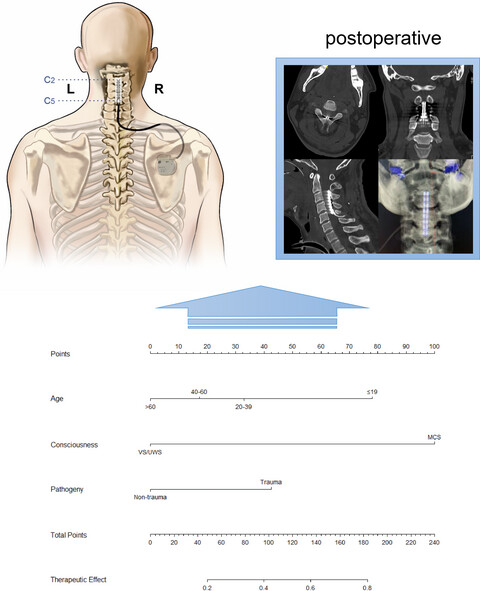
With developments in neurocritical care, the number of patients with disorders of consciousness (DoC) is rapidly growing but the treatment remains challenging. The paper explores the efficiency of SCS in treating patients with DoC at different consciousness levels and summarizes the long-term functional prognosis and related factors of SCS in patients with DoC.
SUMOylation of Kir7.1 participates in neuropathic pain through regulating its membrane expression in spinal cord neurons
- Pages: 1259-1267
- First Published: 27 May 2022
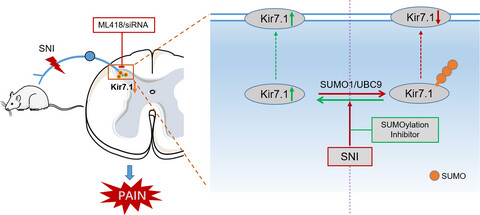
SNI markedly decreased the expression of Kir7.1 and upregulated SUMOylated-Kir7.1 in the spinal dorsal horn accompanied by mechanical hypersensitivity. Blocking Kir7.1 with the specific antagonist or knockdown kir7.1 by siRNA led to mechanical allodynia. Moreover, inhibited SUMOylation can increase the spinal surface Kir7.1 expression. SUMOylation of the Kir7.1 in spinal cord might contribute to the development of SNI-induced mechanical allodynia by decreasing the Kir7.1 surface expression in rats.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
The effect of cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212–2 on anxiety-like behavior and locomotion in a genetic model of absence seizures in the elevated plus-maze
- Pages: 1268-1270
- First Published: 26 April 2022