Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 16 October 2020
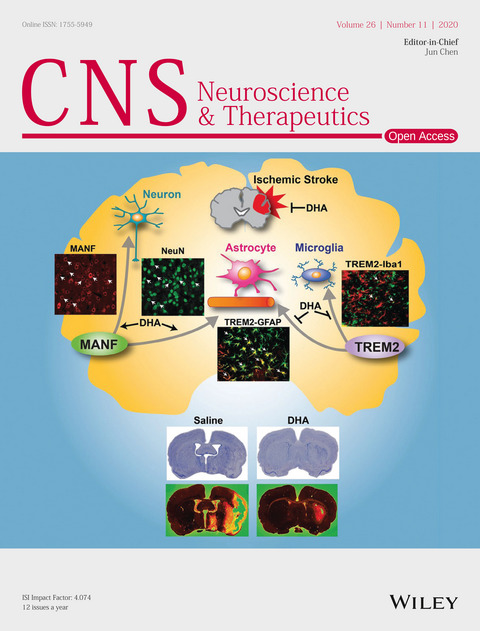
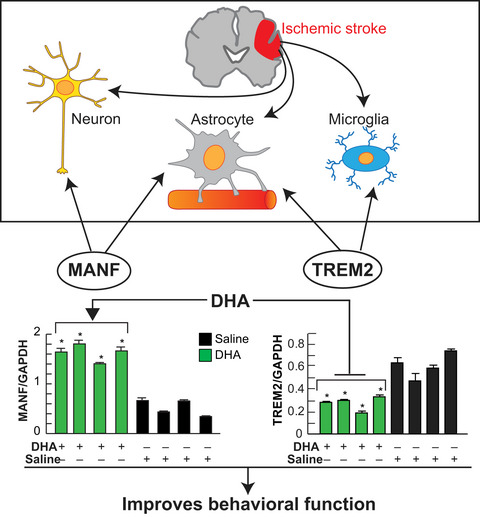
The cover image is based on the Original Article DHA modulates MANF and TREM2 abundance, enhances neurogenesis, reduces infarct size, and improves neurological function after experimental ischemic stroke by Ludmila Belayev et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13444.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Pharmaco-genetic inhibition of pyramidal neurons retards hippocampal kindling-induced epileptogenesis
- Pages: 1111-1120
- First Published: 28 June 2020
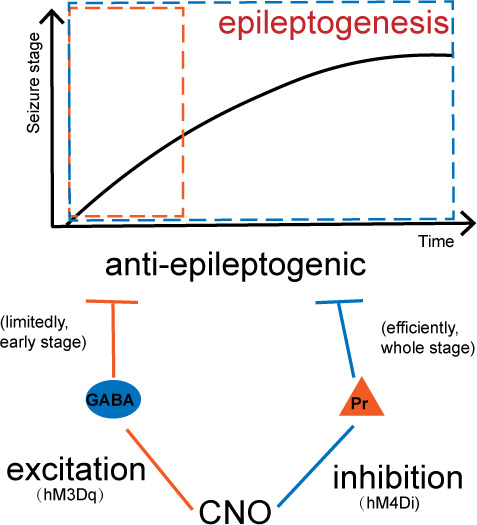
Pharmaco-genetic activating parvalbumin neurons of the seizure focus limitedly retarded the progression of behavioral seizure stage and afterdischarge duration (ADD) during epileptogenesis in hippocampal kindling mice. On the contrary, Pharmaco-genetic inhibiting pyramidal neurons of the seizure focus robustly retarded epileptogenesis.
Dopamine neurons in the ventral periaqueductal gray modulate isoflurane anesthesia in rats
- Pages: 1121-1133
- First Published: 02 September 2020
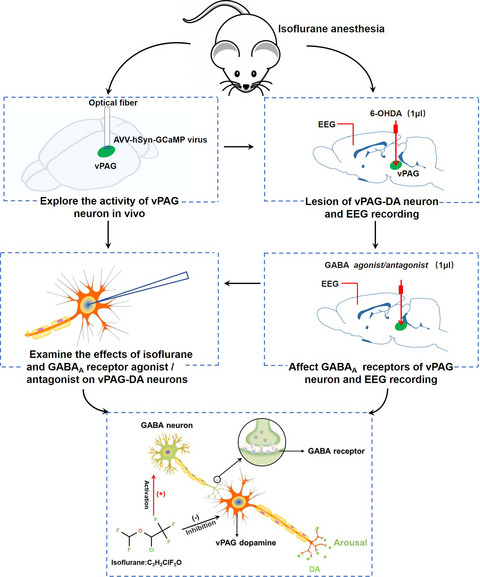
General anesthesia has been widely applied in surgery for more than 170 years. However, its underlying mechanisms are still a mystery. It was reported that dopaminergic pathways in the brain are crucial for the emergence from general anesthesia. We previously also found that reductions of ventral periaqueductal gray (vPAG) dopaminergic neurons numbers shortened the induction time and prolonged the emergence time from propofol anesthesia. However, the role of GABAA receptor in ventral periaqueductal gray (vPAG) dopamine (DA) neurons in the isoflurane-induced unconsciousness has yet to be identified. Here, using real time in vivo fiber photometry, we found that neuronal activity in the vPAG was markedly disinhibited during the recovery from isoflurane anesthesia. Subsequently, microinjection of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) into the vPAG to selectively kill DA neurons shortened the induction time and prolonged the emergence time, with an increase of δ-band power in cortical electroencephalogram (EEG). Then, microinjection of GABAA receptor selective agonist (muscimol) into the vPAG notably accelerated the induction of anesthesia and delayed recovery from isoflurane anesthesia, with a decrease of δ power and an augment of β power. Microinjection of GABAA receptor antagonist (gabazine) generated the opposite effects. Finally, whole-cell patch clamp was applied to further explore the cellular mechanism underlying modulation of GABAA receptor on vPAG-DA neurons under isoflurane anesthesia. Our data demonstrated that the frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSC) of vPAG-DA neurons was enhanced by isoflurane. GABAA receptor agonist enhanced the effect of isoflurane on sIPSC, and its actions were eliminated by application of gabazine. Collectively, these results indicate that isoflurane activates GABAA receptor to affect GABA neuron and vPAG-DA neurons. Then, isoflurane directly suppressed the activity of wake-promoting vPAG-DA neurons to induce anesthesia or activate GABA neuron to indirectly inhibit vPAG-DA neurons causing the reduction of DA. Our results suggest that vPAG-DA neurons are involved in isoflurane anesthesia through activation of the GABAA receptor.
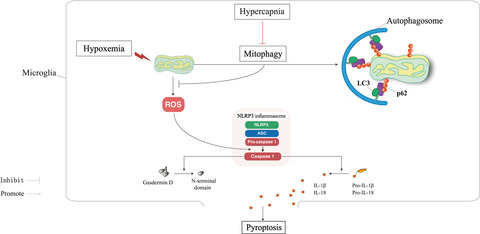
Hypercapnia promotes microglial pyroptosis via inhibiting mitophagy in hypoxemic adult rats
- Pages: 1134-1146
- First Published: 14 July 2020
B3GNT5 is a novel marker correlated with stem-like phenotype and poor clinical outcome in human gliomas
- Pages: 1147-1154
- First Published: 16 July 2020
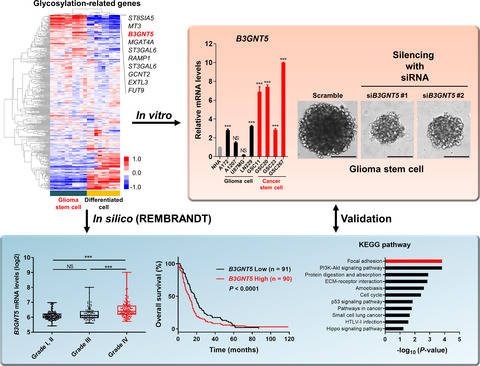
Expression of B3GNT5, the key glycosyltransferase in the biosynthesis of the glycosphingolipid, was significantly elevated in GSCs compared with normal astrocytes, glioma cell lines, and their matched differentiated tumor cells. Knockdown of B3GNT5 in GSCs decreased the neurosphere formation. Patients with high B3GNT5 expression had a short overall survival.
DHA modulates MANF and TREM2 abundance, enhances neurogenesis, reduces infarct size, and improves neurological function after experimental ischemic stroke
- Pages: 1155-1167
- First Published: 05 August 2020
Evaluation of a tumor electric field treatment system in a rat model of glioma
- Pages: 1168-1177
- First Published: 30 July 2020
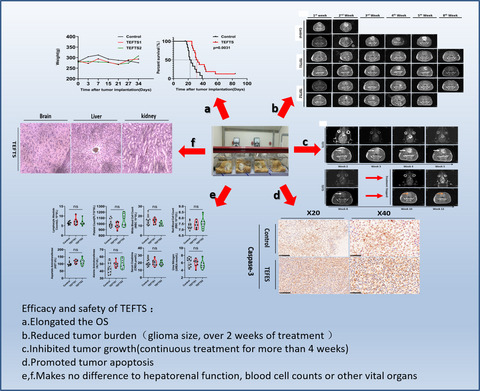
The self-designed TEFTS was proved to be effective and safe to inhibit tumor growth and improve general outcomes of Glioma.The instrument with random sequential electric field direction and adjustable intensity and frequency can apply electric field to the rapidly proliferating tumor cells from all directions in order to achieve the best curative effects.
Variants of genes encoding TNF receptors and ligands and proteins regulating TNF activation in familial multiple sclerosis
- Pages: 1178-1184
- First Published: 20 September 2020
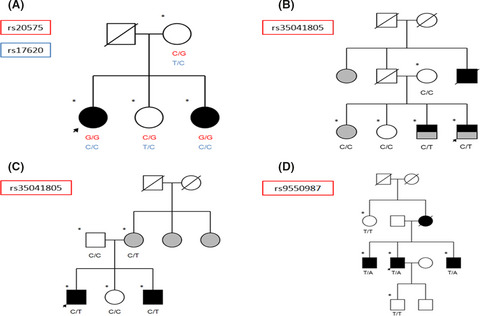
Pathways affecting TNF-α are involved in immune signaling. Whole-exome sequencing in 116 members of 19 families including at least two patients with multiple sclerosis was performed. Several nonsynonymous variants in TNF-α pathways were found. The findings support the idea that the risk of familial MS is associated with variants of TNF-α signaling pathways.
META-ANALYSIS
Efficacy of pharmacotherapeutics for patients comorbid with alcohol use disorders and depressive symptoms—A bayesian network meta-analysis
- Pages: 1185-1197
- First Published: 19 July 2020
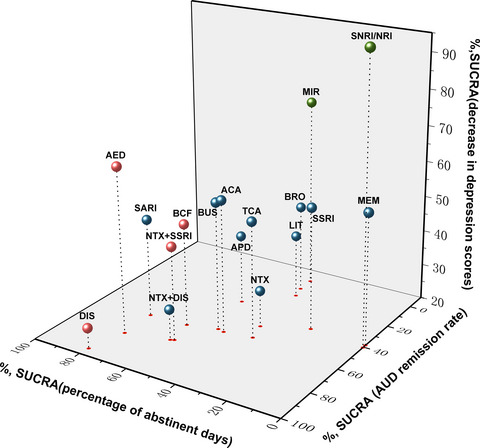
The present study conducts a Bayesian network meta-analysis to compare the efficacy of different pharmacotherapies for patents comorbid with alcohol use disorders and depressive symptoms. Disulfiram was associated with the best efficacy in achieving abstinence, noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor was demonstrated to be the best choice to reduce the scores of depression scales, and antiepileptics might be beneficial to both alcohol-related and depressive symptoms.