Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Image:
- Page: C1
- First Published: 08 July 2021
Cover Caption: Wang et al. (page 1367-1381) report a structure of photosystem I from a higher plant at the highest resolution achieved so far. On the cover: The structure of the PSI-LHCI supercomplex with a view from the stromal side. Novel lipids were found in the gap region and they mediate interactions between the core and antenna. Lhca4 was found to be fl exible, which may moderate energy transfer from LHCIs to PSI core.
Issue information page
Invited Expert Review
From genes to networks: The genetic control of leaf development
- Pages: 1181-1196
- First Published: 21 February 2021
Reviews
Exploring the diversity of plant proteome
- Pages: 1197-1210
- First Published: 02 March 2021
An update on the function and regulation of methylerythritol phosphate and mevalonate pathways and their evolutionary dynamics
- Pages: 1211-1226
- First Published: 04 February 2021
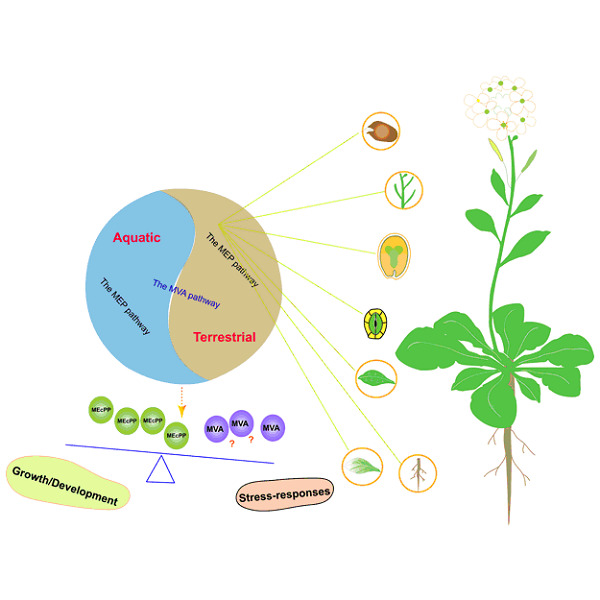
In this review, we summarize recent advances in understanding the roles of the methylerythritol phosphate and mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis pathways in plant growth, development, and stress responses, with an emphasis on emergence of the mevalonate pathway in plants and how it may have facilitated plant adaptation to terrestrial environments.
New Technology
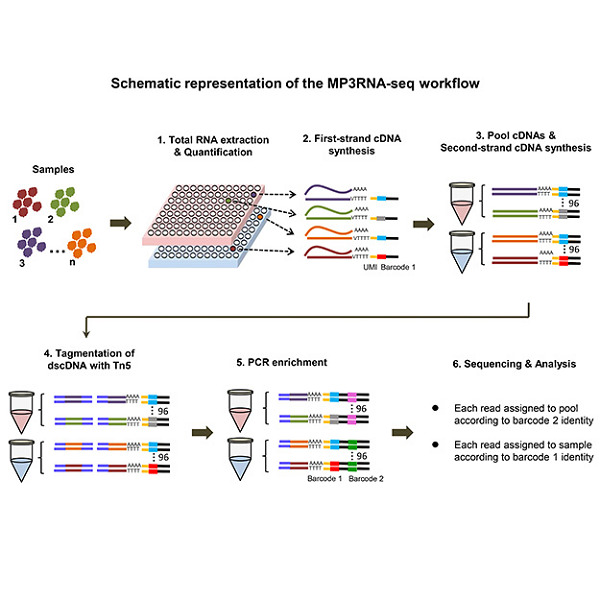
MP3RNA-seq: Massively parallel 3′ end RNA sequencing for high-throughput gene expression profiling and genotyping
- Pages: 1227-1239
- First Published: 09 February 2021
Cell and Developmental Biology
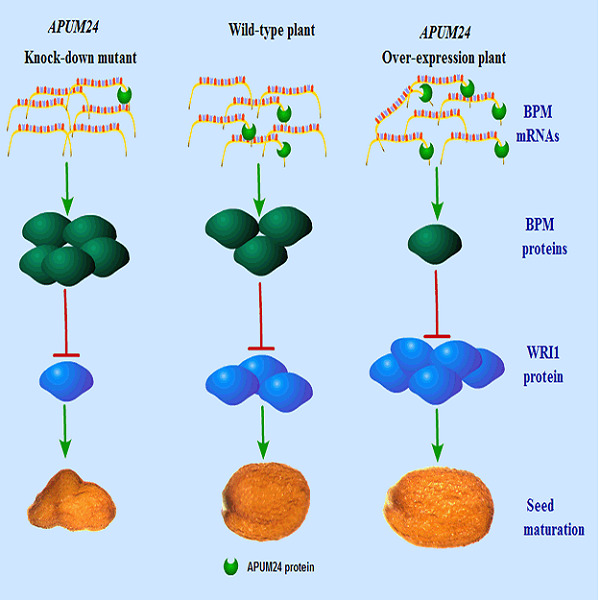
The Pumilio RNA-binding protein APUM24 regulates seed maturation by fine-tuning the BPM-WRI1 module in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 1240-1259
- First Published: 17 March 2021
MiR319-targeted OsTCP21 and OsGAmyb regulate tillering and grain yield in rice
- Pages: 1260-1272
- First Published: 10 April 2021
Functional Omics and Systems Biology
Phylotranscriptomic insights into Asteraceae diversity, polyploidy, and morphological innovation
- Pages: 1273-1293
- First Published: 09 February 2021
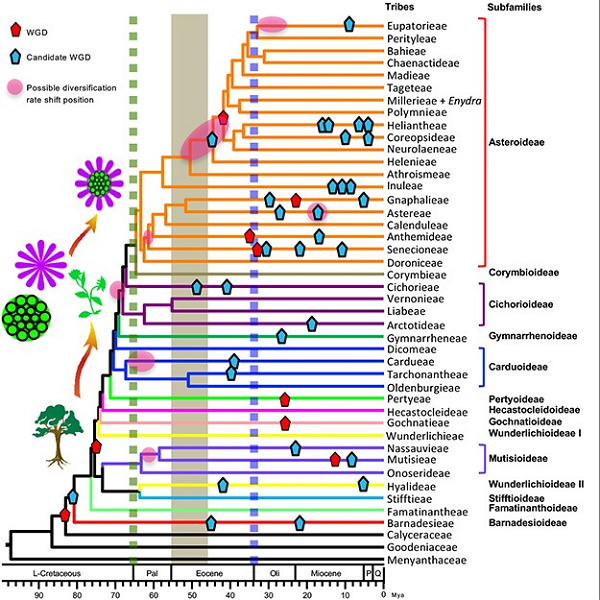
The sunflower family (Asteraceae, >26,000 species) is among the largest and most diverse plant families, but has vastly different species numbers among subfamilies. Molecular evolutionary analyses of 244 genome-wide datasets provide improved understanding of Asteraceae relationships and suggest links among global climate shifts, whole-genome duplications, morphological evolution and increased diversity.
Genome-wide profiling of circular RNAs, alternative splicing, and R-loops in stem-differentiating xylem of Populus trichocarpa
- Pages: 1294-1308
- First Published: 11 February 2021
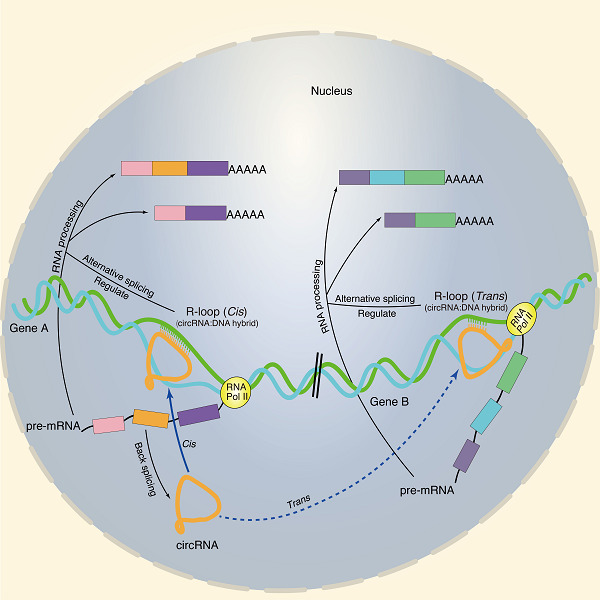
Examination of circular RNAs in stem-differentiating xylem of Populus trichocarpa by integration of multi-omics data, including RNase R-treated RNA sequencing, DNA:RNA hybrid immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (DRIP-seq), and PacBio long-read isoform sequencing reveals circular RNAs associated with R-loop structures in regulating alternative splicing.
Insights into salvianolic acid B biosynthesis from chromosome-scale assembly of the Salvia bowleyana genome
- Pages: 1309-1323
- First Published: 26 February 2021
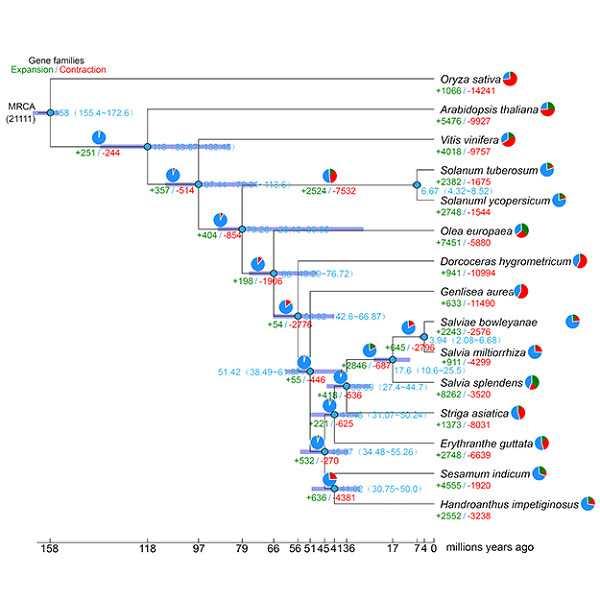
Deeper understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying salvianolic acid B biosynthesis and the evolution of the Labiatae would greatly benefit from a better genome assembly. Our findings provide a valuable genomic resource for understanding salvianolic acid B biosynthesis, and will be useful for exploring the evolution of the Labiatae.
Molecular Physiology
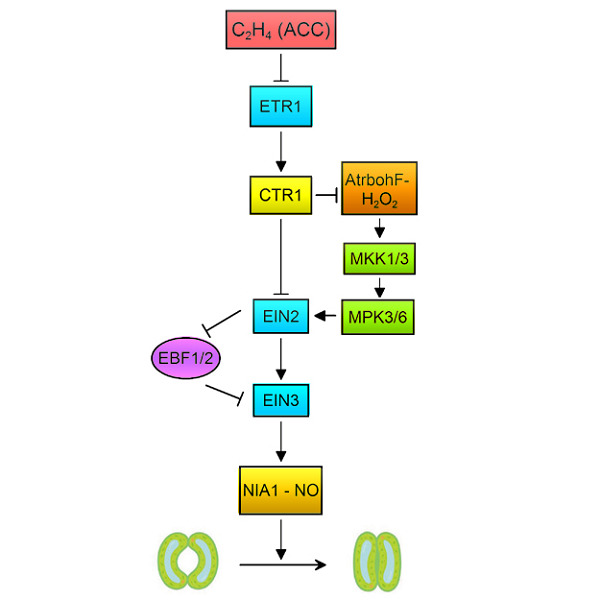
Ethylene-induced stomatal closure is mediated via MKK1/3–MPK3/6 cascade to EIN2 and EIN3
- Pages: 1324-1340
- First Published: 19 February 2021
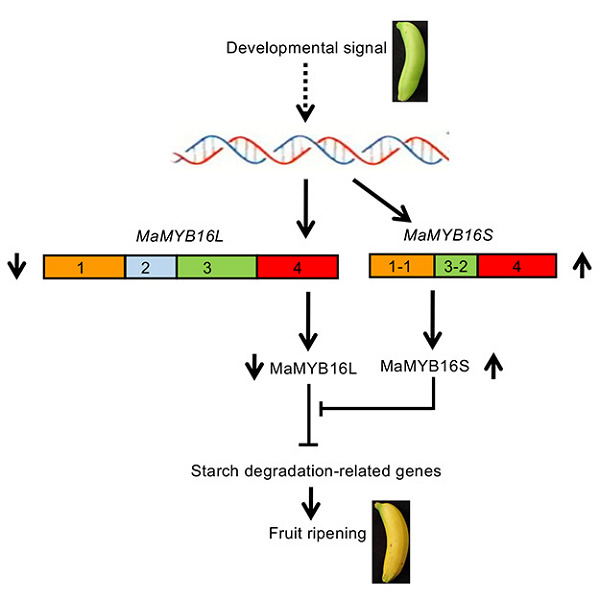
Alternative splicing of MaMYB16L regulates starch degradation in banana fruit during ripening
- Pages: 1341-1352
- First Published: 03 March 2021
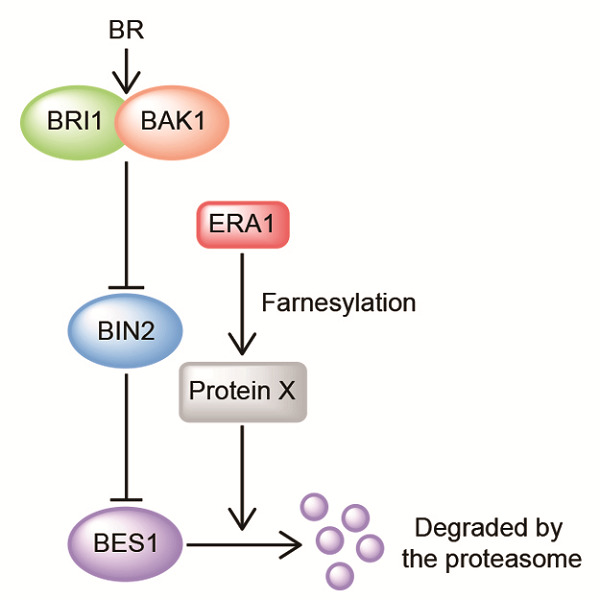
Protein farnesylation negatively regulates brassinosteroid signaling via reducing BES1 stability in Arabidopsis thaliana
- Pages: 1353-1366
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Photosynthesis and Crop Physiology
Structure of plant photosystem I−light harvesting complex I supercomplex at 2.4 Å resolution
- Pages: 1367-1381
- First Published: 31 March 2021
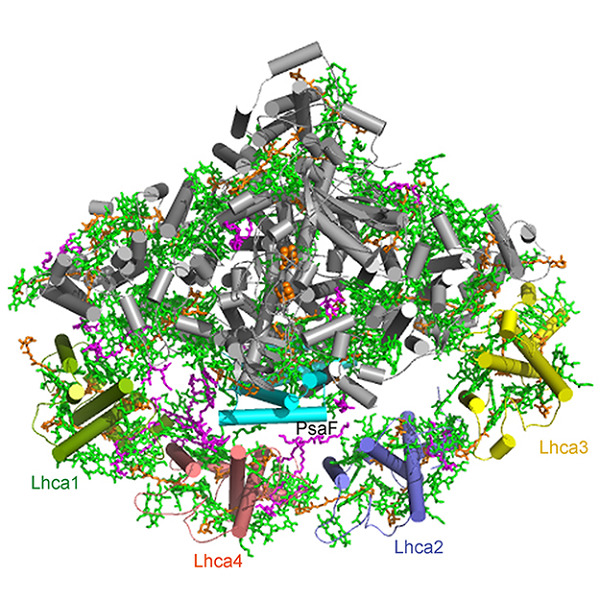
Analysis of the crystal structure of the photosystem I-light harvesting complex I supercomplex from pea (Pisum sativum) at 2.4 Å resolution revealed the shift of Lhca4 away from the photosystem I core and the presence of five new lipids that are important for assembly and energy transfer in this supercomplex.
Plant-biotic Interactions
The Phytophthora effector Avh241 interacts with host NDR1-like proteins to manipulate plant immunity
- Pages: 1382-1396
- First Published: 15 February 2021
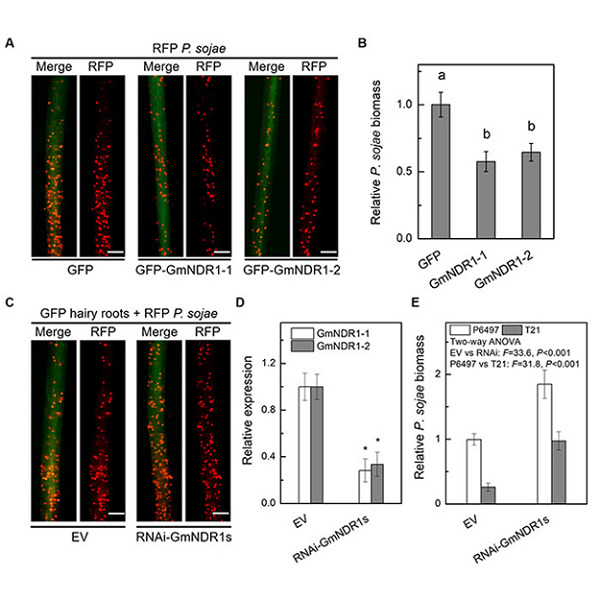
The RxLR effector Avh241 from Phytophthora sojae targets soybean Nonrace specific disease resistance 1 (GmNDR1) protein in the plasma membrane to contribute to pathogen virulence. GmNDR1 interacts with itself, and Avh241 probably disrupts GmNDR1 self-association, thus suppressing NDR1-dependent plant immunity.