Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Aluminum Nanocrystals: Sub-3 nm Aluminum Nanocrystals Exhibiting Cluster-Like Optical Properties (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021

Ultrasmall aluminum nanocrystals (<3 nm) with cluster-like optical properties are prepared with a simple and robust synthetic chemical method in article number 2002524 by Xiaoyu Cheng, Sailing He, and co-workers. Phosphonic acids are used to surface-modify and stabilize aluminum nanocrystals in solution. Ultrasmall aluminum nanocrystals exhibit bright photoluminescence in the ultraviolet range, and their lifetime is ultrashort and wavelength-dependent.
Inside Front Cover
Chemically Modified Superatoms: Toward Controlling the Electronic Structures of Chemically Modified Superatoms of Gold and Silver (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021
Ligand-protected Ag/Au clusters showing novel properties can be viewed as chemically modified superatoms in terms of the electronic structures. In article number 2001439, Tatsuya Tsukuda and co-workers summarize the current understanding on the correlation between the electronic structures and key structural factors of the superatoms such as size, shape, and composition toward better control of the properties.
Inside Back Cover
Gold Nanoclusters: Atomically Precise Gold Nanoclusters: Towards an Optimal Biocompatible System from a Theoretical–Experimental Strategy (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021

In article number 2005499, María Francisca Matus and Hannu Häkkinen discuss the recent advances for using atomically precise gold nanoclusters for biomedical applications and their advantages over the well-known colloidal gold nanoparticles. The ultrasmall size and monodispersity of gold nanoclusters are key factors for their excellent biocompatibility and show great potential for designing a new generation of nanomaterials for biomedicine.
Back Cover
Ligand Exchange: Metal Nanoparticles Confronted with Foreign Ligands: Mere Ligand Exchange or Further Structural Transformation? (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021

In article number 2000609, Zhikun Wu and co-workers first propose that stability is one key factor determining the ligand exchange reaction direction of metal nanoparticles (whether mere ligand exchange or further structural transformation occurs) and afford structure evidence for an SN1-like ligand exchange mechanism.
Masthead
Guest Editorial
Special Issue on “Nanoclusters”: A Glimpse into the Efforts to Redefine Matter at the Nanoscale
- First Published: 08 July 2021
Reviews
Toward Controlling the Electronic Structures of Chemically Modified Superatoms of Gold and Silver
- First Published: 21 July 2020
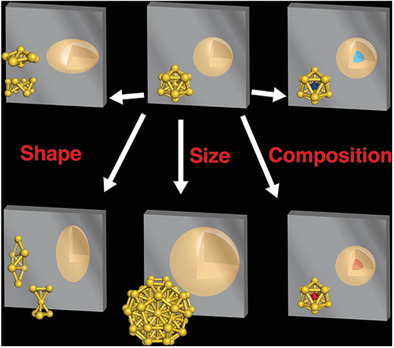
Ligand-protected Ag/Au clusters showing novel properties can be viewed as chemically modified superatoms in terms of the electronic structures. This review summarizes the current understanding on the correlation between the electronic structures and key structural factors of the superatoms such as size, shape, and composition toward better control of the properties.
Magic-Sized Stoichiometric II–VI Nanoclusters
- First Published: 09 November 2020
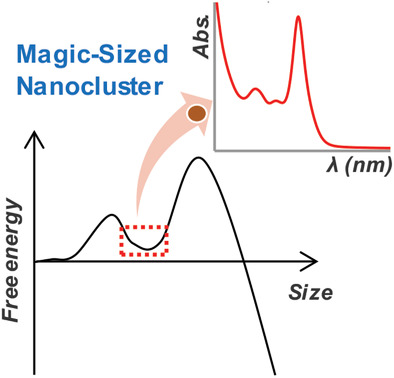
The synthesis, isolation, and atomic structure characterization of the magic-sized semiconductor nanoclusters are essential to evaluate the nucleation and growth mechanisms of the nanocrystals. Recent advances on the chemical synthesis, photophysical, and chemical properties of stoichiometric II–VI semiconductor nanoclusters are reviewed. Important challenges in this research area and possible pathways to tackle them are discussed.
Frontispiece
Metal Nanoclusters: Thiolate-Protected Metal Nanoclusters: Recent Development in Synthesis, Understanding of Reaction, and Application in Energy and Environmental Field (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021

In article number 2005328, Yuichi Negishi and co-workers describe recent progress in the field of thiolate (SR)-protected metal nanoclusters in three areas: synthesis, understanding, and application. The challenges that must be overcome for further development in this field and the possibilities that SR-protected metal NCs can contribute to solving the problems facing modern society are also discussed in this review.
Reviews
Thiolate-Protected Metal Nanoclusters: Recent Development in Synthesis, Understanding of Reaction, and Application in Energy and Environmental Field
- First Published: 01 February 2021
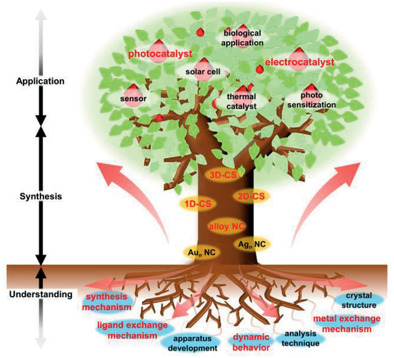
This review describes recent development in the field of thiolate (SR)-protected metal nanoclusters (NCs) in three areas: synthesis, understanding, and application. The challenges that must be overcome for further development in this field and the possibilities that SR-protected metal NCs can contribute to solving the problems facing modern society are also discussed.
Self-Assembly of Precision Noble Metal Nanoclusters: Hierarchical Structural Complexity, Colloidal Superstructures, and Applications
- First Published: 25 January 2021
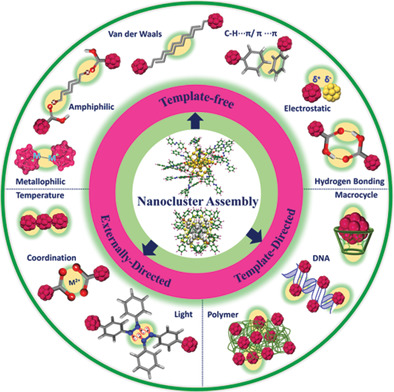
Precision noble metal nanoclusters represent fascinating colloidal-level molecular building blocks. They display hierarchical structural complexity and offer rich surface functionalities. By systematic ligand design and assembly conditions, structurally and functionally diverse supracolloidal structures with advanced optoelectronic, catalytic, nanotherapeutic, and imaging applications are achieved.
Ligand Design in Ligand-Protected Gold Nanoclusters
- First Published: 28 January 2021
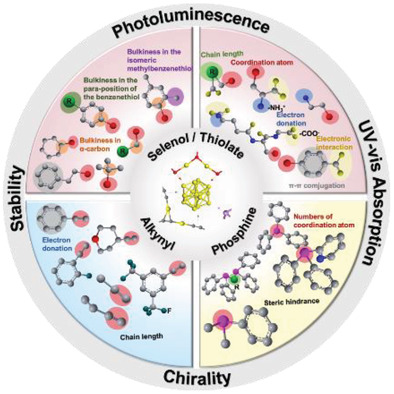
Surface ligands are crucial for ligand-protected gold nanoclusters (Au NCs) because they can not only protect the Au NCs, but also determine their physicochemical properties. The effects of ligands on the synthesis, structure, and properties of ligand-protected Au NCs are discussed systematically, highlighting the principles of ligand design of Au NCs for various emerging applications.
Operando Surface Spectroscopy and Microscopy during Catalytic Reactions: From Clusters via Nanoparticles to Meso-Scale Aggregates
- First Published: 10 March 2021
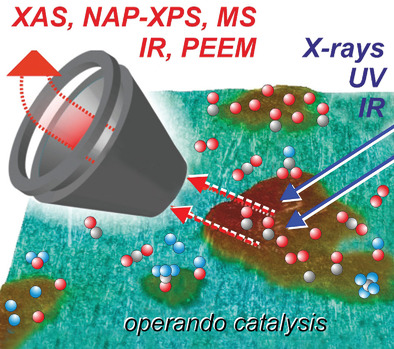
Operando surface spectroscopy and microscopy enable molecular level insight into ongoing catalytic reactions. Employing X-ray, photoelectron and infrared based spectroscopy, the active catalyst state can be determined, including reaction-induced changes. Cluster and nanoparticle restructuring, atom/ligand mobility and surface composition alterations have pronounced effects on catalytic performance. Surface microscopy directly reveals how reactions initiate and spatially evolve.
Concepts
Atomically Precise Gold Nanoclusters: Towards an Optimal Biocompatible System from a Theoretical–Experimental Strategy
- First Published: 02 February 2021
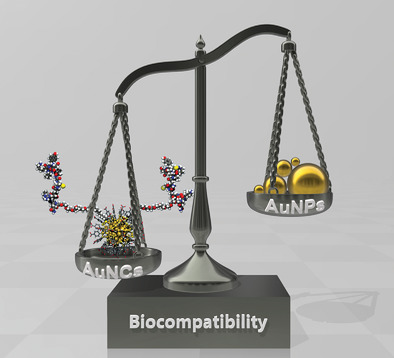
Atomically precise gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) have helped revolutionize nanomedicine's field due to their excellent biocompatibility and extraordinary physicochemical properties. They have emerged as promising materials to overcome the current challenges of cytotoxicity and biostability present in colloidal gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Although this revolution is still in its infancy, theoretical/experimental strategies show that the near future is promising!
Cocrystals of Atomically Precise Noble Metal Nanoclusters
- First Published: 13 November 2020
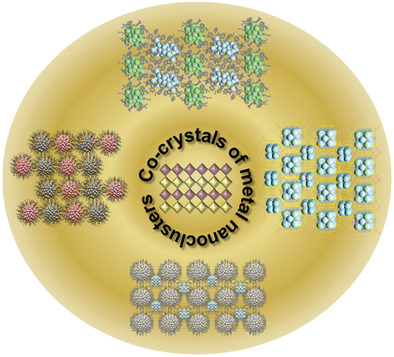
Cocrystallization encompasses the study of multicomponent crystalline solids as well as their design principles. This Concept presents recent advancements in the cocrystallization of atomically precise noble metal cluster systems. The concept of cocrystallization of structurally similar atomically precise nanoclusters, leading to new solids by different approaches is demonstrated.
Communications
Sub-3 nm Aluminum Nanocrystals Exhibiting Cluster-Like Optical Properties
- First Published: 18 August 2020
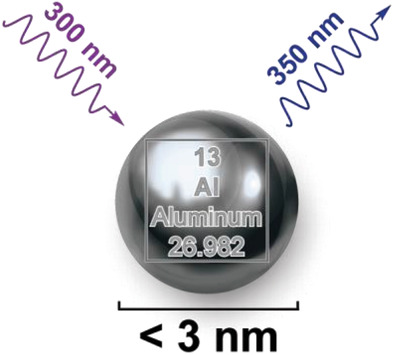
Ultrasmall aluminum nanocrystals (<3 nm) with cluster-like optical properties are prepared with a simple and robust synthetic chemical method. Phosphonic acids are used to surface-modify and stabilize aluminum nanocrystals in solution. Ultrasmall aluminum nanocrystals exhibit bright photoluminescence in the ultraviolet range, and their lifetime is ultrashort and wavelength-dependent.
Metal Nanoparticles Confronted with Foreign Ligands: Mere Ligand Exchange or Further Structural Transformation?
- First Published: 30 July 2020
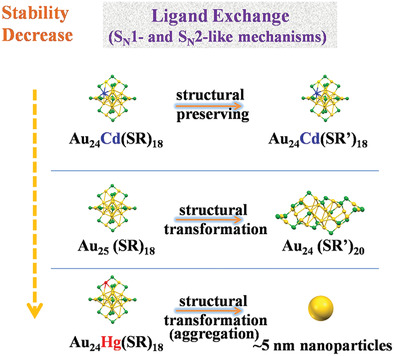
Herein, it is proposed that the intrinsic stability is one key factor determining the ligand exchange reaction direction of metal nanoparticles (whether mere ligand exchange or further structural transformation occurs). Single crystal X-ray crystallography further reveals that the partial surface ligand configuration reverses after ligand exchange, first providing structure evidence for the unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1)-like mechanism.
Isolation and Structural Elucidation of 15-Nuclear Copper Dihydride Clusters: An Intermediate in the Formation of a Two-Electron Copper Superatom
- First Published: 28 October 2020
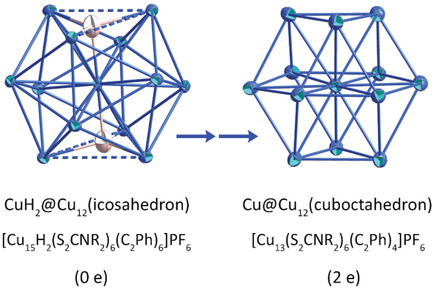
A 15-nuclear copper dihydride cluster [Cu15(H)2(S2CNR2)6(C2Ph)6](PF6) (1) containing a linear [CuH2]− complex embedded in a [Cu14]14+ cage is isolated and structurally characterized. This cluster readily converts to a two-electron superatom cluster [Cu13]11+ at elevated temperatures. Highly luminescent [AuCu12(S2CNR2)6(C2Ph)4]+ cluster is isolated by reacting 1 with Au(I) salts.
[Cu15(PPh3)6(PET)13]2+: a Copper Nanocluster with Crystallization Enhanced Photoluminescence
- First Published: 19 March 2021
![[Cu15(PPh3)6(PET)13]2+: a Copper Nanocluster with Crystallization Enhanced Photoluminescence](/cms/asset/f21f65d6-8003-421f-ae58-5254b67c05ec/smll202006839-gra-0001-m.jpg)
The synthesis of copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) is highly challenging due to the low reduction potential and relatively high reactivity of copper, in comparison with Au and Ag. This work introduces a facile strategy for synthesis of the novel Cu NCs formulated as [Cu15(PPh3)6(PET)13]2+ with bright luminescence in the solid state.
Frontispiece
Gold Electrocatalysis: Enhanced Methanol Electro-Oxidation Activity of Nanoclustered Gold (Small 27/2021)
- First Published: 08 July 2021

In article number 2004541, Anupam Yadav, Didier Grandjean, Peter Lievens, and co-workers uncover the origin of the catalytic activity of 3 nm gold clusters by thorough experimental and computational characterization of their properties. Faceted geometries demonstrate significantly enhanced methanol electro-oxidation activity because of exposed undercoordinated gold atoms on their surface. Vertices and edges are the most active sites because of their favorable CO and OH adsorption energies.
Full Papers
Enhanced Methanol Electro-Oxidation Activity of Nanoclustered Gold
- First Published: 07 February 2021
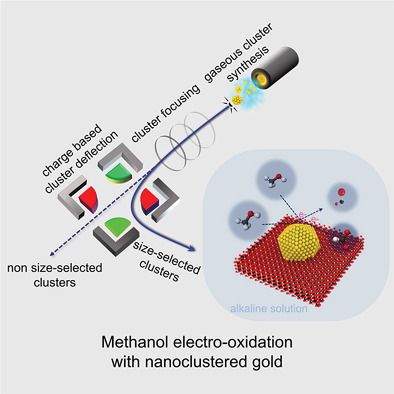
Size-selected Au clusters dispersed by cluster beam deposition on fluorine-doped tin oxide show strong enhancement of methanol electro-oxidation activity. A detailed characterisation of their structure in combination with density functional theory-based modelling attribute this enhancement to the high density of exposed under-coordinated Au atoms at their faceted surface. Vertices and edges are the most active sites due to their favorable CO and OH adsorption energies.
Multiple Ways Realizing Charge-State Transform in AuCu Bimetallic Nanoclusters with Atomic Precision
- First Published: 04 May 2020
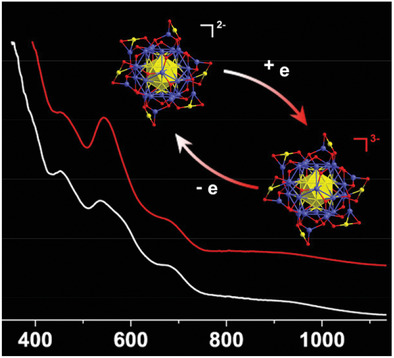
A single electron can be added and removed in the AuCu nanoclusters with several redox methods, which results in the reversible charge state of the nanoclusters. The change of charge states results in the significant difference in their optical properties, electrochemical properties, and magnetism but a less disturbance in the structure frameworks.
Exploration of Formation and Size-Evolution Pathways of Thiolate-Gold Nanoclusters in the CO-Directed [Au25(SR)18]− Synthesis
- First Published: 06 August 2020
![Exploration of Formation and Size-Evolution Pathways of Thiolate-Gold Nanoclusters in the CO-Directed [Au25(SR)18]− Synthesis](/cms/asset/d0fd8699-3224-433f-9d96-11217b6382f8/smll202000627-gra-0001-m.jpg)
An intermolecular association and decarboxylation mechanism is proposed for understanding the stepwise 2e− hopping in the reductant-assisted thiolate-gold cluster synthesis. The atomic pathways of the formation and size conversion of 2e−–8e− gold nanoclusters in the CO-directed [Au25(SR)18]− synthesis are also systematically explored.
Understanding the Chemical Insights of Staple Motifs of Thiolate-Protected Gold Nanoclusters
- First Published: 06 August 2020
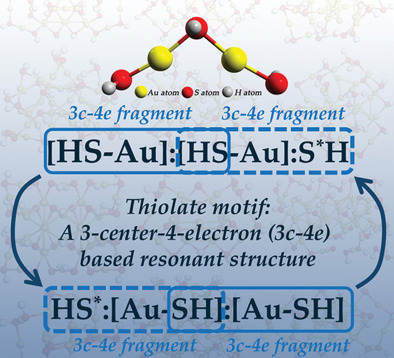
A fundamental understanding of the structures of atomically precise gold nanoclusters is vital to their synthesis and applications. The 3c-4e model is introduced to understand the thiolate ligands. Results show that the central Au is hypervalent and the thiolate motif can be expressed in the resonance form, that is, for motif [HSAuHSAuSH] is [HSAu]:[HSAu]:S*H↔HS*:[AuSH]:[AuSH].
Sequential Growth as a Mechanism of Silver-Glutathione Monolayer-Protected Cluster Formation
- First Published: 28 August 2020
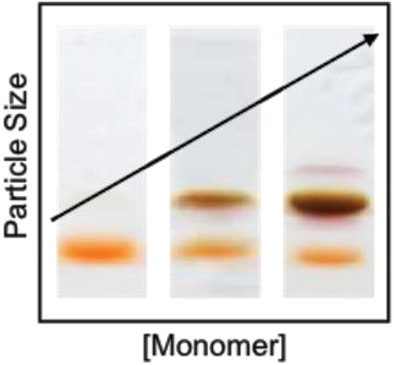
Monolayer-protected clusters (MPCs) have been synthesized for more than two decades but their mechanism of formation remains unclear. Measurements of silver-glutathione MPC formation now establish that they grow systematically, increasing in size sequentially as they transform from one known species to another. Herein, a sequential growth model is proposed, experimentally validated, and studied using simulations to better understand the model's properties.
Understanding the Early Stages of Nickel Sulfide Nanocluster Growth: Isolation of Ni3, Ni4, Ni5, and Ni8 Intermediates
- First Published: 20 September 2020
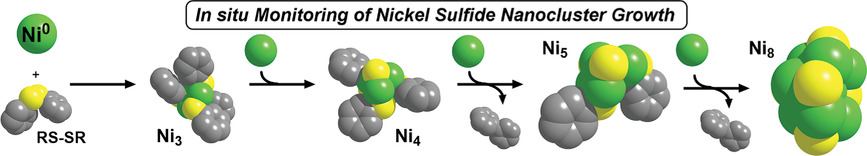
In situ spectroscopic monitoring of nickel sulfide nanocluster formation allows for the identification of the fundamental reaction steps, such as metal atom addition, CS oxidative addition, and CC reductive elimination, that occur during cluster growth. This unprecedented level of detail will enable the targeted synthesis of larger Ni sulfide clusters.
Designing New Metal Chalcogenide Nanoclusters through Atom-by-Atom Substitution
- First Published: 08 November 2020
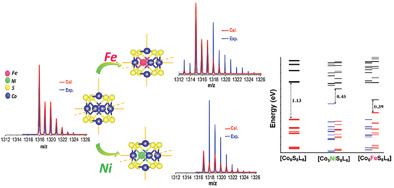
Single Fe an Ni atom substitution to the core of a well-defined cobalt sulfide superatom, [Co6S8(PEt3)6]+, changes the electronic configuration of the cluster. Fe and Ni atom substitution result in different optical, magnetic, and electrochemical properties. This study extends the atom-by-atom substitution strategy to ligated metal chalcogenide clusters and opens a pathway for designing atomically precise alloy metal sulfide superatoms.
Effect of the Metal–Ligand Interface on the Chiroptical Activity of Cysteine-Protected Nanoparticles
- First Published: 27 January 2021
Extrinsic chirality is induced when chiral ligands cover the surface of metal nanoparticles. Here, it is investigated, both theoretically and experimentally, the transfer mechanisms and origin of chiroptical activity of cysteine-protected Au, Ag, Cu nanoparticles with size around 2 nm. The results confirm that the metal–ligand interface is responsible of the optical activity observed in the spectral range of 250–400 nm.
Probing the Thermal Stability of (3-Mercaptopropyl)-trimethoxysilane-Protected Au25 Clusters by In Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy
- First Published: 28 January 2021
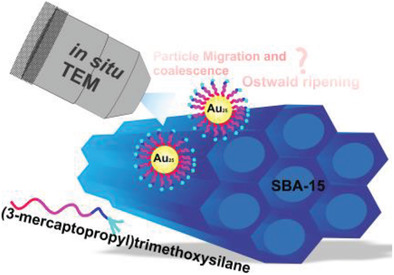
The driving force for agglomeration of Au25 clusters stabilized with 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane on a mesoporous silica support is investigated using environmental in situ transmission electron microscopy analysis. Particle mobility is substantial at temperatures beyond 500 °C, which leads to particle coalescence, followed by Ostwald ripening. Further treatment with tetraethylorthosilicate mitigates sintering by retarding the mobility of Au particles.
Observable but Not Isolable: The RhAu24(PET)181+ Nanocluster
- First Published: 10 November 2020
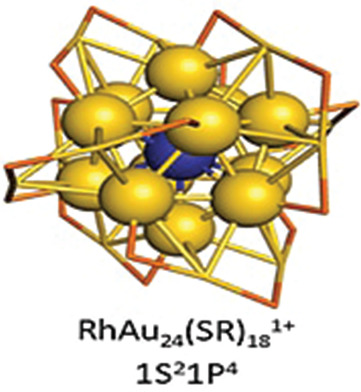
The first experimental observation of a rhodium-doped thiolated gold cluster is described. RhAu24(PET)181+ is a rare example of an alloy gold cluster containing an open d-shell heterometal. Isolation efforts reveal a unique stabilization afforded by cosynthesized reaction products. Persisting exclusively within this supramolecular alloy system, RhAu24(PET)181+ is rationalized within the context of superatom theory.
Spin-Polarized Photoluminescence in Au25(SC8H9)18 Monolayer-Protected Clusters
- First Published: 28 January 2021
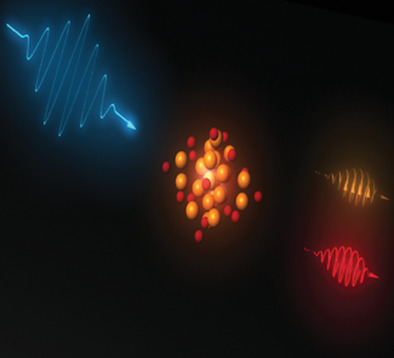
Spin-polarized photoluminescence is observed for quantum-confined Au25(SC8H9)18 monolayer-protected clusters (MPC). Emission mechanisms are determined using variable-temperature variable-field magnetic circular photoluminescence spectroscopy. Spin-polarization amplitudes are correlated to emission by specific nanocluster qauntum states. Atomic-level nanocluster structure determines electronic fine-structure energies, electronic-vibrational coupling, and spin-orbit coupling parameters, which control the degree of spin polarization for each emission pathway.
Site-Specific Electronic Properties of [Ag25(SR)18]− Nanoclusters by X-Ray Spectroscopy
- First Published: 28 January 2021
![Site-Specific Electronic Properties of [Ag25(SR)18]− Nanoclusters by X-Ray Spectroscopy](/cms/asset/7a6dd58c-6b58-4ea0-a855-510dc15c3885/smll202005162-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Thiolate-protected 25-atom Ag nanoclusters Ag25(SR)18 have recently been studied due to their intriguing catalytic, electronic, and optical properties. The structure of these materials resembles that of their Au counterparts, Au25(SR)18. Various experimental and theoretical methods, such as core-level X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, can be used to examine the electronic properties from a site-specific perspective.
Understanding Superatomic Ag Nanohydrides
- First Published: 15 January 2021
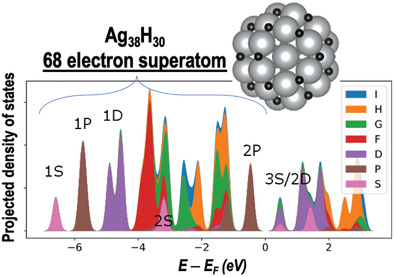
Density-functional theory analysis of Ag nanohydrides finds that adsorbed hydrogen atoms behave as a metal and contribute their 1s electrons to the superatom electron count of the Ag cluster. Angular momentum analyses of the superatomic orbitals suggest a convoluted interaction of geometry, symmetry, and orbital splitting.
Synthesis and Photophysical Properties of Light-Harvesting Gold Nanoclusters Fully Functionalized with Antenna Chromophores
- First Published: 09 February 2021
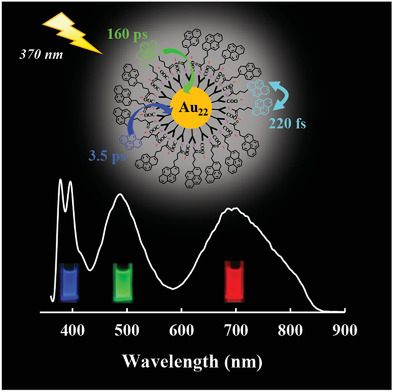
Herein, an effective amide coupling method is developed to produce water-soluble light-harvesting systems based on atomically well-defined gold nanoclusters. The synthesized Au22 nanoclusters densely functionalized with pyrene chromophores show triple-emission in blue, green, and red regions, generating bright white light emission together. Distinct excitation energy transfer processes are first observed in transient absorption anisotropy measurements of the light-harvesting gold nanoclusters.
Luminescent Gold Nanocluster-Methylcellulose Composite Optical Fibers with Low Attenuation Coefficient and High Photostability
- First Published: 25 January 2021
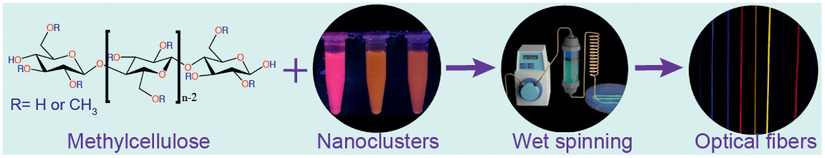
Simple extrusion of shear-thinning aqueous methylcellulose dispersions and its composite hydrogels with gold nanoclusters, cellulose nanocrystals, or cellulose nanocrystal-gold nanocluster hybrids enables mechanically and optically tunable biopolymeric optical fibers. The resulting strong and ductile composite fibers display low attenuation coefficient making them suitable for application in short-distance optical fibers.
Deposition of Extended Ordered Ultrathin Films of Au38(SC2H4Ph)24 Nanocluster using Langmuir–Blodgett Technique
- First Published: 09 February 2021
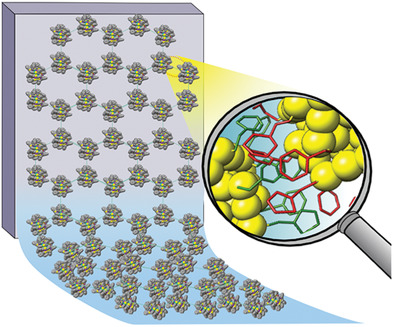
Ordered ultrathin films of Au38(SC2H4Ph)24 nanocluster are formed on the water surface, transferred onto solid supports using Langmuir–Blodgett technique, and analyzed using predominantly (fast) atomic force microscopy and X-ray reflectivity. The effect of surface pressure and compression time on the coverage and ordering type as well as the degree of interdigitation between ligands of neighboring clusters is considered.
The Role of Oxidation during the Synthesis of Silver-Glutathione Monolayer-Protected Clusters
- First Published: 09 February 2021
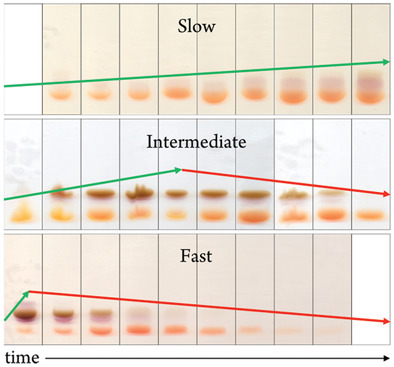
Oxidation plays an important role in determining the product distribution of silver monolayer-protected cluster syntheses. Oxidation reactions involving ambient oxygen and free glutathione ligands can shift the product distributions toward smaller sizes, but via different mechanisms. Understanding the interplay between competing reductive and oxidative reactions should improve the ability to design syntheses, particularly those targeting specific clusters.





