Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Anodes: High Full-Electrode Basis Capacity Template-Free 3D Nanocomposite Secondary Battery Anodes (Small 47/2015)
- Page: 6241
- First Published: 10 December 2015

A unique high full-electrode basis capacity anode design for secondary batteries is described by P. V. Braun and co-workers on page 6265. The design consists of a structurally robust 3D Fe3O4/C composite, which provides efficient pathways for electron and Li-ion transport, and space for the volume changes during cycling. On a full-electrode basis, the template-free nanocomposite anode exhibits attractive electrochemical performance, including a high volumetric capacity which significantly exceeds both the practical and theoretical capacity of a commercial graphite-based anode.
Inside Front Cover
Ferromagnetics: Weak Delocalization in Graphene on a Ferromagnetic Insulating Film (Small 47/2015)
- Page: 6242
- First Published: 10 December 2015
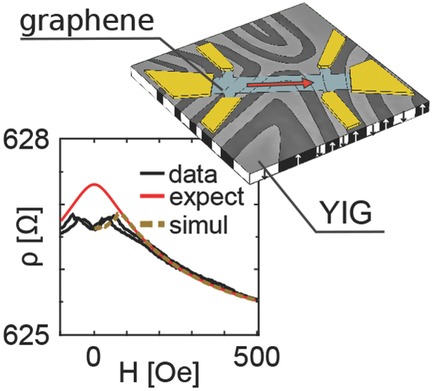
L. E. Hueso and co-workers observe magnetic field lines (as imaged by electron holography) arising from a ferromagnetic insulating substrate which crosses a graphene device. On page 6295, they show how the changes in the weak localisation of the graphene are created by the magnetic domain distribution and cannot be attributed to other more exotic effects, such as magnetic proximity.
Masthead
Contents
Reviews
In situ Endothelialization: Bioengineering Considerations to Translation
- Pages: 6248-6264
- First Published: 13 October 2015
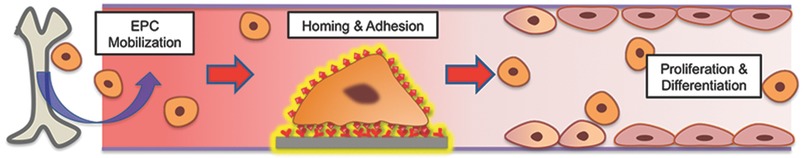
In situ endothelialization offers a practical approach to attain long-term patency of cardiovascular implants. Recent developments using various bio-/nanoengineering strategies on biomaterials are summarized in this review. With the aim to support translational efforts, bioengineering considerations ranging from micro-/nanoscale material biofunctionalization to translational practicality are discussed, followed by a critical analysis of the clinical results of currently used implants.
Communications
High Full-Electrode Basis Capacity Template-Free 3D Nanocomposite Secondary Battery Anodes
- Pages: 6265-6271
- First Published: 19 October 2015
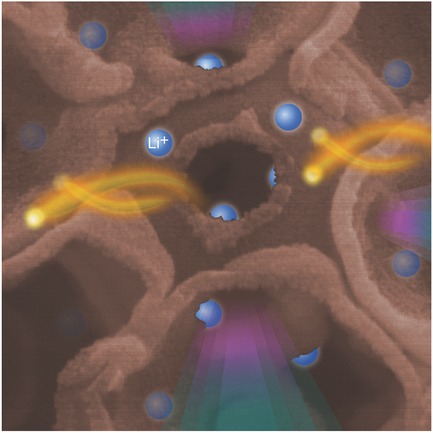
A high full-electrode basis capacity secondary battery anode consisting of a template-free 3D nanostructured Fe3O4/C composite is presented. On a full electrode basis, the nanocomposite exhibits attractive electrochemical performance including a volumetric capacity of 1064 mAh cm−3, which significantly exceeds both the practical (≈300 mAh cm−3) and theoretical (837 mAh cm−3) capacity of a commercial graphite-based anode.
Stretchable Si Logic Devices with Graphene Interconnects
- Pages: 6272-6277
- First Published: 28 October 2015
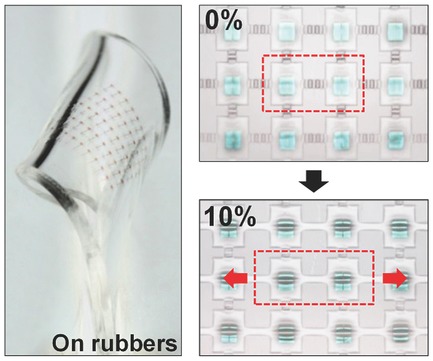
Stretchable integrated circuits consisting of ultrathin Si transistors connected by multilayer graphene are demonstrated. Graphene interconnects act as an effective countervailing component to maintain the electrical performance of Si integrated circuits against external strain. Concentration of the applied strain on the graphene interconnect parts can stably protect the Si active devices against applied strains over 10%.
Hydrophilic Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-doped Molybdenum Carbide Nanosheets for Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution
- Pages: 6278-6284
- First Published: 03 November 2015
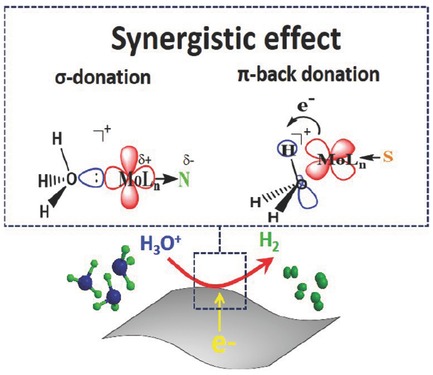
Nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped Mo2C nanosheets provide low operating potential (−86 mV for driving 10 mA cm−2 of current density). Co-doping of N and S heteroatoms can improve the wetting property of the Mo2C electrocatalyst in aqueous solution and induce synergistic effects via σ-donation and π-back donation with hydronium cation.
Full Papers
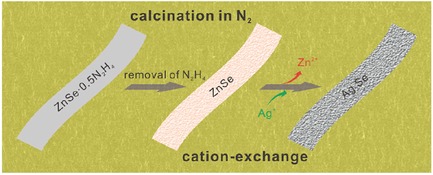
Cation Exchange Synthesis and Unusual Resistive Switching Behaviors of Ag2Se Nanobelts
- Pages: 6285-6294
- First Published: 28 October 2015
Weak Delocalization in Graphene on a Ferromagnetic Insulating Film
- Pages: 6295-6301
- First Published: 27 October 2015
Direct Synthesis of Few-Layer Graphene on NaCl Crystals
- Pages: 6302-6308
- First Published: 02 November 2015
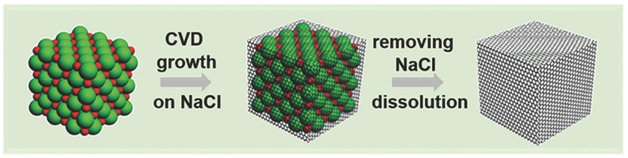
Few-layer graphene is synthesized on cuboidal NaCl crystals via a facile low temperature chemical vapor deposition method. The removal of NaCl substrate can be achieved easily by a water washing process due to its water-soluble nature. Cuboidal graphene boxes can also be obtained by replicating the morphology of NaCl crystals.
Cross-Talk Between Ionic and Nanoribbon Current Signals in Graphene Nanoribbon-Nanopore Sensors for Single-Molecule Detection
- Pages: 6309-6316
- First Published: 26 October 2015
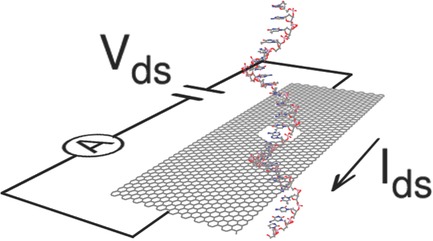
Graphene nanoribbon sensors show a response to single DNA molecules flowing through a nanopore. The response is based on capacitively coupled cross-talk between the ionic and graphene measurement channels. Circuit simulations show the variety of signals which may be observed, and potential field calculations identify parameters that can enhance detection based on a field-effect device response.
Photoswitching and Thermoresponsive Properties of Conjugated Multi-chromophore Nanostructured Materials
- Pages: 6317-6324
- First Published: 28 October 2015
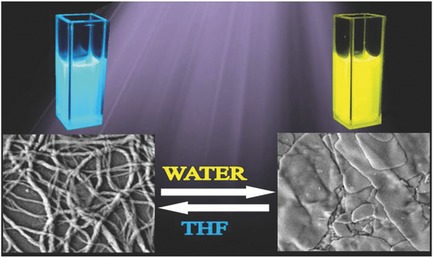
The reversible tuning of the structure of quaterthiophene (QTH) molecules by simply adding more or less water is an easy way to control their properties. This study highlights the relationship between the structure of the QTH material and its photoswitching and thermoresponsive properties. Being able to reversibly switch these properties provides a crucial step forward in the development of organic electronics.
Single Chirality (6,4) Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Fluorescence Imaging with Silicon Detectors
- Pages: 6325-6330
- First Published: 03 November 2015

The (6,4) chirality is the only nanotube fluorophore that can be readily detected with conventional silicon-based charge-coupled devices. Slight changes in pH produce radically different behaviors of single-walled carbon nanotubes during density gradient ultracentrifugation, allowing the separation of ultrahigh purity (6,4) nanotubes. (6,4)'s potential as a clinically relevant NIR-I fluorescence stain is demonstrated through molecular imaging and immunohistochemical staining.
Fabry–Perot Microcavity Modes in Single GaP/GaNP Core/Shell Nanowires
- Pages: 6331-6337
- First Published: 27 October 2015
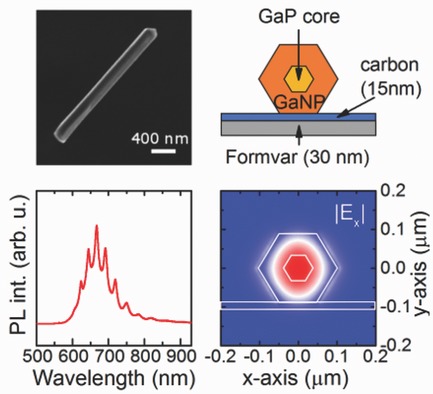
The observation of Fabry–Perot microcavity modes in single GaP/GaNP core/shell nanowires is the first step toward achieving lasing in this quasidirect bandgap semiconductor in nanowire geometry. This is an important advance to cover the yellow-amber spectral range which is, so far, an uncovered gap for semiconductor laser diodes.
Immobilization of ALA-ZnII Coordination Polymer Pro-photosensitizers on Magnetite Colloidal Supraparticles for Target Photodynamic Therapy of Bladder Cancer
- Pages: 6338-6346
- First Published: 30 October 2015
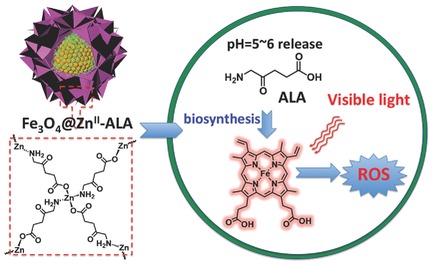
A 2D photosensitive coordination polymer comprising 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and Zn ions is prepared to encapsulate the agarose-stabilized magnetite colloidal supraparticles (Fe3O4@ALA-ZnII). The formed core–shell microspheres allow the pH-sensitive release of prodrug ALA, enable the ALA-mediated biosynthesis of photosensitizer PpIX, and display the remarkable PDT activity against bladder cancer cells as exposed to visible light.
CXCR-4 Targeted, Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) Emitting Nanoprobes for Enhanced Deep Tissue Imaging and Micrometastatic Cancer Lesion Detection
- Pages: 6347-6357
- First Published: 30 October 2015
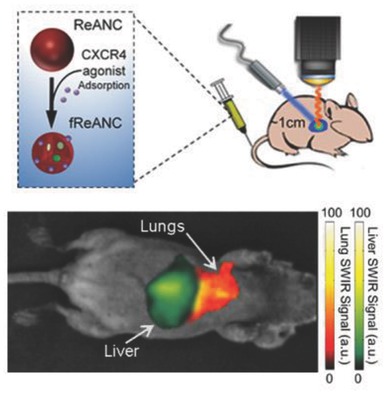
Optical imaging using targeted rare-earth-doped albumin nanocomposites provides a method for subsurface detection of microscale breast cancer metastasis. Particles functionalized to common metastatic receptors molecularly discriminate between cellular populations, which enables minimally invasive determination of tumor phenotype. Improved particle localization to tumor sites allows for detection of microscale tumors in vivo ≈1 cm from the imaging surface.
Surface-Supported Robust 2D Lanthanide-Carboxylate Coordination Networks
- Pages: 6358-6364
- First Published: 02 November 2015
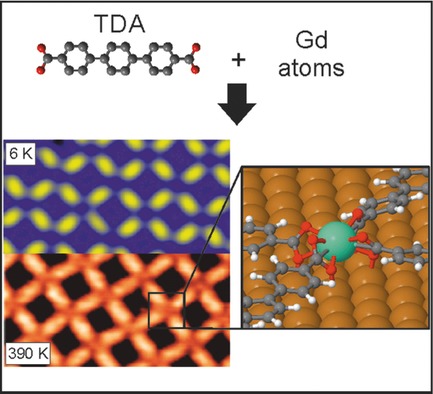
On-surface assembly of robust 2D lanthanide-carboxylate coordination networks. The codeposition of TDA linker species and Gd on Cu(111) results in the formation of reticular networks, based on Gd–carboxylate interactions featuring a unique eightfold mononuclear node, which are thermally stable up to 400 K. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy experiments and density functional theory calculations reveal the predominant ionic nature of the bond.