Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Mercury Detection: Urine for Plasmonic Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ion (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4089
- First Published: 12 December 2013

Hundreds of years after the little boy saved his city with urine, X. Chen and co-workers now use urine to detect deleterious ions in a colorimetric assay. As reported on page 4104, the synergetic effect of uric acid and creatinine decorated on gold nanoparticles is the reason for the selective binding of mercury ions, leading to the aggregation of nanoparticles and thereby causing a visual color change. This work inspires the development of the “turning trash into treasure” strategy and the exploitation of natural products in exploring nanotechnology.
Inside Front Cover
3D Printing: Solvent-Cast Three-Dimensional Printing of Multifunctional Microsystems (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4090
- First Published: 12 December 2013

Various microstructures including straight filaments, layer-by-layer scaffolds and freeform helical spirals are fabricated by a solvent-cast three-dimensional printing technique, as reported by D. Therriault and co-workers on page 4118. The fabrication capabilities of this powerful and flexible process are demonstrated by the printing of three microsystems featuring mechanical, microfluidic and electrical functionalities, such as a high-toughness microstructured fiber, a 3D microchannel and a Ka band antenna. These capabilities can be extended through the utilization of other thermoplastic-based inks and the printing of features at the sub-micrometer- and potentially nanoscale.
Back Cover
Carbon Nanotubes: Functionalization of Carbon Nanoparticles Modulates Inflammatory Cell Recruitment and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4280
- First Published: 12 December 2013
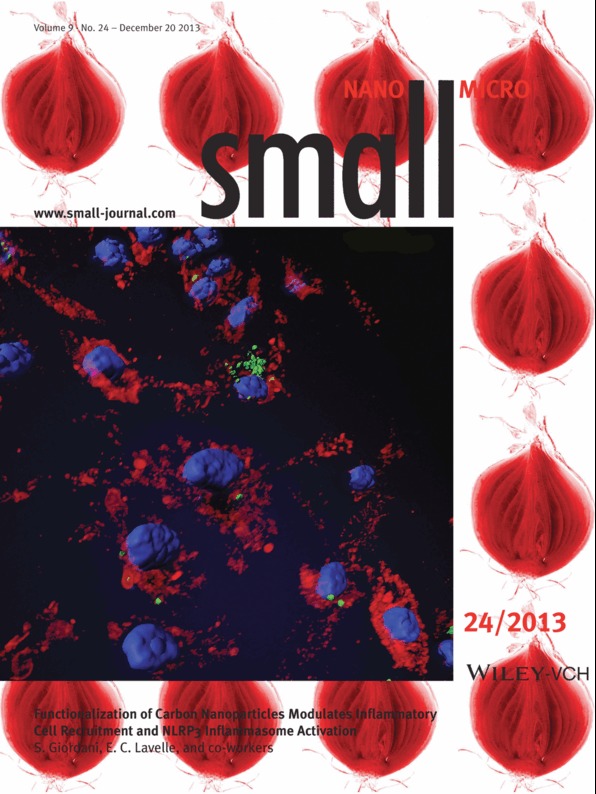
The inflammatory properties of carbon nanoparticles are regarded as a major roadblock in their use for biomedical applications. On page 4194, S. Giordani, E. C. Lavelle and co-workers describe a simple and reproducible strategy to address this issue using a novel purification process combined with surface chemical functionalization. The carbon nano-onions are also shown to promote less inflammation than carbon nanotubes and this can be further reduced by surface functionalization. This is the first report that single walled carbon nanotubes and carbon nano-onions have the ability to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Masthead
Contents
Frontispiece
Self Assembly: Shaping Functional Nano-objects by 3D Confined Supramolecular Assembly (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4098
- First Published: 12 December 2013

Nano-objects are generated through 3D confined supramolecular assembly, followed by a sequential disintegration by rupturing the hydrogen bonding. The shape of the nano-objects is tunable, ranging from nano-disc, nano-cup, to nano-toroid. The nano-objects are pHresponsive. As Z. Z. Yang, J. T. Zhu, and co-workers describe on page 4099, functional materials, for example inorganic nanoparticles, can be easily incorporated into the surface to extend both the composition and microstructure of the nano-objects, which is important in drug delivery, targeting, catalysis, and imaging.
Communications
Shaping Functional Nano-objects by 3D Confined Supramolecular Assembly
- Pages: 4099-4103
- First Published: 04 April 2013
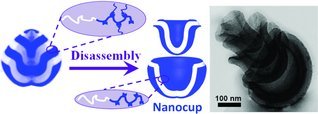
Nano-objects are generated through 3D confined supramolecular assembly, followed by a sequential disintegration by rupturing the hydrogen bonding. The shape of the nano-objects is tunable, ranging from nano-disc, nano-cup, to nano-toroid. The nano-objects are pH-responsive. Functional materials for example inorganic or metal nanoparticles are easily complexed onto the external surface, to extend both composition and microstructure of the nano-objects.
Urine for Plasmonic Nanoparticle-Based Colorimetric Detection of Mercury Ion
- Pages: 4104-4111
- First Published: 28 June 2013
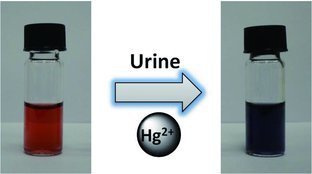
Urine for diagnostics: Urine, a “green” natural product, is used as an active component to produce a simple, inexpensive, and portable colorimetric Hg2+ sensing assay with high selectivity and sensitivity by simply mixing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and urine. The synergetic effect of uric acid and creatinine decorated on AuNPs is the reason for selective binding of Hg2+, leading to the aggregation of gold nanoparticles and thereby causing a visible color change.
Slowing Down DNA Translocation Through Solid-State Nanopores by Pressure
- Pages: 4112-4117
- First Published: 05 July 2013
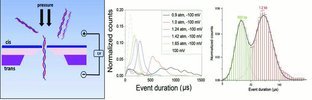
The effect of applied pressure on event duration distributions in 3 kb dsDNA translocation is systematically investigated. The effects of pressure magnitude and nanopore size on the length discrimination between 615 bp and 1.14 kbp dsDNA is studied. The pressure-controlled DNA translocation in solid-state nanopores makes a significant contribution to improve the temporal resolution in DNA single-molecule detection.
Solvent-Cast Three-Dimensional Printing of Multifunctional Microsystems
- Pages: 4118-4122
- First Published: 04 July 2013
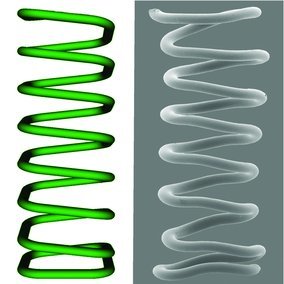
The solvent-cast direct-write fabrication of microstructures is shown using a thermoplastic polymer solution ink. The method employs the robotically controlled microextrusion of a filament combined with a rapid solvent evaporation. Upon drying, the increased rigidity of the extruded filament enables the creation of complex freeform 3D shapes.
Nanoparticle-Programmed Self-Destructive Neural Stem Cells for Glioblastoma Targeting and Therapy
- Pages: 4123-4129
- First Published: 21 July 2013
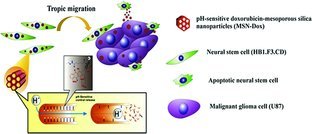
A 3-step glioblastoma-tropic delivery and therapy method using nanoparticle programmed self-destructive neural stem cells (NSCs) is demonstrated in vivo: 1) FDA-approved NSCs for clinical trials are loaded with pH-sensitive MSN-Dox; 2) the nanoparticle conjugates provide a delayed drug-releasing mechanism and allow for NSC migration towards a distant tumor site; 3) NSCs eventually undergo cell death and release impregnated MSN-Dox, which subsequently induces toxicity towards surrounding glioma cells.
Light-Induced Generation of Singlet Oxygen by Naked Gold Nanoparticles and its Implications to Cancer Cell Phototherapy
- Pages: 4130-4134
- First Published: 01 July 2013
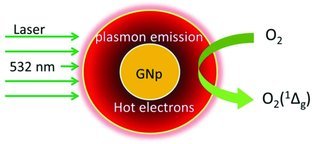
Generation of singlet oxygen by direct irradiation of naked gold nanoparticles is observed using either continuous wave or pulsed laser sources. The underlying mechanism involves plasmon- and hot-electron-mediated reaction pathways and 1O2 seems to significantly amplify the overall death rates during photothermal treatment of cancer cell lines in vitro.
Water Dispersible, Highly Graphitic and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanobubbles
- Pages: 4135-4141
- First Published: 12 July 2013
Dispersible, highly graphitic, and nitrogen-doped carbon hollow nanospheres (25–90 nm), termed ‘nanobubbles’, are prepared via confined carbonization through a silica nanocasting technique. Poly(ionic liquid) nanoparticles are employed as easy-to-make and multifunctional templates, which simultaneously act as both the carbon and nitrogen source. The promising potential of the nanobubbles in oxygen reduction reactions for fuel cells is demonstrated.
Self-Assembly of Semiconducting Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes into Dense, Aligned Rafts
- Pages: 4142-4148
- First Published: 11 July 2013
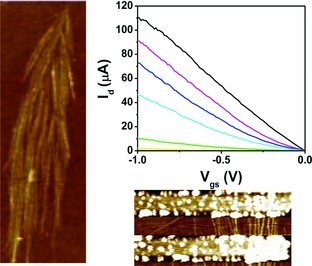
Highly pure semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are separated from bulk materials and self-assembled into densely aligned rafts. Microscopy and spectroscopy reveals ∼100 SWNTs per micrometer within the rafts. Short channel field-effect transistors (FETs) from tens of purely semiconducting SWNTs within a submicrometer channel width achieve unprecedented on-currents (up to 121 μA) with high on/off ratios. The results demonstrate densely aligned semiconducting SWNTs for high-performance nanoelectronics.
Frontispiece
Drug Delivery: Multifunctional Upconversion Mesoporous Silica Nanostructures for Dual Modal Imaging and In Vivo Drug Delivery (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4149
- First Published: 12 December 2013
Incorporating the agents for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), optical imaging and therapy in one nanostructured matrix to construct a multifunctional nanomedical platform has attracted great attention for simultaneous diagnostic and therapeutic applications. A facile methodology is reported on page 4150 by J. Lin and co-workers to construct a multifunctional nanocarrier composed of individual luminescent/magnetic β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+@β-NaGdF4:Yb3+ directly coated with mesoporous silica, followed by functionalization with poly(ethylene glycol), which can act as an effective platform for upconversion luminescence and magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging and in vivo anticancer drug delivery.
Full Papers
Multifunctional Upconversion Mesoporous Silica Nanostructures for Dual Modal Imaging and In Vivo Drug Delivery
- Pages: 4150-4159
- First Published: 11 July 2013
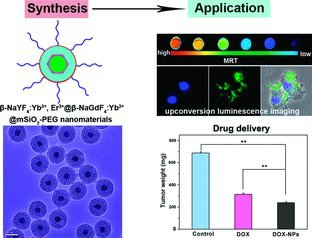
A facile methodology is developed to construct a multifunctional nanocarrier composed of individual luminescent/magnetic β-NaYF4:Yb3+, Er3+@ β-NaGdF4:Yb3+ directly coated with mesoporous silica, followed by functionalization with poly(ethylene glycol), which can act as an effective platform for upconversion luminescence and magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging and in vivo anticancer drug delivery.
“Dual-Template” Synthesis of One-Dimensional Conductive Nanoparticle Superstructures from Coordination Metal–Peptide Polymer Crystals
- Pages: 4160-4167
- First Published: 05 July 2013
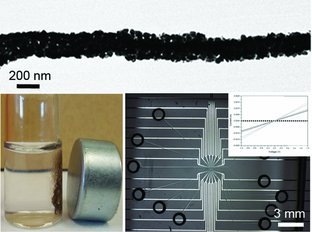
Micrometer-long conductive Ag nanoparticle superstructures are synthesised from coordination metal–peptide polymer crystals by exploiting the self-assembly and recognition capacities of peptides and the selective reduction of Ag(I) to Ag. This “dual-templating” synthesis allows nanoparticle binary superstructures by first assembling nanoparticles on the crystal surfaces, then reducing the coordinated Ag(I) ions to Ag nanoparticles. Multifunctional Fe3O4@Ag nanocomposites that marry magnetic and conductive properties are created.
Tunable Assembly of Gold Nanoparticles on Nanopatterned Poly(ethylene glycol) Brushes
- Pages: 4168-4174
- First Published: 10 July 2013
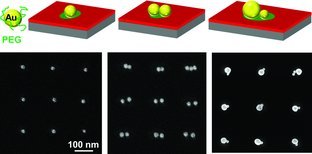
Nanopatterned poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) brushes are used to organize gold nanoparticles into arrays on surfaces. The key aspect of the study is to pattern PEG brushes with high resolution and chemical contrast to provide controllable and specific interaction between NPs and nanopatterns at a single particle level.
Potential-Dependent Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman Spectroscopy at Nanostructured TiO2: A Case Study on Cytochrome b5
- Pages: 4175-4181
- First Published: 17 July 2013
Nanostructured TiO2 electrodes are employed to probe the electron-transfer process of cytochrome b5 by surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy. Concomitant with the increased nanoscopic surface roughness of TiO2, the enhancement factor increases, which can be attributed to the electric field enhancement.
Frontispiece
Quantum Dots: Tracking the Down-Regulation of Folate Receptor-α in Cancer Cells through Target Specific Delivery of Quantum Dots Coupled with Antisense Oligonucleotide and Targeted Peptide (Small 24/2013)
- Page: 4182
- First Published: 12 December 2013
Y.-D. Zhao and co-workers report on page 4183 a new multifunctional quantum dot (QD) probe by coupling anti-hFR-α antisense oligonucleotide (AS-ODN) and targeted peptide p160 with QDs through biotin-streptavidin interaction for realtime tracking of AS-ODN and regulation of hFR-α in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The QD probes enter into the cytoplasm effectively through receptor-mediated endocytosis, and after endosomal release, AS-ODN combines with its target mRNA and blocks hFR-α protein translation. This multifunctional QD probe not only achieves gene silencing in a cell-specific manner but also achieves real-time tracking during AS-ODN intracellular delivery.
Full Papers
Tracking the Down-Regulation of Folate Receptor-α in Cancer Cells through Target Specific Delivery of Quantum Dots Coupled with Antisense Oligonucleotide and Targeted Peptide
- Pages: 4183-4193
- First Published: 05 July 2013
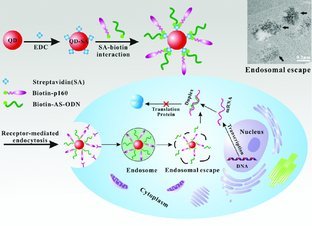
A new multifunctional quantum dot (QD) probe is prepared by coupled with anti-hFR-α antisense oligonucleotide and targeted peptide p160 with QDs through biotin-streptavidin interaction. Down-regulation of hFR-α in a cell-specific manner is achieved. The probe is effectively transported into the cytoplasm through receptor-mediated endocytosis, and finally antisense oligonucleotides combine with hFR-α mRNA and block the protein translation.
Functionalization of Carbon Nanoparticles Modulates Inflammatory Cell Recruitment and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- Pages: 4194-4206
- First Published: 10 July 2013
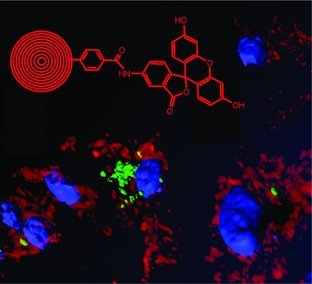
The inflammatory properties of carbon nanoparticles are regarded as a major roadblock in their use for biomedical applications. A simple and reproducible strategy is described to address this issue using a novel purification process combined with surface chemical functionalization. This is also the first report that single walled carbon nanotubes and carbon nano-onions have the ability to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Discontinuous Nanoporous Membranes Reduce Non-Specific Fouling for Immunoaffinity Cell Capture
- Pages: 4207-4214
- First Published: 13 June 2013
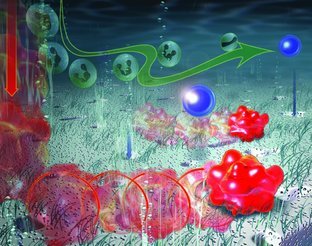
Nanoporous membranes with discontinuous permeability enable high-throughput cell separation by circumventing microfluidic limitations of transport, reaction, and non-specific fouling. The use of impermeable areas near the channel side walls reduces the transport of cells to regions of low shear, limiting excess accumulation of background cells. This technology exhibits excellent target capture efficiency at considerably enhanced flow rates and sample concentrations.
Ultrasensitive Telomerase Activity Detection by Telomeric Elongation Controlled Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering
- Pages: 4215-4220
- First Published: 15 July 2013
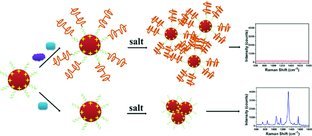
Telomerase activity detection: A facile PCR free telomerase detection protocol termed as TEC-SERS (telomeric elongation controlled surface enhanced Raman scattering) is presented. The detection limit is 1 tumor cell/mL or 1 tumor cell in 1 × 106 normal cells, which is much lower than those of previously published methods. Since no PCR procedure is involved, the TEC-SERS protocol provides excellent reliability and simplicity.
Antibody Conjugated PLGA Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Paclitaxel Palmitate: Efficacy and Biofate in a Lung Cancer Mouse Model
- Pages: 4221-4236
- First Published: 21 July 2013
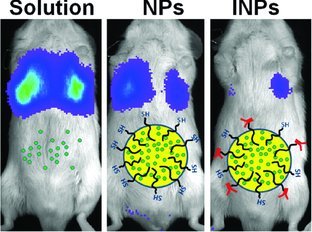
Anchoring of amphiphilic oleyl cysteineamide linker molecules at the nanosphere interface allows thiol surface functionalization of PLGA nanoparticles (NPs) and efficient covalent conjugation to maleimide-activated cetuximab. Cetuximab immunonanoparticles (INPs) enable specific binding to the epidermal growth factor receptor on A549 lung cancer cells, eliciting improved tumor growth inhibition over the non-targeted drug solution and NPs.
Rapid and Low-Cost Prototyping of 3D Nanostructures with Multi-Layer Hydrogen Silsesquioxane Scaffolds
- Pages: 4237-4242
- First Published: 11 July 2013
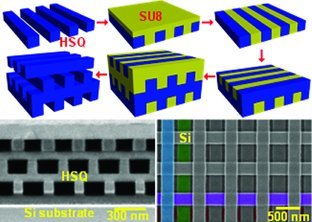
Three dimensional nanostructures are demonstrated through a novel layer-by-layer process. It can rapidly fabricate structures with high-resolution and at low cost. A 4-layer silicon inverse woodpile photonic crystal with a period of 650 nm and a 7-layer HSQ scaffold with a period of 300 nm are realized using this process. It provides a versatile and accessible solution to the fabrication of highly complex 3D nanostructures.
Biochips for Cell Biology by Combined Dip-Pen Nanolithography and DNA-Directed Protein Immobilization
- Pages: 4243-4249
- First Published: 24 July 2013
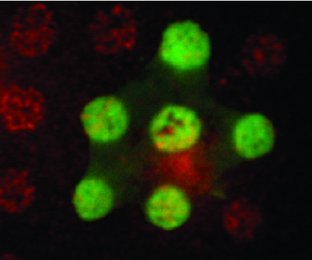
Direct writing of DNA oligonucleotides by dip pen nanolithography (DPN) and subsequent functionalization of the written patterns with DNA-tagged proteins allows one to produce biochips (red spots) for the precise functional manipulation of subcellular areas within cells, as demonstrated by the recruitment and concentration of transmembrane receptors (green spots) in the plasma membrane of a living cell (light green).
Comparative Evaluation of Intestinal Nitric Oxide in Embryonic Zebrafish Exposed to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles
- Pages: 4250-4261
- First Published: 21 July 2013
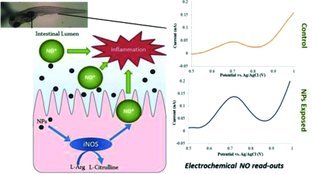
Intestinal nitric oxide (NO) concentrations are monitored quantitatively with a single carbon fiber microelectrode implanted in the intestine of live zebrafish embryos. CuO nanoparticles significantly increase intestinal NO production in a dose depended manner while low concentration of CeO2 nanoparticles reduce physiological NO levels, indicating NO scavenging abilities of these particles in vivo. However, high concentrations CeO2 nanoparticle exposure results in increased NO.
Aptamer-Directed Synthesis of Multifunctional Lanthanide-Doped Porous Nanoprobes for Targeted Imaging and Drug Delivery
- Pages: 4262-4268
- First Published: 11 July 2013
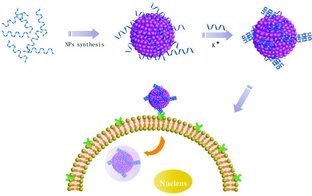
Multifunctional lanthanide-doped porous nanoparticles are prepared via a facile one-step solvothermal route by employing aptamers as the biotemplate. The nanoparticles feature excellent aqueous dispersibility and biospecific properties and could work as effective nanoprobes for targeted imaging and drug delivery.
Laser-Induced Direct Graphene Patterning and Simultaneous Transferring Method for Graphene Sensor Platform
- Pages: 4269-4275
- First Published: 11 July 2013
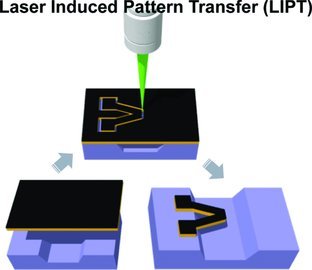
A laser-induced pattern transfer (LIPT) method is proposed for the transferring and simultaneous patterning of graphene in a single processing step. Femtosecond laser ablation is employed to transfer graphene/PMMA microscale patterns onto arbitrary substrates including a flexible film. Suspended cantilever structures are also demonstrated over a prefabricated trench structure.





