Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover
Front Cover: 5-Heptadecylresorcinol, a Biomarker for Whole Grain Rye Consumption, Ameliorates Cognitive Impairments and Neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
- First Published: 05 June 2020

Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1901218
As a biomarker of whole grain rye consumption, 5-heptadecylresorcinol (AR-C17) plays an important role in ameliorating cognitive deficits by reducing neuroinflammation through inhibiting the activation of microglial and astrogliosis and reducing NLRP3 inflammasomes. In article 1901218, Jing Wang and co-workers find that the modulation of AR-C17 on gut microbiota might also play a potential role in neuroprotection of APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Editorial Board
Research Articles
5-Heptadecylresorcinol, a Biomarker for Whole Grain Rye Consumption, Ameliorates Cognitive Impairments and Neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice
- First Published: 09 May 2020
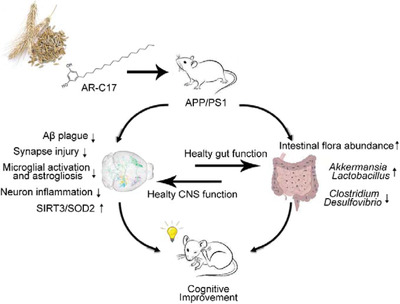
5-heptadecylresorcinol (AR-C17) is a biomarker for whole grain rye consumption, which is also an important active component with potential health benefits. In this study, AR-C17 consumption could ameliorate cognitive impairments and neuroinflammation in amyloid precursor protein (APP)/PS1 transgenic mice through activation of the sirtuin 3/superoxide dismutase 2 signaling pathway and modulating gut microbiota.
Metabolomic-Based Approach to Identify Biomarkers of Apple Intake
- First Published: 03 April 2020
Low AMY1 Copy Number Is Cross-Sectionally Associated to an Inflammation-Related Lipidomics Signature in Overweight and Obese Individuals
- First Published: 07 May 2020
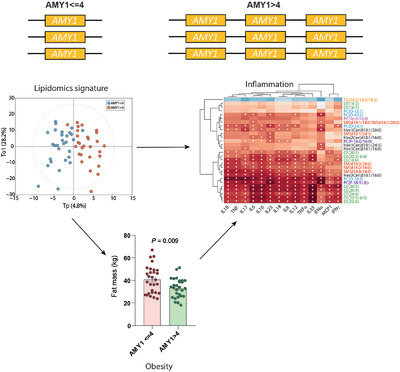
Reduced amylase 1 (AMY1) copy numbers (CN) are associated with metabolic disorders, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. The plasma lipidomic signatures associated with AMY1-CN in the overweight/obese are explored here. A signature is unraveled that involves cholesteryl esters with long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (FA), plasmalogens containing arachidonic acid, and several species containing saturated FA linked to inflammatory cytokines and the AMY1-CN.
Triacylglycerol-Rich Oils of Marine Origin are Optimal Nutrients for Induction of Polyunsaturated Docosahexaenoic Acid Ester of Hydroxy Linoleic Acid (13-DHAHLA) with Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Mice
- First Published: 11 April 2020
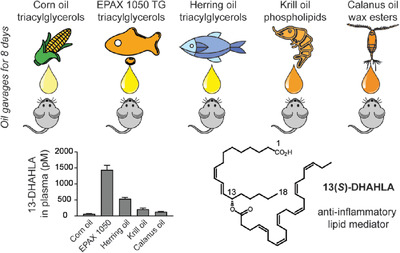
The 13-docosahexaenoic acid ester of hydroxy linoleic acid (DHAHLA) is an anti-inflammatory lipid mediator. DHA-rich marine oils are investigated as potential nutritional sources of 13-DHAHLA precursors and the anti-inflammatory properties of the bioactive lipid are explored. The results suggest that triacylglycerol-based marine oils are superior to marine phospholipids and wax esters in their ability to increase levels of 13-DHAHLA in circulation.
The Preventive Effects of Pterostilbene on the Exercise Intolerance and Circadian Misalignment of Mice Subjected to Sleep Restriction
- First Published: 11 April 2020
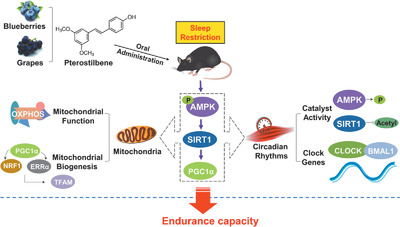
Pterostilbene (PTE), widely found in blueberries and grapes, elicits a curative effect on endurance in sleep-restricted mice, effectively maintains mitochondrial function, and improves mitochondrial biogenesis. The results suggest that PTE is a potential candidate to preserve endurance capacity related to circadian misalignment.
Inhibition of 5-Lipoxygenase-Derived Leukotrienes and Hemiketals as a Novel Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Urolithins
- First Published: 19 April 2020
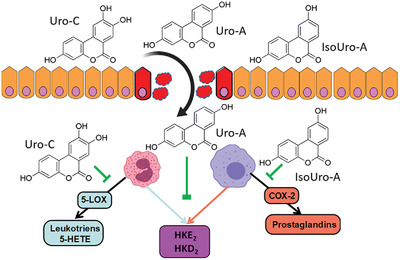
Relevant colonic urolithins (Uro), including Uro-A, IsoUro-A, and Uro-C decrease the formation of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and the newly discovered hemiketal eicosanoids via modulation of the 5-lipoxygenase and the cyclooxygenase-2 pathways in human leukocytes. Due to the importance of these molecules in the modulation of the inflammatory response, this may be a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism of Uro against intestinal inflammation.
Consumption of Diet Soda Sweetened with Sucralose and Acesulfame-Potassium Alters Inflammatory Transcriptome Pathways in Females with Overweight and Obesity
- First Published: 13 April 2020
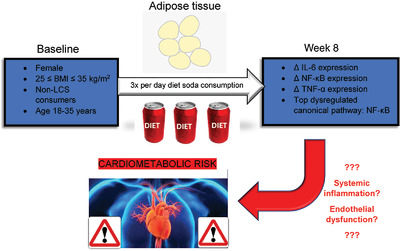
To identify molecular pathways in adipose tissue impacted by low-calorie sweeteners (LCSs), seven females with overweight/obesity, who did not use LCSs, consumed 12 oz of diet soda containing sucralose and acesulfame-potassium (Ace-K) three times daily for 8 weeks. Consumption of diet soda altered genes and molecular pathways involved in inflammation in adipose, but did not alter inflammatory markers in the bloodstream.
Identifying Cranberry Juice Consumers with Predictive OPLS-DA Models of Plasma Metabolome and Validation of Cranberry Juice Intake Biomarkers in a Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Study
- First Published: 13 April 2020
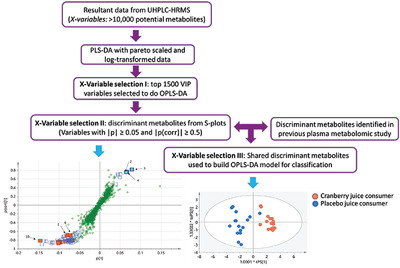
This double-blinded study is aimed to build models with validated biomarkers to verify human consumption of cranberry juice. Discriminant metabolites from a previous 3-day open-label study are re-discovered, and predictive OPLS-DA models are built to identify cranberry juice consumers and non-consumers. The models are able to identify cranberry juice consumers over the placebo juice group with up to 96.9% correction rates.
In Celiac Disease Patients the In Vivo Challenge with the Diploid Triticum monococcum Elicits a Reduced Immune Response Compared to Hexaploid Wheat
- First Published: 06 May 2020
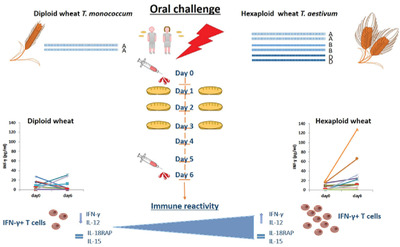
The in vivo immunogenicity of Triticum monococcum (TM) and Triticum aestivum (TA) wheats is assessed in celiacs after 3 days of bread consumption. TM mobilizes a reduced number of IFN-γ-secreting-T cells, and elicits a reduced IL-12A and IFN-γ mRNA expression compared to TA (p<0.05). No differences are detected in the expression of IL-15, IL-18RAP among the two groups of patients.
Red Wine Extract Disrupts Th17 Lymphocyte Differentiation in a Colorectal Cancer Context
- First Published: 18 April 2020
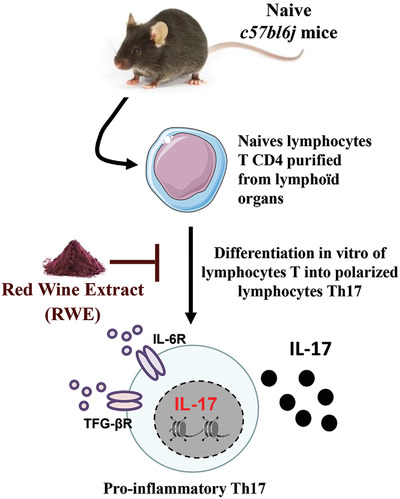
Red Wine extract alters differentiation of lymphocyte T cells into pro-inflammatory T helper 17 through an alteration of nuclear transcriptional factor, the protein RORγt. Subsequently, red wine extract disrupts pro-inflammatory interleukin IL-17. These events are associated in vivo with a decrease of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and with a reduction of colorectal tumor growth.






